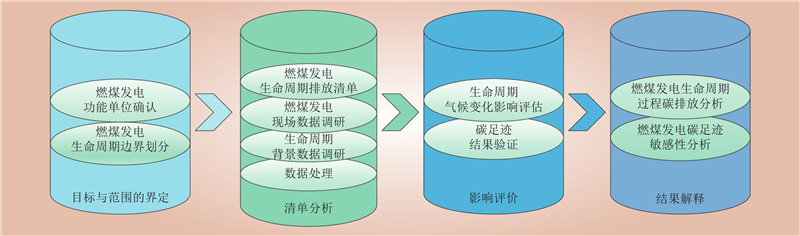
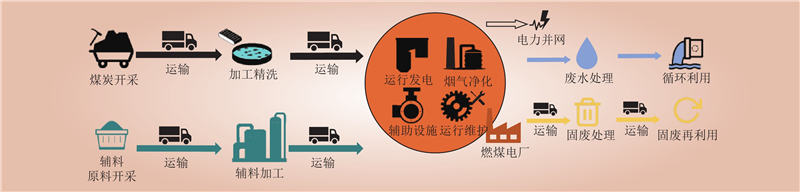
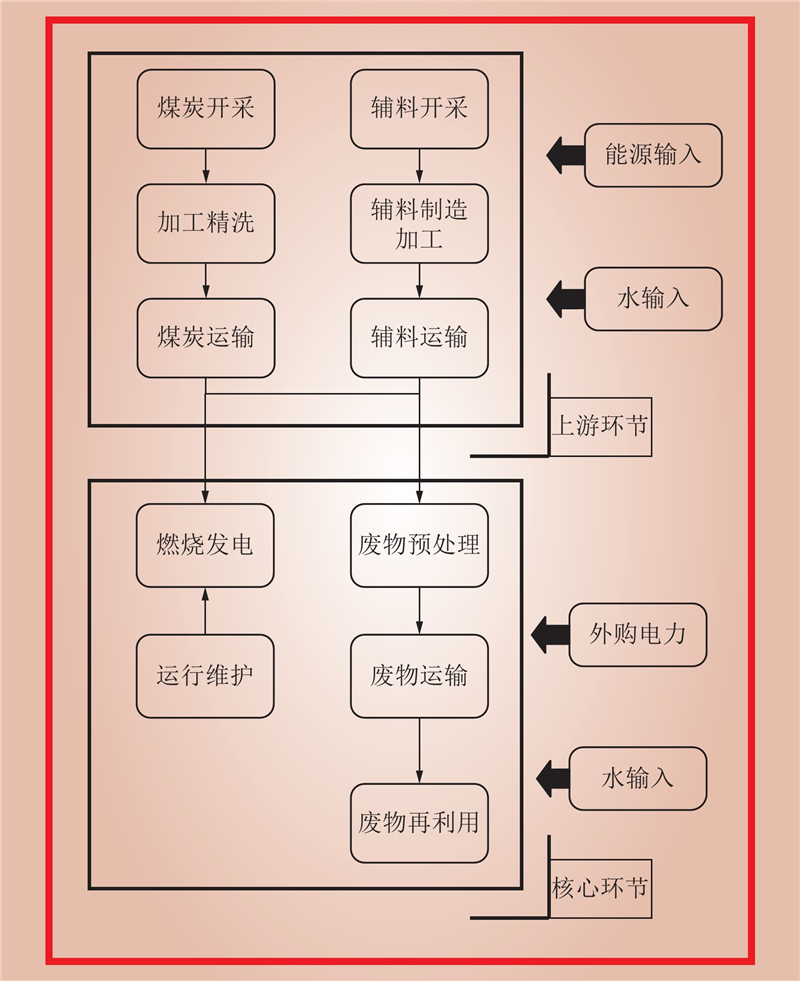
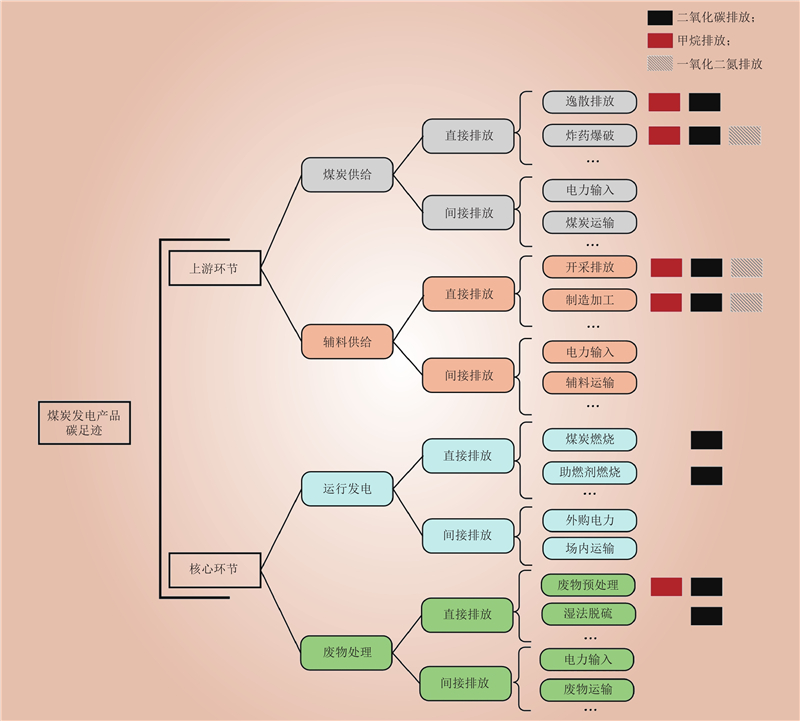
