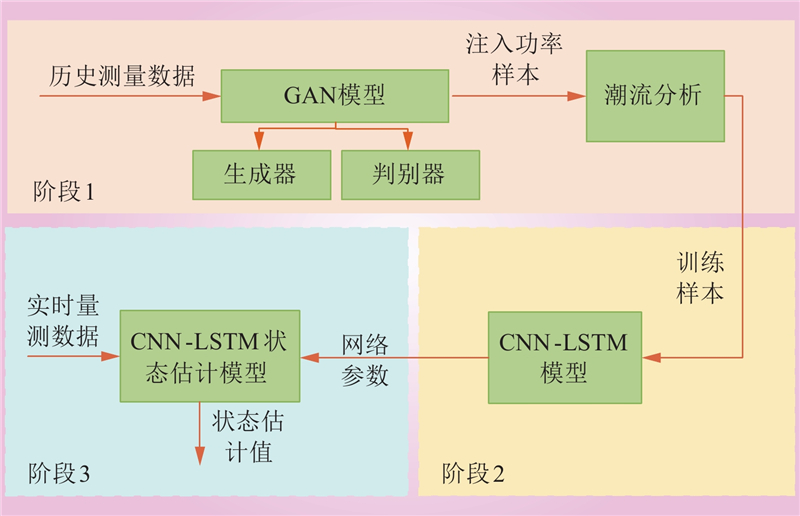
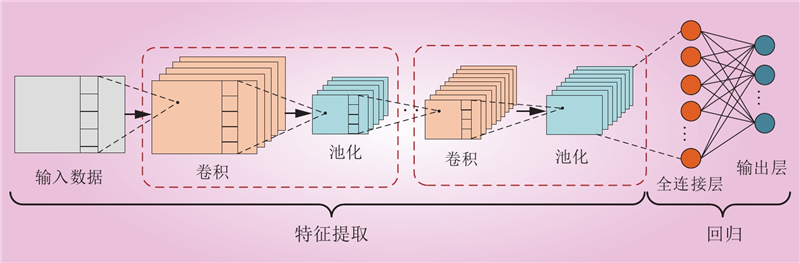
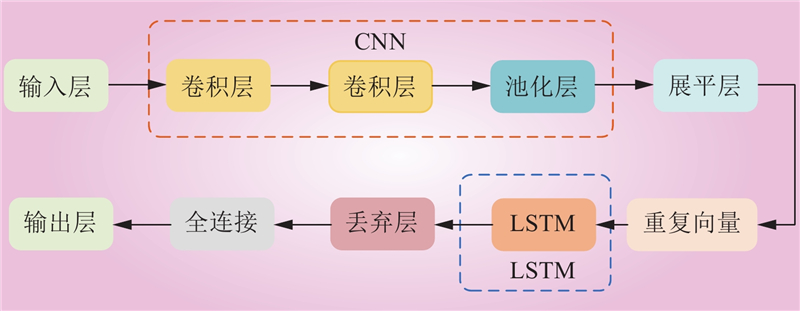
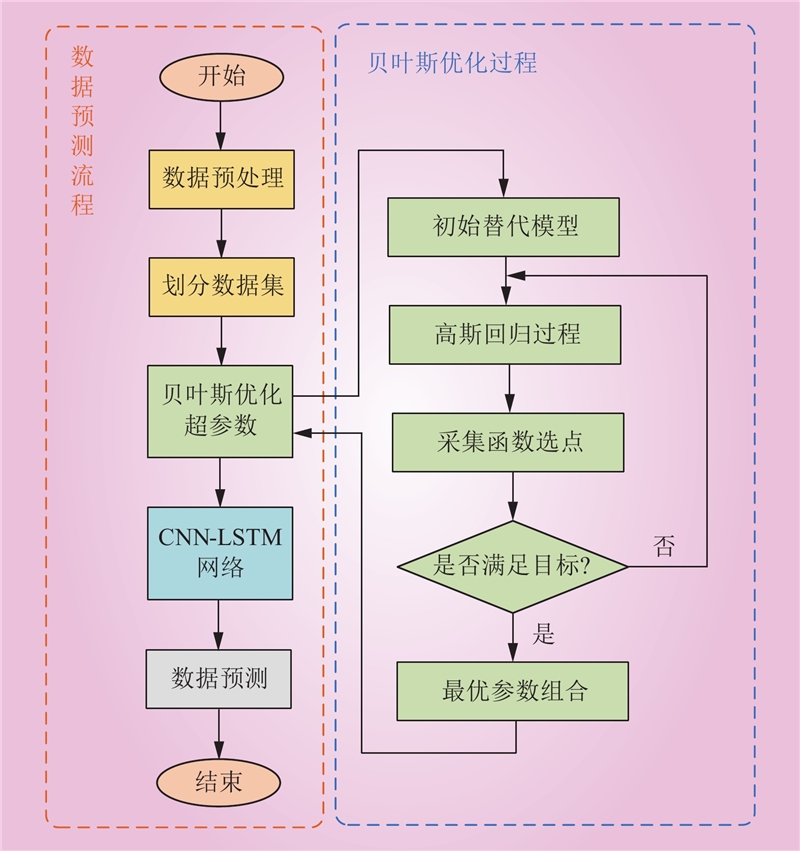
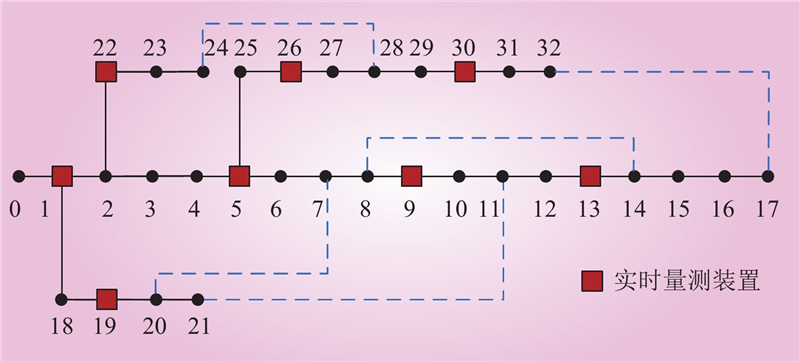
