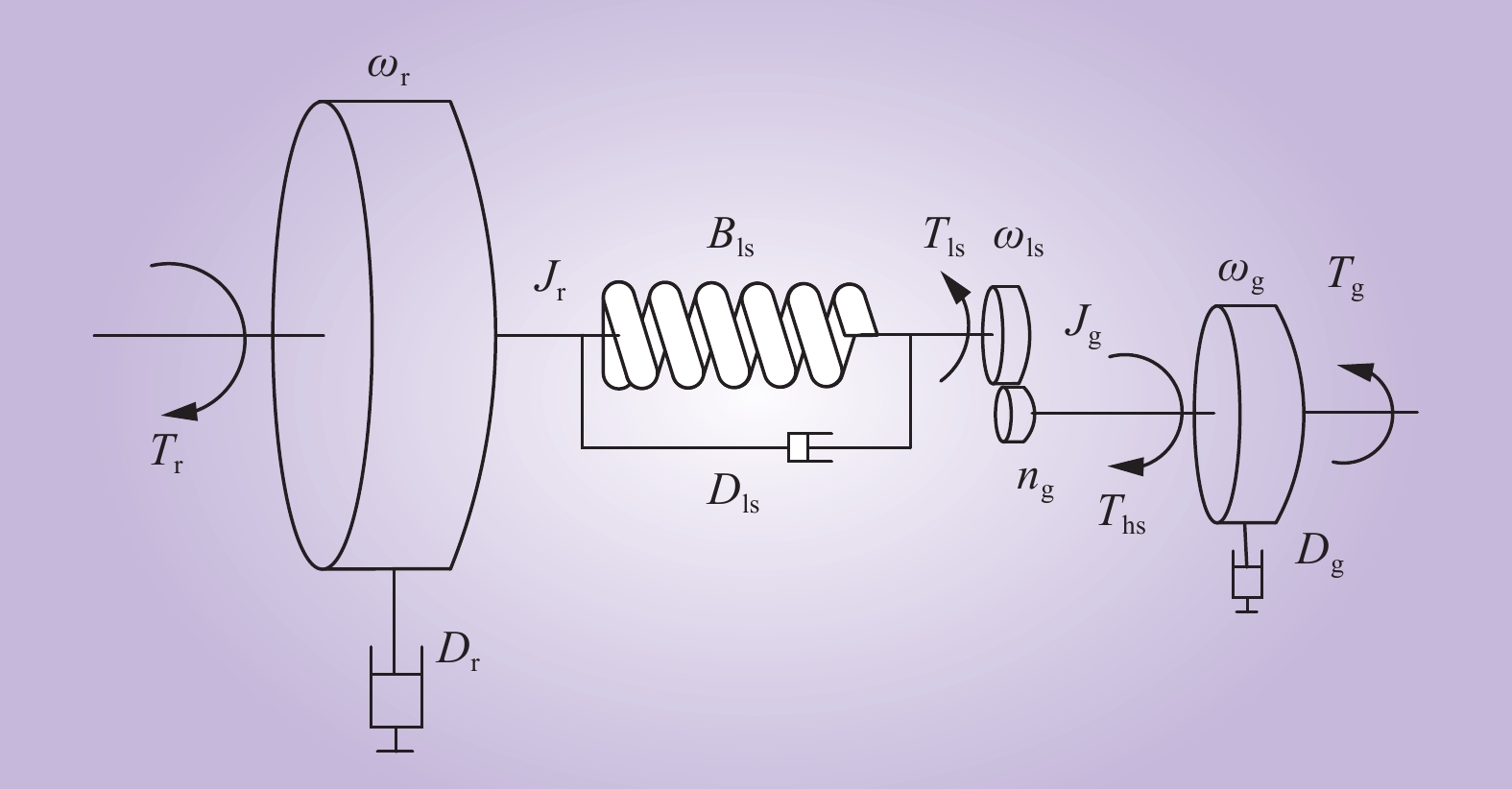
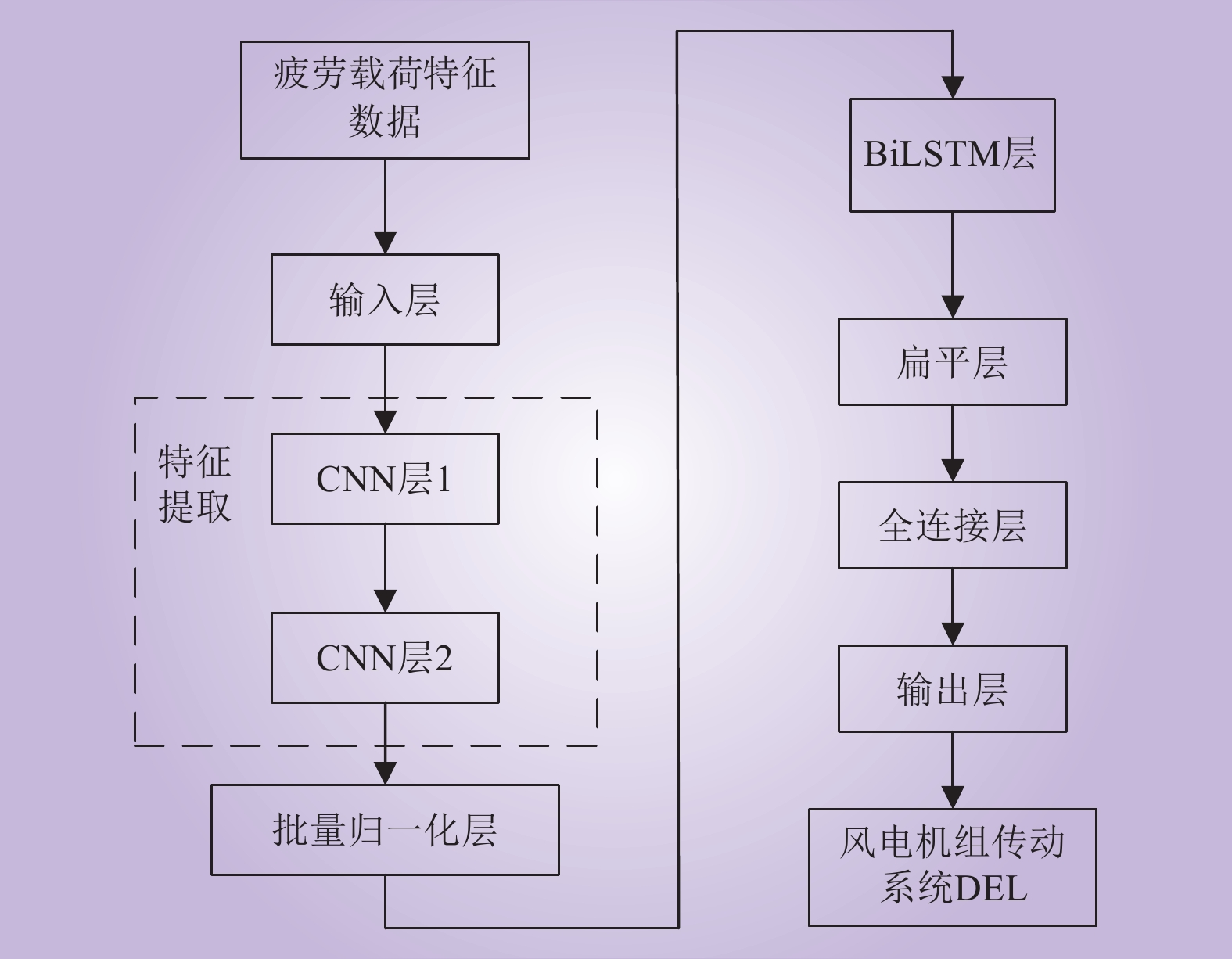
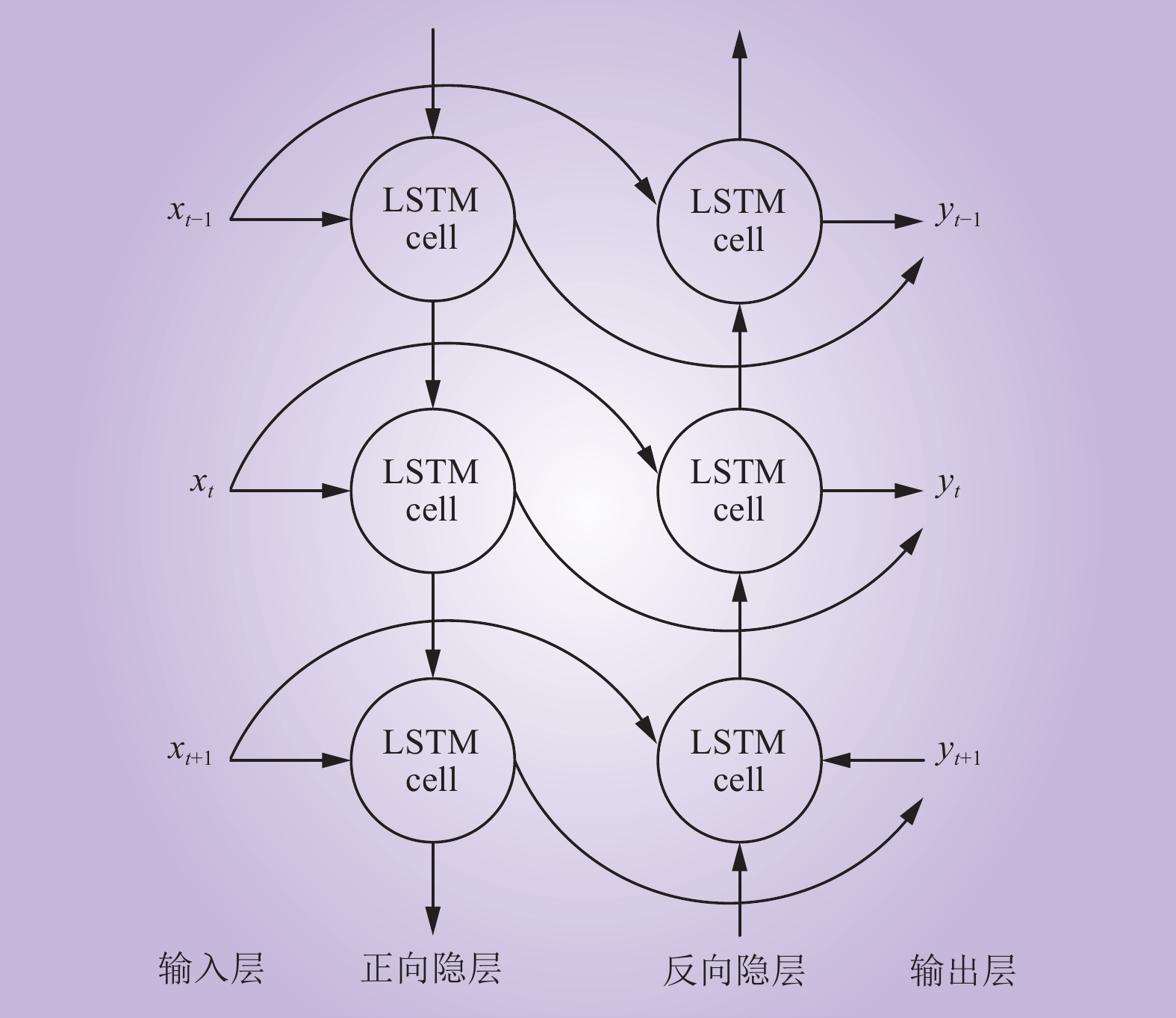
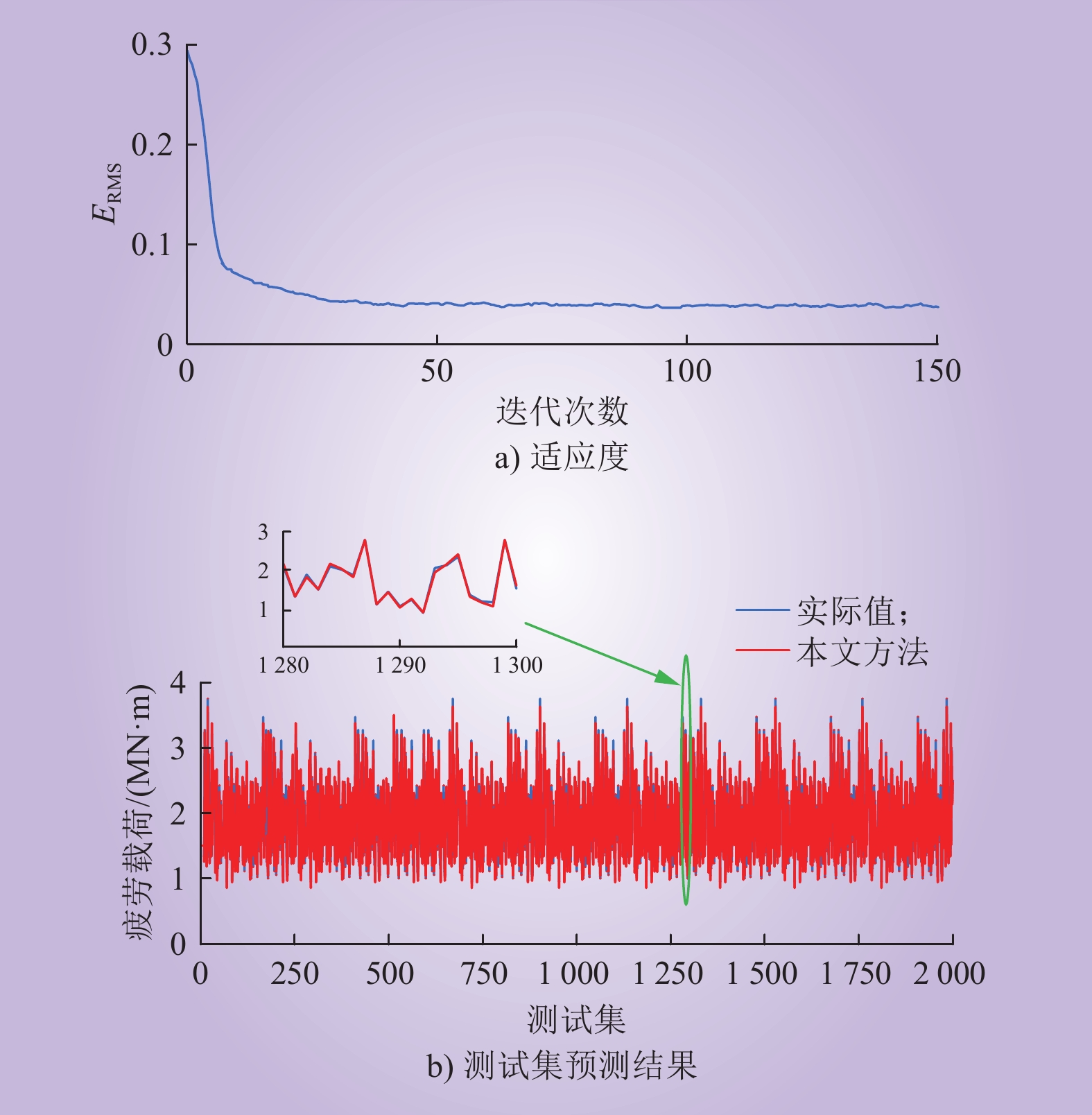
| 1 |
薛磊. 大型风电机组载荷监测与延寿评估技术研究[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2020.
|
|
XUE Lei. Research on load monitoring and life time extension assessment technology of large wind turbine[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University, 2020.
|
| 2 |
