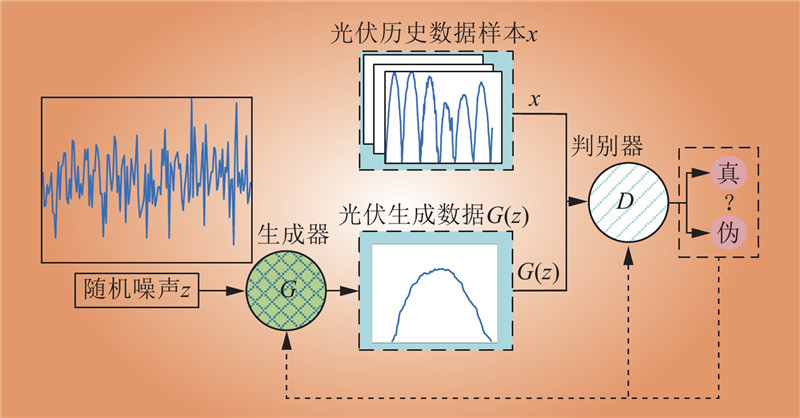
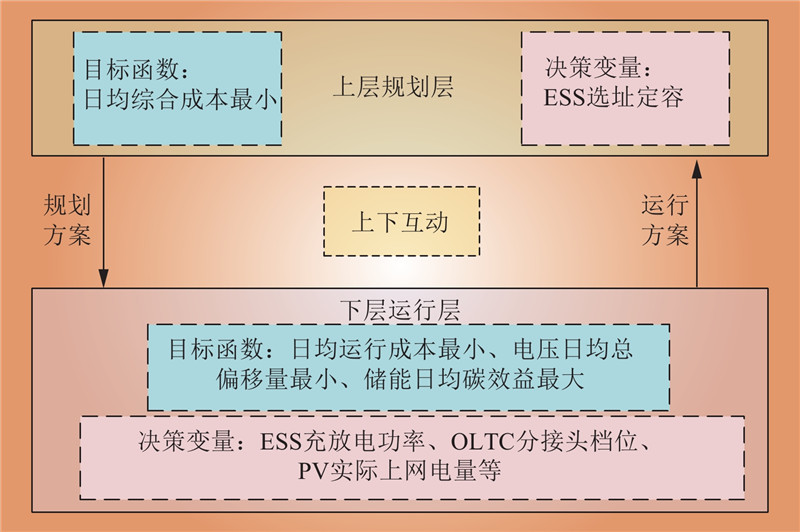
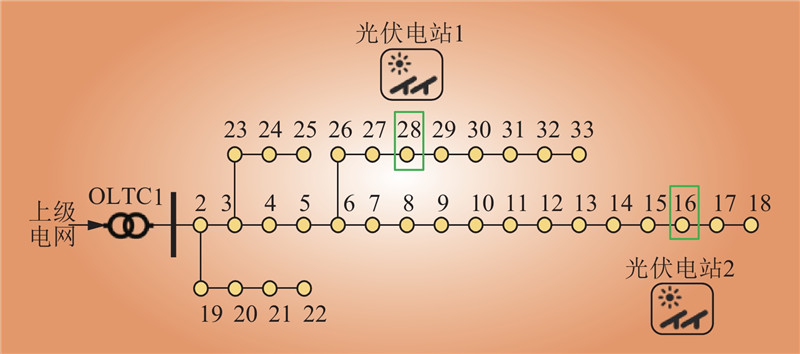
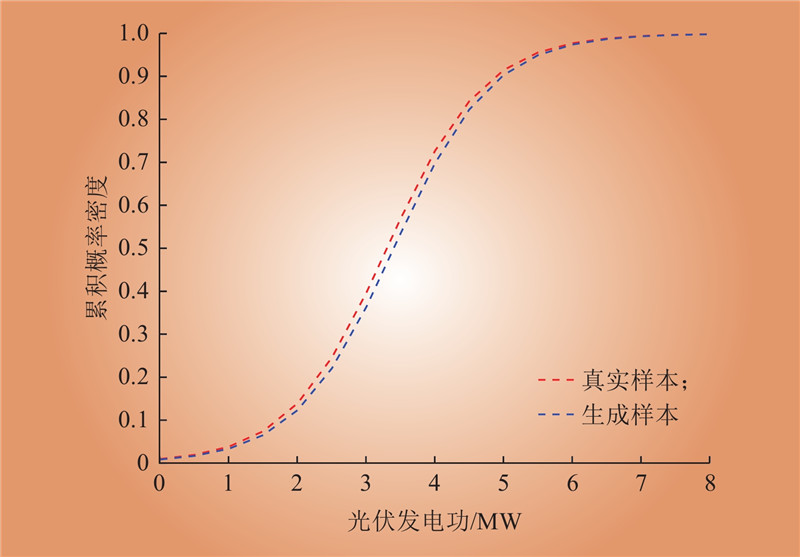
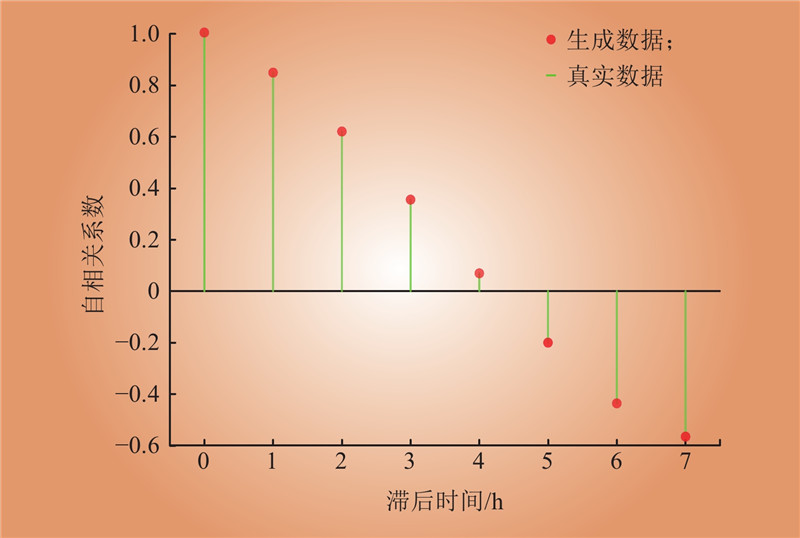
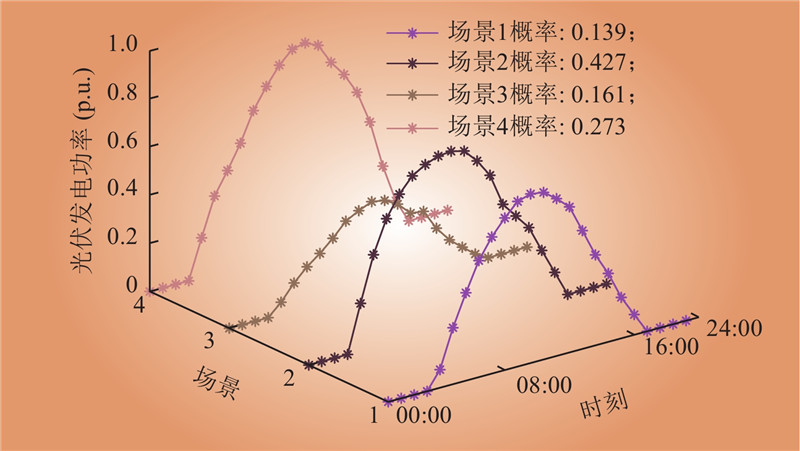
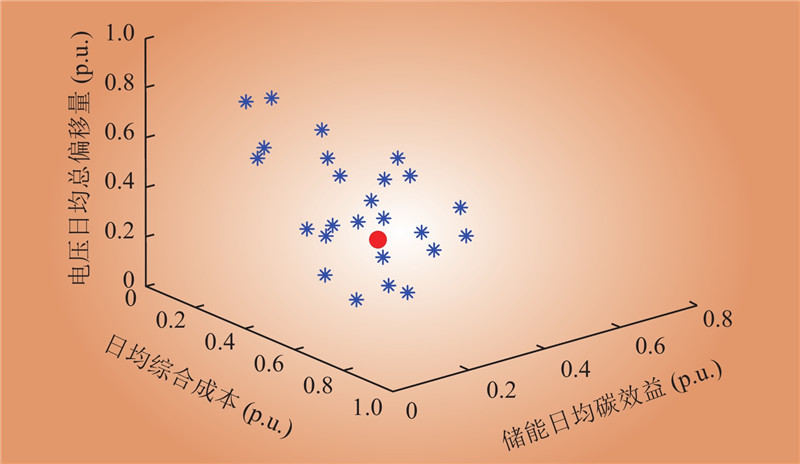
