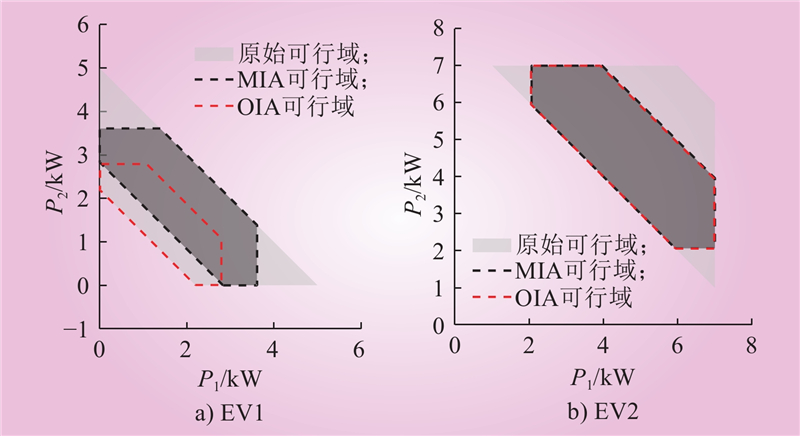
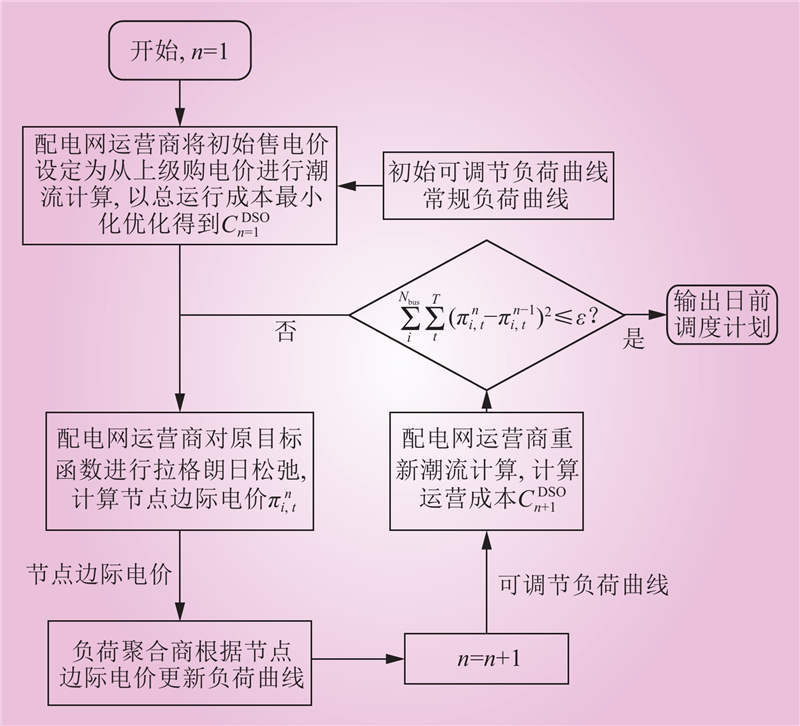
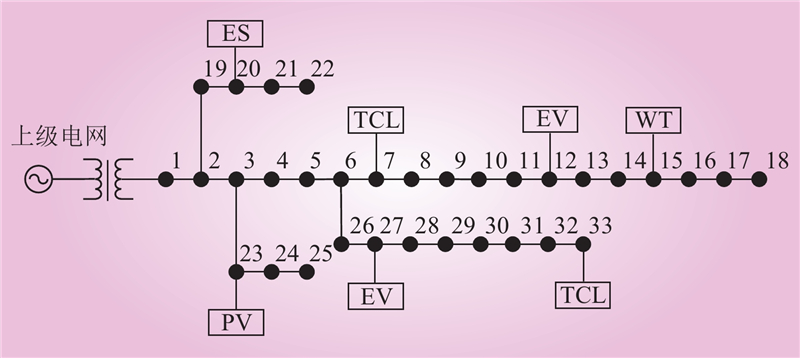
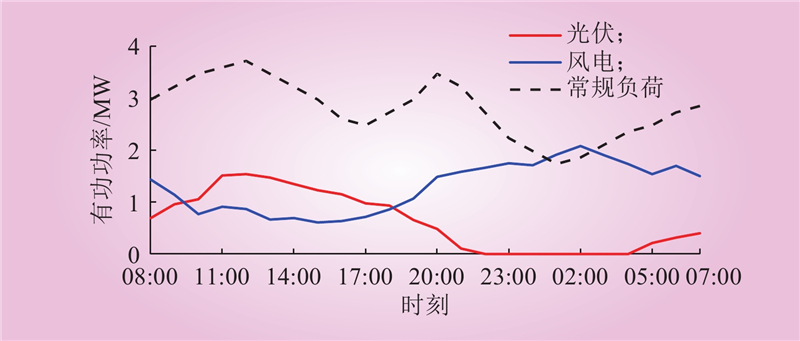
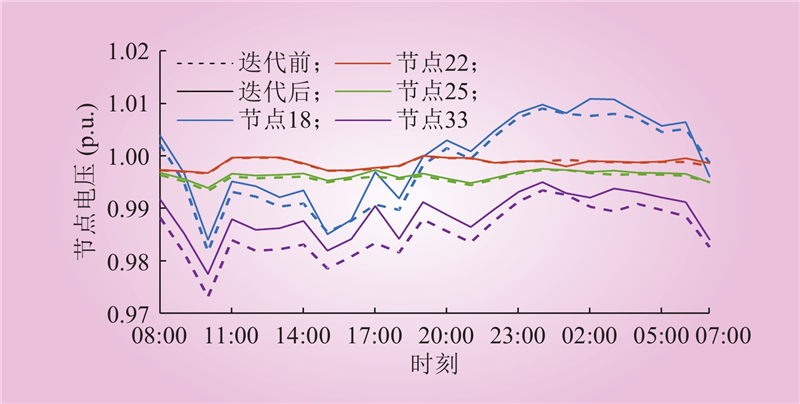
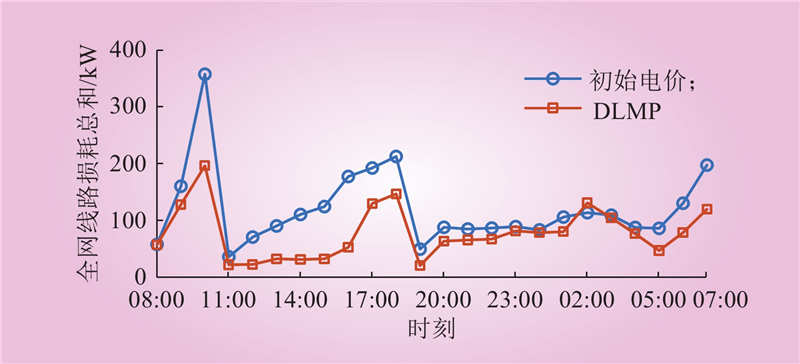
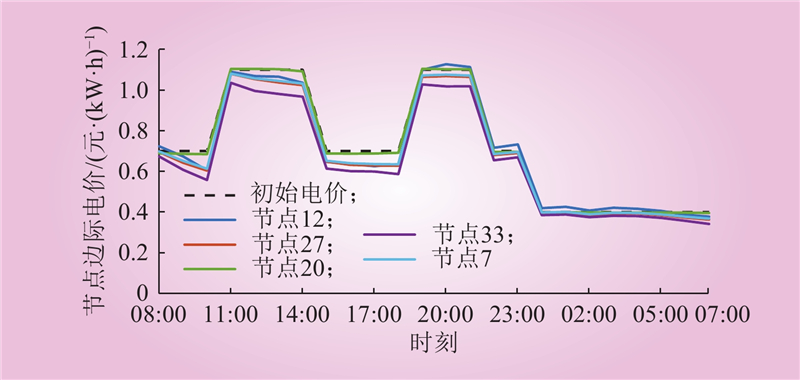
