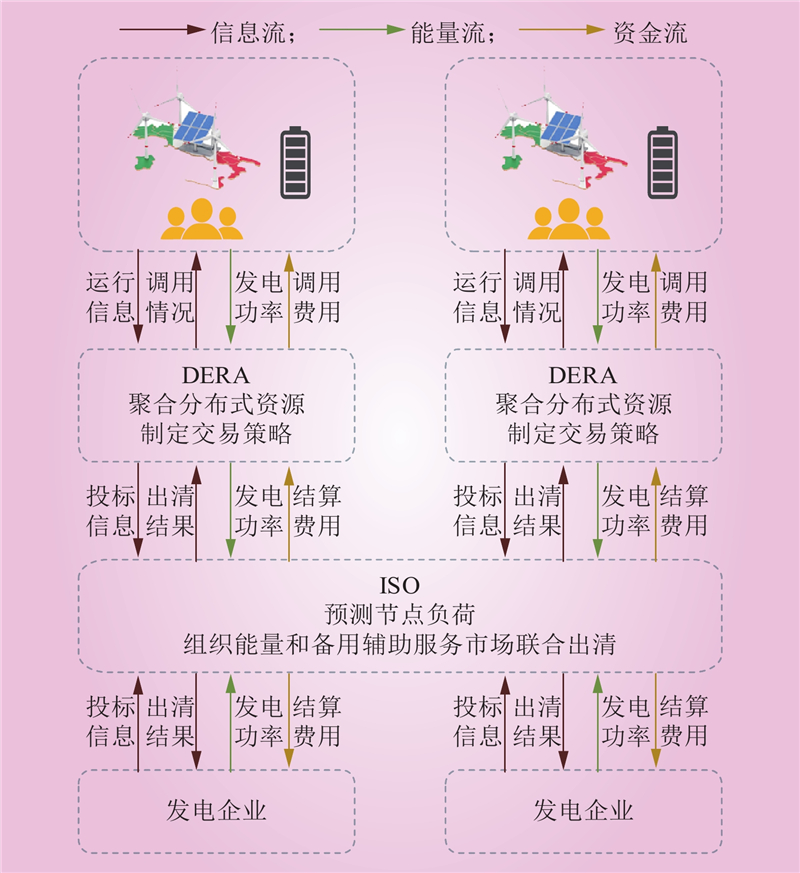
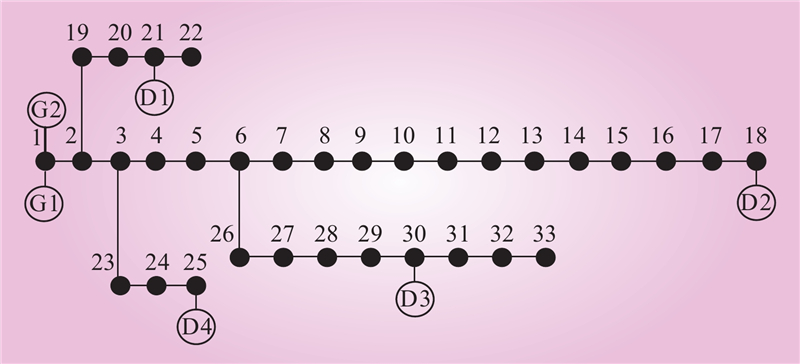
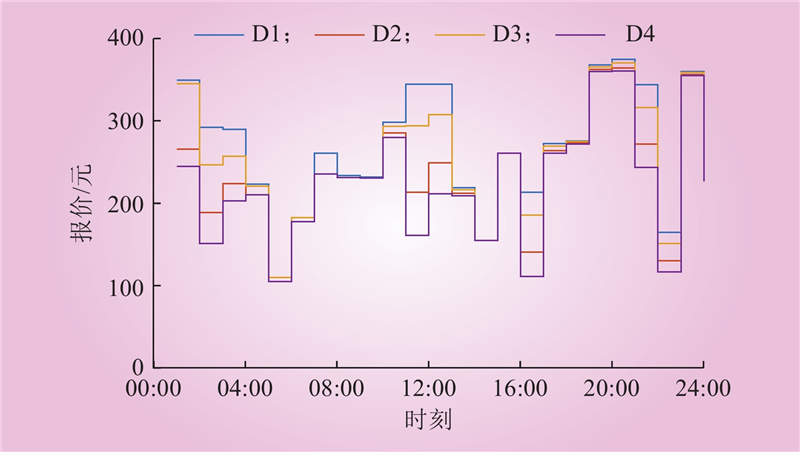
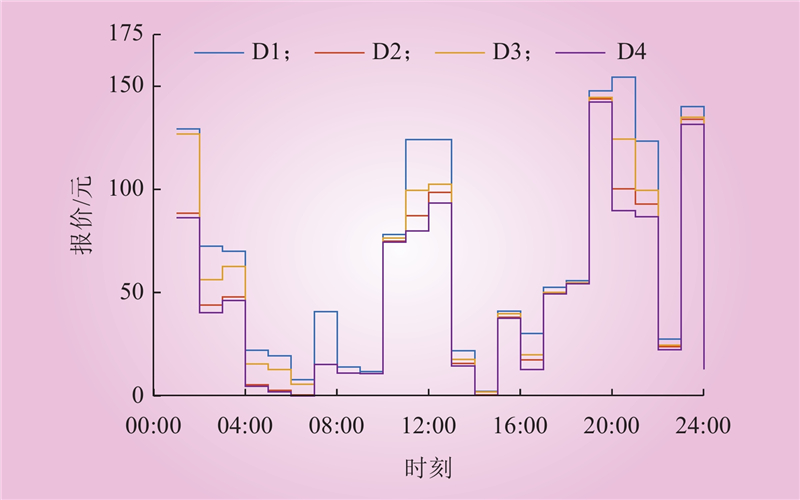
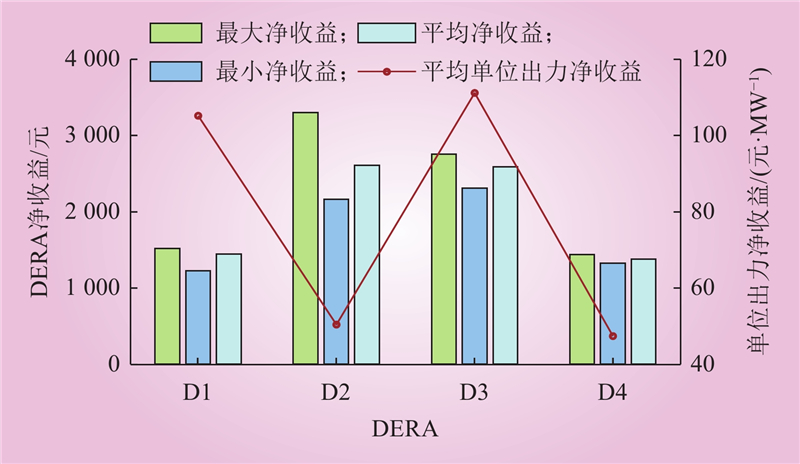
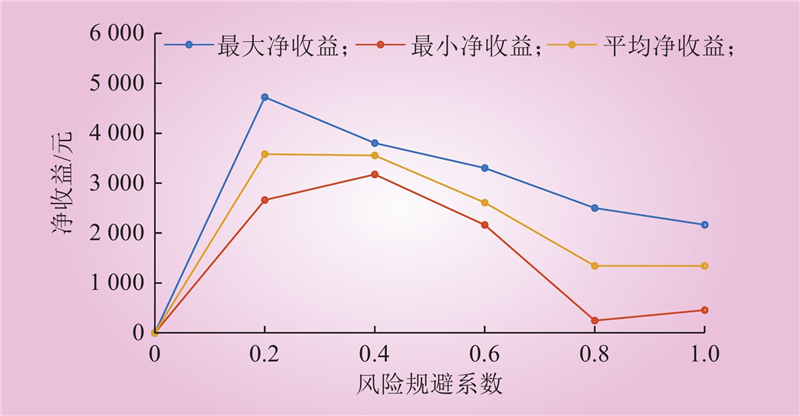
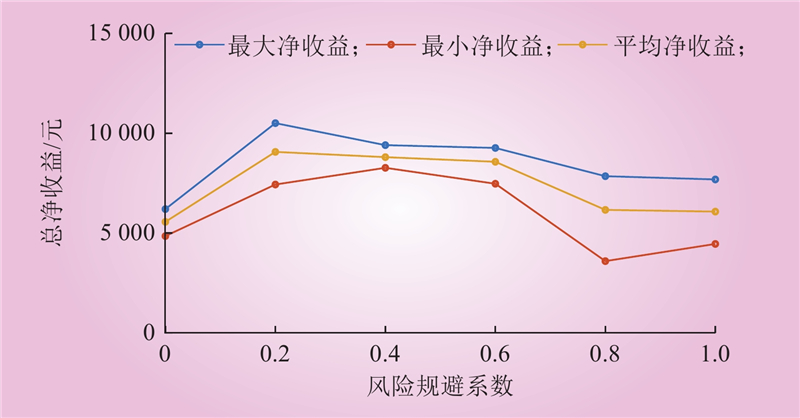
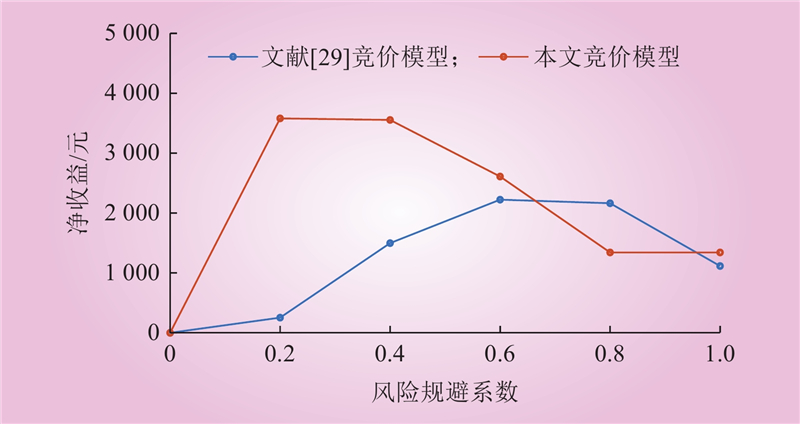
| 1 |
周勤勇, 李根兆, 秦晓辉, 等. 能源革命下的电力系统范式转换分析[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (3): 1- 11.
|
|
ZHOU Qinyong, LI Genzhao, QIN Xiaohui, et al. Analysis of power system paradigm shift under energy revolution[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (3): 1- 11.
|
| 2 |
