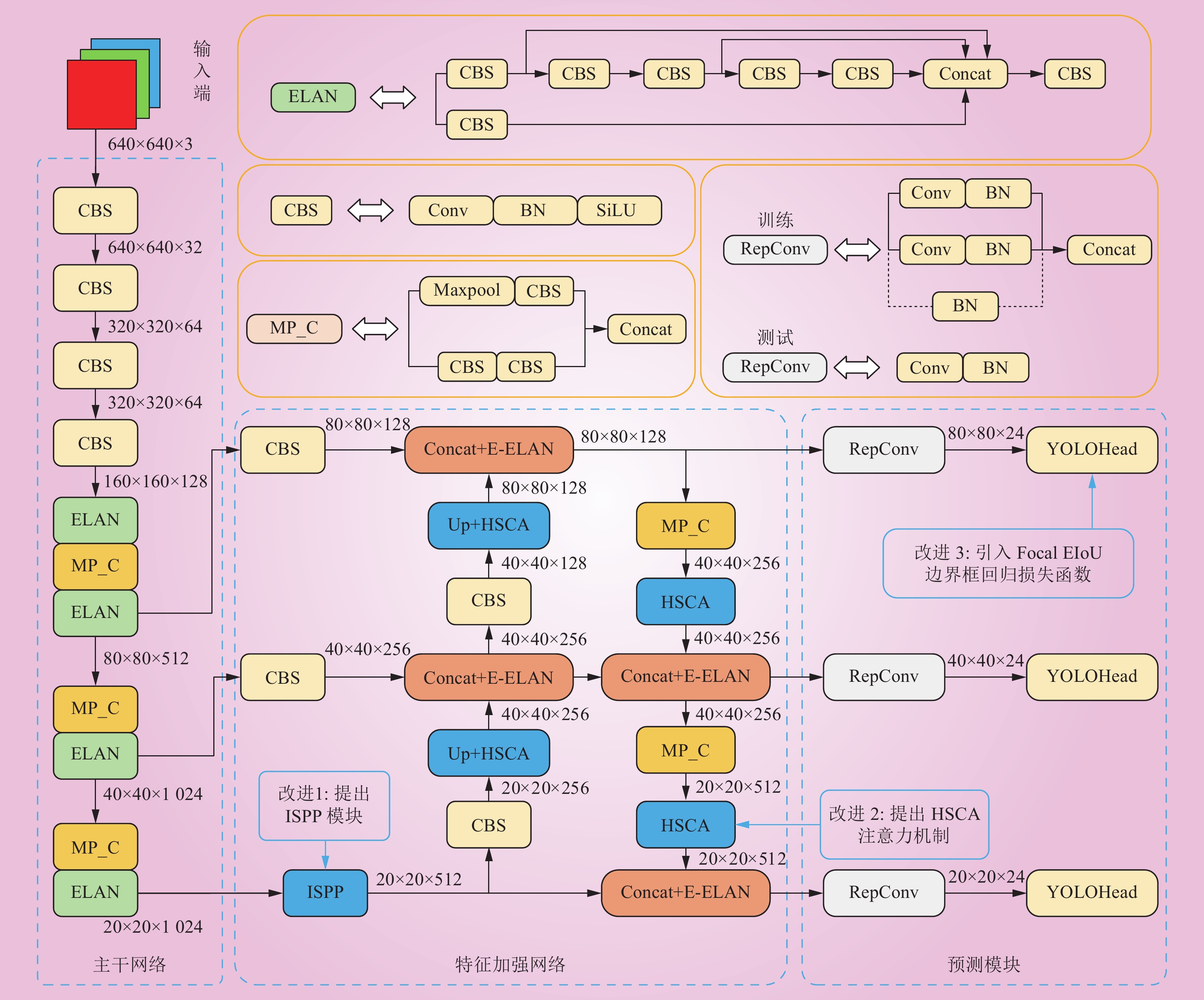
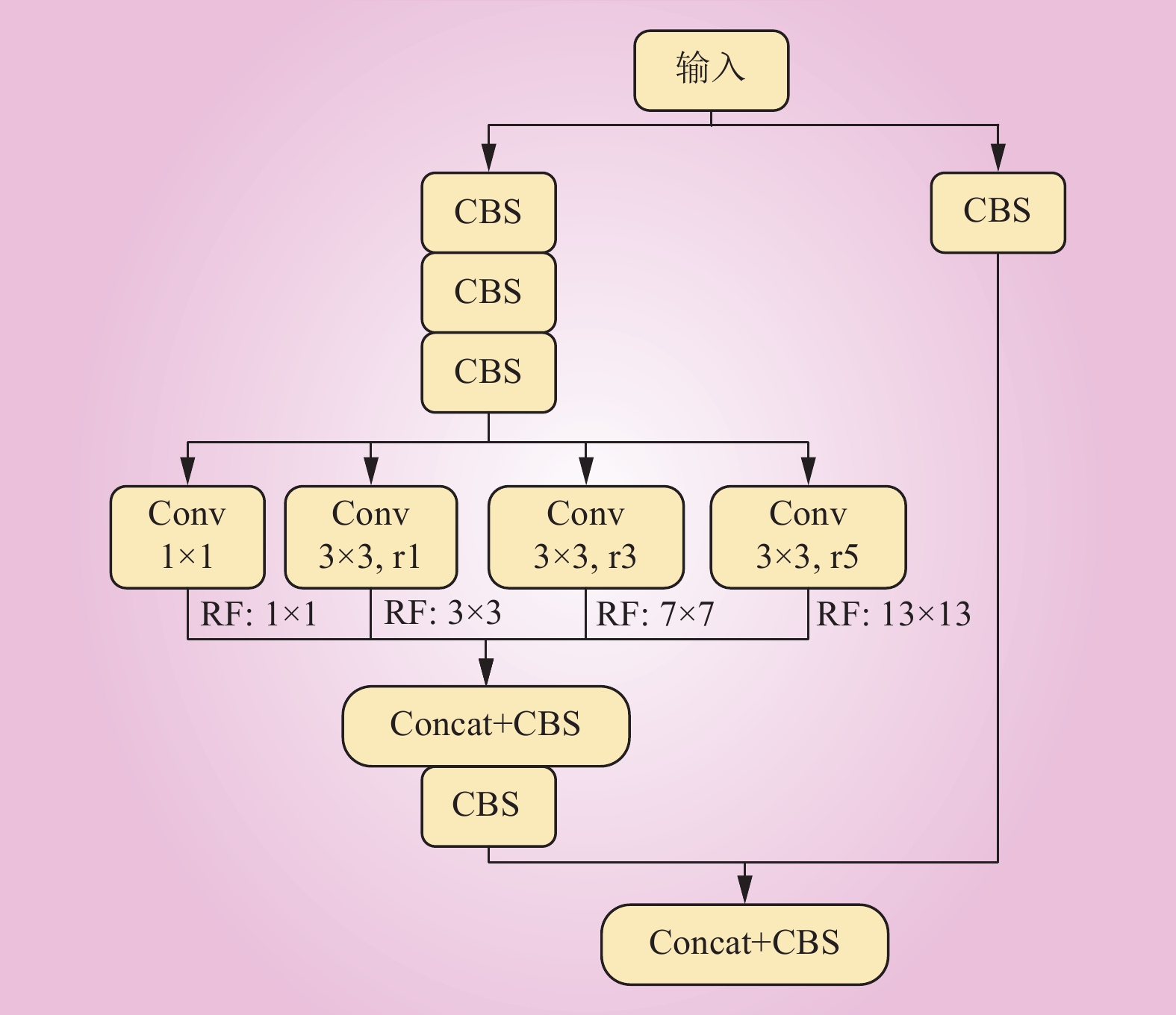
