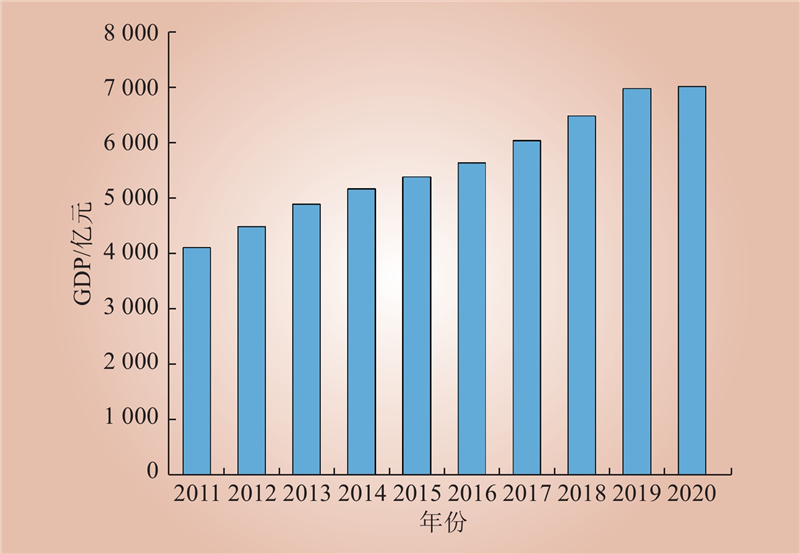
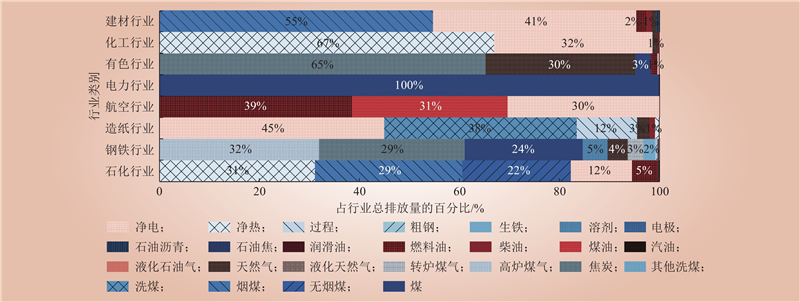
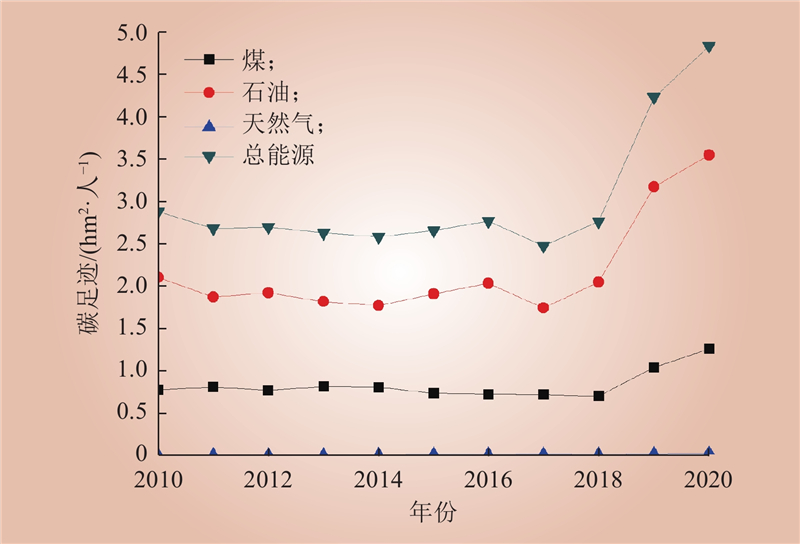
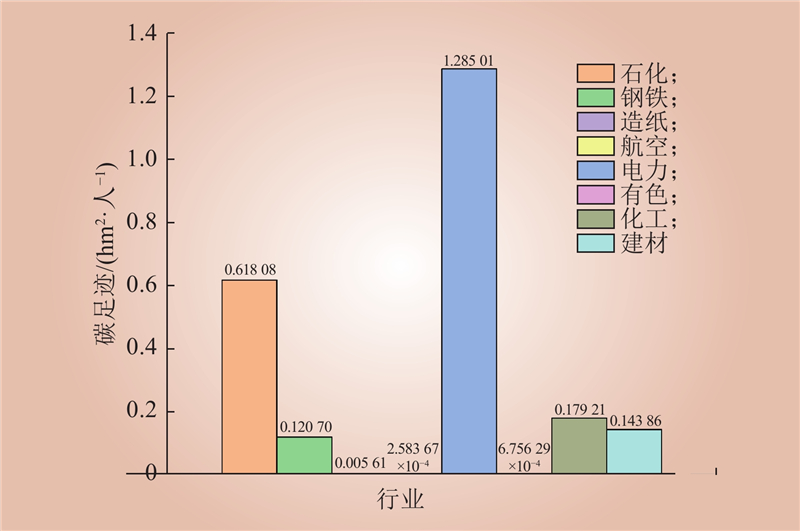
| 1 |
苏志鹏, 王莉, 梁欣怡, 等. 考虑阶梯式碳交易及综合需求响应的虚拟电厂优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 174- 182.
