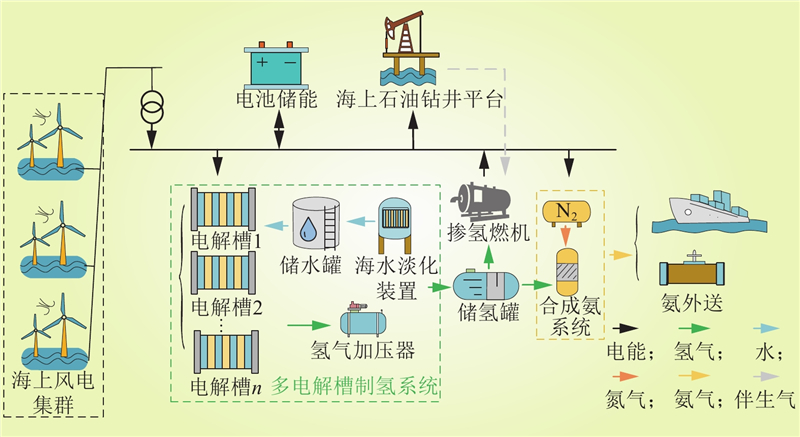
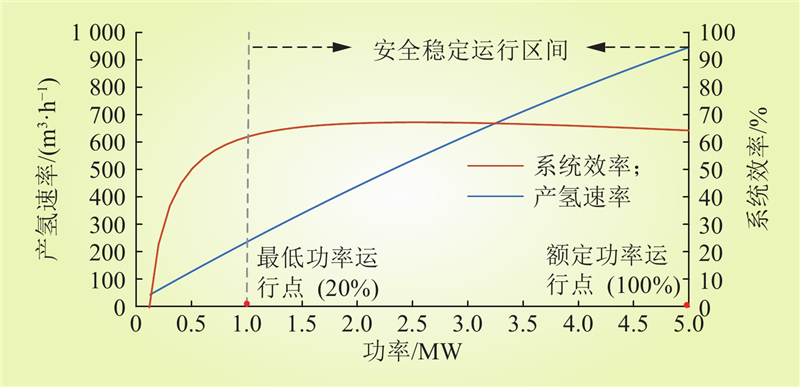
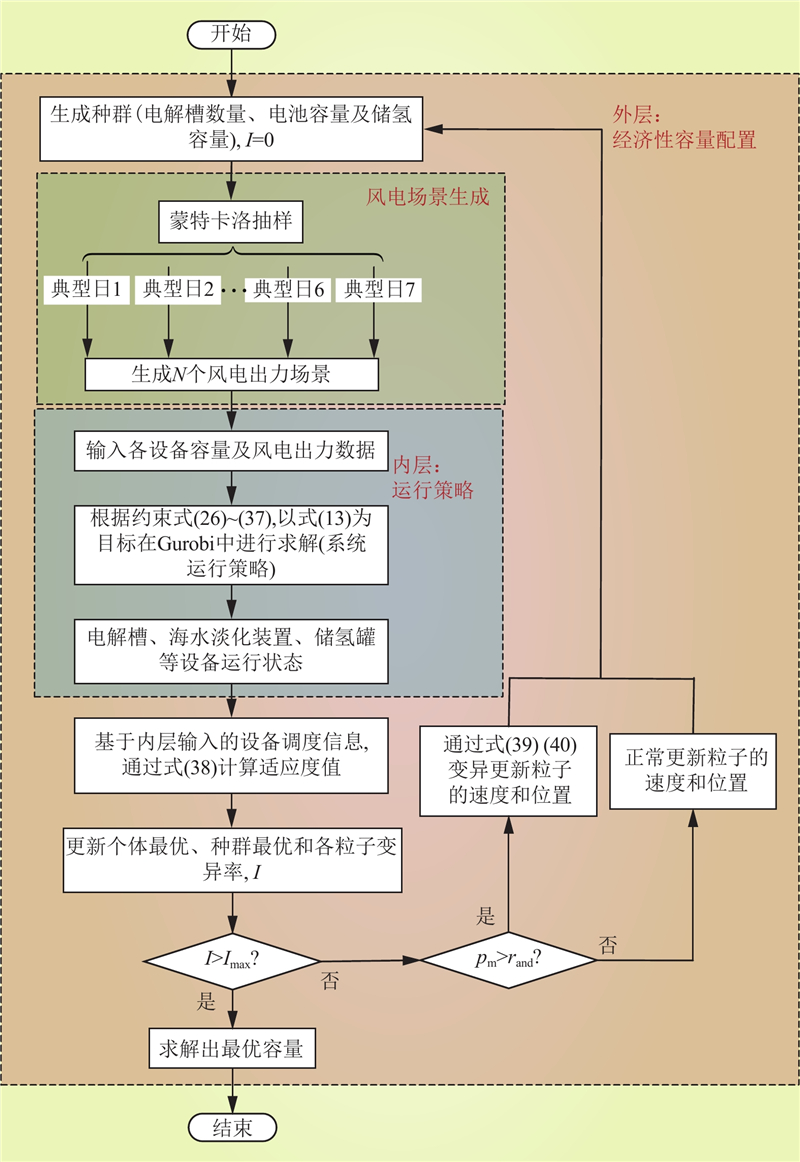
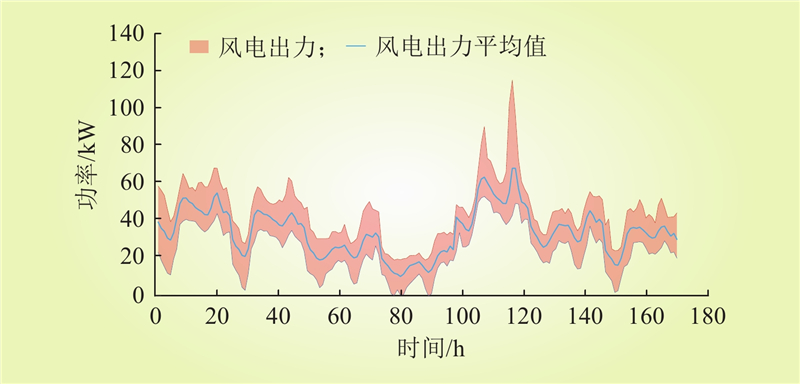
| 1 |
Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC). Global offshore wind report 2022[R]. Brussels, Belgium: GWEC, 2022.
|
| 2 |
杜云飞, 沈欣炜, 郦洪柯, 等. 考虑微观选址的分布式海上风电制氢容量优化配置[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (21): 61- 70.
|
|
DU Yunfei, SHEN Xinwei, LI Hongke, et al. Capacity optimization configuration of distributed offshore wind power to hydrogen considering micro-siting[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (21): 61- 70.
|
| 3 |
丰力, 张莲梅, 韦家佳, 等. 基于全生命周期经济评估的海上风电发展与思考[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (9): 80- 93.
|
|
FENG Li, ZHANG Lianmei, WEI Jiajia , et al. Development & thinking of offshore wind power based on life cycle economic evaluation[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (9): 80- 93.
|
| 4 |
刘钟淇, 刘耀, 侯金鸣. 以深远海风电为核心的能源岛能源外送经济性分析[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (9): 94- 102.
|
|
LIU Zhongqi, LIU Yao, HOU Jinming. Economic analysis of energy transmission for energy island based on deep-sea offshore wind farms[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (9): 94- 102.