宾世杨, 张振, 唐俊杰, 等. 基于机器学习的风电机组机械传动系统故障诊断研究[J]. 机械与电子, 2024, 42 (1): 11- 15.
|
|
BIN Shiyang, ZHANG Zhen, TANG Junjie, et al. Research on fault diagnosis of wind turbine mechanical transmission system based on machine learning[J]. Machinery & Electronics, 2024, 42 (1): 11- 15.
|
| 3 |
张磊, 王满康, 随权, 等. 考虑场间-场内风电机组疲劳载荷均衡的海上风氢系统灵活调度[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (21): 151- 160.
|
|
ZHANG Lei, WANG Mankang, SUI Quan, et al. Flexible scheduling of offshore wind-hydrogen systems considering inter-and intra-field turbine fatigue load balancing[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (21): 151- 160.
|
| 4 |
姚兴佳, 谢洪放, 朱江生, 等. 基于LMI的5MW海上风力发电机组载荷控制技术研究[J]. 可再生能源, 2016, 34 (1): 44- 48.
|
|
YAO Xingjia, XIE Hongfang, ZHU Jiangsheng, et al. LMI-based load control for 5 MW offshore wind turbine[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2016, 34 (1): 44- 48.
|
| 5 |
LI Z P, YANG S Y, ZHANG F, et al. Analysis of load characteristics of wind turbine blade root bolts under loosened and fractured conditions[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2024, 38 (4): 1731- 1741.
|
| 6 |
ZHAO H R, WU Q W, HUANG S J, et al. Fatigue load sensitivity-based optimal active power dispatch for wind farms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2017, 8 (3): 1247- 1259.