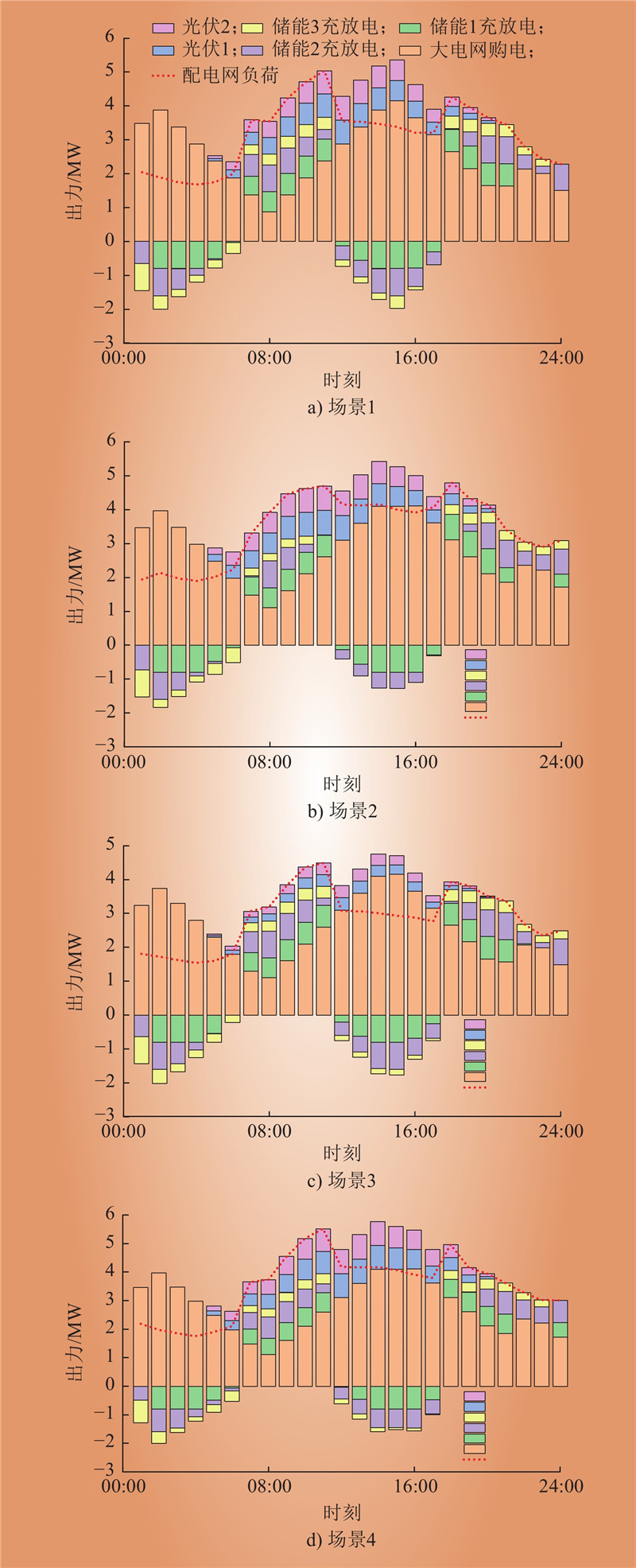
| 1 |
李旭东, 谭青博, 赵浩辰, 等. 碳达峰背景下中国电力行业碳排放因素和脱钩效应[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (5): 88- 98.
|
|
LI Xudong, TAN Qingbo, ZHAO Haochen, et al. Carbon emission factors and decoupling effects of China's power industry under the background of carbon peak[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (5): 88- 98.
|
| 2 |
国家能源局. 国家能源局综合司关于进一步组织实施好“千家万户沐光行动”的通知[EB/OL]. (2025-03-14)[2025-04-11]. https://www.nea.gov.cn/20250320/77110f875bc34fe3a6c19dd1babcfbf0/c.html.