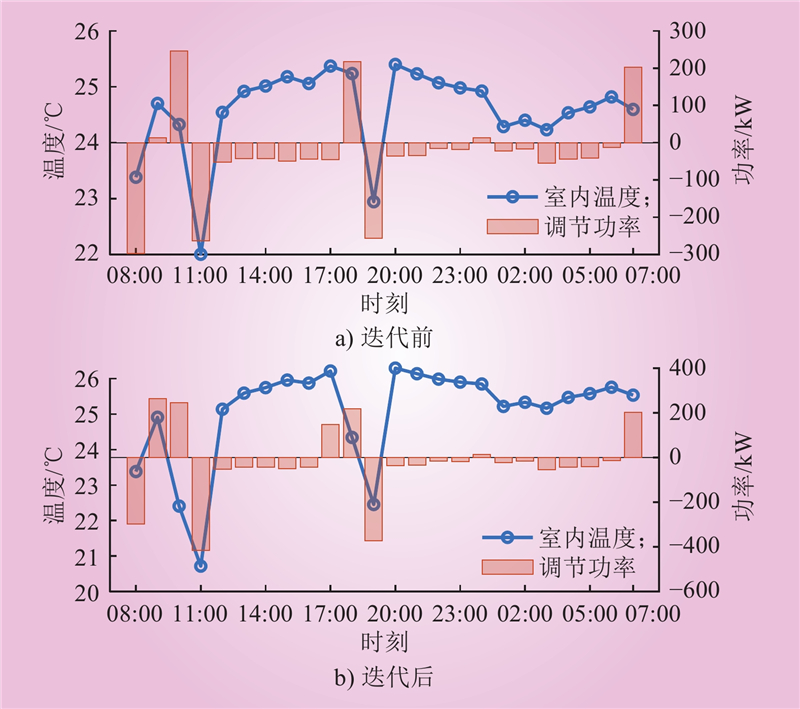
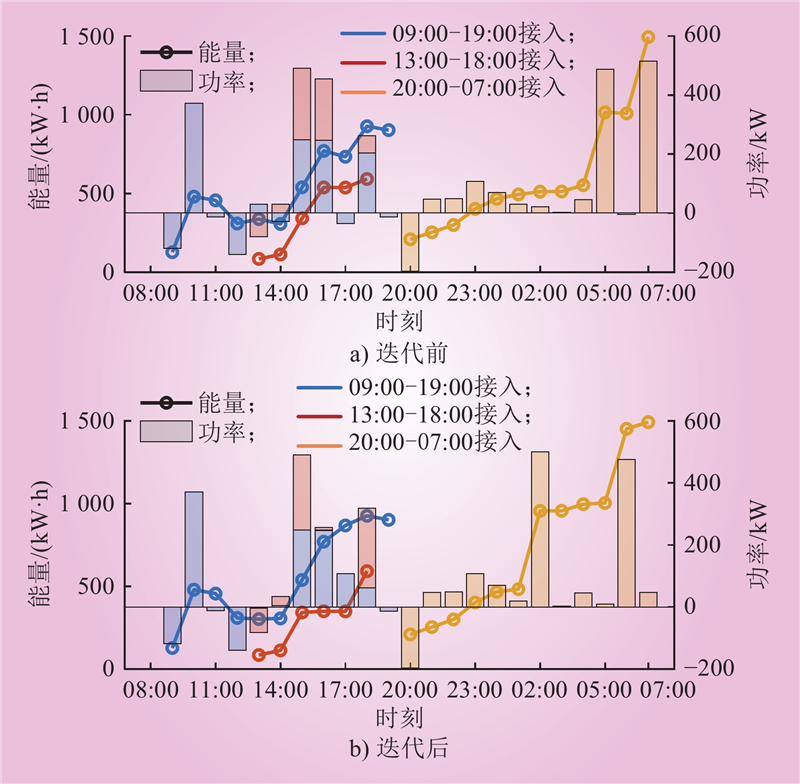
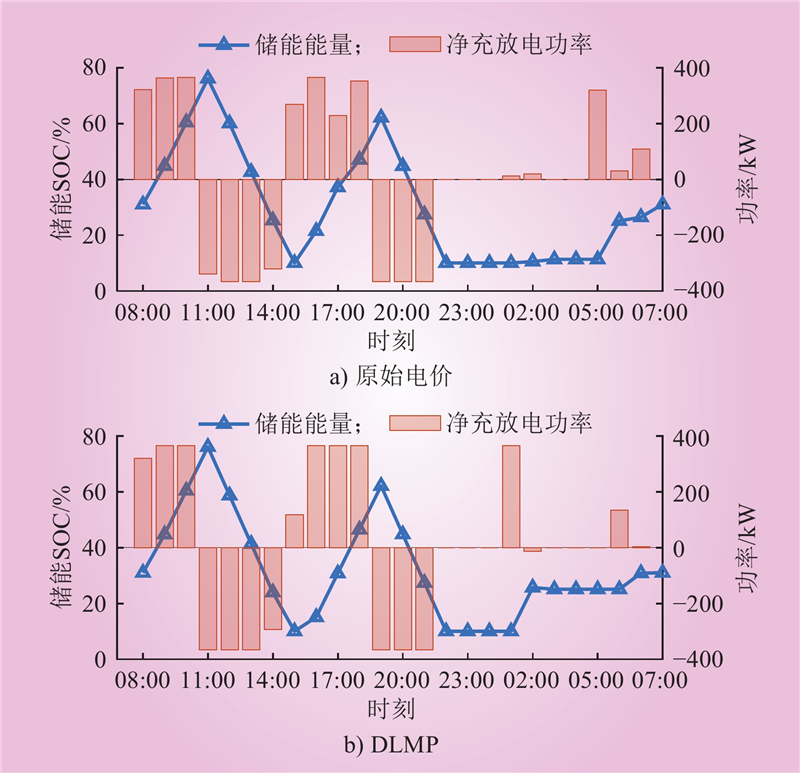
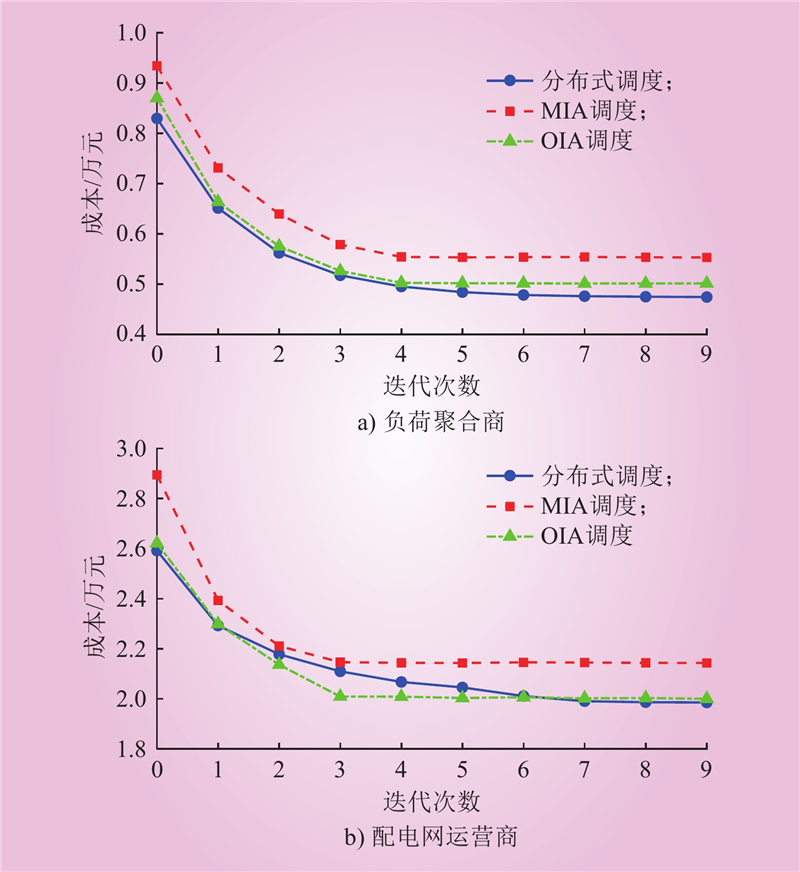
| 1 |
葛鑫鑫, 付志扬, 徐飞, 等. 面向新型电力系统的虚拟电厂商业模式与关键技术[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (18): 129- 146.
|
|
GE Xinxin, FU Zhiyang, XU Fei, et al. Business model and key technologies of virtual power plant for new power system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (18): 129- 146.
|
| 2 |
李彦晨, 贾燕冰, 谢栋, 等. 计及电能质量影响的配电网风储优化配置[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (6): 2391- 2404.
|
|
LI Yanchen, JIA Yanbing, XIE Dong, et al. Optimal configuration of wind turbine and energy storage system in distribution network considering influence of power quality[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (6): 2391- 2404.