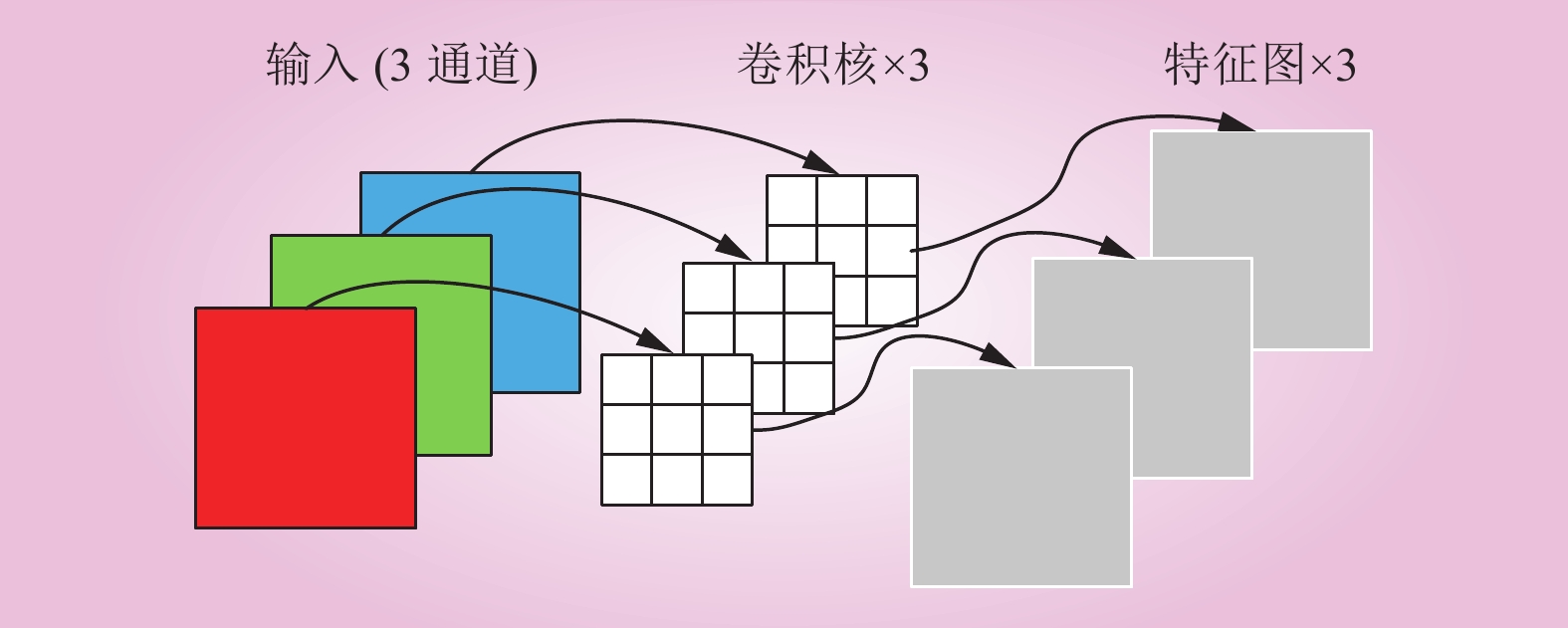