|
| 7 |
KNUDSEN T, BAK T, SVENSTRUP M. Survey of wind farm control: power and fatigue optimization[J]. Wind Energy, 2015, 18 (8): 1333- 1351.
|
| 8 |
XIAOPENG Z, DING J, QIANG Z. The Application of Rain-Flow Counting Method in the Analysis of Load Spectrum[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2009, 27 (3): 67- 73.
|
| 9 |
WEBER F, WU H R, STARKE P. A new short-time procedure for fatigue life evaluation based on the linear damage accumulation by Palmgren–Miner[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2023, 172, 107653.
|
| 10 |
MONTAVON G, SAMEK W, MÜLLER K R. Methods for interpreting and understanding deep neural networks[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2018, 73, 1- 15.
|
| 11 |
王伟, 王海云. 基于Adam优化BP神经网络的风机等效疲劳载荷预测[J]. 现代电子技术, 2023, 46 (17): 102- 106.
|
|
WANG Wei, WANG Haiyun. Wind turbine equivalent fatigue load prediction based on Adam optimized BP neural network[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2023, 46 (17): 102- 106.
|
| 12 |
巫发明, 李晔, 杨从新, 等. 风电机组传动链动态载荷识别算法及验证[J]. 振动测试与诊断, 2022, 42(4): 664-670, 822.
|
|
WU Faming, LI Ye, YANG Congxin, et al. Dynamic load identification algorithm and verification of wind turbine drive train[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2022, 42(4): 664-670, 822.
|
| 13 |
卢晓光, 李凤格. 基于数字孪生的风机实时载荷预估研究[J]. 机械与电子, 2021, 39 (6): 24- 28, 34.
|
|
LU Xiaoguang, LI Fengge. Real time load prediction of wind turbine based on digital twin[J]. Machinery & Electronics, 2021, 39 (6): 24- 28, 34.
|
| 14 |
ZHANG B H, SOLTANI M, HU W H, et al. Optimized power dispatch in wind farms for power maximizing considering fatigue loads[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2018, 9 (2): 862- 871.
|
| 15 |
彭超. 风力发电机组传动链调谐惯量阻尼器研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2018, 39 (7): 2036- 2043.
|
|
PENG Chao. Research of tuned inertia damper for wind turbine drive train[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2018, 39 (7): 2036- 2043.
|
| 16 |
刘颖明, 赵哲, 王晓东, 等. 考虑机组疲劳载荷的风电集群有功功率分配方法[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42 (5): 430- 436.
|
|
LIU Yingming, ZHAO Zhe, WANG Xiaodong, et al. Active power distribution method for wind farm cluster based on cluster analysis[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42 (5): 430- 436.
|
| 17 |
张斌, 朱春生, 贾鈜崴, 等. 数据驱动的风电机组传动系统疲劳载荷计算与主动抑制研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (1): 24- 30.
|
|
ZHANG Bin, ZHU Chunsheng, JIA Hongwei, et al. Fatigue load calculation and active suppression of wind turbine transmission system based on data-driven method[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (1): 24- 30.
|
| 18 |
Wind turbines - Part 13: Measurement of mechanical loads: IEC 61400-13[S]. 2015.
|
| 19 |
臧海祥, 赵勇凯, 张越, 等. 基于低风速功率修正和损失函数改进的超短期风电功率预测[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (7): 248- 257.
|
|
ZANG Haixiang, ZHAO Yongkai, ZHANG Yue, et al. Ultra-short-term wind power prediction based on power correction under low wind speed and improved loss function[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (7): 248- 257.
|
| 20 |
朱乔木, 李弘毅, 王子琪, 等. 基于长短期记忆网络的风电场发电功率超短期预测[J]. 电网技术, 2017, 41 (12): 3797- 3802.
|
|
ZHU Qiaomu, LI Hongyi, WANG Ziqi, et al. Short-term wind power forecasting based on LSTM[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41 (12): 3797- 3802.
|
| 21 |
CHAI Z K. BiLSTM short-term wind power prediction based on attention mechanism[C]//2023 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronic Technology, Communication and Information (ICETCI). Changchun, China. IEEE, 2023: 1341–1346.
|
| 22 |
SHEN Y Z, TANG B P, LI B, et al. Remaining useful life prediction of rolling bearing based on multi-head attention embedded Bi-LSTM network[J]. Measurement, 2022, 202, 111803.
|