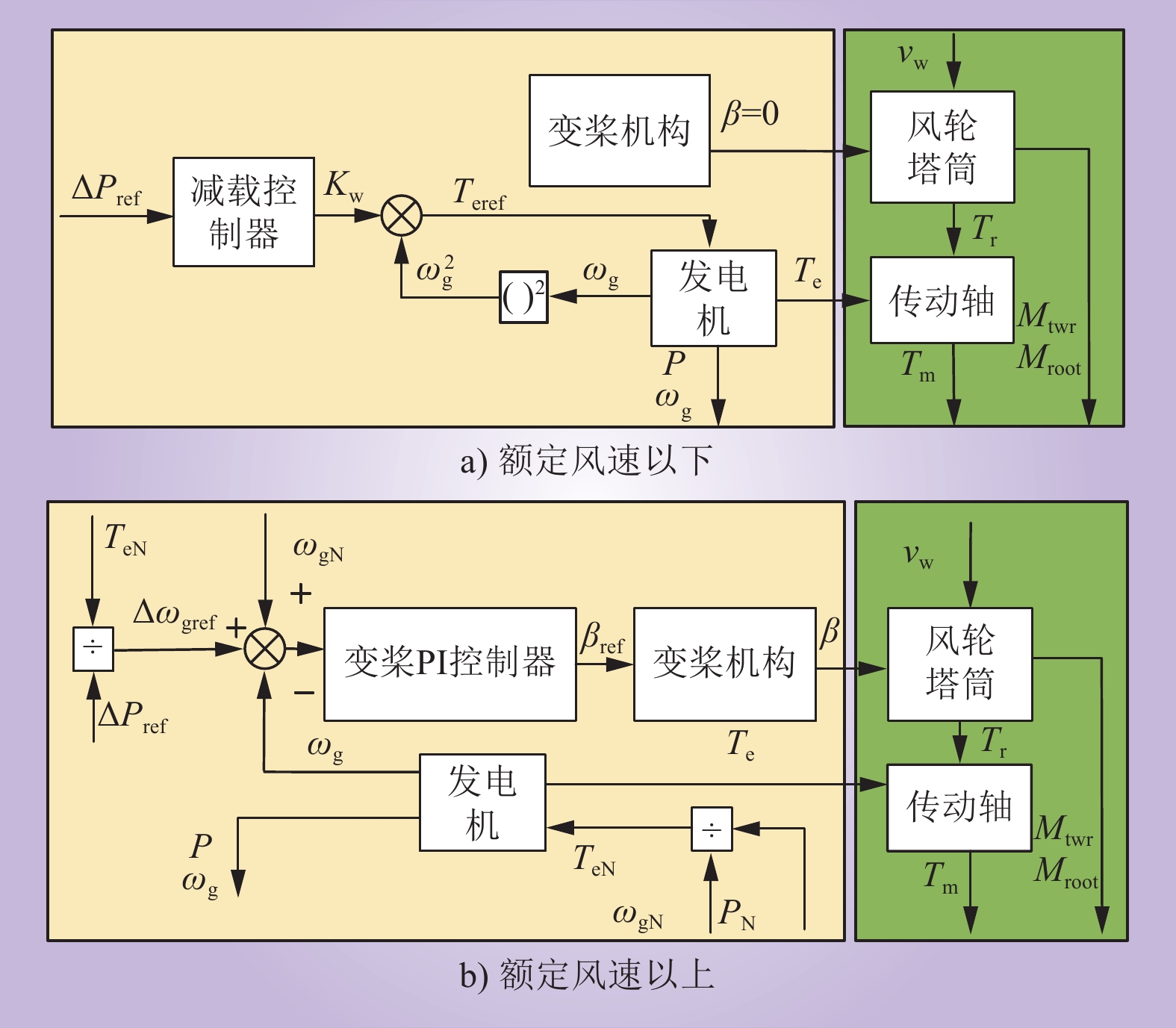
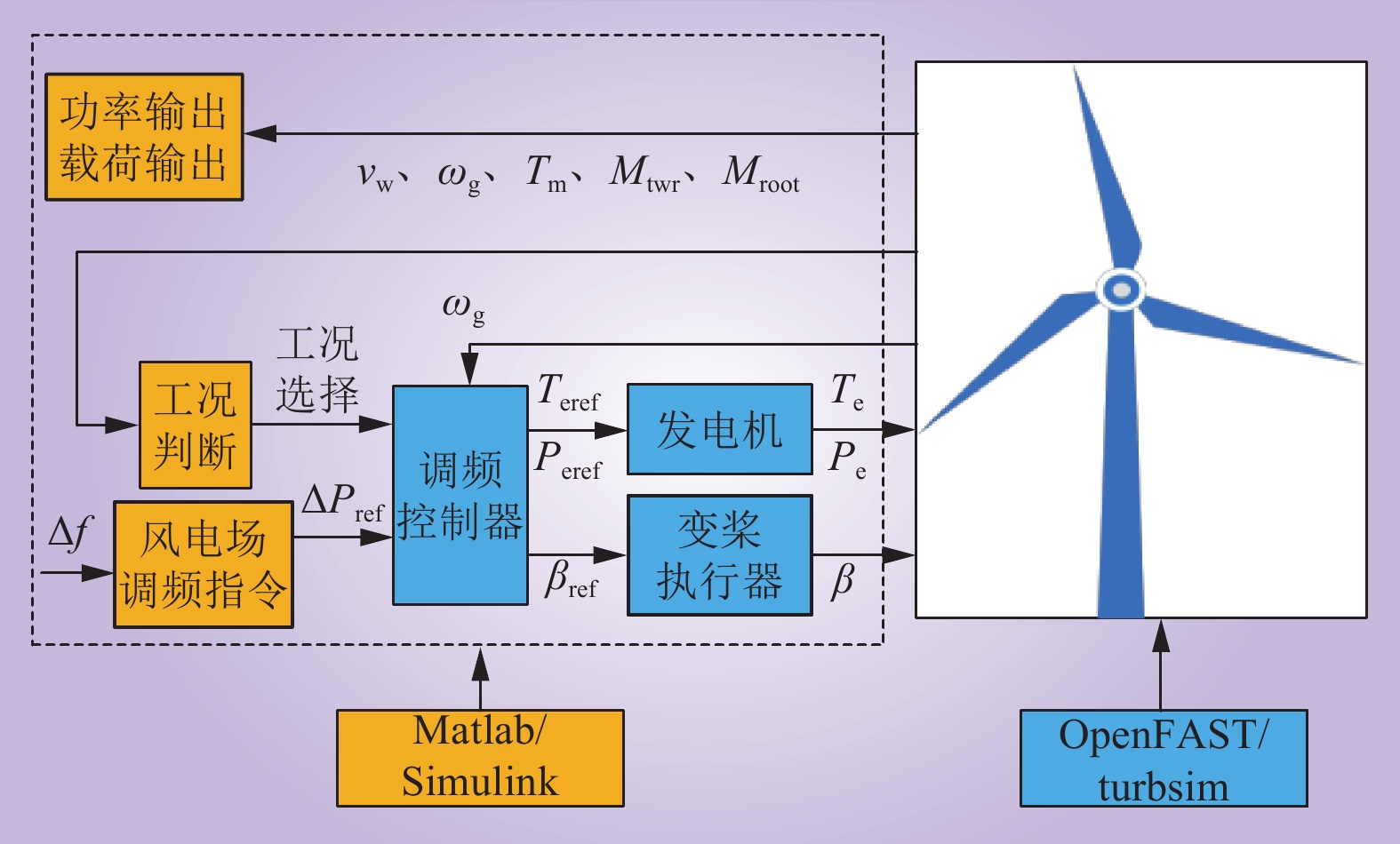
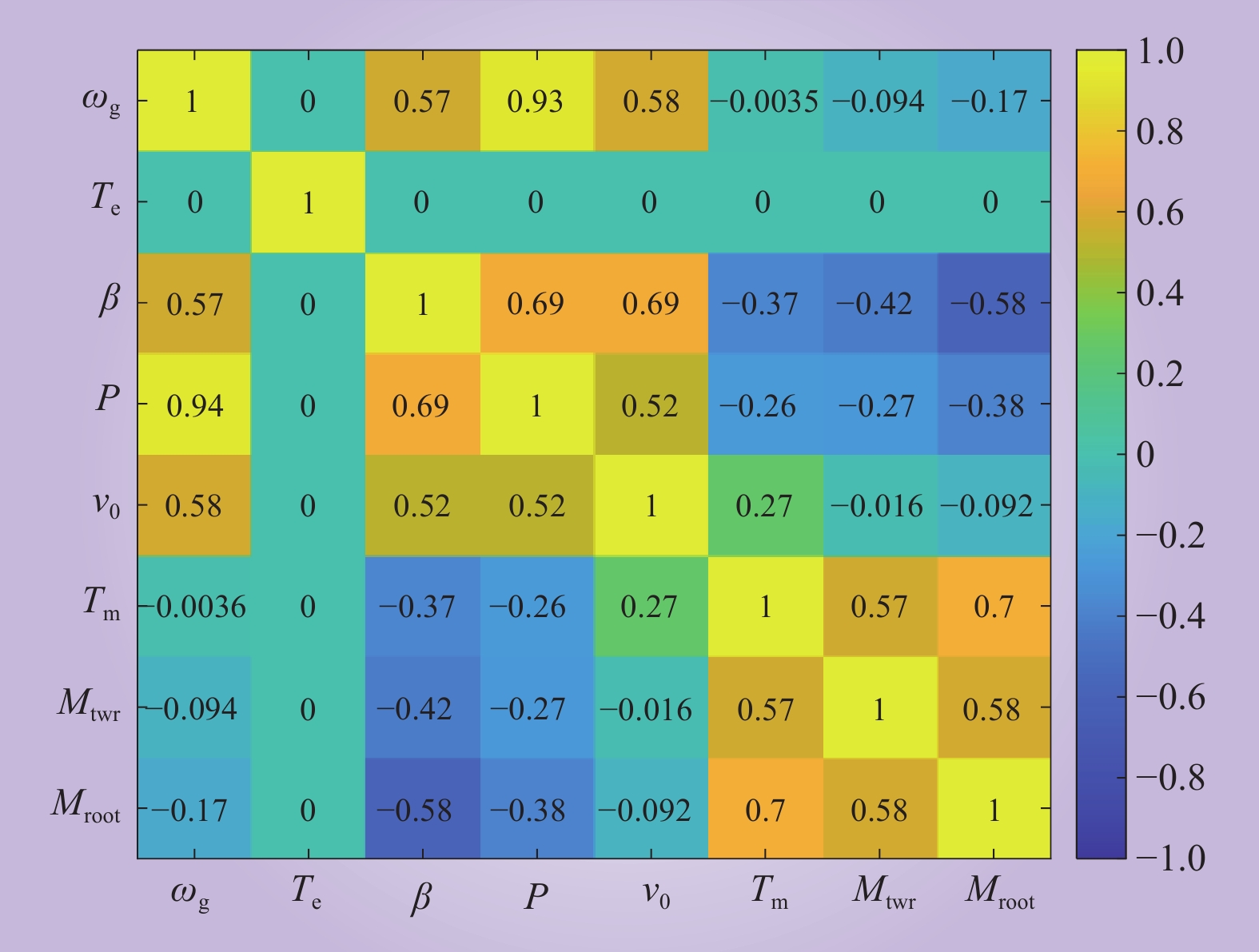
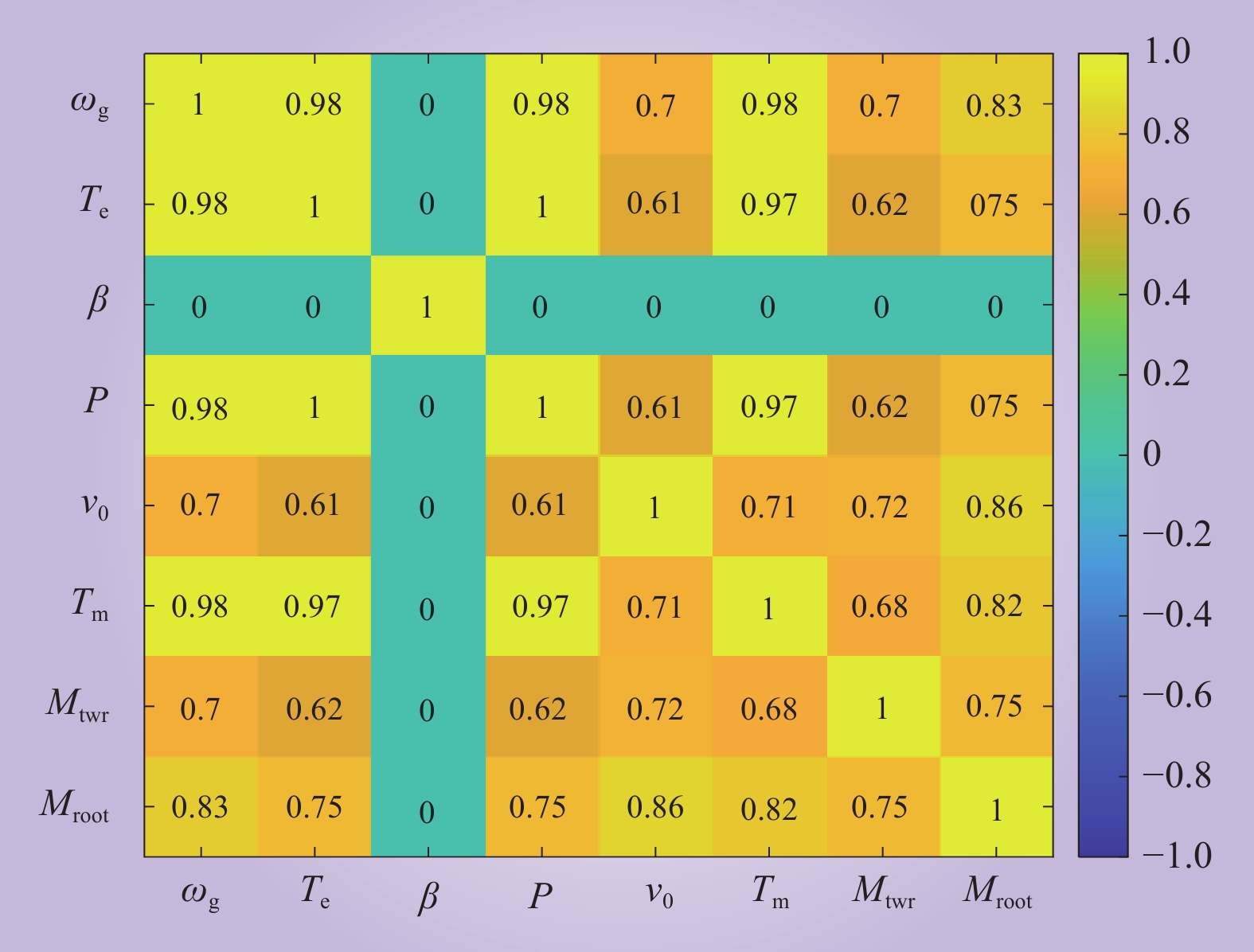
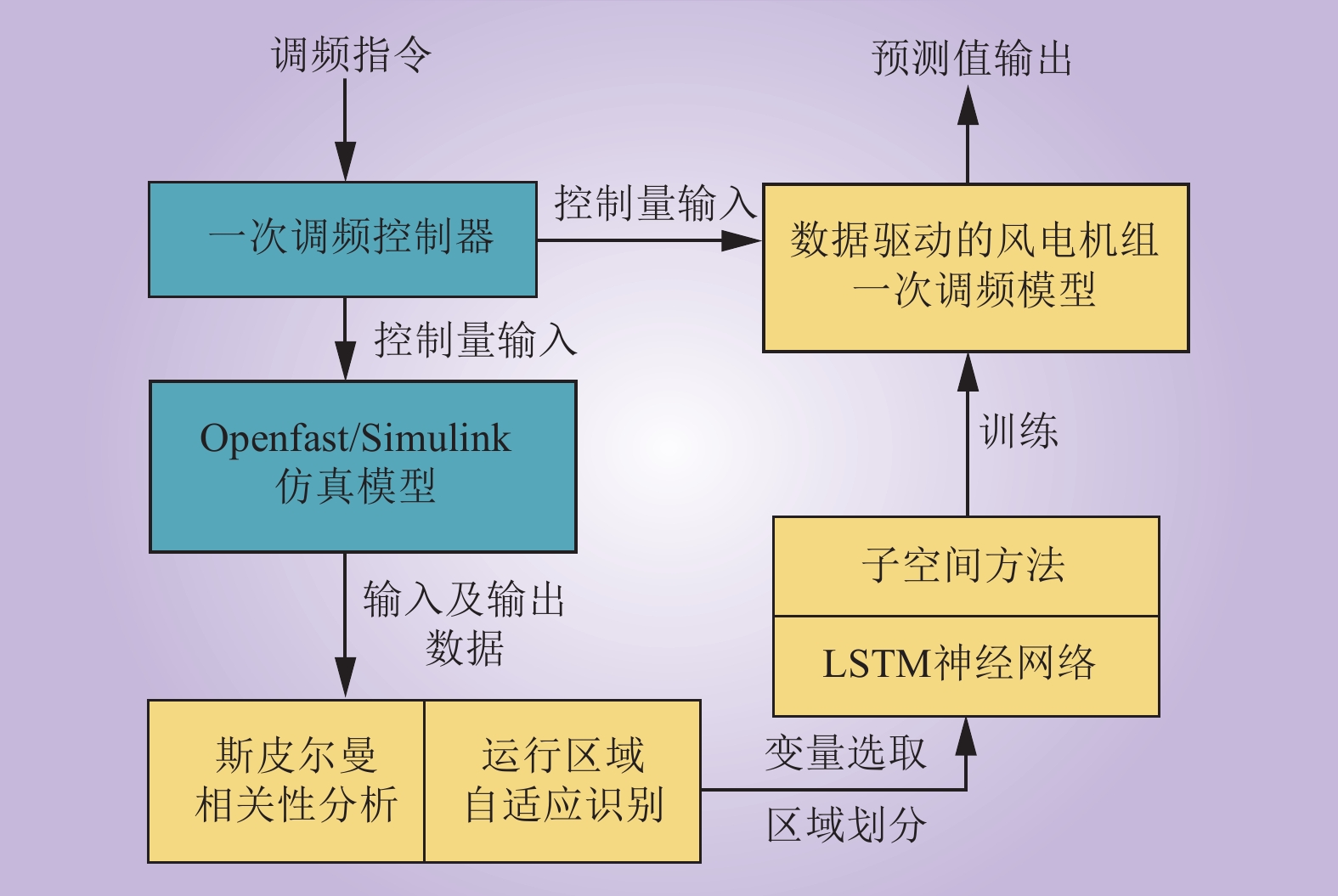
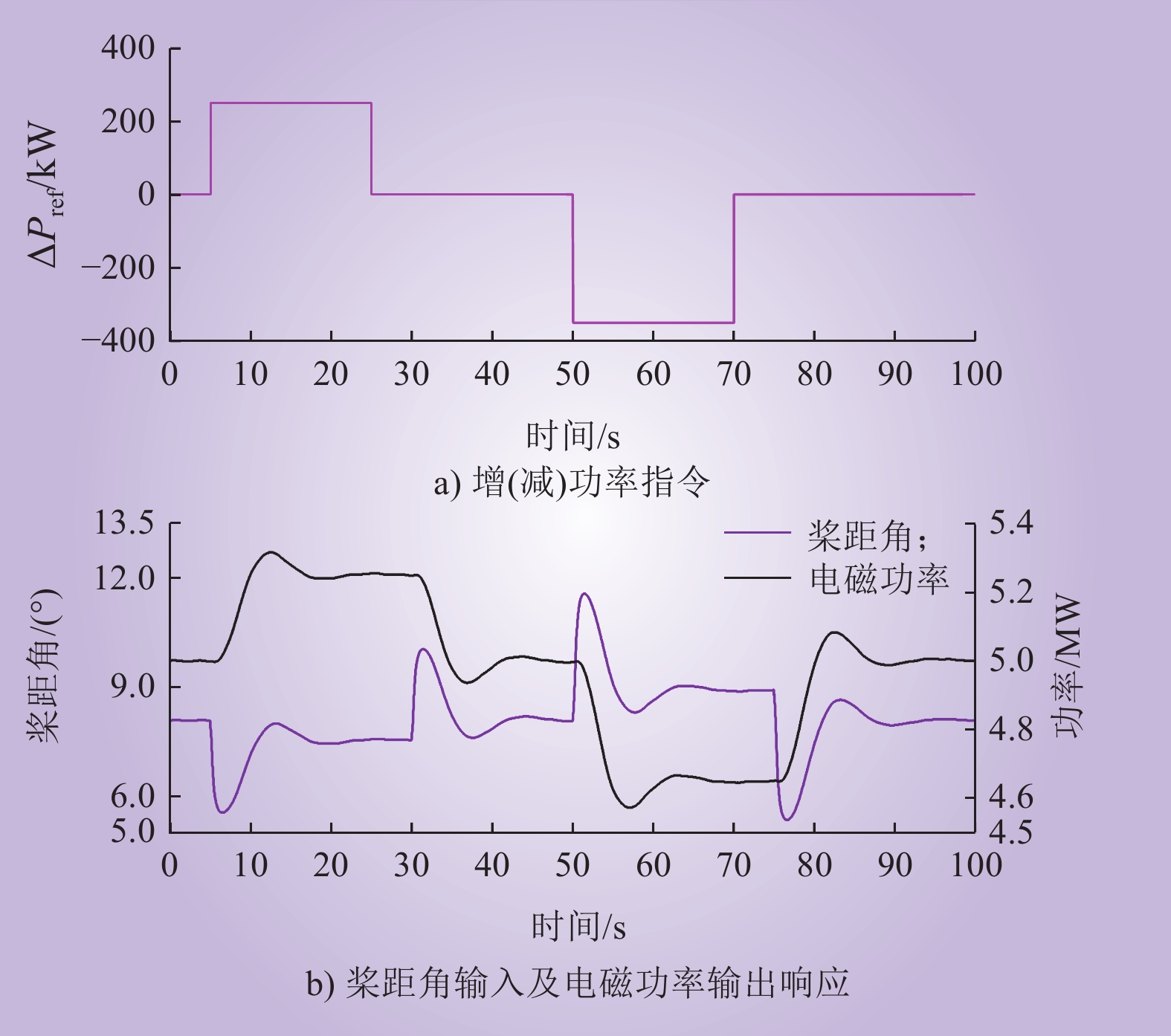
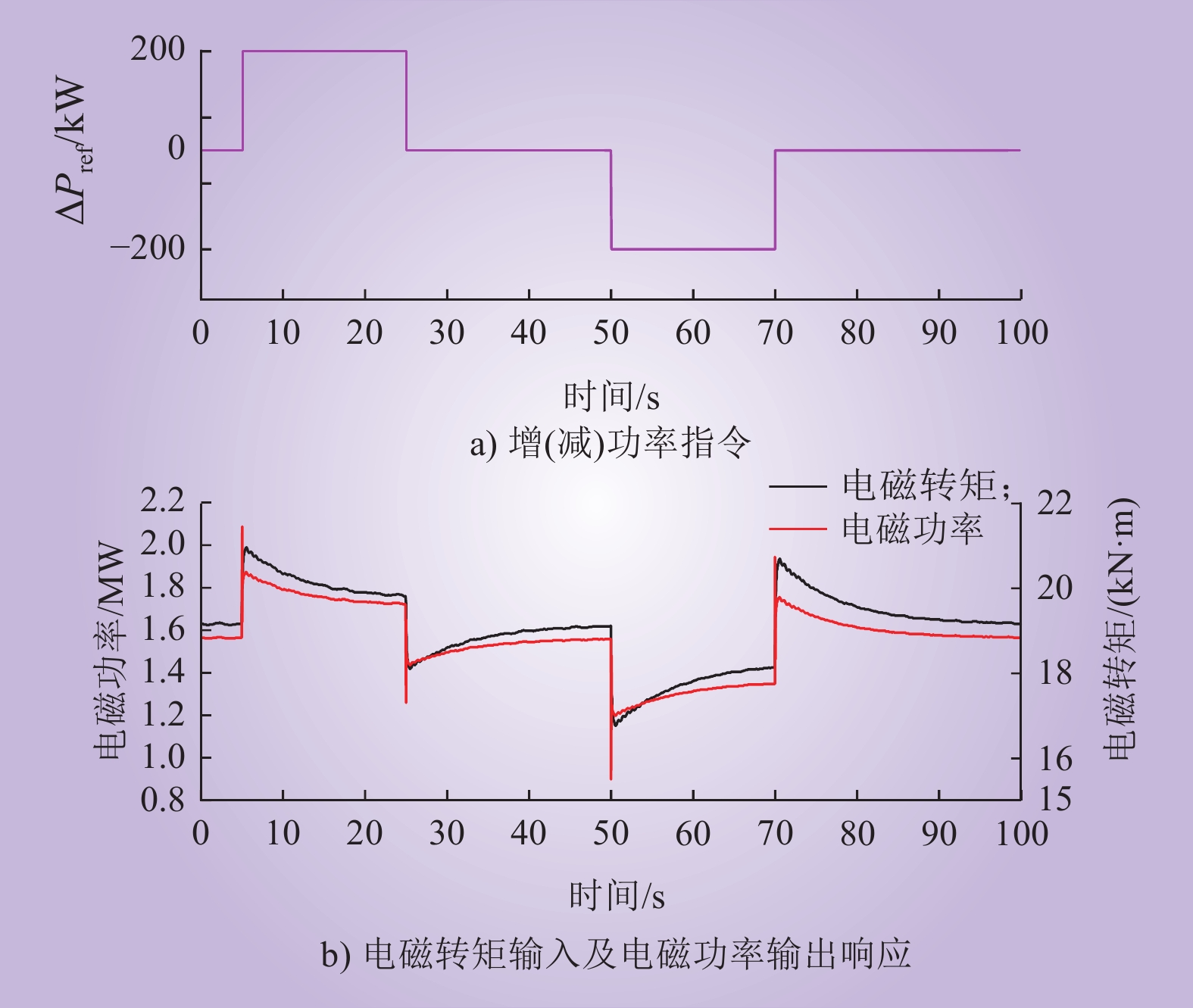
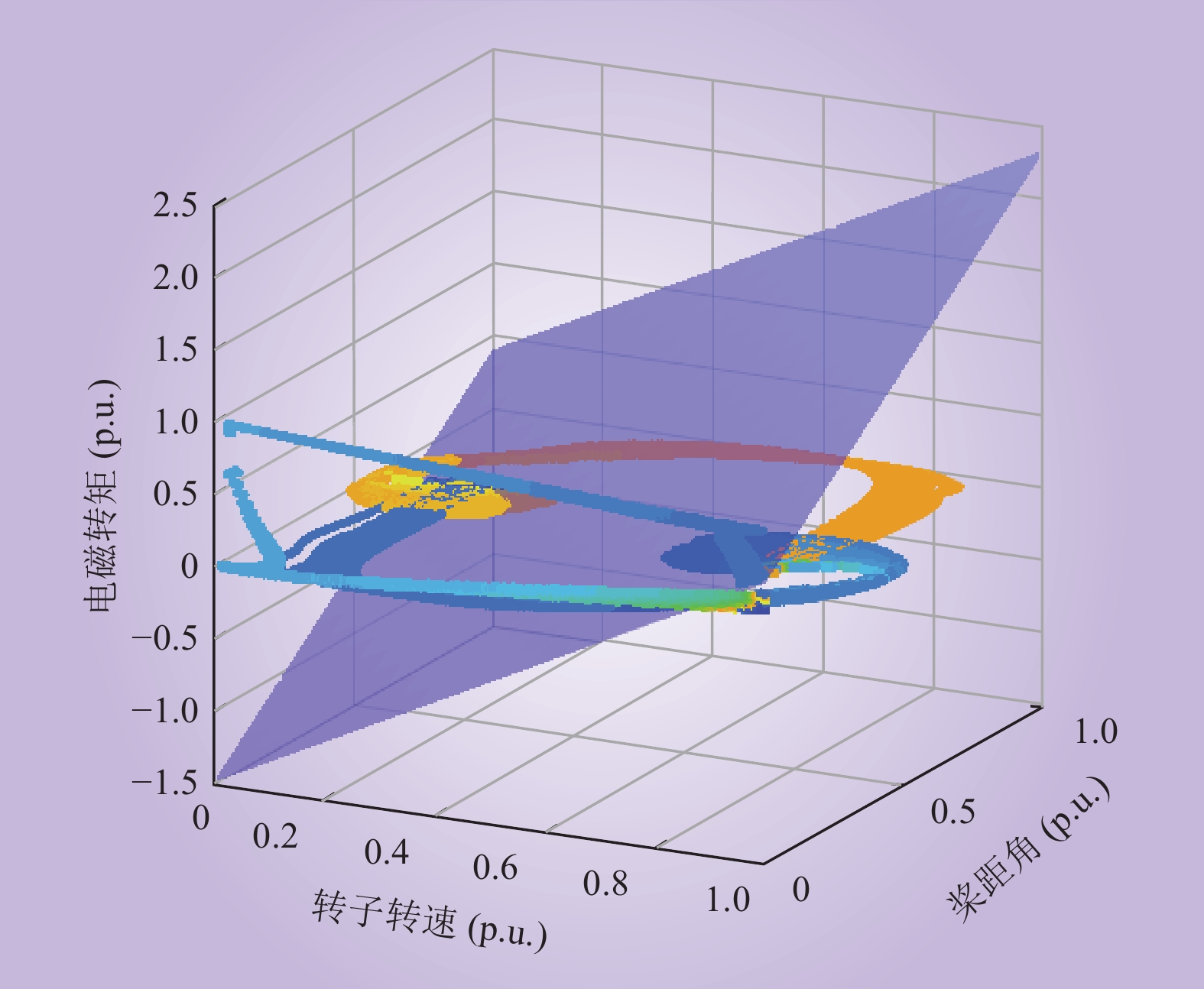
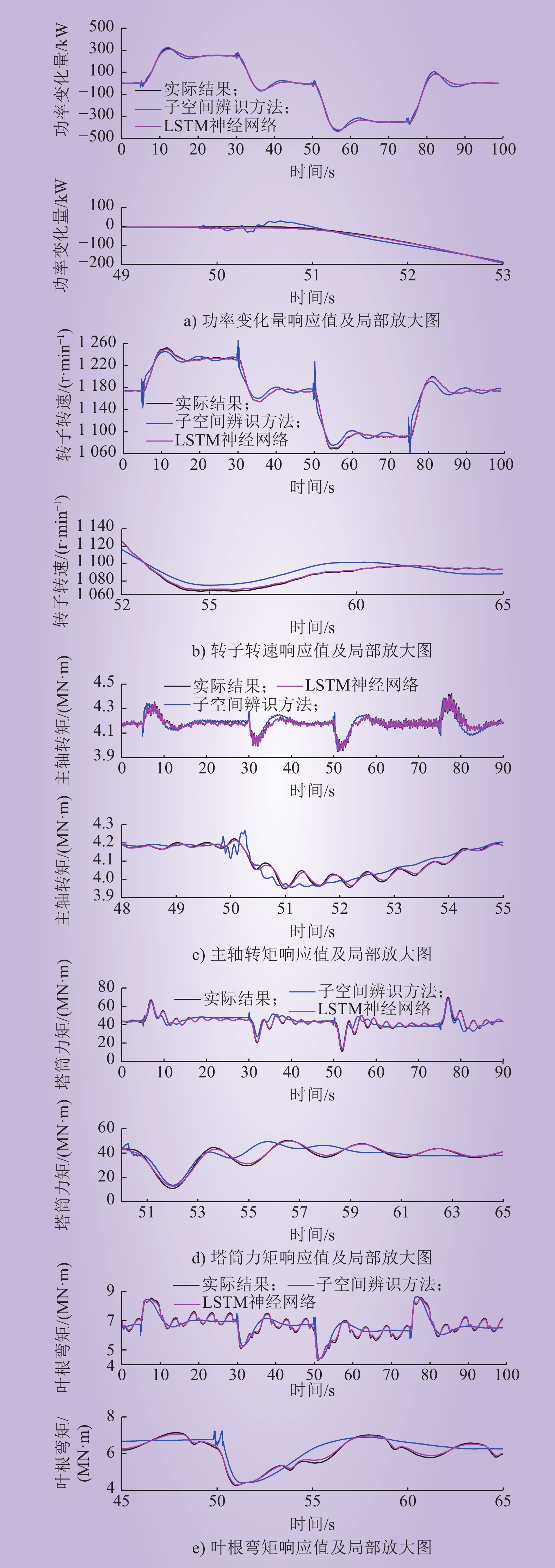
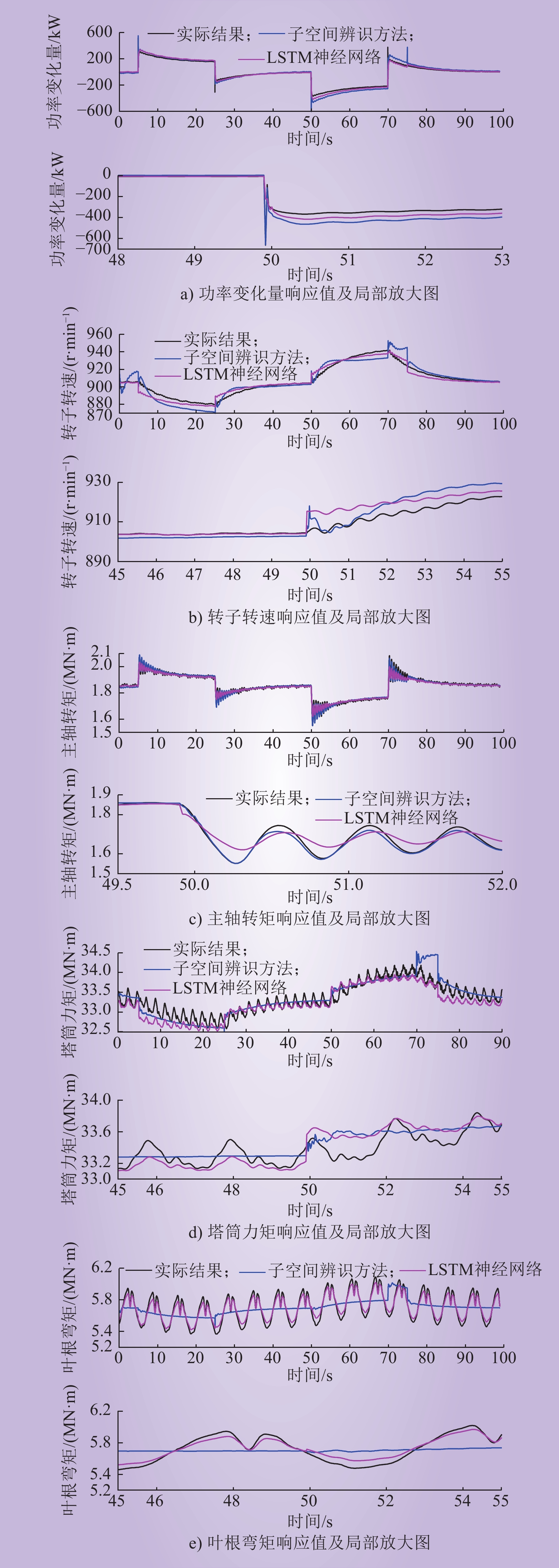
| 1 |
中国电力行业年度发展报告2023(摘要)[N]. 中国电力报, 2023-07-12(3).
|
| 2 |
刘洪波, 彭晓宇, 张崇, 等. 风电参与电力系统调频控制策略综述[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (11): 81- 92.