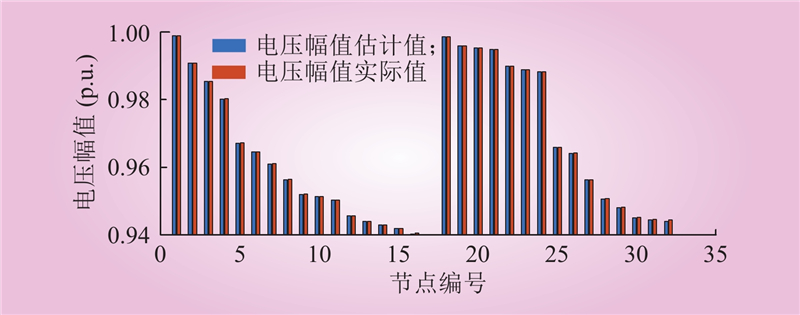
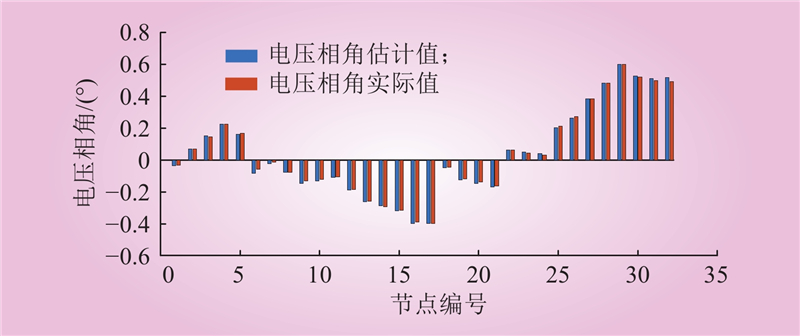
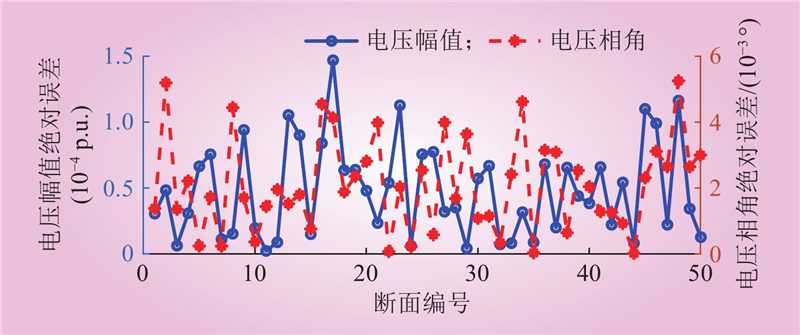
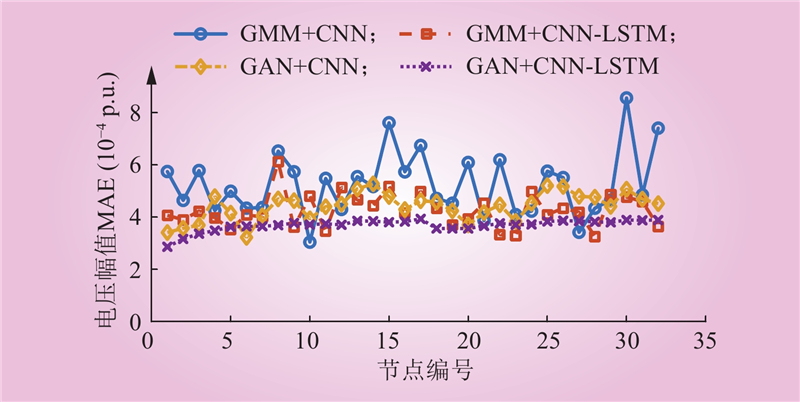
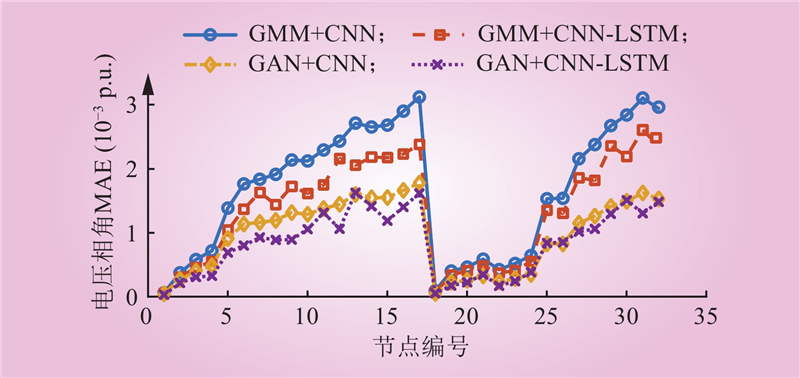