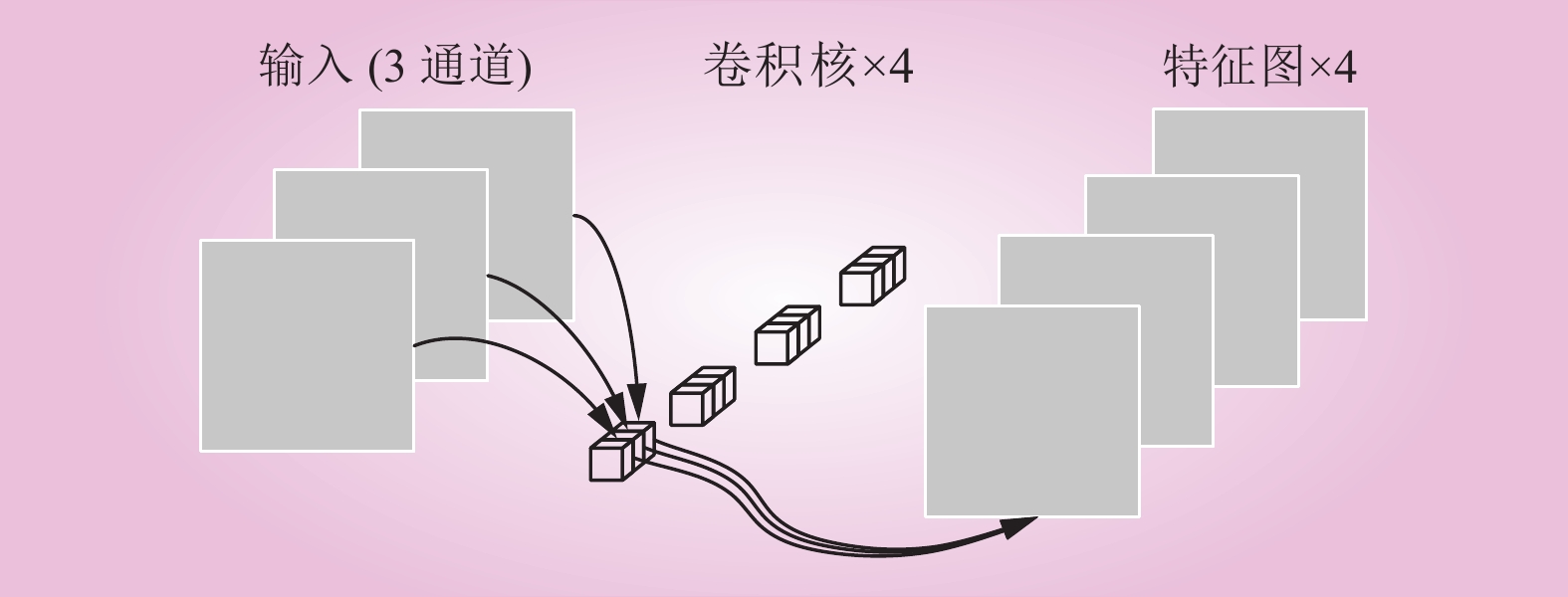
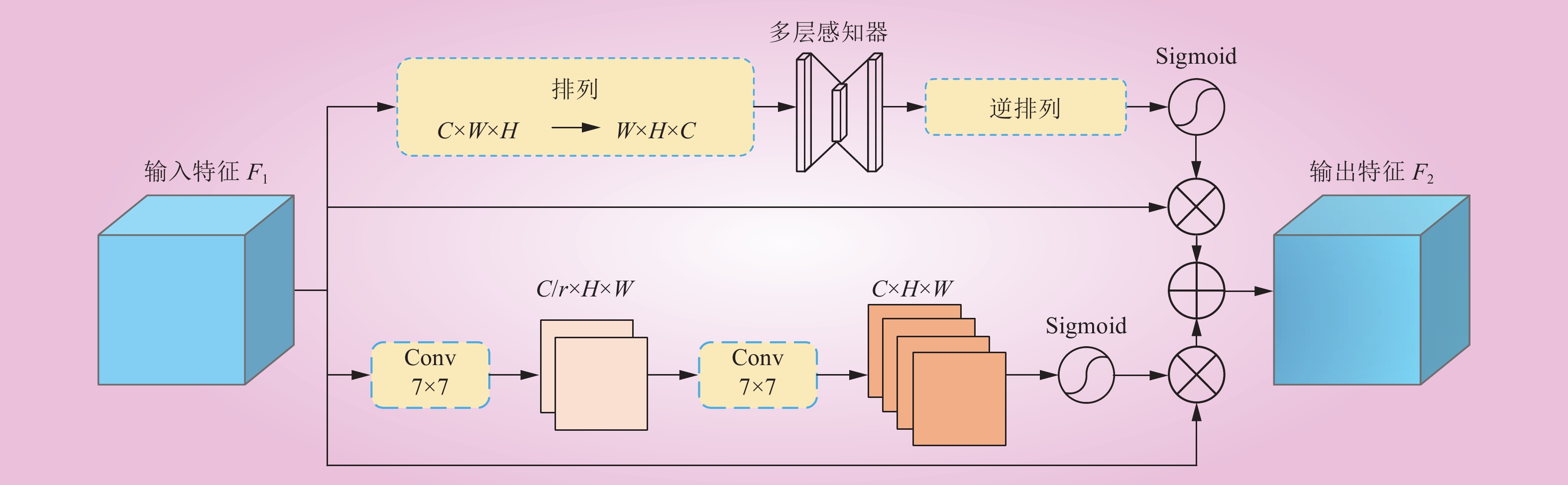