|
|
LIU Hongbo, PENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Chong, et al. Overview of wind power participating in frequency regulation control strategy for power system[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (11): 81- 92.
|
| 3 |
YANG J, ZHENG S Y, SONG D R, et al. Comprehensive optimization for fatigue loads of wind turbines in complex-terrain wind farms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2021, 12 (2): 909- 919.
|
| 4 |
YAO Q, HU Y, ZHAO T Y, et al. Fatigue load suppression during active power control process in wind farm using dynamic-local-reference DMPC[J]. Renewable Energy, 2022, 183, 423- 434.
|
| 5 |
李可心, 安军, 石岩, 等. 基于可用调频能量的风电机组综合虚拟惯性控制参数整定[J]. 电工技术学报, 2025, 40 (5): 1382- 1394.
|
|
LI Kexin, AN Jun, SHI Yan, et al. An integrated virtual inertia control parameter setting method for wind turbine based on available frequency regulation energy[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2025, 40 (5): 1382- 1394.
|
| 6 |
高海淑, 张峰, 丁磊. 风电机组两分段下垂调频控制策略及参数整定方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (18): 111- 121.
|
|
GAO Haishu, ZHANG Feng, DING Lei. Two-segment droop frequency regulation control strategy and parameter setting method for wind turbines[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (18): 111- 121.
|
| 7 |
赵晶晶, 杜明, 刘帅, 等. 基于模型预测控制的双馈风电机组调频与转子转速恢复策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (6): 11- 17.
|
|
ZHAO Jingjing, DU Ming, LIU Shuai, et al. Frequency modulation and rotor speed recovery strategy of