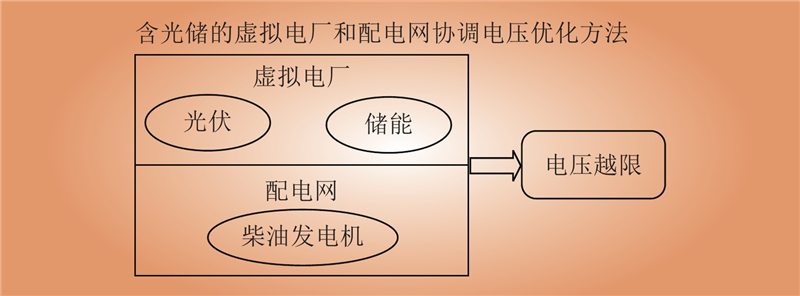
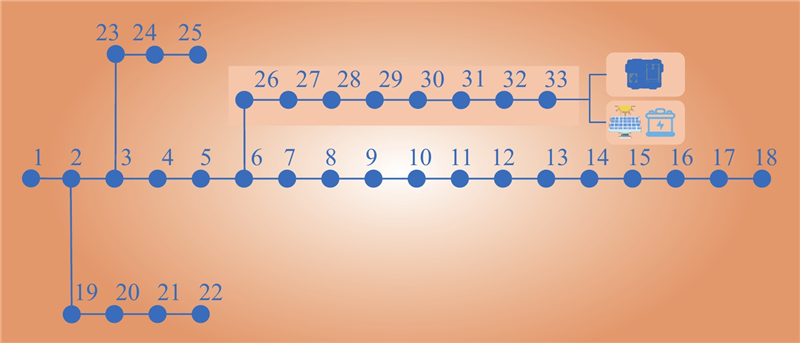
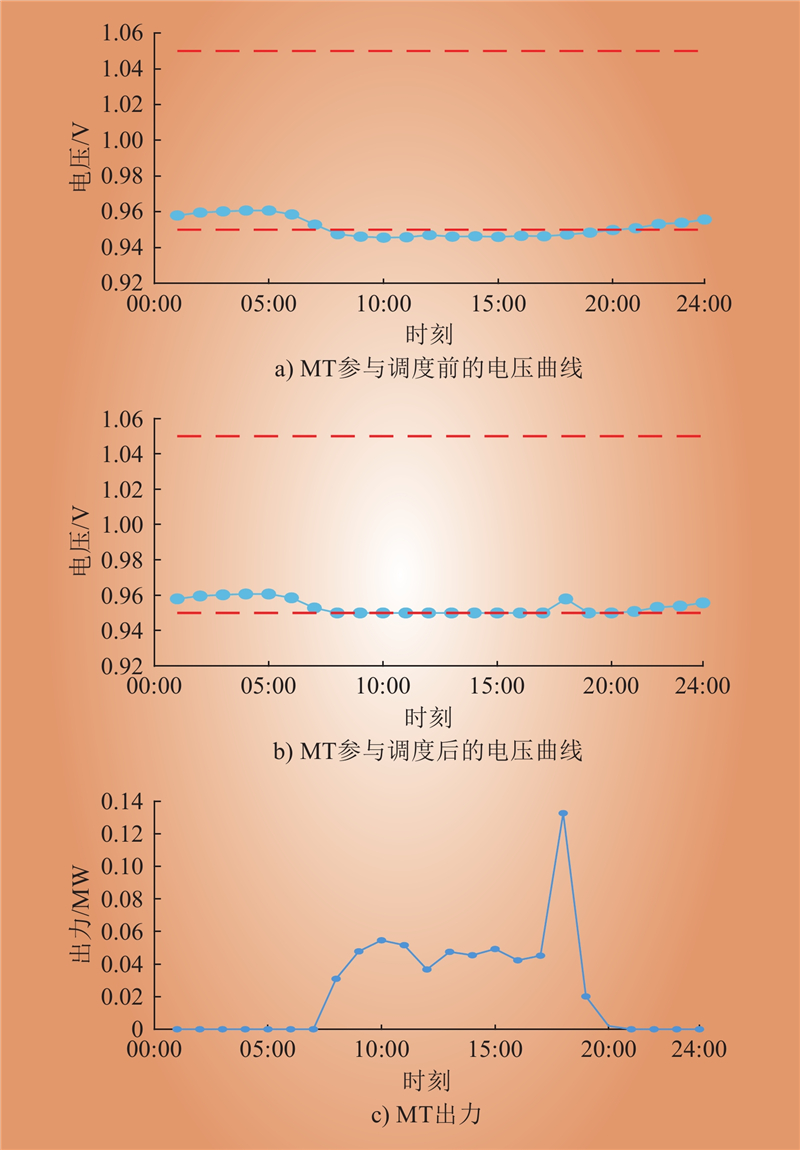
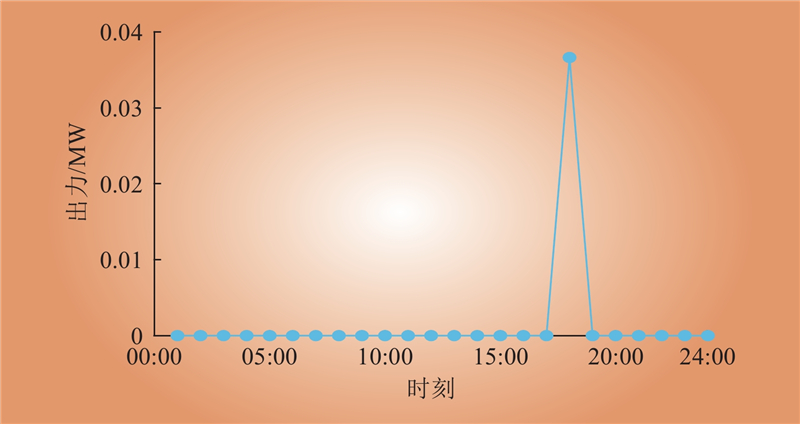
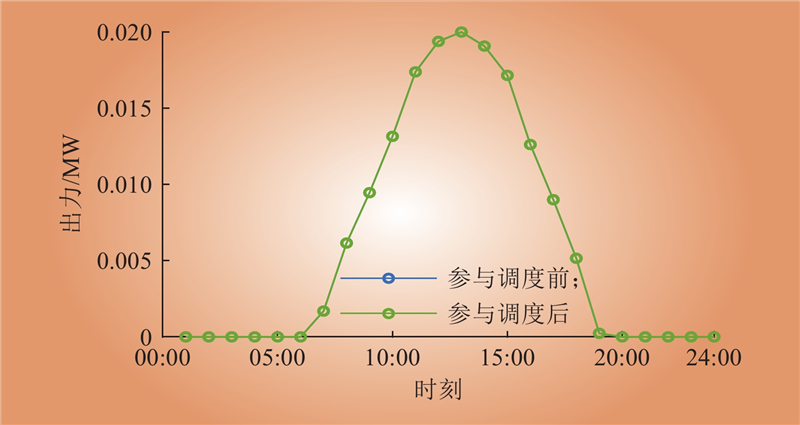
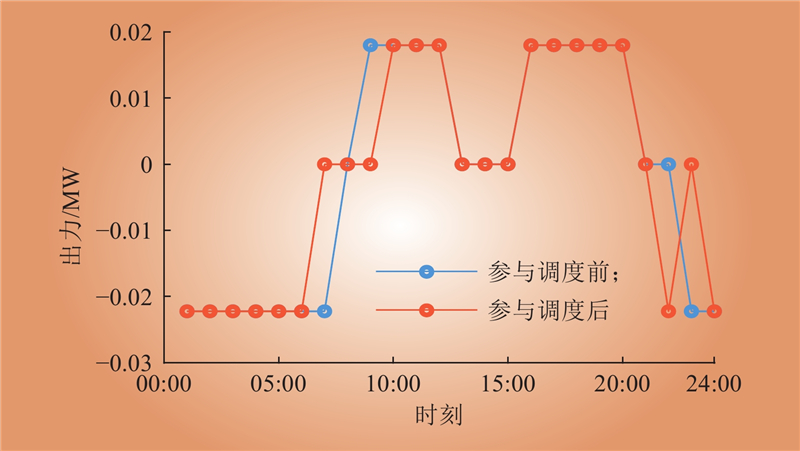
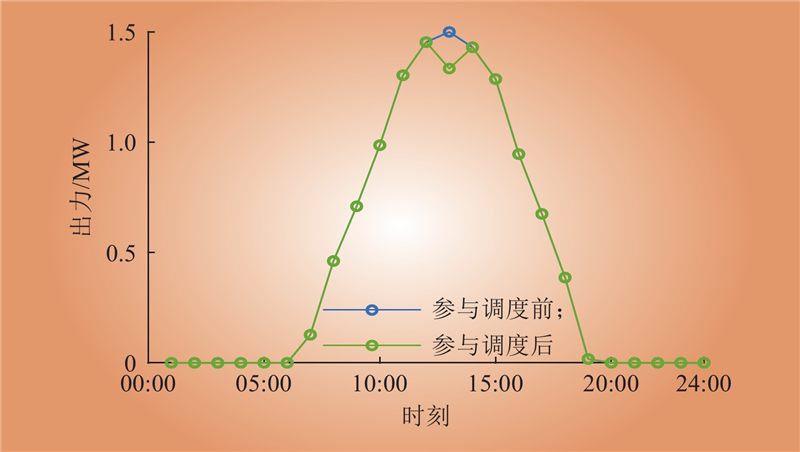
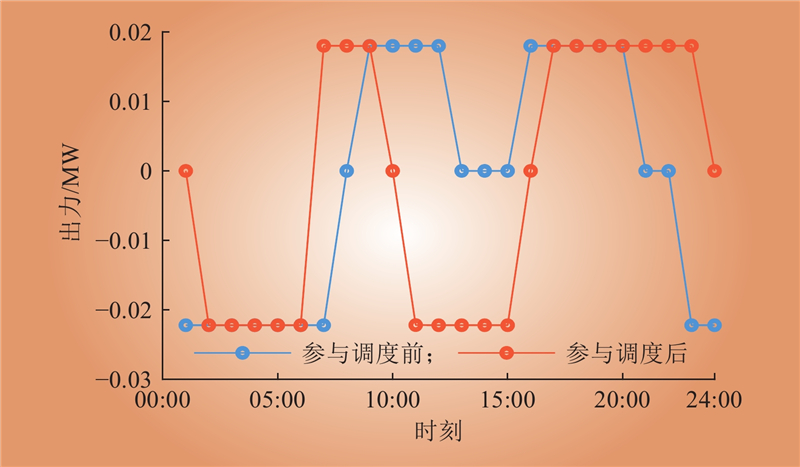
| 1 |
RAZMI D, LU T G, PAPARI B, et al. An overview on power quality issues and control strategies for distribution networks with the presence of distributed generation resources[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11, 10308- 10325.
|
| 2 |
