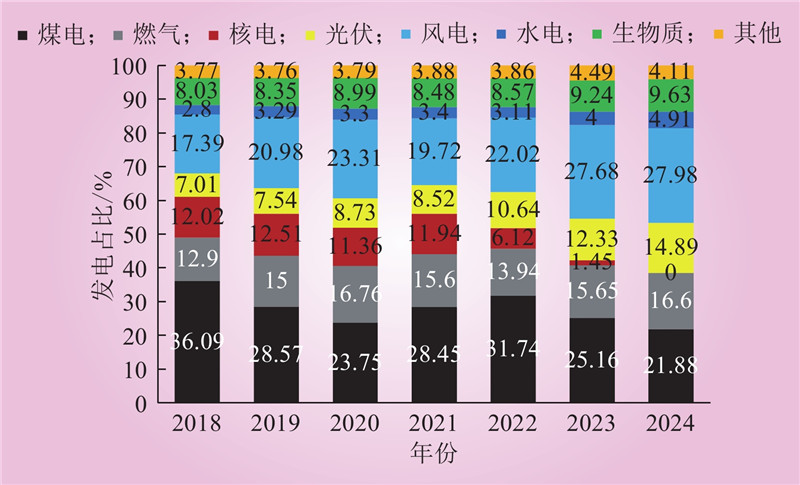
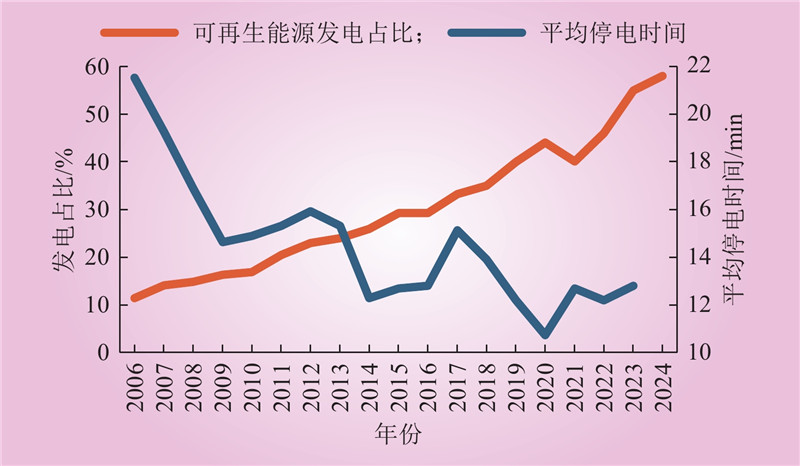
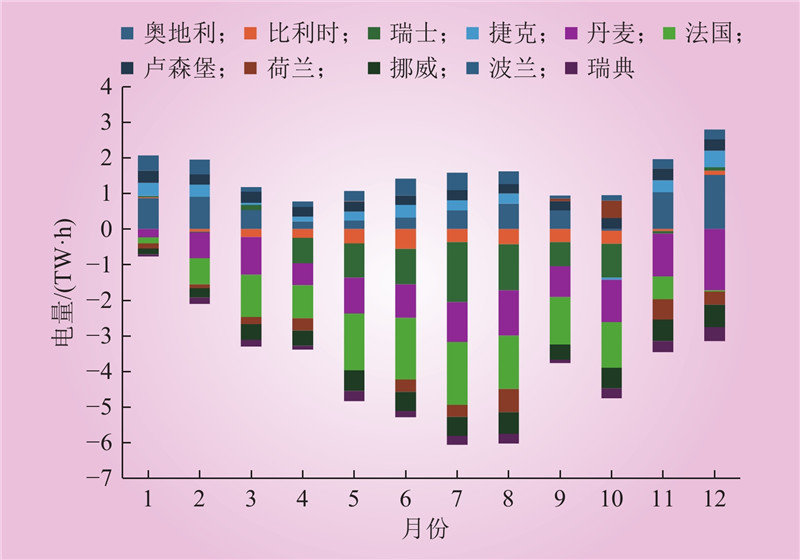
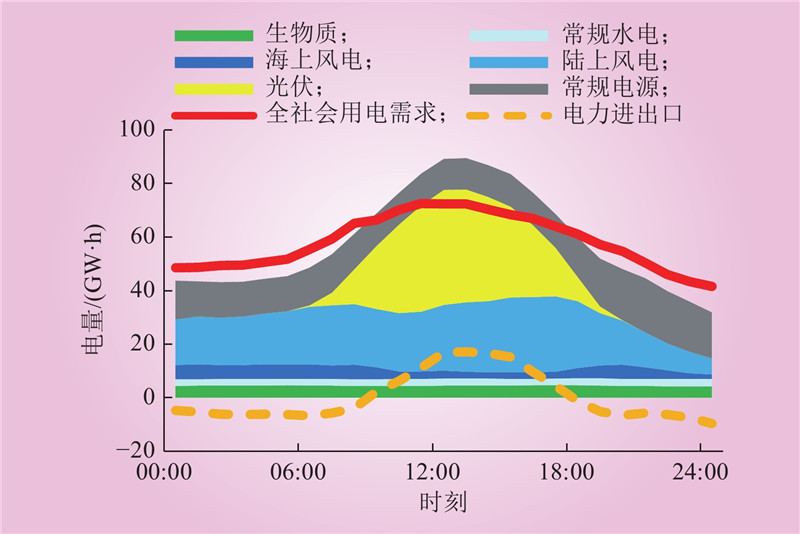
| 1 |
EMBER. Electricity data explorer[EB/OL]. (2025-02-01)[2025-02-23]. https://ember-energy.org/data/electricity-data-explorer/.
|
| 2 |
Agora Energiewende. The German energiewende[EB/OL]. (2025-02-18)[2025-02-23]. https://www.agora-energiewende.org/about-us/the-german-energiewende.
|
| 3 |
李品, 谢晓敏, 黄震. 德国能源转型进程及对中国的启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19 (1): 116- 126.
|
|
LI Pin, XIE Xiaomin, HUANG Zhen. The process of Germany energiewende and its enlightenment to China[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19 (1): 116- 126.
|
| 4 |
LI N. Experience and enlightenment of energy transition in Germany[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 621 (1): 012172.
|
| 5 |
CHEN C, XUE B, CAI G T, et al. Comparing the energy transitions in Germany and China: synergies and recommendations[J]. Energy Reports, 2019, 5, 1249- 1260.
|
| 6 |
叶小宁, 王彩霞, 李琼慧, 等. 国外新能源高占比电力系统电力供应保障措施及启示[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (4): 61- 67.
|
|