|
| 3 |
陈奇芳, 李若凡, 夏明超, 等. 计及多维性能评估的新型配电网光伏选址定容方法[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (10): 172- 178, 207.
|
|
CHEN Qifang, LI Ruofan, XIA Mingchao, et al. Photovoltaic site selection and capacity determination method for new distribution network considering multidimensional performance evaluation[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (10): 172- 178, 207.
|
| 4 |
解大, 代荣荣, 高少炜, 等. 基于保险精算理论的储能运营商利益分配策略[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2024, 39 (5): 247- 261.
|
|
XIE Da, DAI Rongrong, GAO Shaowei, et al. Benefit allocation strategy for energy storage operators based oninsurance actuarial theory[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2024, 39 (5): 247- 261.
|
| 5 |
丁涛, 谢刘双飞, 黄雨涵, 等. 西北地区新型储能发展面临的关键问题及思考建议[J/OL]. 电力系统自动化, 1–18[2025-06-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1180.TP.20250418.1135.006.html.
|
|
DING Tao, XIE Liushuangfei, HUANG Yuhan, et al. Key issues and suggestions for development of new energy storage in northwestern China[J/OL]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 1–18[2025-06-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1180.TP.20250418.1135.006.html.
|
| 6 |
李建林, 孙浩元, 张敏慧, 等. 计及风电平抑的电-氢混合储能容量优化配置[J]. 太阳能学报, 2025, 46 (6): 120- 129.
|
|
LI Jianlin, SUN Haoyuan, ZHANG Minhui, et al. Optimal capacity allocation of electricity-hydrogen hybrid energy storage considering wind power smoothing[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2025, 46 (6): 120- 129.
|
| 7 |
方晓涛, 严正, 王晗, 等. 考虑概率电压不平衡度越限风险的共享储能优化运行方法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2022, 56 (7): 827- 839.
|
|
FANG Xiaotao, YAN Zheng, WANG Han, et al. A shared energy storage optimal operation method considering the risk of probabilistic voltage unbalance factor limit violation[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2022, 56 (7): 827- 839.
|
| 8 |
袁铁江, 郭建华, 杨紫娟, 等. 平抑风电波动的电-氢混合储能容量优化配置[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (4): 1397- 1406.
|
|
YUAN Tiejiang, GUO Jianhua, YANG Zijuan, et al. Optimal allocation of power electric-hydrogen hybrid energy storage of stabilizing wind power fluctuation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (4): 1397- 1406.
|
| 9 |
龚锐, 李华强, 许立雄. 面向配电网综合承载力提升的储能优化配置方法[J/OL]. 电网技术, 1–13[2025-06-12]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2410.tm.20250208.1031.003.html.
|
|
GONG Rui, LI Huaqiang, XU Lixiong, Optimal allocation method of energy storage systems for improving the comprehensive carrying capacity of distribution network[J/OL]. Power System Technology, 1–13[2025-06-12]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2410.tm.20250208.1031.003.html.
|
| 10 |
周勃, 李二超. 一种考虑风光不确定性的热电混合共享储能双层优化配置方法[J]. 太阳能学报, 2025, 46 (3): 189- 198.
|
|
ZHOU Bo, LI Erchao. A two-layer optimal allocation method for hybrid shared energy storage considering the uncertainty of wind power and photovoltaic[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2025, 46 (3): 189- 198.
|
| 11 |
高芊芊, 山雨琦, 朱晓荣. 基于合作博弈的共享混合储能电站规划[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45 (12): 509- 519.
|
|
GAO Qianqian, SHAN Yuqi, ZHU Xiaorong. Planning of shared hybrid energy storage power station based on cooperative game[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45 (12): 509- 519.
|
| 12 |
马楠, 刘国伟, 吴杰康, 等. 租赁市场中储能容量配置双层鲁棒优化模型[J]. 电网技术, 2025, 49 (2): 653- 665.
|
|
MA Nan, LIU Guowei, WU Jiekang, et al. A double-layer robust optimization model for energy storage capacity allocation in the leasing market[J]. Power System Technology, 2025, 49 (2): 653- 665.
