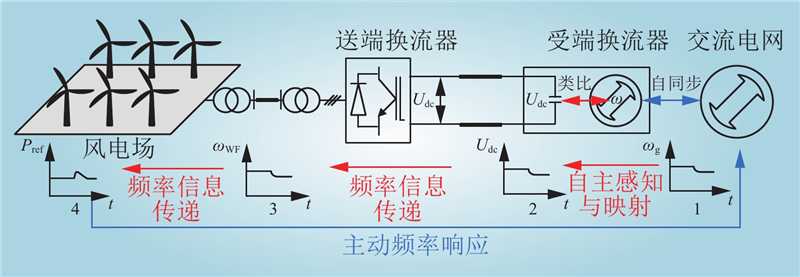
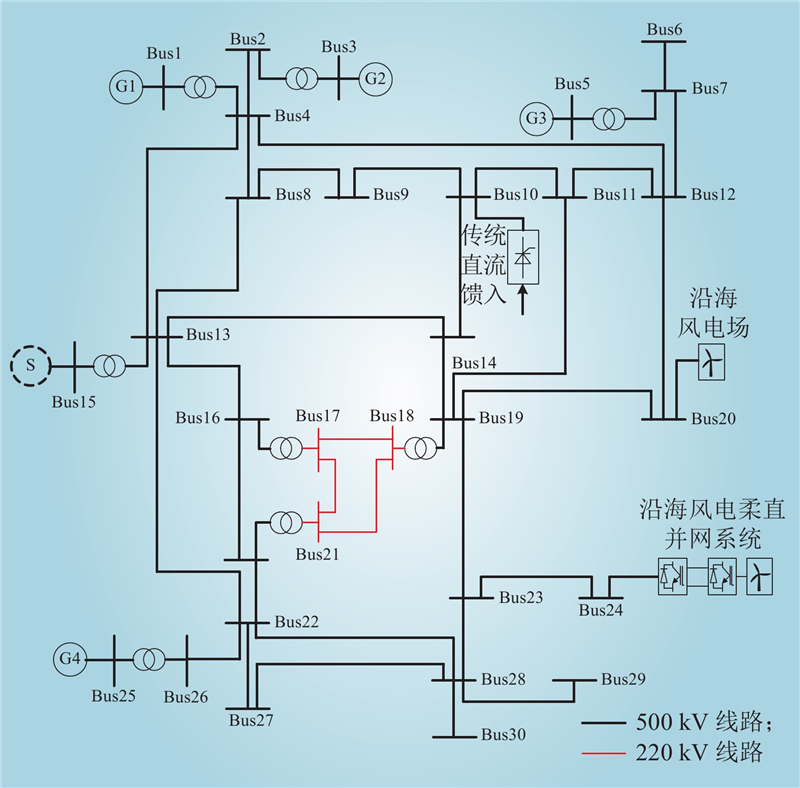
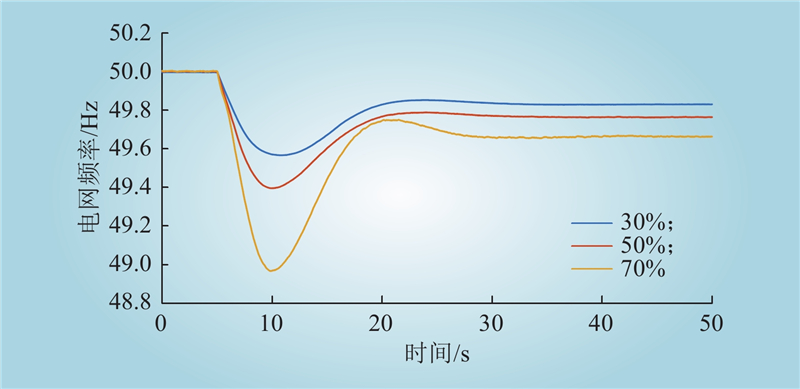
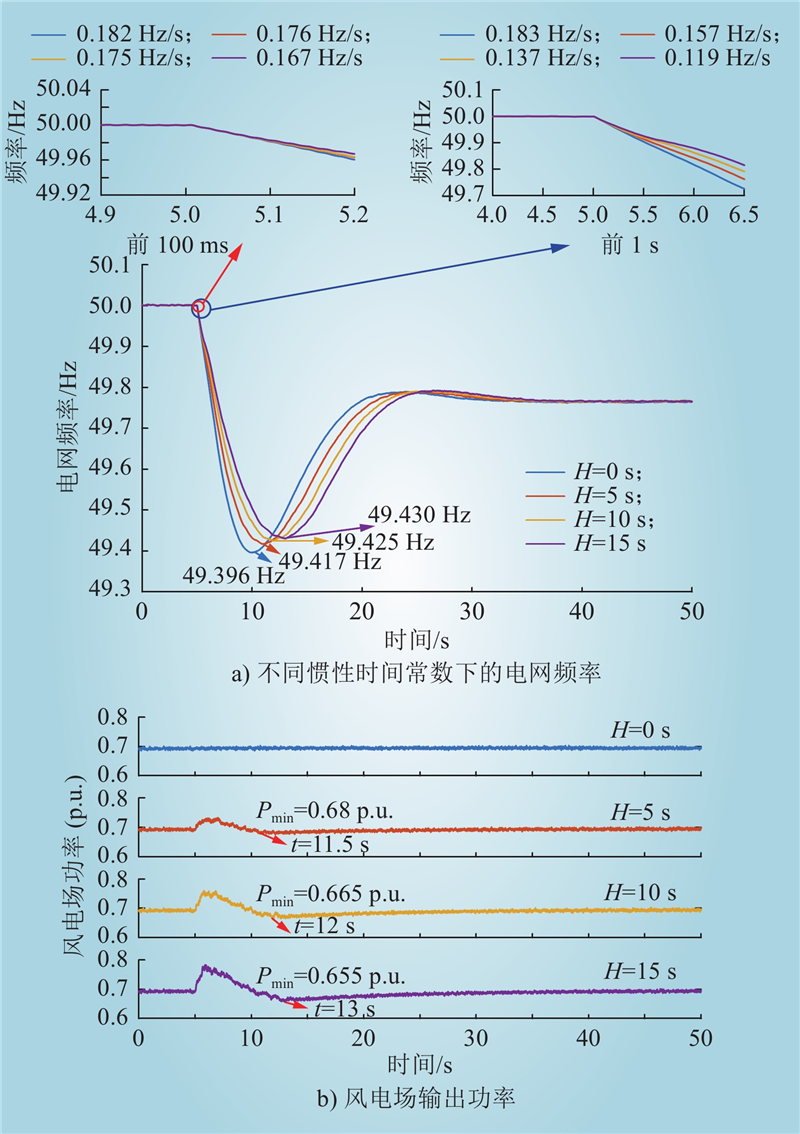
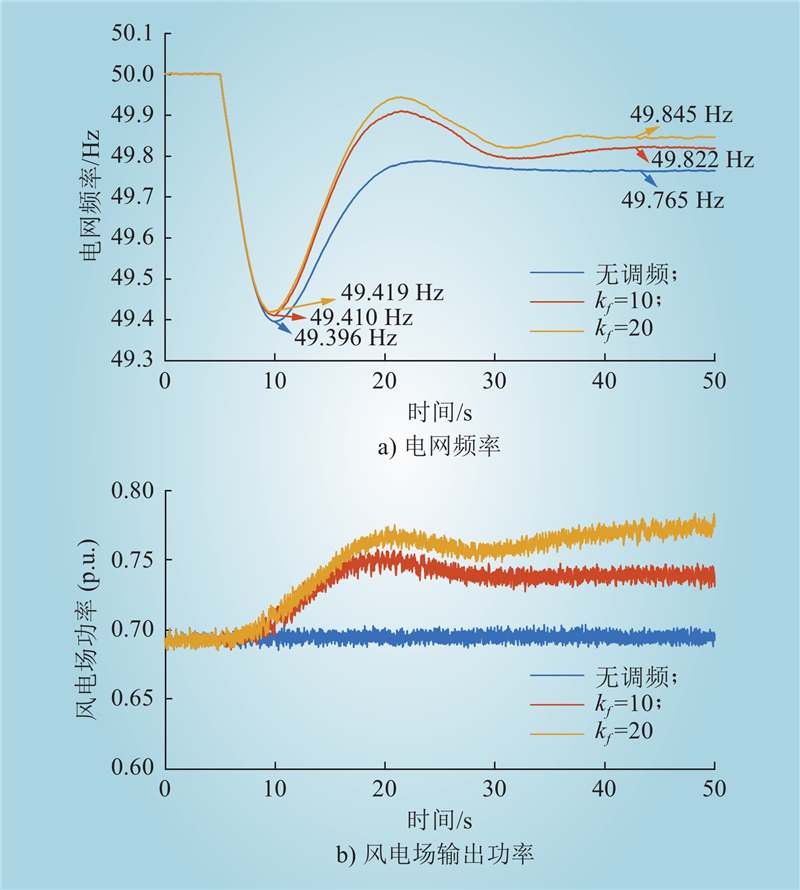
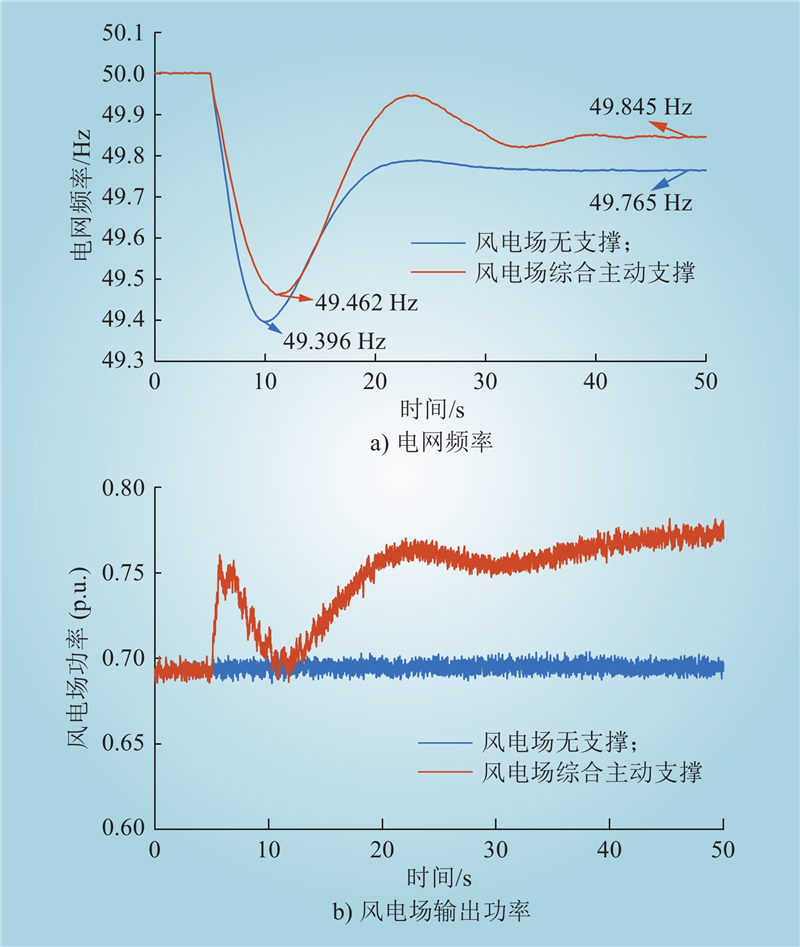