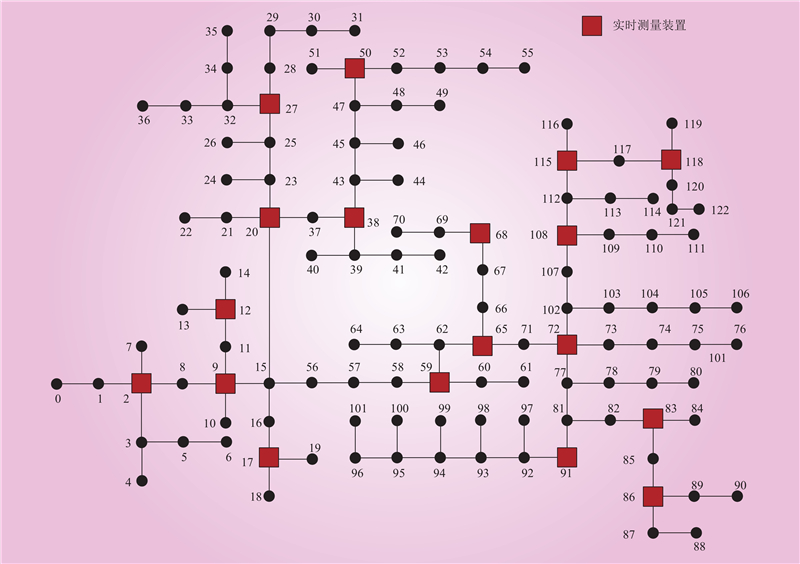
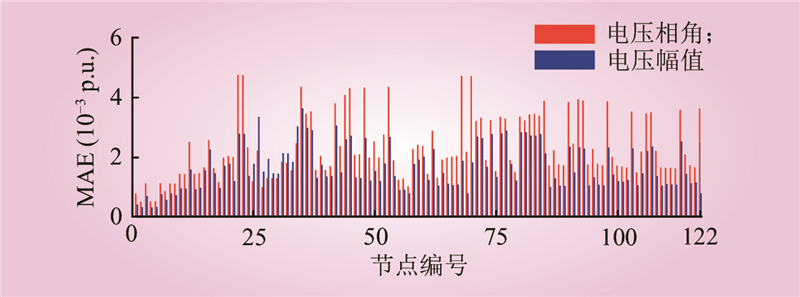
| 1 |
陈子靖, 蒋金琦, 赵健, 等. 基于CNN-AE-MAML的低压配电网自适应分类方法[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (5): 48- 58.