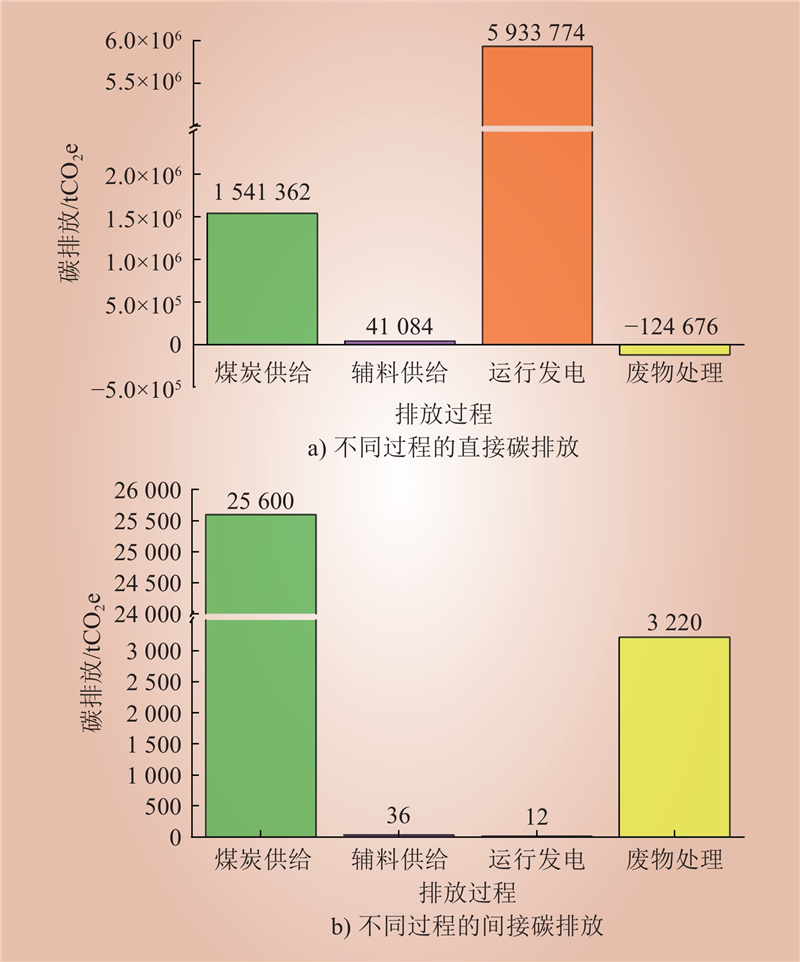
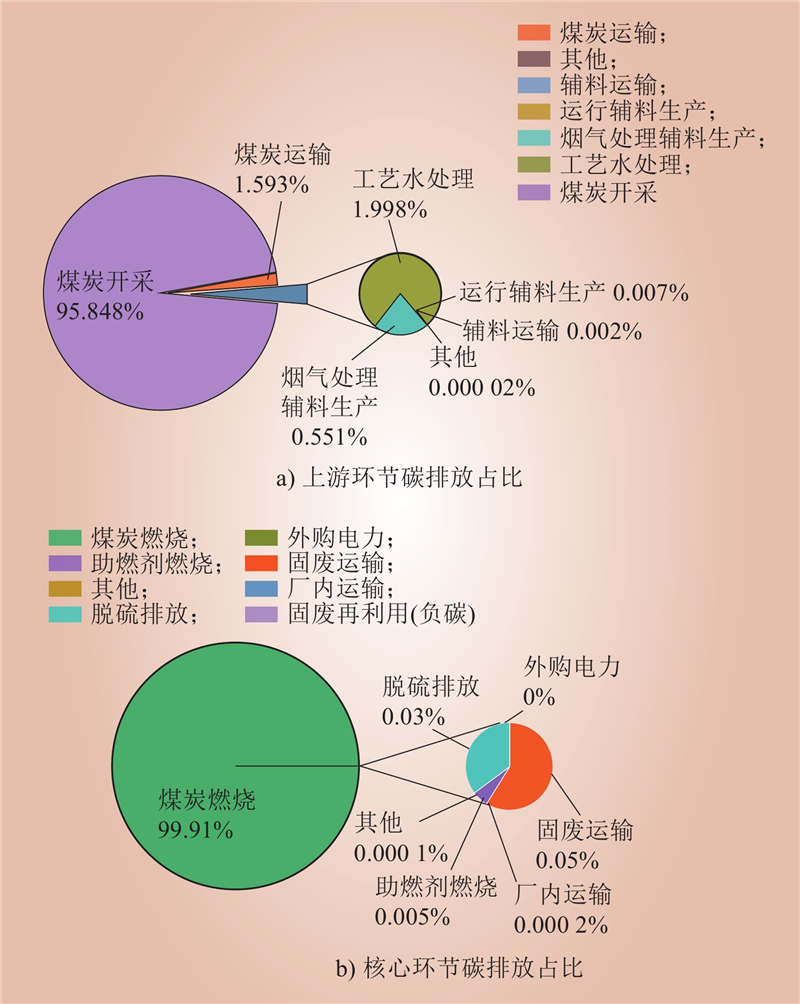
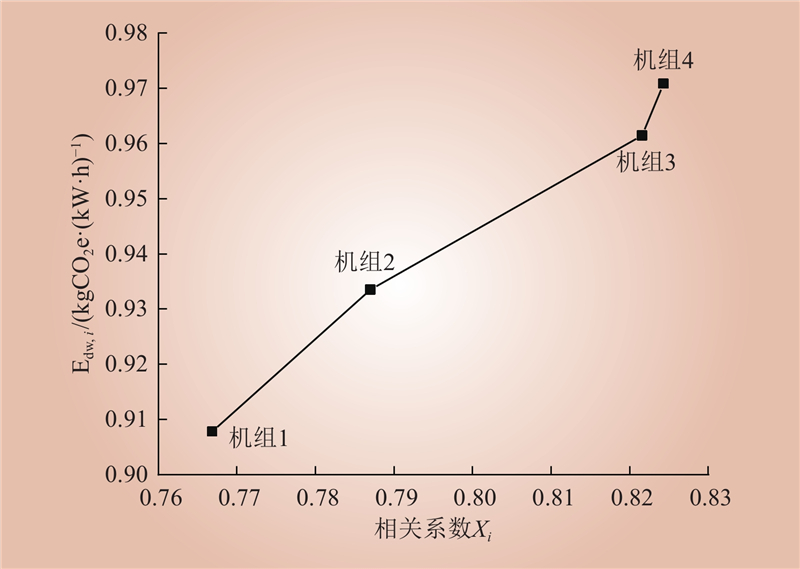
| 1 |
HORTON D E, JOHNSON N C, SINGH D, et al. Contribution of changes in atmospheric circulation patterns to extreme temperature trends[J]. Nature, 2015, 522, 465- 469.