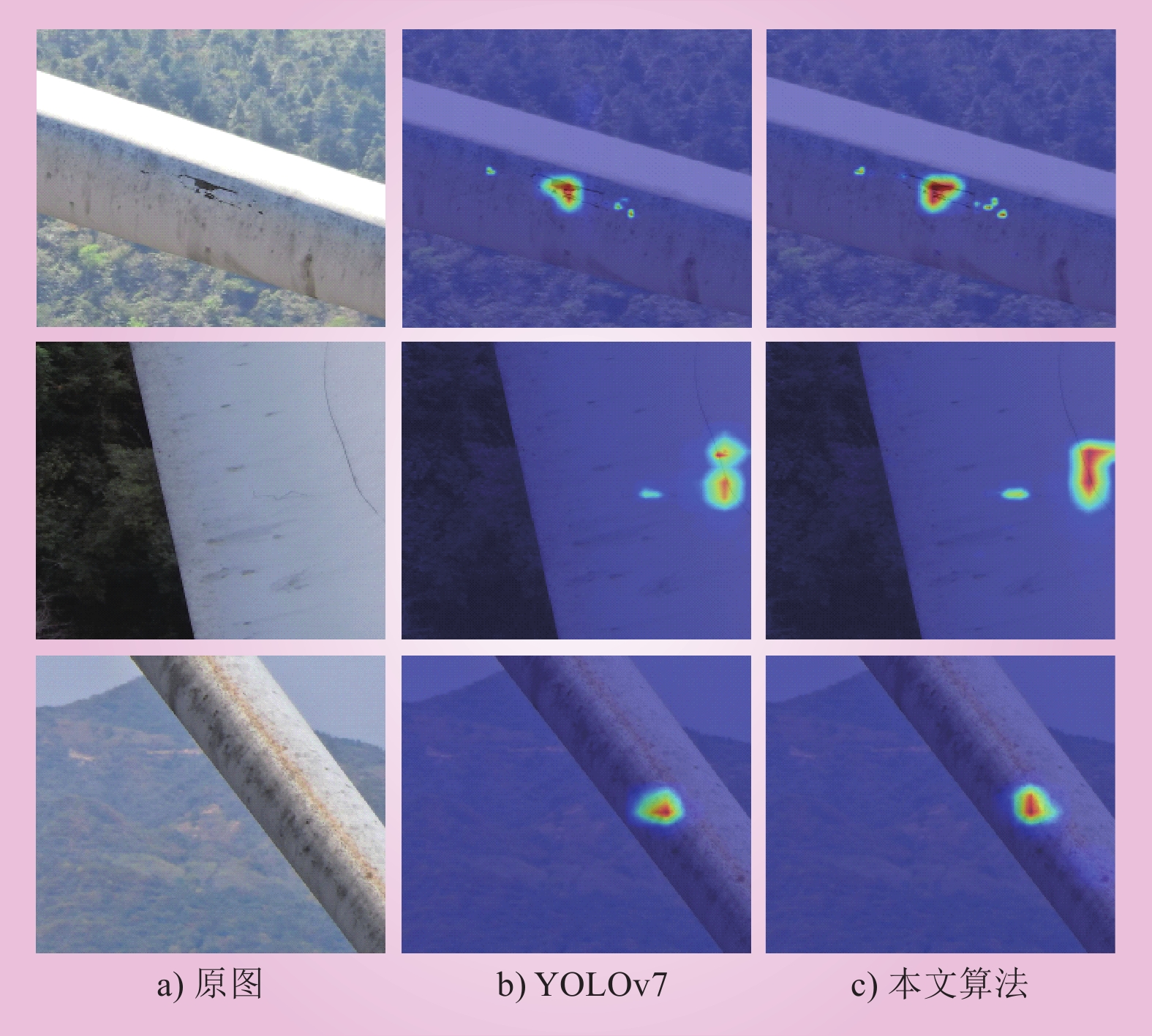