朱瑞, 娄奇鹤, 靳晓凌, 等. 适应新型电力系统的电网基建功能化投资结构演化研究[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (9): 194- 204.
|
|
ZHU Rui, LOU Qihe, JIN Xiaoling, et al. Evolution of functional investment structure of power grid infrastructure suitable for new power system[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (9): 194- 204.
|
| 3 |
刘稼瑾, 冯华, 丁宁, 等. 电碳协同的园区分布式资源集群综合效益评估方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2024, 39 (5): 181- 191.
|
|
LIU Jiajin, FENG Hua, DING Ning, et al. Comprehensive benefit evaluation method for park with distributed resource clusters by electrical and carbon synergy[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2024, 39 (5): 181- 191.
|
| 4 |
李鹏, 刘嘉彦, 李佳蔚, 等. 考虑光伏与电动汽车充电站协同的配电网电压控制方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2024, 39 (6): 121- 130.
|
|
LI Peng, LIU Jiayan, LI Jiawei, et al. A voltage control method for distribution networks considering photovoltaicand electric vehicle charging station coordination[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2024, 39 (6): 121- 130.
|
| 5 |
守正创新扎实推动高质量发展——2024年电工行业经济运行分析及2025年展望[J]. 电器工业, 2025(4): 13–17.
|
| 6 |
华中省间电力调峰及备用辅助服务市场运营规则[EB/OL]. [2022-10-17](2024-07-19). http://www.nea.gov.cn/2022-10/17/c_1310670107.htm.