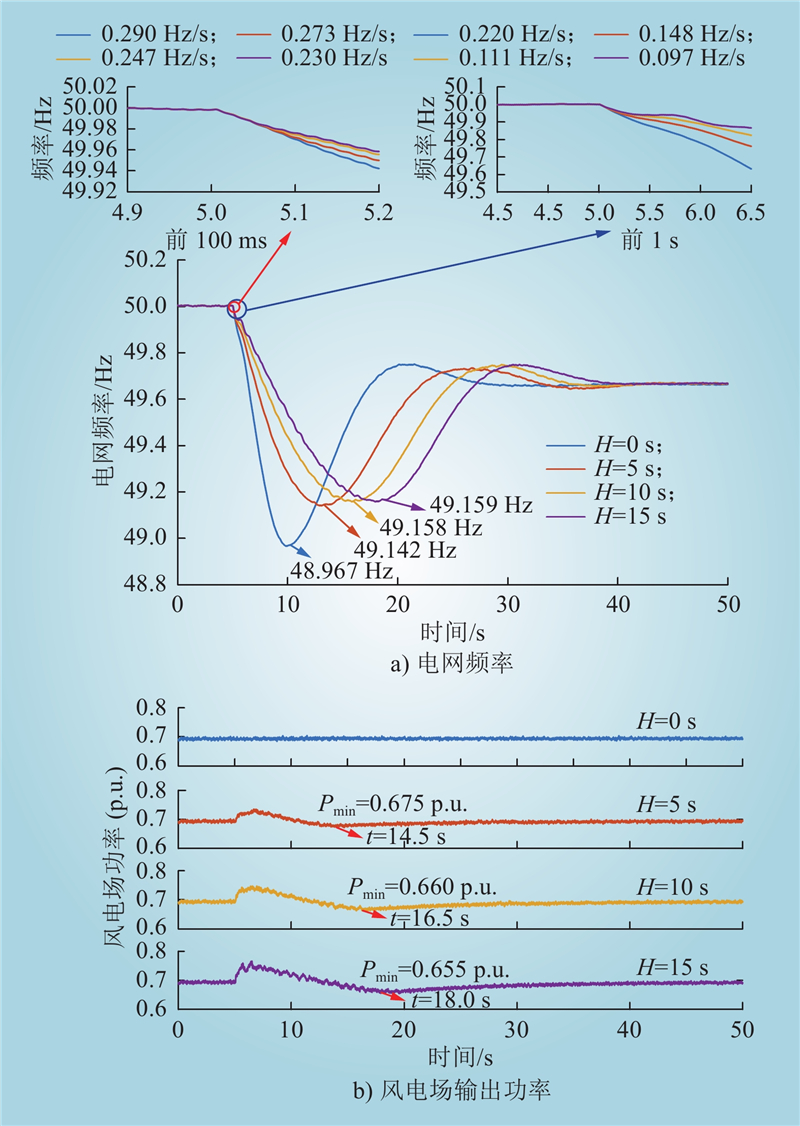
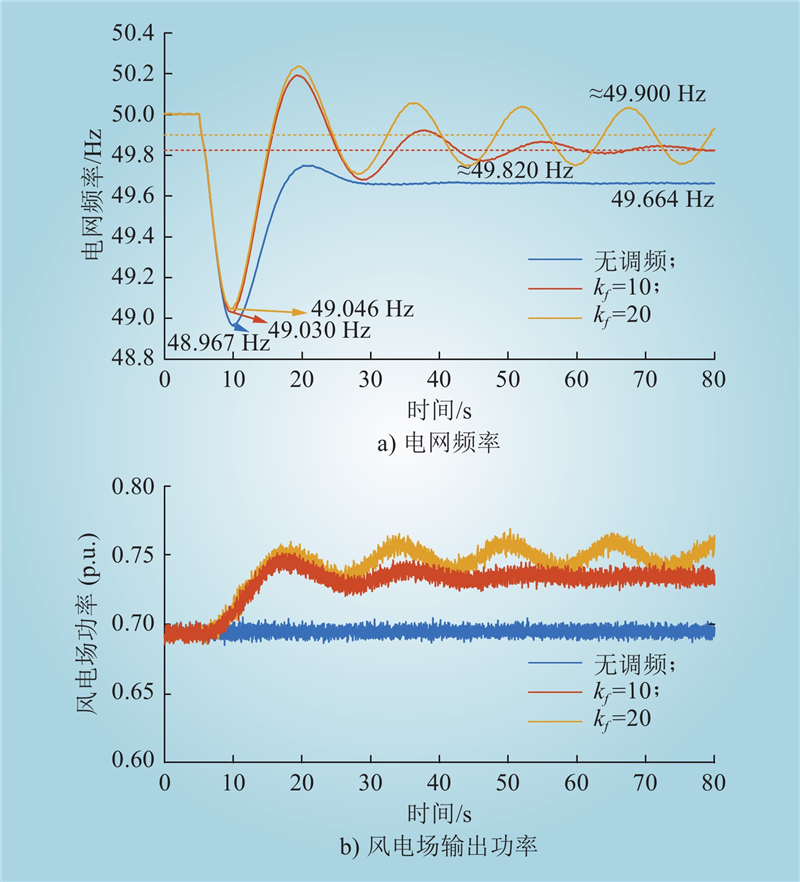
| 1 |
张运洲, 张宁, 代红才, 等. 中国电力系统低碳发展分析模型构建与转型路径比较[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (3): 1- 11.
|
|
ZHANG Yunzhou, ZHANG Ning, DAI Hongcai, et al. Model construction and pathways of low-carbon transition of China's power system[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (3): 1- 11.
|
| 2 |
时智勇, 王彩霞, 李琼慧. “十四五”中国海上风电发展关键问题[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (7): 8- 17.
|
|
SHI Zhiyong, WANG Caixia, LI Qionghui. Key issues of China’s offshore wind power development in the “14 th five-year plan”[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (7): 8- 17.