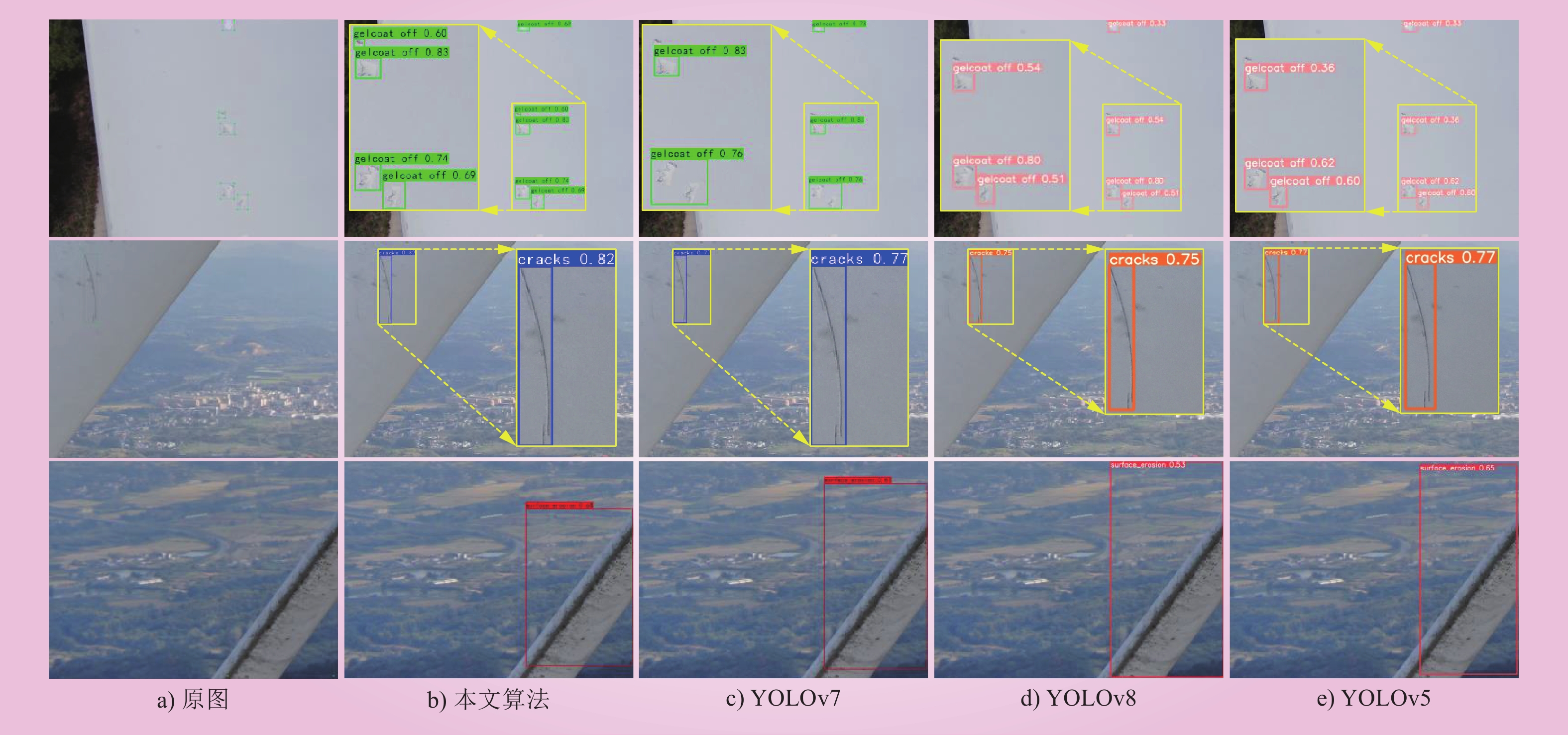
| 1 |
时智勇, 王彩霞, 李琼慧. “十四五”中国海上风电发展关键问题[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (7): 8- 17.