|
| 7 |
李军祥, 梁贤武, 屈德强, 等. 基于区块链技术的光伏产消者集群定价博弈[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (5): 73- 82.
|
|
LI Junxiang, LIANG Xianwu, QU Deqiang, et al. A pricing game for a photovoltaic prosumer cluster based on blockchain technology[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (5): 73- 82.
|
| 8 |
陈雨佳, 裴玮, 马腾飞, 等. 考虑条件风险价值的分布式发电与用户间点对点交易非对称纳什谈判模型[J]. 现代电力, 2025, 42 (2): 333- 342.
|
|
CHEN Yuja, PEI Wei, MA Tengfei, et al. Asymmetric nash bargaining model for P2P transactions between distributed generation and consumers considering conditional value-at-risk[J]. Modern Electric Power, 2025, 42 (2): 333- 342.
|
| 9 |
李军徽, 张靖祥, 穆钢, 等. 辅助服务市场下独立储能调峰调频协同优化调度[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025, 45 (2): 650- 665.
|
|
LI Junhui, ZHANG Jingxiang, MU Gang, et al. Collaborative optimal dispatch of peak shaving and frequency modulation with independent energy storage based on auxiliary service market[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025, 45 (2): 650- 665.
|
| 10 |
郁海彬, 董帅, 陆增洁, 等. 新型电力系统下储能参与电力调峰调频辅助市场的竞标策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (8): 48- 60.
|
|
YU Haibin, DONG Shuai, LU Zengjie, et al. Bidding strategy of energy storage participating in the auxiliary market of peak and frequency modulation in new power system[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (8): 48- 60.
|
| 11 |
李国庆, 闫克非, 范高锋, 等. 储能参与现货电能量-调频辅助服务市场的交易决策研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (17): 45- 54.
|
|
LI Guoqing, YAN Kefei, FAN Gaofeng, et al. Transaction decision-making of energy storage stations participating in the spot energy and frequency modulation ancillary service market[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (17): 45- 54.
|
| 12 |
程杉, 李沣洋, 刘炜炜, 等. 电动汽车协助火电机组参与调频辅助服务优化控制策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (6): 142- 151.
|
|
CHENG Shan, LI Fengyang, LIU Weiwei, et al. Optimal control strategy of thermal power units with electric vehicles participating in frequency regulation auxiliary services[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (6): 142- 151.
|
| 13 |
侯慧, 何梓姻, 罗超, 等. 计及需求响应潜力的电动汽车聚合商多主体日前投标策略[J]. 全球能源互联网, 2024, 7 (2): 220- 227.
|
|
HOU Hui, HE Ziyin, LUO Chao, et al. Multi-agent day-ahead bidding strategy of electric vehicle aggregators upon demand response potential[J]. Journal of Global Energy Interconnection, 2024, 7 (2): 220- 227.
|
| 14 |
姜涛, 吴成昊, 李雪, 等. 考虑电动汽车充放电的输配协同能量-灵活性市场出清机制[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (7): 210- 224.
|
|
JIANG Tao, WU Chenghao, LI Xue, et al. Clearing mechanism of energy and flexibility markets with transmission and distribution coordination considering charging and discharging of electric vehicles[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (7): 210- 224.
|
| 15 |
邓衍辉, 李剑, 卢国强, 等. 考虑分区域动态电价机制引导的电动汽车充电优化策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (7): 33- 44.
|
|
DENG Yanhui, LI Jian, LU Guoqiang, et al. Charging optimization strategy of electric vehicles guided by the dynamic tariff mechanism of a subregion[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (7): 33- 44.
|
| 16 |
曾凯林. 负荷聚合商的负荷削减投标与零售合约定价策略研究[D]. 华南理工大学, 2022.
|
|
ZENG Kailin. Research on load reduction bidding and retail contract pricing strategy of load aggregators[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2022.
|
| 17 |
赵先海, 刘晓峰, 季振亚, 等. 考虑居民用户动态行为的负荷聚合商决策分析[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (10): 179- 189.