doubly-fed induction generator based on model predictive control[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (6): 11- 17.
|
| 8 |
宋子秋, 余照国, 胡阳, 等. 海上漂浮式风电场高比例并网一次调频控制策略研究[J]. 动力工程学报, 2023, 43 (1): 92- 101.
|
|
SONG Ziqiu, YU Zhaoguo, HU Yang, et al. Research on primary frequency regulation control strategy of high-penetration offshore floating wind farm[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2023, 43 (1): 92- 101.
|
| 9 |
秦世耀. 风电机组惯量及一次调频优化控制研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2021.
|
|
QIN Shiyao. Research on optimal control strategy of inertia and primary frequency regulation for wind turbines[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2021.
|
| 10 |
尹诗, 侯国莲, 迟岩, 等. 风电机组发电机前轴承健康度预测方法及实现[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2021, 33 (6): 1323- 1333.
|
|
YIN Shi, HOU Guolian, CHI Yan, et al. Prediction method for health degree of front bearing of wind turbine generator and implementation[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2021, 33 (6): 1323- 1333.
|
| 11 |
孟明, 杨靖, 彭琰, 等. 计及频率响应安全性的双馈风电机组轴系阻尼控制策略研究[J]. 浙江电力, 2023, 42 (2): 43- 49.
|
|
MENG Ming, YANG Jing, PENG Yan, et al. Research on a shaft damping control strategy for DFIG-based wind turbines considering frequency response safety[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2023, 42 (2): 43- 49.
|
| 12 |
刘海军, 陈重阳. 双馈风电机组低电压穿越下载荷控制研究[J]. 电气传动, 2019, 49 (2): 33- 39.
|
|
LIU Haijun, CHEN Chongyang. Research on load control strategy of DFIG wind turbine during LVRT[J]. Electric Drive, 2019, 49 (2): 33- 39.