|
| 5 |
马向辉, 张梓铭, 吴冇, 等. 2 GW海上风电对称单极与对称双极柔直送出方案技术经济性对比[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (2): 30- 38.
|
|
MA Xianghui , ZHANG Ziming, WU Mao, et al. Technical and economical comparisons of 2 GW offshore wind power transmission schemes by symmetrical monopole and symmetrical bipolar VSC-HVDC[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (2): 30- 38.
|
| 6 |
张安安, 张红, 吴建中, 等. 离岸微型综合能源系统多目标随机规划[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (7): 129- 135, 173.
|
|
ZHANG An'an, ZHANG Hong, WU Jianzhong, et al. Effect of compensation parameter on characteristics of series/series compensated wireless power transfer system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (7): 129- 135, 173.
|
| 7 |
LUCAS T R, FERREIRA A F, SANTOS PEREIRA R B, et al. Hydrogen production from the wind float atlantic offshore wind farm: a techno-economic analysis[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 310, 118481.
|
| 8 |
宋鹏飞, 张超, 肖立, 等. 海上风电非上网消纳及制醇氨技术综述[J]. 中外能源, 2023, 28 (11): 16- 23.
|
|
SONG Pengfei, ZHANG Chao, XIAO Li, et al. Study on off-grid consumption of offshore wind power and alcohol and ammonia production technology[J]. SINO-GLOBAL ENERGY, 2023, 28 (11): 16- 23.