|
|
SU Zhipeng, WANG Li, LIANG Xinyi, et al. Optimal dispatch of virtual power plant considering stepped carbon trading and comprehensive demand response[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 174- 182.
|
| 2 |
李强, 王尧, 胡迎迎, 等. 考虑碳交易成本的输储多阶段协调规划方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 199- 205.
|
|
LI Qiang, WANG Yao, HU Yingying, et al. Multi-stage coordinated planning method for transmission network and energy storage considering carbon trading cost[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 199- 205.
|
| 3 |
贺文, 陈珍萍, 胡伏原, 等. 基于一致性的综合能源系统低碳经济调度[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (19): 42- 53.
|
|
HE Wen, CHEN Zhenping, HU Fuyuan, et al. Consensus-based low-carbon economic dispatching of integrated energy systems[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (19): 42- 53.
|
| 4 |
马君亮, 王智冬, 张述铭. 考虑县域光伏潜力评估的源网荷储协同规划[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (3): 82- 90.
|
|
MA Junliang, WANG Zhidong, ZHANG Shuming. Collaborative planning of source-grid-load-storage considering county PV potential assessment[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (3): 82- 90.
|
| 5 |
朱灿元, 杨超, 李舒涛, 等. 考虑清洁能源与储能的分布式数据中心低碳调度策略[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (2): 16- 23.
|
|
ZHU Canyuan, YANG Chao, LI Shutao, et al. Low-carbon scheduling strategy for distributed data centers considering clean energy and energy storage[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (2): 16- 23.
|
| 6 |
TOMÁS M, LÓPEZ L A, MONSALVE F. Carbon footprint, municipality size and rurality in Spain: inequality and carbon taxation[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 266, 121798.
|
| 7 |
杨传明. 新旧常态中国产业全碳足迹复杂网络比较[J]. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35 (2): 313- 328.
|
|
YANG Chuanming. A comparative study on the complex networks of China’s industrial total carbon footprint in the new and old normal periods[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2020, 35 (2): 313- 328.
|
| 8 |
张运洲, 张宁, 代红才, 等. 中国电力系统低碳发展分析模型构建与转型路径比较[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (3): 1- 11.
|
|
ZHANG Yunzhou, ZHANG Ning, DAI Hongcai, et al. Model construction and pathways of low-carbon transition of China’s power system[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (3): 1- 11.
|
| 9 |
FU W, LUO M C, CHEN J C, et al. Carbon footprint and carbon carrying capacity of vegetation in ecologically fragile areas: a case study of Yunnan[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 2020, 120, 102904.
|
| 10 |
孙丽文, 韩莹, 杜娟. 京津冀高能耗产业碳足迹的影响因素: 基于de Bruyn模型[J]. 技术经济, 2019, 38 (8): 86- 92, 118.
|
|
SUN Liwen, HAN Ying, DU Juan. Influencing factors of carbon footprint of high energy consumption industry in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei: based on de Bruyn model[J]. Technology Economics, 2019, 38 (8): 86- 92, 118.
|
| 11 |
石羽, 运迎霞, 刘冲, 等. 辽宁中部城市群建筑碳足迹[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28 (6): 2040- 2046.
|
|
SHI Yu, YUN Yingxia, LIU Chong, et al. Carbon footprint of buildings in the urban agglomeration of central Liaoning, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28 (6): 2040- 2046.
|
| 12 |
ONAT N C, KUCUKVAR M. Carbon footprint of construction industry: a global review and supply chain analysis[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 124, 109783.
