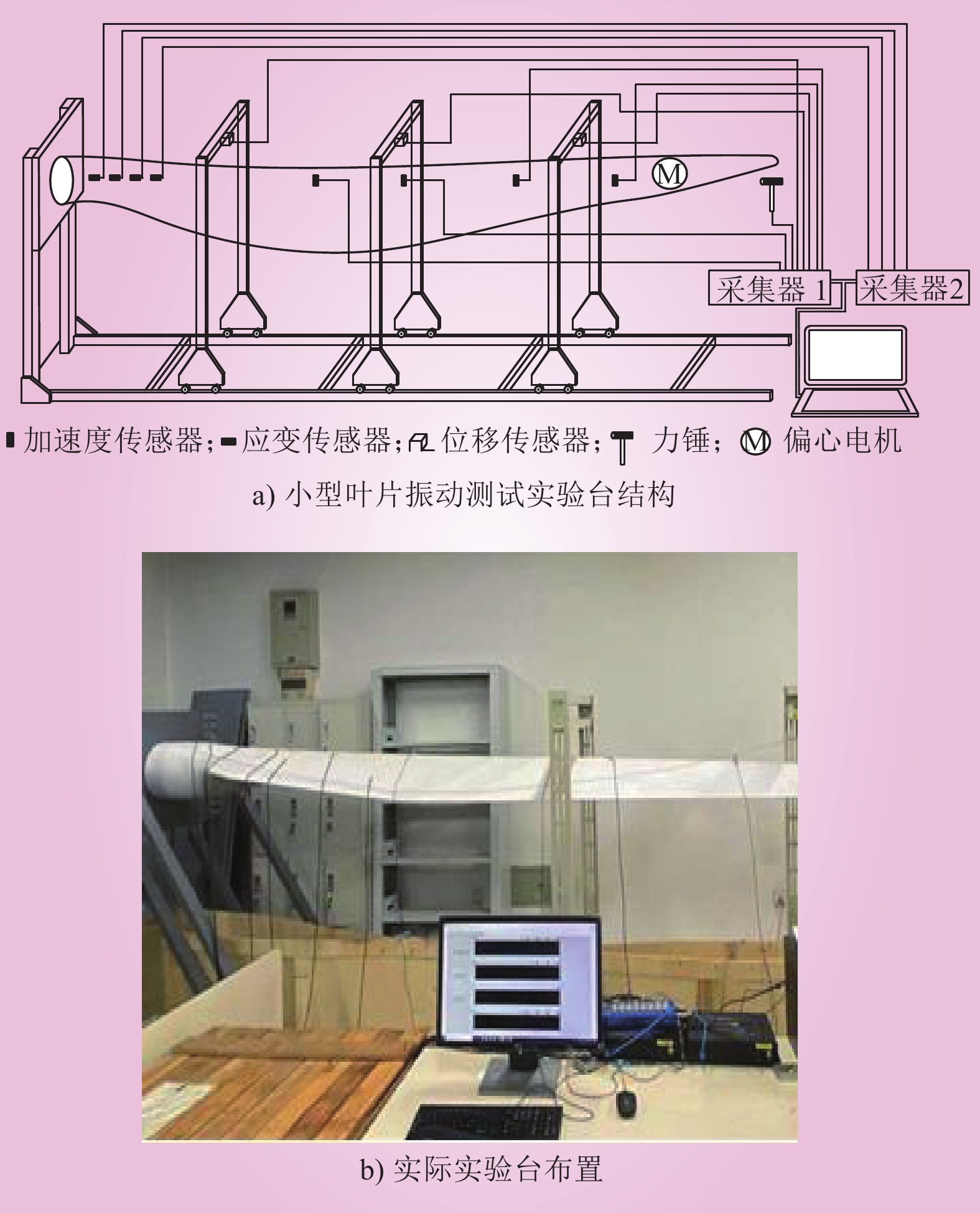
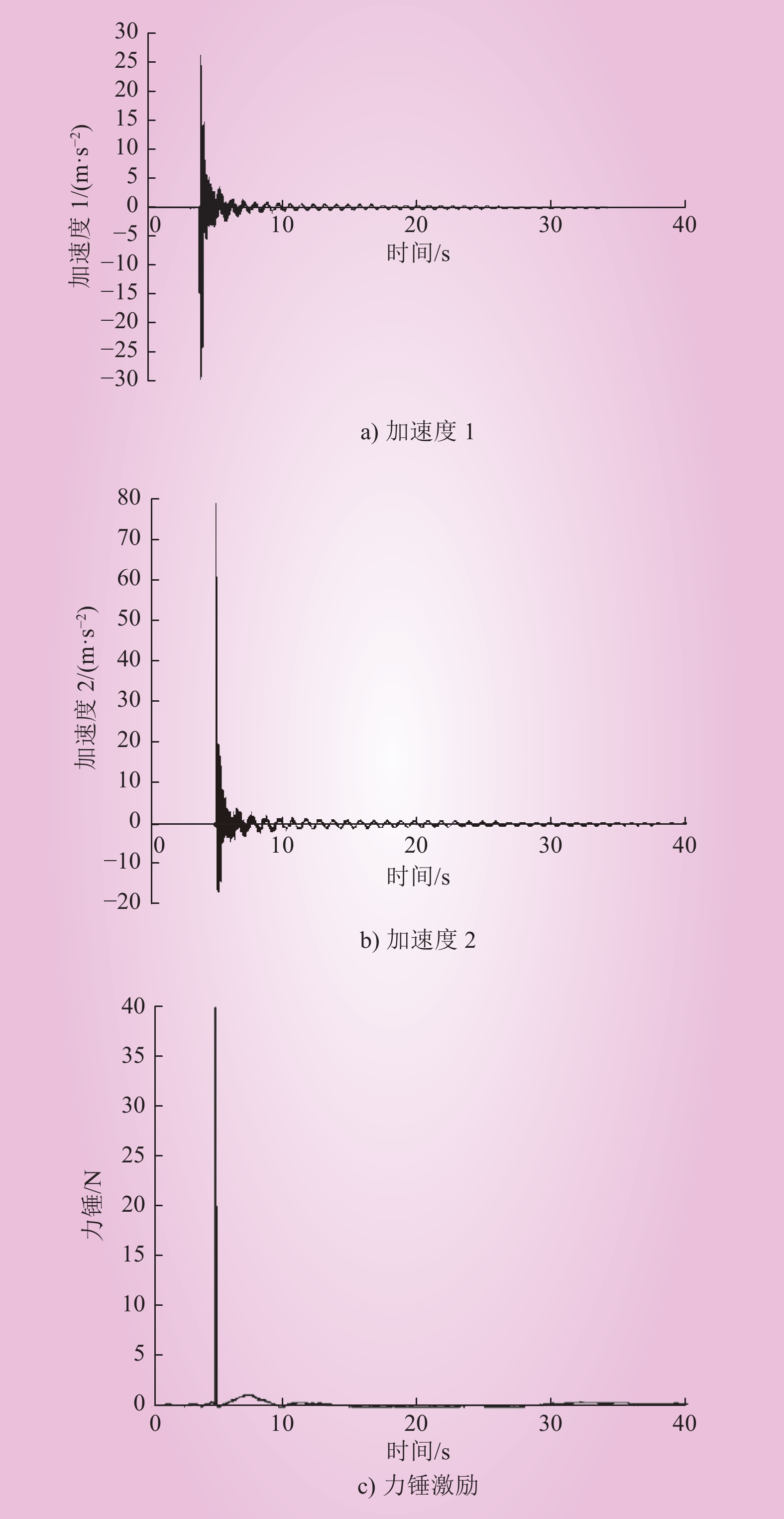
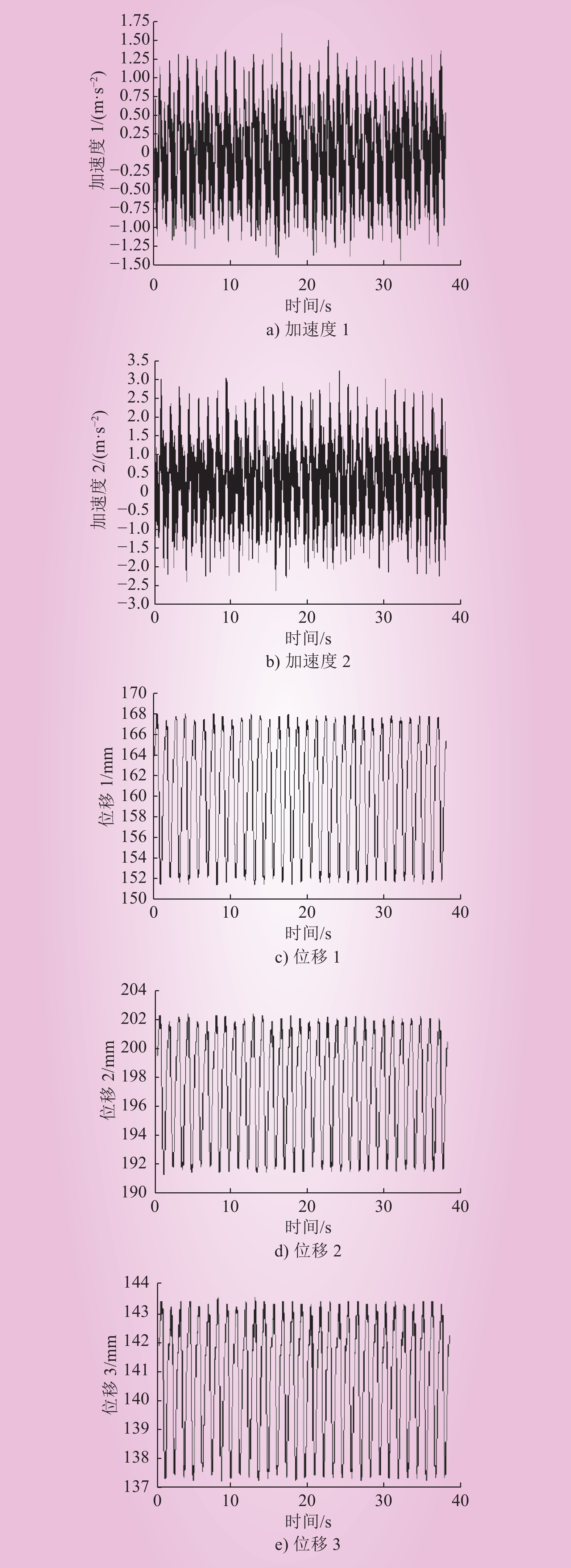
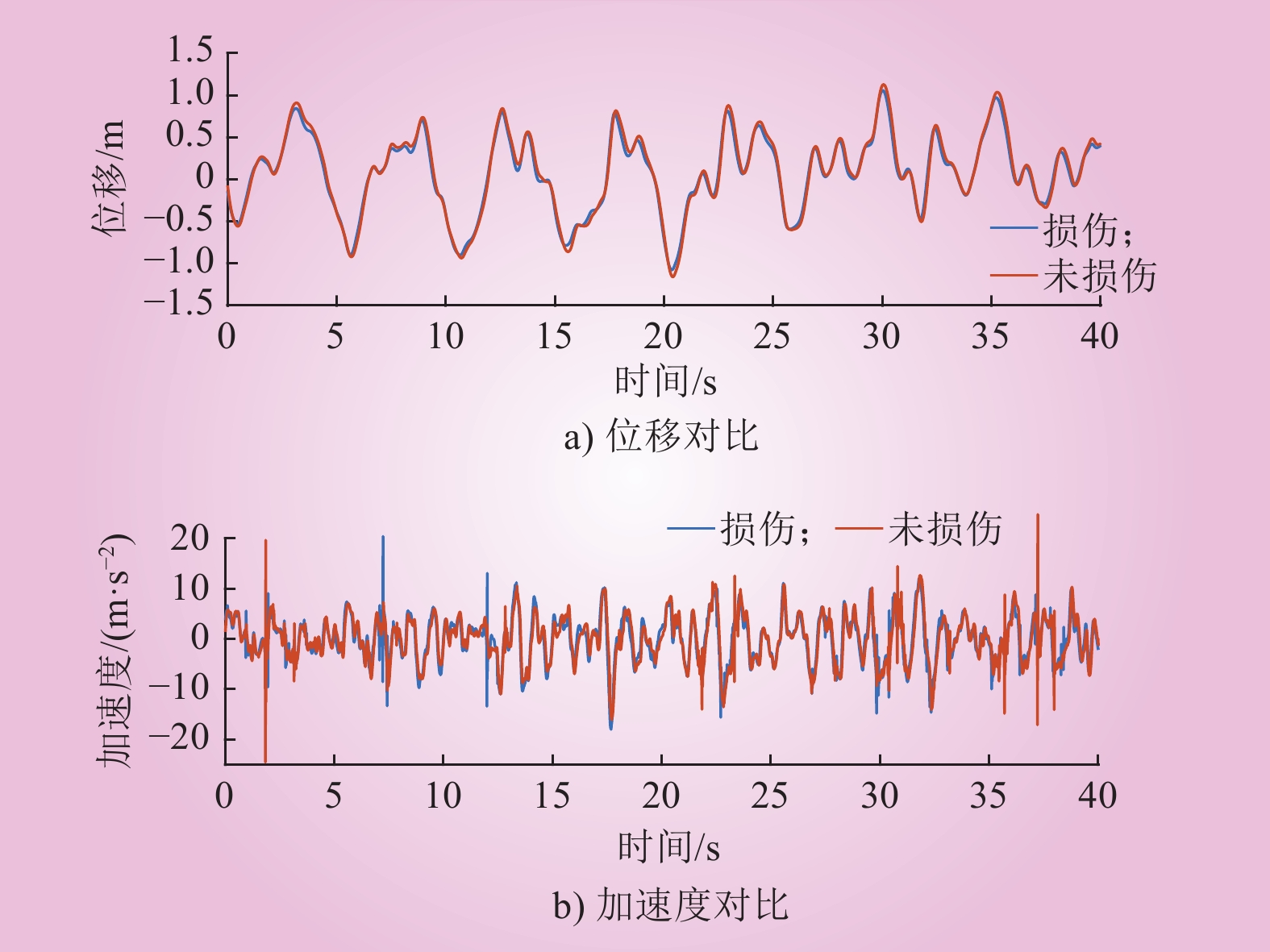
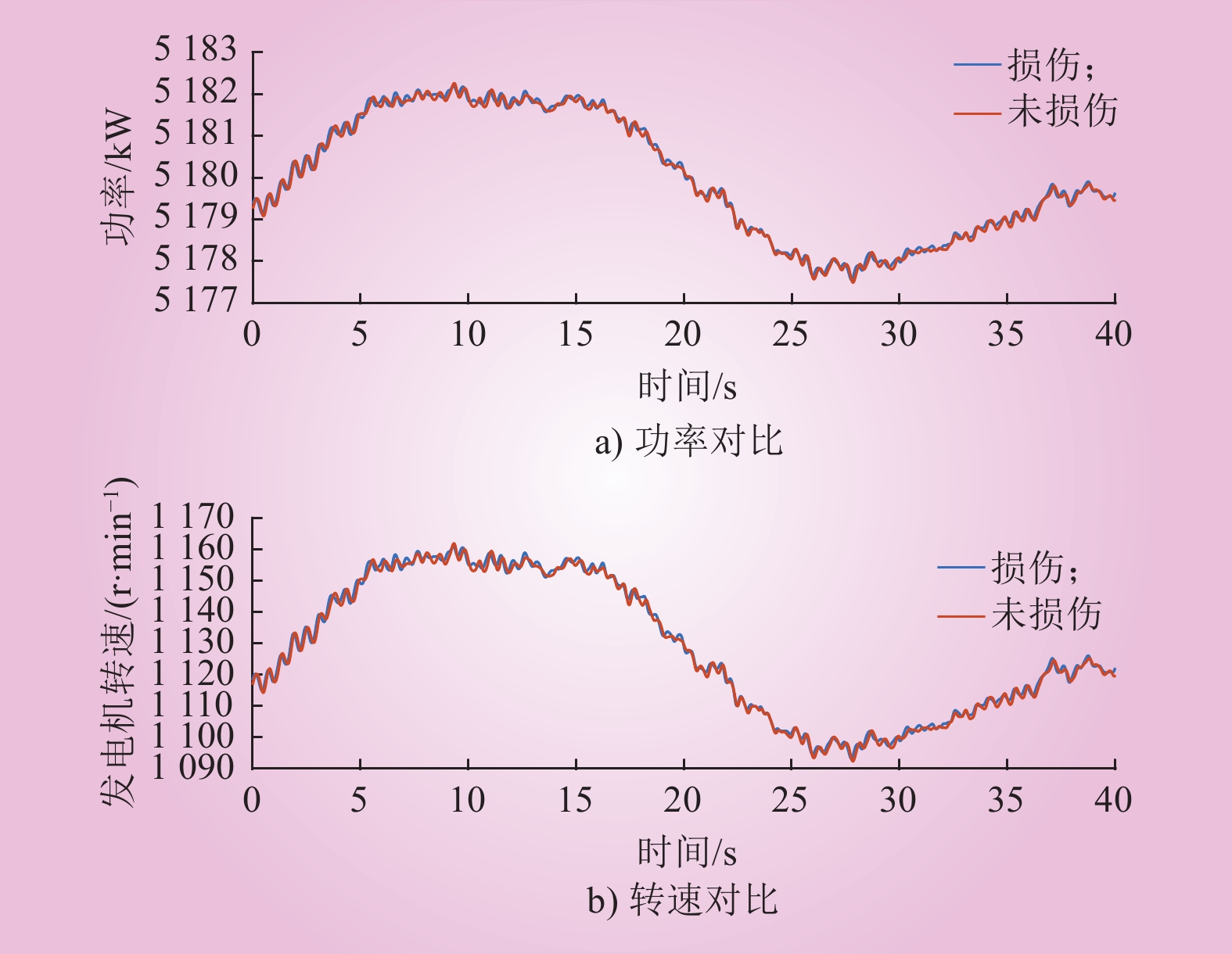
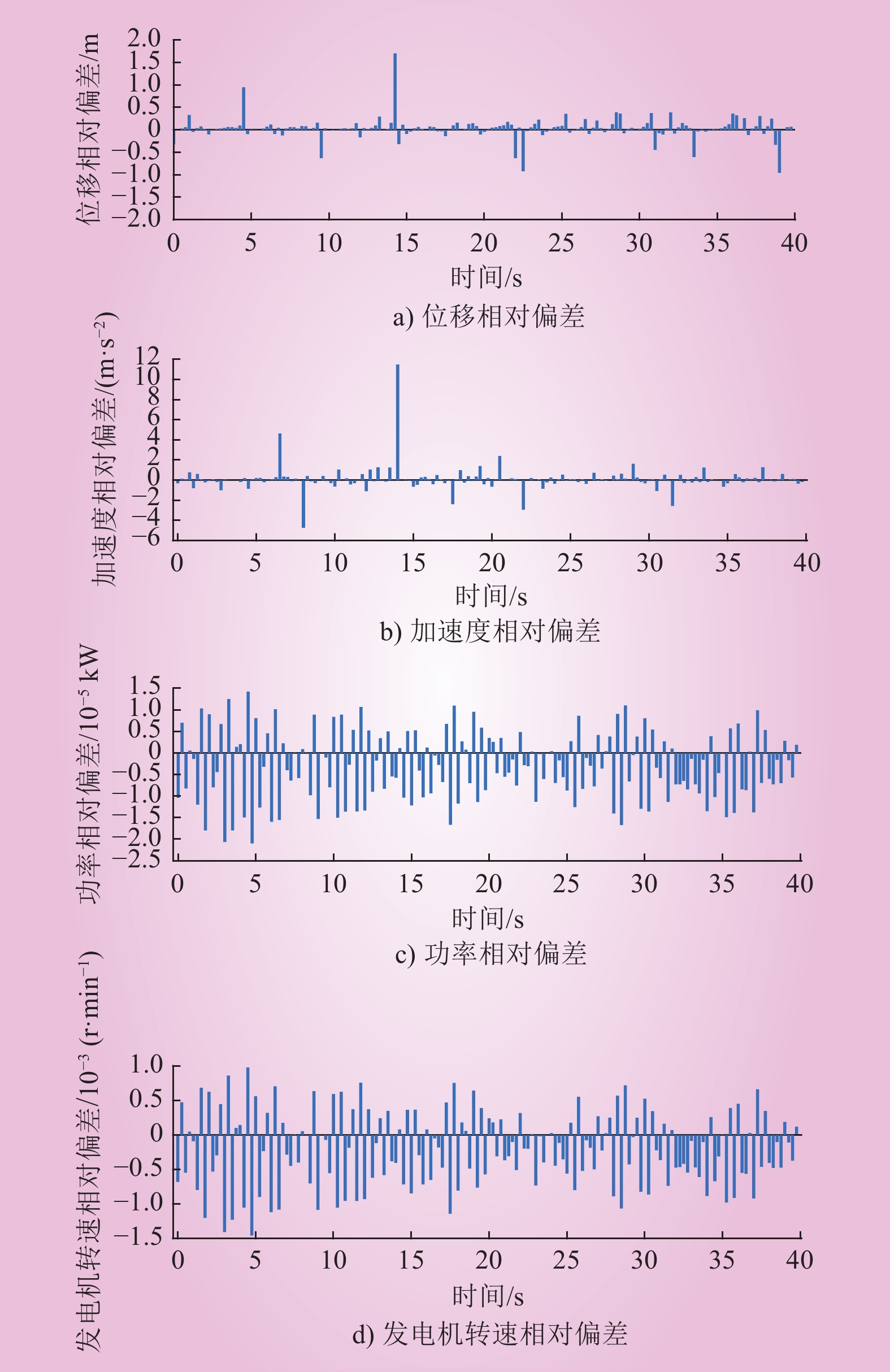
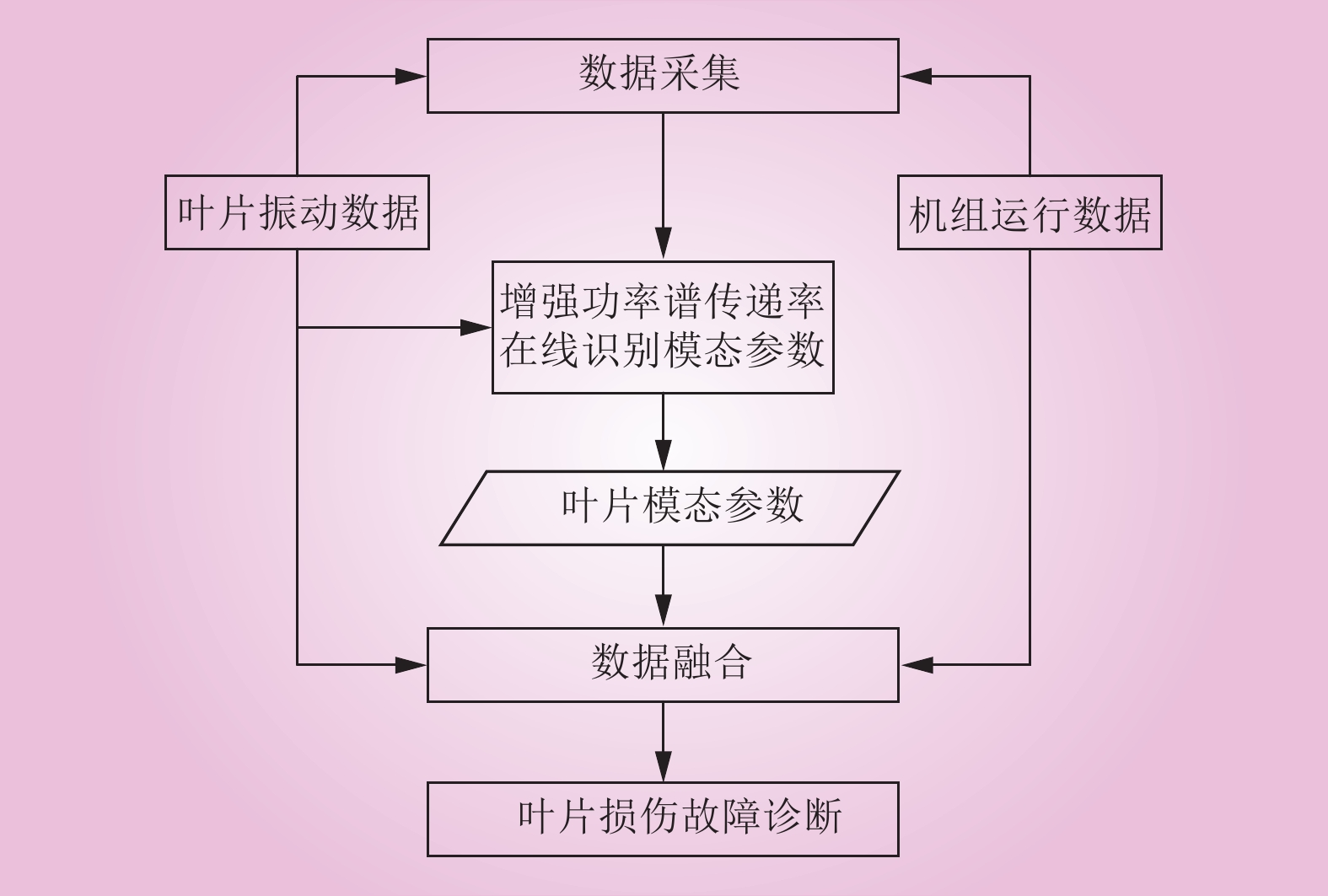
| 1 |