|
|
CHEN Zijing, JIANG Jinqi, ZHAO Jian, et al. Adaptive classification method of low voltage distribution network based on CNN-AE-MAML[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (5): 48- 58.
|
| 2 |
陈维江, 靳晓凌, 吴鸣, 等. 双碳目标下我国配电网形态快速演进的思考[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (17): 6811- 6818.
|
|
CHEN Weijiang, JIN Xiaoling, WU Ming, et al. Thinking on the rapid evolution of distribution network form under the carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (17): 6811- 6818.
|
| 3 |
葛磊蛟, 李元良, 陈艳波, 等. 智能配电网态势感知关键技术及实施效果评价[J]. 高电压技术, 2021, 47 (7): 2269- 2280.
|
|
GE Leijiao, LI Yuanliang, CHEN Yanbo, et al. Key technologies of situation awareness and implementation effectiveness evaluation in smart distribution network[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2021, 47 (7): 2269- 2280.
|
| 4 |
何振武, 姜飞, 欧阳卫, 等. 基于自适应分区和SFVMD-LSTM伪量测建模的新型配电系统抗差状态估计[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (10): 78- 89.
|
|
HE Zhenwu, JIANG Fei, OUYANG Wei, et al. Novel distribution system robust state estimation based on adaptive partitioning and SFVMD-LSTM pseudo-measurement modeling[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (10): 78- 89.
|
| 5 |
刘辉, 杨坤, 王枭枭, 等. 基于ADMM算法的中低压配电网多目标分布式协调优化运行策略[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (9): 100- 112.
|
|
LIU Hui, YANG Kun, WANG Xiaoxiao, et al. Multi-objective distributed optimal scheduling of distribution network with high-permeability distributed photovoltaic resource access[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (9): 100- 112.
|
| 6 |
罗玉春, 王毅, 闪鑫, 等. KLU稀疏直接求解器在状态估计中的应用[J]. 中国电力, 2019, 52 (2): 111- 118.
|
|
LUO Yuchun, WANG Yi, SHAN Xin, et al. Application of KLU sparse direct linear solver in state estimation[J]. Electric Power, 2019, 52 (2): 111- 118.
|
| 7 |
李诗伟, 骆晨, 何叶, 等. 多源量测环境下计及时延融合的配电网区间状态估计[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (12): 120- 129.
|
|
LI Shiwei, LUO Chen, HE Ye, et al. Interval state estimation for distribution network considering time-delay fusion in multi-source measurement environment[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (12): 120- 129.
|
| 8 |
田钧祥, 陈铁, 陈彬. 基于改进自适应UKF算法的中压配电网鲁棒动态状态估计方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (11): 128- 133.
|
|
TIAN Junxiang, CHEN Tie, CHEN Bin. Robust dynamic state estimation method for medium voltage distribution networks based on improved adaptive UKF algorithm[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (11): 128- 133.
|
| 9 |
龚成明, 於益军, 路轶, 等. 加权最小二乘状态估计量测权值计算的实用方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2016, 40 (11): 143- 147.
|
|
GONG Chengming, YU Yijun, LU Yi, et al. Practical method for calculating measurement weights in weighted least square state estimation[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40 (11): 143- 147.
|
| 10 |
朱鹏程, 柳劲松, 范士雄, 等. 考虑混合量测的配电网二次约束二次估计方法[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (3): 841- 847.
|
|
ZHU Pengcheng, LIU Jinsong, FAN Shixiong, et al. A quadratic constraint quadratic estimation method based on hybrid measurements for distribution networks[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (3): 841- 847.
|
| 11 |
马鑫, 郭瑞鹏, 柳劲松, 等. 三相不平衡下交直流配电网状态估计[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (23): 65- 71.
|
|
MA Xin, GUO Ruipeng, LIU Jinsong, et al. State estimation for three-phase unbalanced AC/DC distribution network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (23): 65- 71.
|
| 12 |
张占龙, 马海涛, 施伟成, 等. 一种能适应弱环网的改进配电网支路电流状态估计算法[J]. 中国电力, 2015, 48 (8): 61- 66.