|
| 13 |
严干贵, 沙千理, 李军徽, 等. 调节性能导向的火-储联合调频混合储能双层优化配置策略[J/OL]. 电力系统自动化, 1–14[2025-06-12]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1180.TP.20250114.1759.006.html.
|
|
YAN Gangui, SHA Qianli, LI Junhui, et al. Regulation performance-oriented bi-level optimal configuration strategy of hybrid energy storage for thermal power generation and energy storage frequency regulation[J/OL]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 1–14[2025-06-12]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1180.TP.20250114.1759.006.html.
|
| 14 |
南斌, 董树锋, 唐坤杰, 等. 考虑需求响应和源荷不确定性的光储微电网储能优化配置[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (4): 1340- 1352.
|
|
NAN Bin, DONG Shufeng, TANG Kunjie, et al. Optimal configuration of energy storage in PV-storage microgrid considering demand response and uncertainties in source and load[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (4): 1340- 1352.
|
| 15 |
袁世琦, 潘鹏程, 魏业文, 等. 园区综合能源系统低碳经济优化调度模型研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45 (3): 347- 356.
|
|
YUAN Shiqi, PAN Pengcheng, WEI Yewei, et al. Study on low carbon economic optimal scheduling model of community integrated energy system[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45 (3): 347- 356.
|
| 16 |
王小虎, 楚春礼, 曹植, 等. 分布式光伏-储能系统经济-碳排放-能源效益实证分析——以山东省胶州光伏及其储能系统为例[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42 (1): 402- 414.
|
|
WANG Xiaohu, CHU Chunli, CAO Zhi, et al. Empirical analysis of cost-CO2-energy benefits of distributed pho-tovoltaic-battery storage system—taking (PV-BSS) in a case study in rural Jiaozhou Shandong[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42 (1): 402- 414.
|
| 17 |
郝婷, 樊小朝, 王维庆, 等. 阶梯式碳交易下考虑源荷不确定性的储能优化配置[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (1): 101- 112.
|
|
HAO Ting, FAN Xiaochao, WANG Weiqing, et al. Optimal configuration of energy storage considering the source-load uncertainty under ladder-type carbon trading[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (1): 101- 112.
|
| 18 |
巩晋通. 考虑辅助服务和碳效益的光伏电站电化学储能优化配置[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2022.
|
|
GONG Jintong. Optimal configuration of battery energy storage system for photovoltaic power station considering ancillary service and carbon benefits[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2022.
|
| 19 |
刘道兵, 李珏岑, 齐越, 等. 考虑碳效益和运行策略的风电场储能优化配置[J]. 太阳能学报, 2025, 46 (2): 664- 675.
|
|
LIU Daobing, LI Juecen, QI Yue, et al. Wind farm energy storage optimization configuration considering carbon benefit and operation strategy[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2025, 46 (2): 664- 675.
|
| 20 |
赵璐, 巩晋通, 李园林, 等. 考虑碳效益和辅助调峰的光伏电站储能配置方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2023, 56 (1): 80- 88.
|
|
ZHAO Lu, GONG Jintong, LI Yuanlin, et al. Energy storage configuration method of photovoltaic power station considering carbon benefits and auxiliary peak shaving[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2023, 56 (1): 80- 88.
|
| 21 |
李军徽, 张靖祥, 穆钢, 等. 辅助服务市场下独立储能调峰调频协同优化调度[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025, 45 (2): 650- 665.
|
|
LI Junhui, ZHANG Jingxiang, MU Gang, et al. Collaborative optimal dispatch of peak shaving and frequency modulation with independent energy storage based on auxiliary service market[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025, 45 (2): 650- 665.
|
| 22 |
刘行, 黎灿兵, 刘健哲, 等. 机组组合中电池储能调峰调频联合调度方法[J/OL]. 上海交通大学学报, 1–26[2025-05-28]. https://doi.org/10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2024.404.
|
|
LIU Hang, LI Canbing, LIU Jianzhe. Joint, et al. Scheduling method for peak regulation and frequency regulation in unit commitment using battery energy storage systems[J/OL]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 1–26[2025-05-28]. https://doi.org/10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2024.404.
|
| 23 |
薛文浩, 吕泉, 齐楚, 等. 现货市场环境下独立储能参与一次调频市场运营策略[J/OL]. 电力自动化设备, 1–10[2025-06-10]. https://doi.org/10.16081/j.epae.202504019.