|
| 3 |
杨涛, 周洪, 魏凤, 等. 新型电力系统下的电网安全挑战与对策研究[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (8): 18- 26.
|
|
YANG Tao, ZHOU Hong, WEI Feng, et al. Challenges and countermeasures of grid security towards a new type of power system[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (8): 18- 26.
|
| 4 |
李鹏, 刘嘉彦, 李佳蔚, 等. 考虑光伏与电动汽车充电站协同的配电网电压控制方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2024, 39 (6): 121- 130.
|
|
LI Peng, LIU Jiayan, LI Jiawei, et la. A voltage control method for distribution networks considering photovoltaic and electric vehicle charging station coordination[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2024, 39 (6): 121- 130.
|
| 5 |
康田园, 刘科研, 贾东梨, 等. 计及分布式电源出力不确定性的虚拟电厂鲁棒优化调度[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (2): 16- 24.
|
|
KANG Yuantan, LIU Keyan, JIA Dongli, et al. Robust optimal scheduling of virtual power plant considering output uncertainty of distributed generation[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (2): 16- 24.
|
| 6 |
王永恒, 何玮珊, 李静静, 等. 基于5G NR-U的分布式新能源采集调控策略[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (4): 86- 91.
|
|
WANG Yongheng, HE Weishan, LI Jingjing, et al. Acquisition and regulation strategy of distributed new energy based on 5G NR-U[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (4): 86- 91.
|
| 7 |
裴林, 黄成, 杨啸, 等. 考虑隐私保护和去中心化的分布式能源交易模式研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (2): 143- 154.
|
|
PEI Lin, HUANG Cheng, YANG Xiao, et al. A distributed energy trading model considering privacy protection and decentralization[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (2): 143- 154.
|
| 8 |
陈心宜, 胡秦然, 石庆鑫, 等. 新型电力系统居民分布式资源管理综述[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (5): 157- 175.
|
|
CHEN Xinyi, HU Qinran, SHI Qingxin, et al. Review on residential distributed energy resource management in new power system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (5): 157- 175.
|
| 9 |
陈国平, 董昱, 梁志峰. 能源转型中的中国特色新能源高质量发展分析与思考[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (17): 5493- 5506.
|
|
CHEN Guoping, DONG Yu, LIANG Zhifeng. Analysis and reflection on high-quality development of new energy with Chinese characteristics in energy transition[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (17): 5493- 5506.
|
| 10 |
翟苏巍, 李银银, 杜凡, 等. 考虑海量分布式能源接入的配电网分布式无功控制策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (8): 138- 144.
|
|
ZHAI Suwei, LI Yinyin, DU Fan, et al. Distributed reactive power control strategy of distribution network considering massive distributed energy access[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (8): 138- 144.
|
| 11 |
孙改平. 新型电力系统下考虑灵活性支撑的分布式能源聚合优化运行研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2022.
|
|
SUN Gaiping. Research on distributed energy resource aggregation and optimal operation of novel power system considering flexibility support[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2022.
|
| 12 |
翟哲, 陈梓煜, 刘起兴, 等. 计及风险管理的分布式资源聚合商电力市场交易模型[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (6): 56- 66, 155.
|
|
ZHAI Zhe, CHEN Ziyu, LIU Qixing, et al. An electricity market trading model for distributed resource aggregators considering risk management[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (6): 56- 66, 155.
|
| 13 |
陈璨, 王晶, 于宗民, 等. 配电网自治单元规划研究综述与展望[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 9- 19.
|
|
CHEN Can, WANG Jing, YU Zongmin, et al. Review and outlook of autonomous unit planning of distribution network[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 9- 19.
|
| 14 |
HAN D L, JIAN J B, YANG L F. Outer approximation and outer-inner approximation approaches for unit commitment problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2014, 29 (2): 505- 513.
|
| 15 |
YAN D X, MA C B, CHEN Y. Distributed coordination of charging stations considering aggregate EV power flexibility[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2023, 14 (1): 356- 370.
|
| 16 |
WEN Y L, HU Z C, YOU S, et al. Aggregate feasible region of DERs: exact formulation and approximate models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2022, 13 (6): 4405- 4423.
|
| 17 |
BAROT S, TAYLOR J A. A concise, approximate representation of a collection of loads described by polytopes[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2017, 84, 55- 63.