ALGHASSAB M A, NOUR A M M, HATATA A Y, et al. Two-layer hybrid control scheme for distribution network integrated with photovoltaic sources based self-tuning H-infinity and fuzzy logic controller[J]. IET Renewable Power Generation, 2025, 19 (1): e12709.
|
| 3 |
PINTHURAT W, HREDZAK B, KONSTANTINOU G, et al. Techniques for compensation of unbalanced conditions in LV distribution networks with integrated renewable generation: an overview[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2023, 214, 108932.
|
| 4 |
刘宗, 何俊, 黄文涛, 等. 基于态势感知的高渗透率电动汽车接入电网后电压调整策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (2): 32- 44.
|
|
LIU Zong, HE Jun, HUANG Wentao, et al. Voltage adjustment strategy for high-penetration electric vehicles connected to power grid based on situation awareness[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (2): 32- 44.
|
| 5 |
祁向龙, 陈健, 赵浩然, 等. 多时间尺度协同的配电网分层深度强化学习电压控制策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (18): 53- 64.
|
|
QI Xianglong, CHEN Jian, ZHAO Haoran, et al. Multi-time scale cooperative voltage control strategy of a distribution network based onhierarchical deep reinforcement learning[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (18): 53- 64.
|
| 6 |
曹敬, 金玉龙, 郑涛, 等. 计及分布式电源集群不确定性的配电网分散鲁棒电压控制[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (22): 155- 166.