|
| 3 |
蔡旭, 杨仁炘, 周剑桥, 等. 海上风电直流送出与并网技术综述[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (21): 2- 22.
|
|
CAI Xu, YANG Renxin, ZHOU Jianqiao, et al. Review on offshore wind power integration via DC transmission[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (21): 2- 22.
|
| 4 |
付红军, 陈惠粉, 赵华, 等. 高渗透率下风电的调频技术研究综述[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (1): 104- 115.
|
|
FU Hongjun, CHEN Huifen, ZHAO Hua, et al. Review on frequency regulation technology with high wind power penetration[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (1): 104- 115.
|
| 5 |
MAURICIO J M, MARANO A, GOMEZ-EXPOSITO A, et al. Frequency regulation contribution through variable-speed wind energy conversion systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2009, 24 (1): 173- 180.
|
| 6 |
曹军, 王虹富, 邱家驹. 变速恒频双馈风电机组频率控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2009, 33 (13): 78- 82.
|
|
CAO Jun, WANG Hongfu, QIU Jiaju. Frequency control strategy of variable-speed constant-frequency doubly-fed induction generator wind turbines[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2009, 33 (13): 78- 82.
|
| 7 |
刘櫂芮, 贾祺, 严干贵, 等. 基于惯量响应的双馈风电机组动态协调机理研究[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (7): 142- 151.
|
|
LIU Zhaorui, JIA Qi, YAN Gangui, et al. Research on dynamic coordination mechanism of DFIGs based on inertia response[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (7): 142- 151.
|
| 8 |
李军军, 吴政球. 风电参与一次调频的小扰动稳定性分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2011, 31 (13): 1- 9.
|
|
LI Junjun, WU Zhengqiu. Small signal stability analysis of wind power generation participating in primary frequency regulation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2011, 31 (13): 1- 9.
|
| 9 |
那广宇, 王亮, 刘雨桐, 等. 基于VSG的改进型虚拟阻尼控制策略与特性分析[J]. 智慧电力, 2020, 48 (4): 48- 54.
|
|
NA Guangyu, WANG Liang, LIU Yutong, et al. VSG based improved virtual damping control strategy and characteristics analysis[J]. Smart Power, 2020, 48 (4): 48- 54.
|
| 10 |
钟庆昌. 虚拟同步机与自主电力系统[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37 (2): 336- 349.
|
|
ZHONG Qingchang. Virtual synchronous machines and autonomous power systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37 (2): 336- 349.
|
| 11 |
桑顺, 张琛, 蔡旭, 等. 全功率变换风电机组的电压源控制(一): 控制架构与弱电网运行稳定性分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (16): 5604- 5616.
|
|
SANG Shun, ZHANG Chen, CAI Xu, et al. Voltage source control of wind turbines with full-scale converters (part Ⅰ): control architecture and stability analysis under weak grid conditions[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (16): 5604- 5616.
|
| 12 |
FU Y, WANG Y, ZHANG X. Integrated wind turbine controller with virtual inertia and primary frequency responses for grid dynamic frequency support[J]. IET Renewable Power Generation, 2017, 11 (8): 1129- 1137.
|
| 13 |
CAI Y, LI Z, CAI X. Optimal inertia reserve and inertia control strategy for wind farms[J]. Energies, 2020, 13 (5): 1067.
|
| 14 |
SANG S, ZHANG C, CAI X, et al. Control of a type-IV wind turbine with the capability of robust grid-synchronization and inertial response for weak grid stable operation[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 58553- 58569.
|
| 15 |
LIU H Z, CHEN Z. Contribution of VSC-HVDC to frequency regulation of power systems with offshore wind generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2015, 30 (3): 918- 926.
|
| 16 |
李宇骏, 杨勇, 李颖毅, 等. 提高电力系统惯性水平的风电场和VSC-HVDC协同控制策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34 (34): 6021- 6031.
|
|
LI Yujun, YANG Yong, LI Yingyi, et al. Coordinated control of wind farms and VSC-HVDC to improve inertia level of power system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34 (34): 6021- 6031.
|
| 17 |
杨仁炘, 张琛, 蔡旭. 具有频率实时镜像和自主电网同步能力的风场–柔直系统控制方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37 (2): 496- 506.
|
|
YANG Renxin, ZHANG Chen, CAI Xu. Control of VSC-HVDC with real-time frequency mirroring and self-synchronizing capability for wind farm integration[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37 (2): 496- 506.
|