|
| 13 |
SCHUELER M, HANSEN S, PAULSEN H M. Discrimination of milk carbon footprints from different dairy farms when using IPCC Tier 1 methodology for calculation of GHG emissions from managed soils[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 177, 899- 907.
|
| 14 |
陈家兴, 王春玲, 刘春明. 基于改进碳排放流理论的电力系统动态低碳调度方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (3): 162- 172.
|
|
CHEN Jiaxing, WANG Chunling, LIU Chunming. Dynamic low-carbon dispatching method of power system based on improved carbon emission flow theory[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (3): 162- 172.
|
| 15 |
陈厚合, 茅文玲, 张儒峰, 等. 基于碳排放流理论的电力系统源-荷协调低碳优化调度[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49 (10): 1- 11.
|
|
CHEN Houhe, MAO Wenling, ZHANG Rufeng, et al. Low-carbon optimal scheduling of a power system source-load considering coordination based on carbon emission flow theory[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49 (10): 1- 11.
|
| 16 |
黄大为, 李赛龙, 孔令国. 计及中长期合同电量分解与风电报价的日前市场出清模型研究[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (4): 45- 56.
|
|
HUANG Dawei, LI Sailong, KONG Lingguo. Research on day-ahead electricity market clearing ModelConsidering medium and long-term ContractsDecomposition and wind power producer bidding[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (4): 45- 56.
|
| 17 |
HU J M, LIU G Y, MENG F X, et al. Subnational carbon flow pattern analysis using multi-scale input-output model[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2020, 431, 109138.
|
| 18 |
彭水军, 张文城, 孙传旺. 中国生产侧和消费侧碳排放量测算及影响因素研究[J]. 经济研究, 2015, 50 (1): 168- 182.
|
|
PENG Shuijun, ZHANG Wencheng, SUN Chuanwang. China’s production-based and consumption-based carbon emissions and their determinants[J]. Economic Research Journal, 2015, 50 (1): 168- 182.
|
| 19 |
黄景光, 熊华健, 李振兴, 等. 基于生命周期法和碳权交易的综合能源系统低碳经济调度[J]. 电测与仪表, 2022, 59 (3): 82- 91.
|
|
HUANG Jingguang, XIONG Huajian, LI Zhenxing, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatch of integrated energy system based on life cycle method and carbon trading[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2022, 59 (3): 82- 91.
|
| 20 |
LUO W, ZHANG Y R, GAO Y L, et al. Life cycle carbon cost of buildings under carbon trading and carbon tax system in China[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021, 66, 102509.
|
| 21 |
杨花, 杜斌, 吕锋骅, 等. 基于IPCC排放清单和LEAP模型的山西省CO2排放研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2014, 36 (3): 103- 109.
|
|
YANG Hua, DU Bin, LV Fenghua, et al. Study on CO2 emissions in Shanxi Province base on IPCC listing and LEAP model[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2014, 36 (3): 103- 109.
|
| 22 |
张国兴, 苏钊贤. 黄河流域交通运输碳排放的影响因素分解与情景预测[J]. 管理评论, 2020, 32 (12): 283- 294.
|
|
ZHANG Guoxing, SU Zhaoxian. Analysis of influencing factors and scenario prediction of transportation carbon emissions in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Management Review, 2020, 32 (12): 283- 294.
|
| 23 |
王兴民, 吴静, 白冰, 等. 中国CO2排放的空间分异与驱动因素: 基于198个地级及以上城市数据的分析[J]. 经济地理, 2020, 40 (11): 29- 38.
|
|
WANG Xingmin, WU Jing, BAI Bing, et al. Spatial differentiation and driving factors of CO2 emissions: analysis based on 198 cities at prefecture level and above in China[J]. Economic Geography, 2020, 40 (11): 29- 38.
|
| 24 |
曲嘉伟, 朱乐为, 刘泽宇, 等. 计及压缩空气储能的综合能源微网可靠性评估[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2022, 42 (6): 8- 18, 105.
|
|
QU Jiawei, ZHU Lewei, LIU Zeyu, et al. Reliability assessment for integrated energy microgrid system with compressed air energy storage[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2022, 42 (6): 8- 18, 105.
|
| 25 |
李怀慎, 夏能弘, 张俊. 地铁杂散电流影响下的地表电位计算及敏感性因素分析[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38 (2): 105- 113.
|
|
LI Huaishen, XIA Nenghong, ZHANG Jun. Calculation of surface potential and analysis of sensitivity factors under the influence of stray current in metro systems[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38 (2): 105- 113.
|