|
|
CAO Jing, JIN Yulong, ZHENG Tao, et al. A decentralized robust voltage control method for distribution networks consideringthe uncertainty of distributed generation clusters[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (22): 155- 166.
|
| 7 |
杨婧颖, 王武林, 张明敏, 等. 考虑分布式光伏和储能参与的配电网电压分层控制方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38 (5): 111- 120,215.
|
|
YANG Jingying, WANG Wulin, ZHANG Mingmin, et al. Voltage hierarchical control method of distribution network considering distributedphotovoltaic and energy storage[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38 (5): 111- 120,215.
|
| 8 |
郭旭春, 强德太, 钱羚, 等. 基于PSO-SVM算法的电压越限成因诊断方法[J]. 电工技术, 2023, (11): 47- 49.
|
|
GUO Xuchun, QIANG Detai, QIAN Ling, et al. Diagnosis method for voltage overlimit based on PSO-SVM algorithm[J]. Electric Engineering, 2023, (11): 47- 49.
|
| 9 |
张小平. 潮流和最优潮流分析中FACTS控制器的建模(英文)[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2005, (16): 22- 29, 65.
|
|
ZHANG Xiaoping. Modeling of FACTS in power flow and optimal power flow analysis[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2005, (16): 22- 29, 65.
|
| 10 |
黄聪, 杭乃善, 李璨, 等. 利用发电机调节的稳态潮流控制[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2012, 32 (5): 90- 93.
|
|
HUANG Cong, HANG Naishan, LI Can, et al. Steady-state power flow control by generator regulation[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2012, 32 (5): 90- 93.
|
| 11 |
孙华鹏, 丁孝华, 吴志, 等. 计及自动电压控制系统限值优化调整的配电网调压策略[J/OL]. 电力系统自动化, 1–13[2025-05-12]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1180.TP.20240325.1655.005.html.
|
|
SUN Huapeng, DING Xiaohua, WU Zhi, et al. Voltage regulation strategy for distributed generation considering optimized adjustment of AVC system limits[J/OL]. Automation of Electric Power Systems: 1–13[2025-05-12]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1180.TP.20240325.1655.005.html.
|
| 12 |
程益生, 陆振纲, 汪可友, 等. 电力弹簧稳态运行范围及越限失灵机理分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41 (14): 147- 152.
|
|
CHENG Yisheng, LU Zhengang, WANG Keyou, et al. Analysis on steady-state operating range and off-limits malfunction mechanism of electrical spring[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41 (14): 147- 152.
|
| 13 |
刘雁澄. 电力系统电压越限直接校正控制的研究[J]. 大连海事大学报, 1996, (4): 102- 105.
|
|
LIU Yancheng. Research of direct corrective control of the abnormal voltage problem in power systems[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 1996, (4): 102- 105.
|
| 14 |
林雪. 基于网络拓扑优化理论的电压越限解决方法研究[J]. 电子技术与软件工程, 2021, (1): 224- 225.
|
| 15 |
何满. 节点电压越限的电源直接控制潮流算法[J]. 电气开关, 2015, 53 (1): 41- 44.
|
|
HE Man. Research on power flow solution with voltage source direct control considering voltage limit violation[J]. Electric Switchgear, 2015, 53 (1): 41- 44.
|
| 16 |
张士涛, 赵迪. 基于灵敏度分析的电压越限处理方法[J]. 农村电气化, 2012(10): 19-20.
|
| 17 |
XU X, ZHANG T, QIU Z W, et al. Multi-mode control of a hybrid transformer for the coordinated regulation of voltage and reverse power in active distribution network[J]. Processes, 2024, 12 (2): 265.
|
| 18 |
郭伟, 安佳坤, 刘洋, 等. 混杂Petri-net的配电网多层级节点电压混杂控制[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (9): 140- 148, 167.
|
|
GUO Wei, AN Jiakun, LIU Yang, et al. Hybrid Petri-net based voltage hybrid control for multi-level nodes in distribution networks[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (9): 140- 148, 167.
|
| 19 |
ANDERSON T, MURALIDHARAN M, SRIVASTAVA P, et al. Frequency regulation with heterogeneous energy resources: a realization using distributed control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12 (5): 4126- 4136.