YE Xiaoning, WANG Caixia, LI Qionghui, et al. Power supply ensuring measures and implications of foreign countries' power systems with high proportion of new energy[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (4): 61- 67.
|
| 7 |
刘之琳, 许传龙, 郑海峰, 等. 德国关停核电前后保供应促消纳经验分析[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (10): 145- 152.
|
|
LIU Zhilin, XU Chuanlong, ZHENG Haifeng, et al. Empirical analysis of ensuring electricity supply and promoting renewable power consumption before and after the shutdown of nuclear power plants: the Germany case[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (10): 145- 152.
|
| 8 |
黄越辉, 王跃峰. 德国新能源消纳的经验与启示[J]. 国家电网, 2017, (7): 83- 85.
|
| 9 |
OLBRICH S, BAUKNECHT D, SPÄTH P. Policy mixes for net-zero energy transitions: insights from energy sector integration in Germany[J]. Energy Research & Social Science, 2024, 118, 103822.
|
| 10 |
陈启鑫, 张维静, 滕飞, 等. 欧洲跨国电力市场的输电机制与耦合方式[J]. 全球能源互联网, 2020, 3 (5): 423- 429.
|
|
CHEN Qixin, ZHANG Weijing, TENG Fei, et al. Transmission mechanisms and coupling approaches in European transnational electricity markets[J]. Journal of Global Energy Interconnection, 2020, 3 (5): 423- 429.