|
| 9 |
田甜, 李怡雪, 黄磊, 等. 海上风电制氢技术经济性对比分析[J]. 电力建设, 2021, 42 (12): 136- 144.
|
|
Tian Tian, Li Yixue, Huang Lei, et al. Comparative analysis on the economy of hydrogen production technology for offshore wind power consumption[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2021, 42 (12): 136- 144.
|
| 10 |
杨胜, 樊艳芳, 侯俊杰, 等. 考虑平抑风光波动的ALK-PEM电解制氢系统容量优化模型[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (1): 85- 96.
|
|
YANG Sheng, FAN Yanfang, HOU Junjie, et al. Capacity optimization model for an ALK-PEM electrolytic hydrogen production system considering the stabilization of wind and PV fluctuations[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (1): 85- 96.
|
| 11 |
LUO Z, WANG X, WEN H, et al. Hydrogen production from offshore wind power in south China[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47 (58): 24558- 24568.
|
| 12 |
FLÓREZ-ORREGO D, FREIRE R A, DA SILVA J A M, et al. Centralized power generation with carbon capture on decommissioned offshore petroleum platforms[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 252, 1- 19.
|
| 13 |
张安安, 张红, 李茜, 等. 电-气联合储能的海上微能系统模糊随机规划[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (20): 5915- 5925, 6172.
|
|
ZHANG An'an, ZHANG Hong, LI Qian, et al. Two-stage stochastic optimization for operation scheduling and capacity allocation of integrated energy production unit considering supply and demand uncertainty[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (20): 5915- 5925, 6172.
|
| 14 |
李茜, 黄海涛, 晏小彬, 等. 海上油气微能系统的低碳优化运行研究[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (3): 13- 22.
|
|
LI Qian, HUANG Haitao, YAN Xiaobin, et al. Reserch on low-carbon optimal operation of offshore oil and gas micro integrated energy system[J]. ELECTRIC POWER, 2023, 56 (3): 13- 22.
|
| 15 |
HANG Q, ZHANG H R, YAN Y M, et al. Sustainable and clean oilfield development: how access to wind power can make offshore platforms more sustainable with production stability[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 294: 126225.
|
| 16 |
董辉, 葛维春, 张诗钽, 等. 海上风电制氢与电能直接外送差异综述[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43 (6): 869- 879.
|
|
DONG Hui, GE Weichun, ZHANG Shitan, et al. Summary of differences between hydrogen production from offshore wind power and direct outward transmission of electric energ[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2022, 43 (6): 869- 879.
|
| 17 |
JANG D , KIM K , KIM K H, et al. Techno-economic analysis and Monte Carlo simulation for green hydrogen production using offshore wind power plant[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 263: 115695.
|
| 18 |
李佳蓉, 林今, 陈凯旋, 等. 考虑尾流效应的分布式海上风电制氢集群容量优化配置[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (11): 9- 17.
|
|
LI Jiarong, LIN Jin, CHEN Kaixuan, et al. Optimal capacity configuration of distributed offshore wind power-to-hydrogen cluster considering wake effect[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (11): 9- 17.
|
| 19 |
FANG R, LIANG Y. Control strategy of electrolyzer in a wind-hydrogen system considering the constraints of switching times[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44 (46): 25104- 11.
|
| 20 |
沈小军, 聂聪颖, 吕洪. 计及电热特性的离网型风电制氢碱性电解槽阵列优化控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(3): 463-472.
|
|
SHEN Xiaojun, NIE Congying, LV Hong. Coordination control strategy of wind power-hydrogen alkaline electrolyzer bank considering electrothermal characteristics[J]Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(3): 463-472.
|
| 21 |
王加荣, 杨博, 张芮, 等. 基于风电预测的碱性电解槽系统优化控制[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (7): 2940- 2947.
|
|
WANG Jiarong, YANG Bo, ZHANG Rui, et al. Optimization control of alkaline electrolyzer system based on wind power prediction[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (7): 2940- 2947.
|
| 22 |
贺明智, 陈茂林, 孟鑫. 基于规划算法的并联制氢装置效率优化控制方法[J]. 可再生能源, 2023, 41 (10): 1401- 1407.
|
|
HE Mingzhi, CHEN Maolin, MENG Xin. Efficiency optimization control method of parallel hydrogen production unit based on programming algorithm[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2023, 41 (10): 1401- 1407.