|
| 13 |
田德, 黄明月, 唐世泽, 等. 大型风电机组输出功率与塔架载荷自抗扰控制[J]. 太阳能学报, 2023, 44 (5): 466- 472.
|
|
TIAN De, HUANG Mingyue, TANG Shize, et al. Output power and tower load control of large-scale wind turbines based on active disturbance rejection control[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2023, 44 (5): 466- 472.
|
| 14 |
易怀洋, 梁辉, 晋永荣. 基于FAST的大型风电机组叶根载荷反馈独立变桨距控制策略[J]. 科学技术创新, 2022, (27): 89- 92.
|
|
YI Huaiyang, LIANG Hui, JIN Yongrong. Blade root load feedback individual pitch control strategy for large-scale wind turbines based on FAST[J]. Scientific and Technological Innovation, 2022, (27): 89- 92.
|
| 15 |
李世春, 黄悦华, 王凌云, 等. 基于转速控制的双馈风电机组一次调频辅助控制系统建模[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37 (24): 7077- 7086, 7422.
|
|
LI Shichun, HUANG Yuehua, WANG Lingyun, et al. Modeling primary frequency regulation auxiliary control system of doubly fed induction generator based on rotor speed control[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37 (24): 7077- 7086, 7422.
|
| 16 |
杨超, 李东翰, 雷显帅, 等. 虚拟惯量控制对直驱风电机组载荷影响的分析及评估[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (7): 258- 266.
|
|
YANG Chao, LI Donghan, LEI Xianshuai, et al. Analysis and evaluation of impact of virtual inertia control on load of direct-drive wind turbine[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (7): 258- 266.
|
| 17 |
NOVAES MENEZES E J, ARAÚJO A M, ROHATGI J S, et al. Active load control of large wind turbines using state-space methods and disturbance accommodating control[J]. Energy, 2018, 150, 310- 319.
|
| 18 |
潘晨阳, 胡阳, 奚芸华. 大型风机主导机械动态的智能灰箱建模及其线性状态空间表征[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37 (6): 1260- 1269.
|
|
PAN Chenyang, HU Yang, XI Yunhua. Intelligent grey-box modeling and linear state-space representation of dominating mechanical dynamics for large-scale wind turbine[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37 (6): 1260- 1269.
|
| 19 |
梁宏涛, 孔翎超, 刘国柱, 等. 融合数字孪生的风电机组故障检测ASL-CatBoost方法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2024, 36 (4): 873- 887.
|
|
LIANG Hongtao, KONG Lingchao, LIU Guozhu, et al. ASL-CatBoost method for wind turbine fault detection integrated with digital twin[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2024, 36 (4): 873- 887.
|
| 20 |
胡阳, 王蔚然, 房方, 等. 风电机组运行动态数字孪生建模及半物理仿真[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2024, 36 (3): 636- 648.
|
|
HU Yang, WANG Weiran, FANG Fang, et al. Dynamic digital twin modelling and semi-physical simulation of wind turbine operation[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2024, 36 (3): 636- 648.
|
| 21 |
杨晓峰, 方逸航, 赵鹏臻, 等. 基于K-means和BPNN的风机状态识别[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (6): 158- 166, 175.
|
|
YANG Xiaofeng, FANG Yihang, ZHAO Pengzhen, et al. State recognition of wind turbines based on K-means and BPNN[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (6): 158- 166, 175.
|
| 22 |
许扬, 蔡安民, 张林伟, 等. 基于BP神经网络和多因素权重法的风电机组载荷预测和分析[J]. 热力发电, 2022, 51 (8): 42- 49.
|
|
XU Yang, CAI Anmin, ZHANG Linwei, et al. Load prediction and analysis of wind turbine based on BP neural network and multi-factor weight method[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2022, 51 (8): 42- 49.
|
| 23 |
邓子豪, 李录平, 刘瑞, 等. 基于SCADA数据特征提取的风电机组偏航齿轮箱故障诊断方法研究[J]. 动力工程学报, 2021, 41 (1): 43- 50.
|
|
DENG Zihao, LI Luping, LIU Rui, et al. Research on diagnosis method of wind turbine yaw gearbox based on SCADA data feature extraction[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2021, 41 (1): 43- 50.
|
| 24 |
魏乐, 胡晓东, 尹诗. 基于优化XGBoost的风电机组发电机前轴承故障预警[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2021, 33 (10): 2335- 2343.
|
|
WEI Le, HU Xiaodong, YIN Shi. Optimized-XGBoost early warning of wind turbine generator front bearing fault[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2021, 33 (10): 2335- 2343.
|
| 25 |
贾科, 杨哲, 魏超, 等. 基于斯皮尔曼等级相关系数的新能源送出线路纵联保护[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44 (15): 103- 111.
|
|
JIA Ke, YANG Zhe, WEI Chao, et al. Pilot protection based on spearman rank correlation coefficient for transmission line connected to renewable energy source[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44 (15): 103- 111.
|
| 26 |
JONKMAN J, BUTTERFIELD S, MUSIAL W, et al. Definition of a 5-MW reference wind turbine for offshore system development[J]. Contract, 2009, (February): 1- 75.
|
| 27 |
刘兴, 王艳, 纪志成. 基于随机森林的风电功率短期预测方法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2021, 33 (11): 2606- 2614.
|
|
LIU Xing, WANG Yan, JI Zhicheng. Short-term wind power prediction method based on random forest[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2021, 33 (11): 2606- 2614.
|
| 28 |
COSTA A G, MALDONADO J L B, ROMERO F A, et al. N4SID method applied to obtain a discrete-time linear state space system as a mathematical model of a jaw crusher prototype[C]//2017 CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON). Pucon. IEEE, 2017: 1–6.
|
| 29 |
JONKMAN B J, BUHL M L J. Turbsim user's guide[R], Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI), 2006.
|