YANG X Y, ZHANG Y F, LV W, et al. Image recognition of wind turbine blade damage based on a deep learning model with transfer learning and an ensemble learning classifier[J]. Renewable Energy, 2021, 163, 386- 397.
|
| 2 |
王雪平, 张建斐, 李万润, 等. 基于机器视觉的风电叶片风沙侵蚀程度检测方法研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2020, 41 (5): 166- 173.
|
|
WANG Xueping, ZHANG Jianfei, LI Wanrun, et al. Study on monitoring method of wind power blades erosion severity under wind-sand storm based on machine vision technology[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2020, 41 (5): 166- 173.
|
| 3 |
赵肖懿, 董朝轶, 周鹏, 等. 基于无人机机器视觉的风力机叶片损伤诊断研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42 (7): 390- 397.
|
|
ZHAO Xiaoyi, DONG Chaoyi, ZHOU Peng, et al. Diagnosis of wind power generator blade damage based on unmanned aerial vehicle machine vision[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42 (7): 390- 397.
|
| 4 |
吴晓伦. 基于深度学习的大型风电机组叶片表面损伤边云协同检测架构及方法研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2021.
|
|
WU Xiaolun. Research on collaborative detection framework and method of edge cloud for blade surface damage of large wind turbine based on deep learning[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021.
|
| 5 |
CHEN B, YU S, YU Y, et al. Acoustical damage detection of wind turbine blade using the improved incremental support vector data description[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 156, 548- 557.
|
| 6 |
BEALE C, NIEZRECKI C, INALPOLAT M. An adaptive wavelet packet denoising algorithm for enhanced active acoustic damage detection from wind turbine blades[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 142, 106754.
|
| 7 |
XU D, LIU P F, CHEN Z P. Damage mode identification and singular signal detection of composite wind turbine blade using acoustic emission[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 255, 112954.