|
| 23 |
张智泉, 陈晓杰, 符杨, 等. 含海上风电制氢的综合能源系统分布鲁棒低碳优化运行[J]. 电网技术, 2025, 49 (1): 41- 51.
|
|
ZHANG Zhiquan, CHEN Xiaojie, FU Yang, et al. Distributionally robust low-carbon optimal operation for integrated energy system including hydrogen production from offshore wind power[J]. Power System Technology, 2025, 49 (1): 41- 51.
|
| 24 |
张帅龙, 郑可迪, 刘学, 等. 基于藤Copula 理论的海上风电建模及电力市场运行分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (11): 134- 142.
|
|
ZHANG Shuailong, ZHENG Kedi, LIU Xue, et al. Modeling of offshore wind power based on vine copula theory and electricity market operation analysis[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (11): 134- 142.
|
| 25 |
彭春华, 熊志盛, 张艺, 等. 基于多场景置信间隙决策的风光储联合鲁棒规划[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (16): 178- 187.
|
|
PENG Chunhua, XIONG Zhisheng, ZHANG Yi, et al. Joint robust planning of wind-photovoltaic-energy storage system based on multi-scenario confidence gap decision[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (16): 178- 187.
|
| 26 |
周永斐, 梅亚东, 王现勋, 等. 基于场景概率的不确定性主从博弈调度[J]. 水电与抽水蓄能, 2024, 10 (6): 10- 15.
|
|
ZHOU Yongfei, MEI Yadong, WANG Xianxun, et al. Uncertainty stackelberg game scheduling based on scenario probability[J]. Hydropower and Pumped Storage, 2024, 10 (6): 10- 15.
|
| 27 |
左逢源, 张玉琼, 赵强, 等. 计及源荷不确定性的综合能源生产单元运行调度与容量配置两阶段随机优化[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (22): 8205- 8215.
|
|
ZUO Fengyuan, ZHANG Yuqiong, ZHAO Qiang, et al. Two-stage stochastic optimization for operation scheduling and capacity allocation of integrated Energy production unit considering supply and demand uncertainty[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (22): 8205- 8215.
|
| 28 |
高宇歌, 任洲洋, 程欢, 等. 考虑电解槽动态效率特性的电-氢混合储能优化运行方法[J]. 电网技术, 2025, 49 (2): 533- 541.
|
|
GAO Yuge, REN Zhouyang, CHENG Huan, et al. Optimized operation of hybrid electric-hydrogen energy storage considering dynamic efficiency characteristics of electrolysers[J]. Power System Technology, 2025, 49 (2): 533- 541.
|
| 29 |
楚帅, 董辉, 葛维春, 等. 海水淡化负荷消纳弃风电量的集群优化调度策略[J]. 高电压技术, 2021, 47 (9): 3085- 3095.
|
|
CHU Shuai, DONG Hui, GE Weichun, et al. Cluster optimal dispatch strategy for seawater desalination using abandoned wind power[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2021, 47 (9): 3085- 3095.
|
| 30 |
周步祥, 朱文聪, 朱杰, 等. 风光制氢合成氨系统的多时段可调度域分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (1): 160- 174.
|
|
ZHOU Buxiang, ZHU Wencong, ZHU Jie, et al. Multi-stage dispatchable region analysis of wind and solar power-based hydrogen production and ammonia synthesis system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (1): 160- 174.
|
| 31 |
李梓丘, 乔颖, 鲁宗相. 海上风电-氢能系统运行模式分析及配置优化[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (8): 104- 112.
|
|
LI Ziqiu, QIAO Ying, LU Zongxiang. Operation mode analysis and configuration optimization of offshore wind-hydrogen system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (8): 104- 112.
|
| 32 |
袁铁江, 郭建华, 杨紫娟, 等. 平抑风电波动的电-氢混合储能容量优化配置[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (4): 1397- 1406.
|
|
YUAN Tiejiang, GUO Jianhua, YANG Zijuan, et al. Optimal allocation of power electric-hydrogen hybrid energy storage of stabilizing wind power fluctuation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (4): 1397- 1406.
|
| 33 |
夏威夷, 任洲洋, 潘珍. 考虑子母站灵活互联的分布式供氢网和配电网多主体协调规划方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (23): 9187- 9200.
|
|
XIA Weiyi, REN Zhouyang, PAN Zhen. A multi-agent cooperative planning method for the distributed hydrogen supply network and the power distribution network considering the flexible interconnections between on-site and off-site hydrogen refueling stations[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (23): 9187- 9200.
|