|
| 11 |
高政南, 姜楠, 陈启鑫, 等. 德国电力市场能源转型建设及启示[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (6): 204- 214.
|
|
GAO Zhengnan, JIANG Nan, CHEN Qixin, et al. Construction experience of German electricity market adapting to energy transition[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (6): 204- 214.
|
| 12 |
杜云龙, 戴强晟, 苏大威, 等. 德国新型储能政策及市场机制对江苏的启示[J]. 电力需求侧管理, 2024, 26 (1): 113- 118.
|
|
DU Yunlong, DAI Qiangsheng, SU Dawei, et al. Enlightenment of Germany's new energy storage policy and market mechanism to Jiangsu[J]. Power Demand Side Management, 2024, 26 (1): 113- 118.
|
| 13 |
梁志峰, 礼晓飞, 郭琳润, 等. 德国电力系统转型对我国新能源发展运行的启示[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (7): 2884- 2894.
|
|
LIANG Zhifeng, LI Xiaofei, GUO Linrun, et al. Enlightenment of Germany's power system transformation on the development and operation of renewable energy in China[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (7): 2884- 2894.
|
| 14 |
Agora Energiewende. Coal phase-out in Germany. The multi-stakeholder commission as a policy tool[R]. Germany: Agora Energiewende, 2024.
|
| 15 |
SCOTT, J., THUY, N. N., LITZ, P., et al. Coal phase-out in Germany: the role of coal exit auctions[R]. Germany: Agora Energiewende and Aurora Energy Research, 2022.
|
| 16 |
European Commission. State aid: lignite-fired power plants in Germany[EB/OL]. (2021-03-02)[2025-04-06]. https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/ip_21_972.
|
| 17 |
TIEDEMANN S, MÜLLER-HANSEN F. Auctions to phase out coal power: lessons learned from Germany[J]. Energy Policy, 2023, 174, 113387.
|
| 18 |
Bundesnetzagentur. Information on the completed tendering procedures for the coal phase-out[EB/OL]. (2023-08-25) [2025-02-27]. https://www.bundesnetzagentur.de/DE/Fachthemen/ElektrizitaetundGas/Kohleausstieg/BeendeteAusschreibungen/start.html.
|
| 19 |
SMARD. Electricity-energy data compact[EB/OL]. (2023-08-25)[2025-02-27]. https://www.smard.de/en/energy-data-compact/electricity.
|
| 20 |
Bundesnetzagentur. Results of final coal phase-out tendering process[EB/OL]. (2023-08-25)[2025-02-28]. https://www.bundesnetzagentur.de/SharedDocs/Pressemitteilungen/EN/2023/20230825_Kohle.html.
|
| 21 |
陈宋宋, 董家伟, 王舒杨, 等. 德国电力平衡单元机制及其启示[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (10): 4157- 4167.
|
|
CHEN Songsong, DONG Jiawei, WANG Shuyang, et al. German balance group mechanism and its inspiration[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (10): 4157- 4167.
|
| 22 |
Clean Energy Wire. What's new in Germany's renewable energy act 2021[EB/OL]. (2021-04-23)[2025-03-01]. https://www.cleanenergywire.org/factsheets/whats-new-germanys-renewable-energy-act-2021.
|
| 23 |
PV Magazine. Germany raises feed-in tariffs for solar up to 750 KW[EB/OL]. (2022-07-07)[2025-03-01]. https://www.pv-magazine.com/2022/07/07/germany-raises-feed-in-tariffs-for-solar-up-to-750-kw/.
|
| 24 |
PV Magazine. Germany introduces new rules for solar remuneration during negative prices[EB/OL]. (2025-02-17)[2025-03-01]. https://www.pv-magazine.com/2025/02/17/germany-introduces-new-rules-for-solar-remuneration-during-negative-prices/#:~:text=The%20German%20Parliament%20approved%20the,exceeding%202%20kW%20in%20size.
|
| 25 |
IEA. Integrating solar and wind[R]. Paris: IEA, 2024.