|
| 8 |
ZHANG Y N, AVALLONE F, WATSON S. Wind turbine blade trailing edge crack detection based on airfoil aerodynamic noise: an experimental study[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2022, 191, 108668.
|
| 9 |
张亚楠. 基于声发射信号处理的风力机叶片损伤演化研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2020.
|
|
ZHANG Yanan. Study on damage evolution of wind turbine blades based on acoustic emission signal processing[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2020.
|
| 10 |
OH K Y, PARK J Y, LEE J S, et al. A novel method and its field tests for monitoring and diagnosing blade health for wind turbines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2015, 64 (6): 1726- 1733.
|
| 11 |
SIERRA-PÉREZ J, TORRES-ARREDONDO M A, GÜEMES A. Damage and nonlinearities detection in wind turbine blades based on strain field pattern recognition. FBGs, OBR and strain gauges comparison[J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 135, 156- 166.
|
| 12 |
DOWNEY A, UBERTINI F, LAFLAMME S. Algorithm for damage detection in wind turbine blades using a hybrid dense sensor network with feature level data fusion[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2017, 168, 288- 296.
|
| 13 |
GARCÍA D, TCHERNIAK D. An experimental study on the data-driven structural health monitoring of large wind turbine blades using a single accelerometer and actuator[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 127, 102- 119.
|
| 14 |
TCHERNIAK D, MØLGAARD L L. Active vibration-based structural health monitoring system for wind turbine blade: demonstration on an operating Vestas V27 wind turbine[J]. Structural Health Monitoring:an International Journal, 2017, 16 (5): 536- 550.
|
| 15 |
JOSHUVA A, SUGUMARAN V. A data driven approach for condition monitoring of wind turbine blade using vibration signals through best-first tree algorithm and functional trees algorithm: a comparative study[J]. ISA Transactions, 2017, 67, 160- 172.
|
| 16 |
JIANG S C, LIN P, CHEN Y M, et al. Mixed-signal extraction and recognition of wind turbine blade multiple-area damage based on improved Fast-ICA[J]. Optik, 2019, 179, 1152- 1159.
|
| 17 |
LEE K, AIHARA A, PUNTSAGDASH G, et al. Feasibility study on a strain based deflection monitoring system for wind turbine blades[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 82, 117- 129.
|
| 18 |
DONG X F, LIAN J J, WANG H J, et al. Structural vibration monitoring and operational modal analysis of offshore wind turbine structure[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 150, 280- 297.
|
| 19 |
JARAMILLO F, GUTIÉRREZ J M, ORCHARD M, et al. A Bayesian approach for fatigue damage diagnosis and prognosis of wind turbine blades[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 174, 109067.
|
| 20 |
PACHECO-CHÉRREZ J, PROBST O. Vibration-based damage detection in a wind turbine blade through operational modal analysis under wind excitation[J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2022, 56, 291- 297.
|
| 21 |
MOVSESSIAN A, GARCÍA CAVA D, TCHERNIAK D. An artificial neural network methodology for damage detection: demonstration on an operating wind turbine blade[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2021, 159, 107766.
|
| 22 |
张鑫. 深度学习在风机叶片结构损伤识别中的仿真研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学, 2016.
|
|
ZHANG Xin. Simulation research on deep learning in wind trbine blade structural damage identification[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Jiatong University, 2016.
|
| 23 |
李芒芒. 风力机叶片机械损伤动态监测方法与技术研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学, 2012.
|
|
LI Mangmang. Research on dynamic monitoring method and technology of mechanical damage of wind turbine blades[D]. Changsha: Changsha University of Science & Technology, 2012.
|
| 24 |
李孟珠, 刘纲, 黎华, 等. 大型风力机叶片状态监测方法研究进展[J]. 热力发电, 2022, 51 (12): 18- 29.
|
|
LI Mengzhu, LIU Gang, LI Hua, et al. Research progress of blade condition monitoring methods for large wind turbines[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2022, 51 (12): 18- 29.
|
| 25 |
廖礼. 风力机叶片模态分析及应用[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2021.
|
|
LIAO Li. Modal analysis and application of wind turbine blades[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021.
|