DOI
|
| 2 |
胡道成, 王睿, 赵瑞, 等. 二氧化碳捕集技术及适用场景分析[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (4): 502- 513.
|
|
HU Daocheng, WANG Rui, ZHAO Rui, et al. Research on carbon dioxide capture technology and suitable scenarios[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (4): 502- 513.
|
| 3 |
Energy Institute. Statistical review of world energy 2023[EB/OL]. (2023-06-01) [2024-04-30]. https://kpmg.com/cn/zh/home/campaigns/2023/10/statistical-review-of-world-energy-2023.html.
|
| 4 |
燕志鹏, 于泽民, 顾新莲. 我国碳排放价格与煤炭期货价格的传导机制研究[J]. 经济问题, 2022, (6): 67- 74.
DOI
|
|
YAN Zhipeng, YU Zemin, GU Xinlian. Research on conduction mechanism between carbon price and coal future price in China[J]. On Economic Problems, 2022, (6): 67- 74.
DOI
|
| 5 |
王一蓉, 陈浩林, 林立身, 等. 考虑电力行业碳排放的全国碳价预测[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (5): 79- 87.
|
|
WANG Yirong, CHEN Haolin, LIN Lishen, et al. National carbon price prediction considering carbon emissions from the power industry[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (5): 79- 87.
|
| 6 |
IEA. Electricity 2024[EB/OL]. (2024-01-04) [2024-04-30]. https://www.iea.org/reports/electricity-2024.
|
| 7 |
王月明, 姚明宇, 张一帆, 等. 煤电的低碳化发展路径研究[J]. 热力发电, 2022, 51 (1): 11- 20.
|
|
WANG Yueming, YAO Mingyu, ZHANG Yifan, et al. Study on low-carbon development path of coal-fired power generation[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2022, 51 (1): 11- 20.
|
| 8 |
汤芳, 代红才, 张宁, 等. 能耗双控向碳排放双控转变影响分析及推进路径设计[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 255- 261.
|
|
TANG Fang, DAI Hongcai, ZHANG Ning, et al. Effect analysis and promotion path design for transformation from energy consumption "dual control" to carbon "dual control"[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 255- 261.
|
| 9 |
METZ B, KUIJPERS L, SOLOMON S, et al. IPCC/TEAP special report on safe guarding the ozone layer and the global climate system: issues related to hydro fluorocarbons and perfluoro carbons[M]. Cambridge: Published for the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [M] Cambridge University Press, 2005.
|
| 10 |
王斯一, 张彩虹, 米锋. 资源价值流视角下发电企业碳足迹与经济成本评价: 燃煤发电与生物质发电比较研究[J]. 工业技术经济, 2018, 37 (12): 78- 85.
DOI
|
|
WANG Siyi, ZHANG Caihong, MI Feng. Evaluation of carbon footprint and economic cost from the perspective of resource value flow of power generation enterprises[J]. Journal of Industrial Technological Economics, 2018, 37 (12): 78- 85.
DOI
|
| 11 |
贾亚雷, 王继选, 韩中合, 等. 基于LCA的风力发电、光伏发电及燃煤发电的环境负荷分析[J]. 动力工程学报, 2016, 36 (12): 1000- 1009.
|
|
JIA Yalei, WANG Jixuan, HAN Zhonghe, et al. Analysis on environmental load of wind, PV and coal-fired power generation based on life cycle assessment[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2016, 36 (12): 1000- 1009.
|
| 12 |
宋国辉, 唐璐, 姜武, 等. 2×200MW级某天然气热电联产项目的生命周期环境影响评价[J]. 中国电力, 2014, 47 (12): 149- 155.
|
|
SONG Guohui, TANG Lu, JIANG Wu, et al. Life-cycle environmental impact assessment of a typical 2 × 200 MW natural gas combined cycle-combined heat and power plant[J]. Electric Power, 2014, 47 (12): 149- 155.
|
| 13 |
刘顺妮, 林宗寿, 张小伟. 硅酸盐水泥的生命周期评价方法初探[J]. 中国环境科学, 1998, 18 (4): 328- 332.
DOI
|
|
LIU Shunni, LIN Zongshou, ZHANG Xiaowei. Studies on the life circle assessment of Portland cement[J]. China Environmental Science, 1998, 18 (4): 328- 332.