|
|
XUE Wenhao, LÜ Quan, QI Chu, et al. Operation strategy of independent energy storage participating in primary frequency regulation market under spot market environment[J/OL]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 1–10[2025-06-10]. https://doi.org/10.16081/j.epae.202504019.
|
| 24 |
田圆, 陈红坤, 刘颖杰, 等. 辅助服务市场背景下灵活性资源调峰补偿价格决策方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2024, 44 (9): 154- 161, 188.
|
|
TIAN Yuan, CHEN Hongkun, LIU Yingjie, et al. Compensation price decision method for peak shaving of flexible resources in context of ancillary service market[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2024, 44 (9): 154- 161, 188.
|
| 25 |
徐宁, 周波, 凌云鹏, 等. 现货市场下独立储能参与电能量与辅助服务协同优化策略[J]. 现代电力, 2025, 42 (1): 109- 116.
|
|
XU Ning, ZHOU Bo, LING Yunpeng, et al. Collaborative optimization strategy of energy and auxiliary services with independent energy storage participating under the spot market[J]. Modern Electric Power, 2025, 42 (1): 109- 116.
|
| 26 |
王坤峰, 苟超, 段艳杰, 等. 生成式对抗网络GAN的研究进展与展望[J]. 自动化学报, 2017, 43 (3): 321- 332.
|
|
WANG Kunfeng, GOU Chao, DUAN Yanjie, et al. Generative adversarial networks: the state of the art and beyond[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43 (3): 321- 332.
|
| 27 |
ARJOVSKY M, CHINTALA S, BOTTOU L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney: JMLR. org, 2017: 214–223.
|
| 28 |
GULRAJANI I, AHMED F, ARJOVSKY M, et al. Improved training of Wasserstein GANs[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach: Curran Associates Inc., 2017: 5769–5779.
|
| 29 |
雷大勇. 交直流混合主动配电网规划模型及其求解方法研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2022.
|
|
LEI Dayong. Research on the planning model and solution method of AC/DC hybrid active distribution network [D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2022.
|
| 30 |
米阳, 周杰, 卢长坤, 等. 基于改进生成对抗网络与碳足迹的配电网多目标双层规划[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (21): 8421- 8435.
|
|
MI Yang, ZHOU Jie, LU Changkun, et al. A multi-objective bi-level planning of distribution network based on improved generative adversarial network and carbon footprint[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (21): 8421- 8435.
|
| 31 |
张忠会, 雷大勇, 蒋昌辉, 等. 基于二阶锥规划和NNC法的交直流混合配电网双层规划模型及其求解方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (1): 70- 85.
|
|
ZHANG Zhonghui, LEI Dayong, JIANG Changhui, et al. A bi-level planning model and its solution method of AC/DC hybrid distribution network based on second-order cone programming and NNC method[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (1): 70- 85.
|
| 32 |
颜远, 林舜江, 刘明波. 考虑备用动作约束的含风电场电力系统多目标动态优化调度[J]. 电网技术, 2018, 42 (2): 479- 486.
|
|
YAN Yuan, LIN Shunjiang, LIU Mingbo. Multi-objective optimal dynamic dispatch of power system with wind farms considering reserve action constraints[J]. Power System Technology, 2018, 42 (2): 479- 486.
|
| 33 |
赵书强, 汤善发. 基于改进层次分析法、CRITIC法与逼近理想解排序法的输电网规划方案综合评价[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2019, 39 (3): 143- 148, 162.
|
|
ZHAO Shuqiang, TANG Shanfa. Comprehensive evaluation of transmission network planning scheme based on improved analytic hierarchy process, CRITIC method and TOPSIS[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2019, 39 (3): 143- 148, 162.
|
| 34 |
朱天曈, 丁坚勇, 郑旭. 基于改进TOPSIS法和德尔菲——熵权综合权重法的电网规划方案综合决策方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46 (12): 91- 99.
|
|
ZHU Tiantong, DING Jianyong, ZHENG Xu. A comprehensive decision-making method for power network planning schemes based on the combination of the improved TOPSIS method with Delphi-entropy weight method[J]. Power System Protection and Control[1], 2018, 46 (12): 91- 99.
|