|
|
ZHANG Zhanlong, MA Haitao, SHI Weicheng, et al. A revised branch-current-based state estimation method for weak looped distribution network[J]. Electric Power, 2015, 48 (8): 61- 66.
|
| 13 |
YILMAZ U C, ABUR A. A robust parallel distributed state estimation for large scale distribution systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2024, 39 (2): 4437- 4445.
|
| 14 |
孙国强, 殷岩岩, 卫志农, 等. 基于深度确定性策略梯度的主动配电网有功-无功协调优化调度[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44 (11): 33- 42.
|
|
SUN Guoqiang, YIN Yanyan, WEI Zhinong, et al. Coordinated optimal dispatch of active and reactive power in active distribution networks using deep deterministic strategy gradient[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2023, 44 (11): 33- 42.
|
| 15 |
齐韵英, 许潇, 殷科, 等. 基于深度强化学习的含储能有源配电网电压联合调控技术[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44 (11): 64- 74.
|
|
QI Yunying, XU Xiao, YIN Ke, et al. Voltage co-regulation technology of active distribution network with energy storage based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2023, 44 (11): 64- 74.
|
| 16 |
高岩, 吴汉斌, 张纪欣, 等. 基于组合深度学习的光伏功率日前概率预测模型[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (4): 100- 110.
|
|
GAO Yan, WU Hanbin, ZHANG Jixin, et al. Day-ahead probabilistic prediction model for photovoltaic power based on combined deep learning[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (4): 100- 110.
|
| 17 |
AHMAD F, TARIQ M, FAROOQ A. A novel ANN-based distribution network state estimator[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2019, 107, 200- 212.
|
| 18 |
TRAN M Q, ZAMZAM A S, NGUYEN P H, et al. Multi-area distribution system state estimation using decentralized physics-aware neural networks[J]. Energies, 2021, 14 (11): 3025.
|
| 19 |
兰浦哲, 韩冬, 徐潇源, 等. 基于长短期记忆的电-气耦合综合能源系统贝叶斯状态估计[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (20): 18- 28.
|
|
LAN Puzhe, HAN Dong, XU Xiaoyuan, et al. Bayesian state estimation for electricity-gas coupled integrated energy system based on long short-term memory[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (20): 18- 28.
|
| 20 |
刘晓莉, 曾祥晖, 黄翊阳, 等. 联合粒子滤波和卷积神经网络的电力系统状态估计方法[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (9): 3361- 3367.
|
|
LIU Xiaoli, ZENG Xianghui, HUANG Yiyang, et al. State estimation based on particle filtering and convolutional neural networks for power systems[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (9): 3361- 3367.
|
| 21 |
夏添梁, 张玉敏, 杨明, 等. 联合长短期记忆神经网络和粒子滤波的配电网预测辅助鲁棒状态估计方法[J]. 高电压技术, 2022, 48 (4): 1343- 1355.
|
|
XIA Tianliang, ZHANG Yumin, YANG Ming, et al. Robust forecasting-aided state estimation method of distribution network based on long-short term memory neural network and particle filter[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2022, 48 (4): 1343- 1355.
|
| 22 |
梁栋, 刘啸宇, 曾林, 等. 基于潮流引导神经网络的配电网贝叶斯状态估计[J]. 高电压技术, 2024, 50 (11): 4864- 4874.
|
|
LIANG Dong, LIU Xiaoyu, ZENG Lin, et al. Bayesian state estimation for distribution networks based on power flow-informed neural networks[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2024, 50 (11): 4864- 4874.
|
| 23 |
王守相, 陈海文, 潘志新, 等. 采用改进生成式对抗网络的电力系统量测缺失数据重建方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (1): 56- 64, 320.
|
|
WANG Shouxiang, CHEN Haiwen, PAN Zhixin, et al. A reconstruction method for missing data in power system measurement using an improved generative adversarial network[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (1): 56- 64, 320.
|
| 24 |
张汪洋, 樊艳芳, 侯俊杰, 等. 基于集成深度神经网络的配电网分布式状态估计方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (3): 128- 140.
|
|
ZHANG Wangyang, FAN Yanfang, HOU Junjie, et al. Distribution network distributed state estimation method based on an integrated deep neural network[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (3): 128- 140.
|
| 25 |
SINGH P, CHAUDHURY S, PANIGRAHI B K. Hybrid MPSO-CNN: multi-level particle swarm optimized hyperparameters of convolutional neural network[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2021, 63, 100863.
|