|
|
SHI Zhiyong, WANG Caixia, LI Qionghui. Key issues of China’s offshore wind power development in the “14 th five-year plan”[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (7): 8- 17.
|
| 2 |
胡蓓, 吴永康, 郭子君, 等. 风力发电叶片裂缝监测技术综述[J]. 高压电器, 2022, 58 (7): 93- 100.
|
|
HU Bei, WU Yongkang, GUO Zijun, et al. Review of wind turbine blade crack monitoring technology[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2022, 58 (7): 93- 100.
|
| 3 |
海涛, 范恒, 王楷杰, 等. 基于PSO-SVM算法的风电机组结冰故障诊断[J]. 智慧电力, 2021, 49 (4): 1- 6, 74.
|
|
HAI Tao, FAN Heng, WANG Kaijie, et al. Fault diagnosis of wind turbine icing based on PSO-SVM algorithm[J]. Smart Power, 2021, 49 (4): 1- 6, 74.
|
| 4 |
WANG W J, XUE Y, HE C K, et al. Review of the typical damage and damage-detection methods of large wind turbine blades[J]. Energies, 2022, 15 (15): 5672.
|
| 5 |
MCGUGAN M, MISHNAEVSKY L. Damage mechanism based approach to the structural health monitoring of wind turbine blades[J]. Coatings, 2020, 10 (12): 1223.
|
| 6 |
黄子恒, 许钊源, 伍剑波, 等. 基于优化模态分解和Xgblr的风机叶片故障诊断方法[J]. 机械设计, 2022, 39 (7): 56- 62.
|
|
HUANG Ziheng, XU Zhaoyuan, WU Jianbo, et al. Fault diagnosis method of fan blade based on optimized modal decomposition and Xgblr[J]. Journal of Machine Design, 2022, 39 (7): 56- 62.
|
| 7 |
AWADALLAH M, EL-SINAWI A. Effect and detection of cracks on small wind turbine blade vibration using special Kriging analysis of spectral shifts[J]. Measurement, 2020, 151, 107076.
|
| 8 |
葛畅, 阎洁, 刘永前, 等. 海上风电场运行控制维护关键技术综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (12): 4278- 4292.
|
|
GE Chang, YAN Jie, LIU Yongqian, et al. Review of key technologies for operation control and maintenance of offshore wind farm[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (12): 4278- 4292.
|
| 9 |
陶显, 侯伟, 徐德. 基于深度学习的表面缺陷检测方法综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47 (5): 1017- 1034.
|
|
TAO Xian, HOU Wei, XU De. A survey of surface defect detection methods based on deep learning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47 (5): 1017- 1034.
|
| 10 |
孙月莹, 陈俊霖, 张胜茂, 等. 基于改进YOLOv7的毛虾捕捞渔船作业目标检测与计数方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2023, 39 (10): 151- 162.
|
|
SUN Yueying, CHEN Junlin, ZHANG Shengmao, et al. Target detection and counting method for Acetes chinensis fishing vessels operation based on improved YOLOv7[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39 (10): 151- 162.
|
| 11 |
张艳君, 沈平, 郭安辉, 等. 融合CBAM-YOLOv7模型的路面缺陷智能检测方法研究[J/OL]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学): 1–7[2023-07-04]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1205.T.20230629.1123.002.html.