|
| 26 |
刘秋华, 姜亚熙, 张正延, 等. 德国与英国电力市场平衡机制对比分析及启示[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (14): 8- 15.
|
|
LIU Qiuhua, JIANG Yaxi, ZHANG Zhengyan, et al. Comparative analysis on electricity market balancing mechanisms of Germany and UK and its enlightenment[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (14): 8- 15.
|
| 27 |
Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action. Agreement on power station strategy[EB/OL]. (2024-05-02)[2025-02-28]. https://www.bmwk.de/Redaktion/EN/Pressemitteilungen/2024/02/20240205-agreement-on-power-station-strategy.html#:~:text=The%20Power%20Station%20Strategy%20provides,the%20Climate%20and%20Transformation%20Fund.
|
| 28 |
Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action. National hydrogen strategy update[R]. Germany: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action, 2023.
|
| 29 |
DOUCET F, BLOHM M, VON DÜSTERLHO E, et al. Green hydrogen for the energy transition in Germany-potentials, limits, and priorities[C]//2024 20th International Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM). Istanbul, Turkiye. IEEE, 2024: 1–6.
|
| 30 |
AN K X, ZHENG X Z, SHEN J X, et al. Repositioning coal power to accelerate net-zero transition of China's power system[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16, 2311.
|
| 31 |
CUI R Y, HULTMAN N, CUI D Y, et al. A plant-by-plant strategy for high-ambition coal power phaseout in China[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12 (1): 1468.
|
| 32 |
舒印彪, 张丽英, 张运洲, 等. 我国电力碳达峰、碳中和路径研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2021, 23 (6): 1- 14.
|
|
SHU Yinbiao, ZHANG Liying, ZHANG Yunzhou, et al. Carbon peak and carbon neutrality path for China's power industry[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2021, 23 (6): 1- 14.
|
| 33 |
辛保安, 陈梅, 赵鹏, 等. 碳中和目标下考虑供电安全约束的我国煤电退减路径研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (19): 6919- 6931.
|
|
XIN Baoan, CHEN Mei, ZHAO Peng, et al. Research on coal power generation reduction path considering power supply adequacy constraints under carbon neutrality target in China[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (19): 6919- 6931.
|
| 34 |
魏泓屹, 卓振宇, 张宁, 等. 中国电力系统碳达峰·碳中和转型路径优化与影响因素分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (19): 1- 12.
|
|
WEI Hongyi, ZHUO Zhenyu, ZHANG Ning, et al. Transition path optimization and influencing factor analysis of carbon emission peak and carbon neutrality for power system of China[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (19): 1- 12.
|
| 35 |
WU D, ZHANG Y Q, LIU B, et al. Optimization of coal power phaseout pathways ensuring energy security: evidence from Shandong, China's largest coal power province[J]. Energy Policy, 2024, 192, 114180.
|
| 36 |
傅观君, 张富强, 夏鹏, 等. 天然气发电在新型电力系统中的功能定位及发展前景研判[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (8): 67- 74.
|
|
FU Guanjun, ZHANG Fuqiang, XIA Peng, et al. Functional orientation and development prospect of natural gas power generation in new power system[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (8): 67- 74.
|
| 37 |
孙启星, 张超, 李成仁, 等. “碳达峰、碳中和” 目标下的电力系统成本及价格水平预测[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (1): 9- 16.
|
|
SUN Qixing, ZHANG Chao, LI Chengren, et al. Prediction of power system cost and price level under the goal of "carbon peak and carbon neutralization"[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (1): 9- 16.
|
| 38 |
余潇潇, 宋福龙, 李隽, 等. 含高比例新能源电力系统极端天气条件下供电安全性的提升[J]. 现代电力, 2023, 40 (3): 303- 313.
|
|
YU Xiaoxiao, SONG Fulong, LI Jun, et al. Power supply security improvement of power grid with high proportion of renewable energy under extreme weather events[J]. Modern Electric Power, 2023, 40 (3): 303- 313.
|