DOI
|
| 14 |
国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 环境管理生命周期评价 原则与框架: GB/T 24040—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.
|
| 15 |
TONG R P, WANG Y R, ZHAO X, et al. Modeling health impacts of air pollutant emissions from the coal-fired power industry based on LCA and oriented by WTP: a case study[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2022, 29 (23): 34486- 34499.
DOI
|
| 16 |
MODAHL I S, ASKHAM C, LYNG K A, et al. Weighting of environmental trade-offs in CCS—an LCA case study of electricity from a fossil gas power plant with post-combustion CO2 capture, transport and storage[J]. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 2012, 17 (7): 932- 943.
DOI
|
| 17 |
SCHMIDT M, NILL M, SCHOLZ J. Determining the scope 3 emissions of companies[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2022, 45 (7): 1218- 1230.
|
| 18 |
张振芳. 露天煤矿碳排放量核算及碳减排途径研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2013.
|
|
ZHANG Zhenfang. Study on carbon emissions accounting and carbon emission reduction approach of surface coal mine[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2013.
|
| 19 |
邵志翔, 亢银虎, 卢啸风. 计及脱硫方式的CFB锅炉碳排放规律研究[J]. 电力学报, 2023, 38 (4): 278- 286.
|
|
SHAO Zhixiang, KANG Yinhu, LU Xiaofeng. Study on carbon emission law of CFB boiler considering desulfurization method[J]. Journal of Electric Power, 2023, 38 (4): 278- 286.
|
| 20 |
VASSILEV S V, VASSILEVA C G. A new approach for the classification of coal fly ashes based on their origin, composition, properties, and behaviour[J]. Fuel, 2007, 86 (10/11): 1490- 1512.
|
| 21 |
YAN P F, MA Z G, LI H B, et al. Laboratory tests, field application and carbon footprint assessment of cement-stabilized pure coal solid wastes as pavement base materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 366, 130265.
DOI
|
| 22 |
CELLURA M, CUSENZA M A, LONGO S. Energy-related GHG emissions balances: IPCC versus LCA[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 628, 1328- 1339.
|
| 23 |
刘明达, 蒙吉军, 刘碧寒. 国内外碳排放核算方法研究进展[J]. 热带地理, 2014, 34 (2): 248- 258.
|
|
LIU Mingda, MENG Jijun, LIU Bihan. Progress in the studies of carbon emission estimation[J]. Tropical Geography, 2014, 34 (2): 248- 258.
|
| 24 |
中华人民共和国生态环境部. 企业温室气体排放核算与报告指南发电设施[R/OL]. (2022-12-21) [2023-06-30]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk06/202212/t20221221_1008430.html.
|
| 25 |
ROSENTRETER J A, LARUELLE G G, BANGE H W, et al. Coastal vegetation and estuaries are collectively a greenhouse gas sink[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2023, 13 (6): 579- 587.
DOI
|
| 26 |
ZAMPORI L, PANT R. Suggestions for updating the Product Environmental Footprint (PEF) method[M]. Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019.
|
| 27 |
中国工业节能与清洁生产协会. T/CIECCPA 055-2023燃煤发电产品碳足迹量化与评价方法[S]. 北京: 中国工业节能与清洁生产协会, 2023: 4–5.
|
| 28 |
TAO M, CHENG W Q, NIE K M, et al. Life cycle assessment of underground coal mining in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 805, 150231.
DOI
|
| 29 |
SONG X C, DU S, DENG C N, et al. Carbon emissions in China's steel industry from a life cycle perspective: Carbon footprint insights[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2025, 148, 650- 664.
DOI
|
| 30 |
彭美春, 朱兵禄, 胡红斐, 等. 重型货运车辆碳排放特性研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2016, 16 (1): 269- 272.
|
|
PENG Meichun, ZHU Binglu, HU Hongfei, et al. Study on the carbon emission characteristics of the heavy duty freight trucks[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2016, 16 (1): 269- 272.
|
| 31 |
生态环境部. 关于做好2023—2025年发电行业企业温室气体排放报告管理有关工作的通知[EB/OL]. (2023-02-04) [2023-10-23]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk06/202302/t20230207_1015569.html.
|
| 32 |
侯萍, 王洪涛, 张浩, 等. 用于组织和产品碳足迹的中国电力温室气体排放因子[J]. 中国环境科学, 2012, 32 (6): 961- 967.