|
|
ZHAO Xianhai, LIU Xiaofeng, JI Zhenya, et al. Decision Analysis of Load Aggregator Considering Dynamic Behavior of Residential Users[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (10): 179- 189.
|
| 18 |
张凡, 高红均, 吴子豪, 等. 局域能源市场多产消者P2P交易框架设计[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2022, 42 (12): 17- 25.
|
|
ZHANG Fan, GAO Hongjun, WU Zihao, et al. Design of P2P trading framework for multiple prosumers in local energy market[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022, 42 (12): 17- 25.
|
| 19 |
张书涵, 艾芊, 李晓露, 等. 适用于多虚拟电厂交易的改进拜占庭容错算法共识机制[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (1): 71- 81, 157.
|
|
ZHANG Shuhan, AI Qian, LI Xiaoxia, et al. Robust simplified modeling of microgrid in the context of constructing new power systems[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (1): 71- 81, 157.
|
| 20 |
周玮, 党伟, 芝昕雨, 等. 基于灵活性资源调节和网络重构的P2P交易的阻塞管理方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (20): 83- 93.
|
|
ZHOU Wei, DANG Wei, ZHI Xinyu, et al. A congestion management approach for P2P transactions based on flexible resourceregulation and network reconfiguration[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (20): 83- 93.
|
| 21 |
李方姝, 余昆, 陈星莺, 等. 碳约束下基于双重博弈的电力零售商售电价格决策优化[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 ((5): 126- 136.
|
|
LI Fangshu, Yu Kun, CHEN Xingying, et al. Price Decision Optimization for Electricity Retailers Based on Dual Gameunder Carbon Constraints[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 ((5): 126- 136.
|
| 22 |
ŞENGÖR İ, ÇIÇEK A, KÜBRA ERENOĞLU A, et al. User-comfort oriented optimal bidding strategy of an electric vehicle aggregator in day-ahead and reserve markets[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2020, 122, 106194.
|
| 23 |
WEI C Y, WU Q W, XU J, et al. Bi-level retail pricing scheme considering price-based demand response of multi-energy buildings[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2022, 139, 108007.
|
| 24 |
刘杨, 刘天羽. 含电动汽车和热电联产的区域微电网参与电网辅助服务调度[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2024, 41 (4): 67- 72, 105.
|
|
LIU Yang, LIU Tianyu. Regional microgrids including electric vehicles and cogeneration participate in grid auxiliary service dispatch[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2024, 41 (4): 67- 72, 105.
|
| 25 |
周挺, 谭玉东, 孙晋, 等. 虚拟电厂参与能量与辅助服务市场的协同优化策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (1): 61- 70.
|
|
ZHOU Ting, TAN Yudong, SUN Jin, et al. Collaborative Optimization Strategy for Virtual Power Plant Participating inEnergy and Ancillary Service Market[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (1): 61- 70.
|
| 26 |
王俊, 徐箭, 王晶晶, 等. 基于条件风险价值的虚拟电厂参与能量及备用市场的双层随机优化[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 ((6): 2502- 2510.
|
|
WANG Jun, XU Jian, WANG Jingjing, et al. Bi-level stochastic optimization for a virtual power plant participating in energy and reserve market based on conditional value at risk[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 ((6): 2502- 2510.
|
| 27 |
李媛媛, 刘飞, 张鑫, 等. 考虑光热虚拟电厂参与的能量-辅助服务市场日前竞价策略[J]. 现代电力, 2024, 41 ((6): 1156- 1166.
|
|
LI Yuanyuan, LIU Fei, ZHANG Xin, et al. A day-ahead bidding strategy of the energy-auxiliary service market considering the participation of photothermal virtual power plants[J]. Modern Electric Power, 2024, 41 ((6): 1156- 1166.
|
| 28 |
KARIMI H, JADID S. A strategy-based coalition formation model for hybrid wind/PV/FC/MT/DG/battery multi-microgrid systems considering demand response programs[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2022, 136, 107642.
|
| 29 |
BAHRAMARA S, YAZDANI-DAMAVANDI M, CONTRERAS J, et al. Modeling the strategic behavior of a distribution company in wholesale energy and reserve markets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9 (4): 3857- 3870.
|