|
| 18 |
ZHAO L, ZHANG W, HAO H, et al. A geometric approach to aggregate flexibility modeling of thermostatically controlled loads[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 32 (6): 4721- 4731.
|
| 19 |
李晓露, 徐婉云, 柳劲松, 等. 考虑时序相关性的需求侧资源可调节功率域聚合方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (15): 58- 68.
|
|
LI Xiaolu, XU Wanyun, LIU Jinsong, et al. Adjustable power domain aggregation method for demand-side resourcesconsidering temporal correlation[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (15): 58- 68.
|
| 20 |
赵文猛, 黄豪江, 朱建全, 等. 内近似约束空间整合的灵活性资源集群响应方法[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (7): 2621- 2632.
|
|
ZHAO Wenmeng, HUANG Haojiang, ZHU Jianquan, et al. Flexible resource cluster response based on inner approximate and constraint space integration[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (7): 2621- 2632.
|
| 21 |
李英量, 孙楠, 王德明, 等. 含分布式储能系统的交直流配电网动态故障恢复策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (18): 179- 187.
|
|
LI Yingliang, SUN Nan, WANG Deming, et al. A dynamic fault recovery strategy for an AC/DC distribution network with distributed energy storage system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (18): 179- 187.
|
| 22 |
XU D L, XU J J, QIAN C, et al. A pseudo-measurement modelling strategy for active distribution networks considering uncertainty of DGs[J]. Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 2024, 9 (5): 1- 15.
|
| 23 |
张粒子, 丛野, 陶文斌, 等. 电力现货市场环境下提供位置信号电价机制的协同作用[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (9): 9- 18, 46.
|
|
ZHANG Lizi, CONG Ye, TAO Wenbin, et al. Coordination functions of electricity price providing locational signals under the circumstance of electricity spot market[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (9): 9- 18, 46.
|
| 24 |
陈泽宇, 陈艳波. 考虑储能循环寿命的市场出清机制及电价成因量化分析[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2025, 45 (3): 40- 49, 63.
|
|
CHEN Zeyu, CHEN Yanbo. Market clearing mechanism considering cycle life of energy storage and quantitative analysis of locational marginal price forming cause[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2025, 45 (3): 40- 49, 63.
|
| 25 |
刘一欣, 张帅, 郭力, 等. 计及电能量-备用耦合的配电网与光储充电站协调优化调度方法[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (8): 3175- 3185.
|
|
LIU Yixin, ZHANG Shuai, GUO Li, et al. Coordinated optimization scheduling method for distribution networks and photovoltaic storage charging stations considering the coupling of energy and reserve[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (8): 3175- 3185.
|
| 26 |
陈星宇, 张亚超, 黄张浩, 等. 考虑节点边际电价的配电网与多微电网双层鲁棒经济调度[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43 (11): 51- 58.
|
|
CHEN Xingyu, ZHANG Yachao, HUANG Zhanghao, et al. Bi-level robust economic dispatch of distribution network and multiple microgrids considering locational marginal price[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43 (11): 51- 58.
|
| 27 |
刘伟佳, 吴秋伟, 文福拴, 等. 电动汽车和可控负荷参与配电系统阻塞管理的市场机制[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2014, 38 (24): 26- 33, 101.
|
|
LIU Weijia, WU Qiuwei, WEN Fushuan, et al. A market mechanism for participation of electric vehicles and dispatchable loads in distribution system congestion management[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2014, 38 (24): 26- 33, 101.
|
| 28 |
赵一奇, 郭力, 刘一欣, 等. 计及阻塞管理的交直流柔性配电网协调优化调度方法[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (2): 622- 633.
|
|
ZHAO Yiqi, GUO Li, LIU Yixin, et al. Coordinated optimal scheduling method of AC/DC flexible distribution network considering congestion management[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (2): 622- 633.
|
| 29 |
BAI L Q, WANG J H, WANG C S, et al. Distribution locational marginal pricing (DLMP) for congestion management and voltage support[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33 (4): 4061- 4073.
|
| 30 |
朱佳男, 艾芊, 李嘉媚. 基于分布鲁棒优化的广义共享储能容量配置方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (8): 185- 194.
|
|
ZHU Jianan, AI Qian, LI Jiamei. Capacity allocation method for generalized shared energy storage based on distributionally robust optimization[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (8): 185- 194.
|