|
|
ZHANG Yanjun, SHEN Ping, GUO Anhui, et al. . Research on intelligent detection method of pavement defects incorporating CBAM-YOLOv7 model[J/OL]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science): 1–7[2023-07-04]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1205.T.20230629.1123.002.html.
|
| 12 |
仝卫国, 仪小龙, 李冰, 等. 融合多尺度特征与注意力机制的风机桨叶缺陷检测方法[J]. 电子测量技术, 2022, 45 (24): 166- 172.
|
|
TONG Weiguo, YI Xiaolong, LI Bing, et al. Fan blade defect detection method combining multi-scale features and attention mechanism[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2022, 45 (24): 166- 172.
|
| 13 |
GUO J H, LIU C, CAO J F, et al. Damage identification of wind turbine blades with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Renewable Energy, 2021, 174, 122- 133.
|
| 14 |
ZHANG J J, COSMA G, WATKINS J. Image enhanced mask R-CNN: a deep learning pipeline with new evaluation measures for wind turbine blade defect detection and classification[J]. Journal of Imaging, 2021, 7 (3): 46.
|
| 15 |
WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, LIAO H Y M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors[EB/OL](2022-07-15)[2022-12-21].https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.02696.
|
| 16 |
GE Z, LIU S, WANG F, et al. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021[J/OL]. 2021. DOI:10.48550/arXiv.2107.08430.
|
| 17 |
郑果, 姜玉松, 沈永林. 基于改进YOLOv7的水稻害虫识别方法[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2023, 42 (3): 143- 151.
|
|
ZHENG Guo, JIANG Yusong, SHEN Yonglin. Recognition of rice pests based on improved YOLOv7[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2023, 42 (3): 143- 151.
|
| 18 |
LIU Y C, SHAO Z R, HOFFMANN N. Global attention mechanism: retain information to enhance channel-spatial interactions[EB/OL](2021-12-10)[2022-12-21].https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.05561.
|
| 19 |
ZHANG Y F, REN W Q, ZHANG Z, et al. Focal and efficient IOU loss for accurate bounding box regression[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 506, 146- 157.
|
| 20 |
谭兴国, 张高明. 基于无人机巡检的风机叶片表面缺陷检测技术[J/OL]. 电测与仪表: 1–10[2023-04-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1202.T H.20221013.1050.004.html.
|
|
TAN Guoxing, ZHANG Gaoming. UAV-based inspection of wind turbine blade surface defects detection technology[J/OL]. Electrical Measure-ment & Instrumentation: 1–10[2023-02-02]. http:// kns.cnki.net/ kcms/de-tail/23.1202.TH.20221013. 1050.004.html.
|
| 21 |
焦嵩鸣, 白健鹏, 首云锋. 风机叶片精准巡视的无人机控制策略研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (10): 3822- 3832.
|
|
JIAO Songming, BAI Jianpeng, SHOU Yunfeng. Research on UAV control strategy for accurate inspection of wind turbine blades[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (10): 3822- 3832.
|
| 22 |
赵文清, 杨盼盼. 双向特征融合与注意力机制结合的目标检测[J]. 智能系统学报, 2021, 16 (6): 1098- 1105.
|
|
ZHAO Wenqing, YANG Panpan. Target detection based on bidirectional feature fusion and an attention mechanism[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2021, 16 (6): 1098- 1105.
|
| 23 |
WANG J W, XU C, YANG W, et al. A normalized Gaussian Wasserstein distance for tiny object detection[EB/OL](2021-10-26)[2022-12-21].https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13389.
|
| 24 |
LIU Y C, SHAO Z R, TENG Y Y, et al. NAM: normalization-based attention module[EB/OL](2021-11-24)[2022-12-21].https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.12419.
|
| 25 |
黄冬梅, 王玥琦, 胡安铎, 等. 融合多维度特征的绝缘子状态边缘识别方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (1): 133- 141.
|
|
HUANG Dongmei, WANG Yueqi, HU Anduo, et al. An edge recognition method for insulator state based on multi-dimension feature fusion[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (1): 133- 141.
|