DOI
|
|
HOU Ping, WANG Hongtao, ZHANG Hao, et al. GreenHouse gas emission factors of Chinese power grids for organization and product carbon footprint[J]. China Environmental Science, 2012, 32 (6): 961- 967.
DOI
|
| 33 |
OROZCO C, BABEL S, TANGTERMSIRIKUL S, et al. Comparison of environmental impacts of fly ash and slag as cement replacement materials for mass concrete and the impact of transportation[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2024, 39, e00796.
DOI
|
| 34 |
李莹, 段鹏选, 倪文, 等. 基于生命周期的工业副产石膏制备胶凝材料碳足迹评价[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2023, 42 (6): 1921- 1930.
|
|
LI Ying, DUAN Pengxuan, NI Wen, et al. Carbon footprint assessment of cementitious materials prepared from industrial by-product gypsum based on life cycle[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2023, 42 (6): 1921- 1930.
|
| 35 |
NATH P, SARKER P K, BISWAS W K. Effect of fly ash on the service life, carbon footprint and embodied energy of high strength concrete in the marine environment[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2018, 158, 1694- 1702.
DOI
|
| 36 |
LIANG X Y, WANG Z H, ZHOU Z J, et al. Up-to-date life cycle assessment and comparison study of clean coal power generation technologies in China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2013, 39, 24- 31.
DOI
|
| 37 |
刘韵, 师华定, 曾贤刚. 基于全生命周期评价的电力企业碳足迹评估: 以山西省吕梁市某燃煤电厂为例[J]. 资源科学, 2011, 33 (4): 653- 658.
|
|
LIU Yun, SHI Huading, ZENG Xiangang. A life-cycle carbon footprint assessment of electric power companies[J]. Resources Science, 2011, 33 (4): 653- 658.
|
| 38 |
JUNG H S, RYOO S G, KANG Y T. Life cycle environmental impact assessment of Taean coal power plant with CO2 capture module[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 357, 131663.
DOI
|
| 39 |
PETRESCU L, BONALUMI D, VALENTI G, et al. Life Cycle Assessment for supercritical pulverized coal power plants with post-combustion carbon capture and storage[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 157, 10- 21.
DOI
|
| 40 |
RASHEED R, JAVED H, RIZWAN A, et al. Life cycle assessment of a cleaner supercritical coal-fired power plant[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 279, 123869.
DOI
|
| 41 |
KOORNNEEF J, VAN KEULEN T, FAAIJ A, et al. Life cycle assessment of a pulverized coal power plant with post-combustion capture, transport and storage of CO2[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2008, 2 (4): 448- 467.
DOI
|
| 42 |
WU X D, GUO J L, CHEN G Q. The striking amount of carbon emissions by the construction stage of coal-fired power generation system in China[J]. Energy Policy, 2018, 117, 358- 369.
DOI
|
| 43 |
孙友源, 郑张, 秦亚琦, 等. 火电机组碳排放特性研究及管理建议[J]. 中国电力, 2018, 51 (3): 144- 149, 169.
|
|
SUN Youyuan, ZHENG Zhang, QIN Yaqi, et al. Study on carbon emission characteristics and suggestions on carbon emission management of coal-fired power plant[J]. Electric Power, 2018, 51 (3): 144- 149, 169.
|
| 44 |
宋铜铜. 燃煤电厂碳排放强度核算及影响因素研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2021.
|
|
SONG Tongtong. Study on accounting and influencing factors of carbon emission intensity of coal-fired power plants[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021.
|
| 45 |
郭喜燕, 刘嘉康, 白雪, 等. 基于碳排放特性及碳交易规则的热电联产机组经济性分析[J]. 热力发电, 2023, 52 (4): 14- 23.
|
|
GUO Xiyan, LIU Jiakang, BAI Xue, et al. Economic analysis of cogeneration units based on carbon emission characteristics and carbon trading rules[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2023, 52 (4): 14- 23.
|
| 46 |
王宁玲, 刘嘉康, 陈宏彬, 等. 计及碳交易和调峰灵活性的多场景热电负荷优化分配[J]. 华北电力大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 50 (6): 76- 84.
|
|
WANG Ningling, LIU Jiakang, CHEN Hongbin, et al. Optimal thermoelectric load dispatching and operation considering carbon trading and peak shaving[J]. Journal of North China Electric Power University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 50 (6): 76- 84.
|