|
| 20 |
LIU J Q, HU H J, YU S S, et al. Virtual power plant with renewable energy sources and energy storage systems for sustainable power grid-formation, control techniques and demand response[J]. Energies, 2023, 16 (9): 3705.
|
| 21 |
NADEEM T B, SIDDIQUI M, KHALID M, et al. Distributed energy systems: a review of classification, technologies, applications, and policies[J]. Energy Strategy Reviews, 2023, 48, 101096.
|
| 22 |
杨佳霖, 赵鹏翔, 杨宪, 等. 含分布式光伏接入的配电网电压主动调控研究[J]. 河南科学, 2023, 41 (8): 1176- 1181.
|
|
YANG Jialin, ZHAO Pengxiang, YANG Xian, et al. Active voltage control of distribution network with distributed photovoltaic accessed[J]. Henan Science, 2023, 41 (8): 1176- 1181.
|
| 23 |
YE C, GUO C, DING Y. Voltage violations assessment considering reactive power compensation provided by smart inverters[M]. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2023: 83–98.
|
| 24 |
李圣清, 刘博文, 李焕平, 等. 基于一致性算法光伏逆变器和储能分组协调电压控制策略[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45 (9): 345- 352.
|
|
LI Shengqing, LIU Bowen, LI Huanping, et al. Coordinated voltage control strategy of photovoltaic inverter and energy storage group based on consensus algorithm[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45 (9): 345- 352.
|
| 25 |
张江林, 庄慧敏, 刘俊勇, 等. 分布式储能系统参与调压的主动配电网两段式电压协调控制策略[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2019, 39 (5): 15- 21, 29.
|
|
ZHANG Jianglin, ZHUANG Huimin, LIU Junyong, et al. Two-stage coordinated voltage control scheme of active distribution network with voltage support of distributed energy storage system[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2019, 39 (5): 15- 21, 29.
|
| 26 |
李佳琪, 陈健, 张文, 等. 高渗透率光伏配电网中电池储能系统综合运行控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34 (2): 437- 446.
|
|
LI Jiaqi, CHEN Jian, ZHANG Wen, et al. Integrated control strategy for battery energy storage systems in distribution networks with high photovoltaic penetration[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34 (2): 437- 446.
|
| 27 |
韩璟琳, 胡平, 侯若松, 等. 计及多光储一体机的配电网电压优化控制策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (6): 69- 77, 152.
|
|
HAN Jinglin, HU Ping, HOU Ruosong, et al. Voltage optimal control strategy for distribution networks with multiple integrated photovoltaic and energy storage machines[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (6): 69- 77, 152.
|
| 28 |
吴旭, 汤庆峰, 赵天阳. 考虑负荷静态特性的主动配电网多目标调压策略[J]. 分布式能源, 2017, 2 (4): 47- 52.
|
|
WU Xu, TANG Qingfeng, ZHAO Tianyang. Multi-objective voltage regulation method for active distribution network considering load static characteristics[J]. Distributed Energy, 2017, 2 (4): 47- 52.
|
| 29 |
张科杰, 张国彦, 徐宝昌, 等. 计及高比例新能源配电网电压风险的储能容量优化配置方法[J]. 电瓷避雷器, 2023, (6): 85- 93.
|
|
ZHANG Kejie, ZHANG Guoyan, XU Baochang, et al. Optimal allocation method for energy storage capacity considering voltage risks with high proportion of new energy distribution network[J]. Insulators and Surge Arresters, 2023, (6): 85- 93.
|
| 30 |
陈厚合, 刘丽娜, 姜涛, 等. 提升配电网电压质量的分布式储能经济优化配置方法[J]. 电网技术, 2018, 42 (7): 2127- 2135.
|
|
CHEN Houhe, LIU Lina, JIANG Tao, et al. Optimal economic configuration of distributed energy storage systems for improving voltage quality in distribution network[J]. Power System Technology, 2018, 42 (7): 2127- 2135.
|
| 31 |
NORD POOL. https://www.nordpoolgroup.com/en/Market-data1/Dayahead/Area-Prices/ALL1/Hourly/?view=table[EB/OL].
|