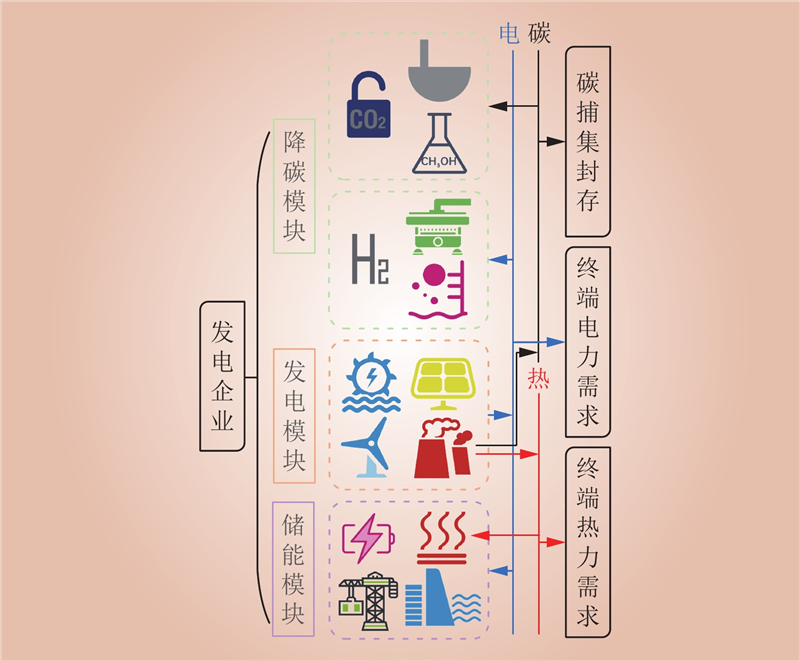
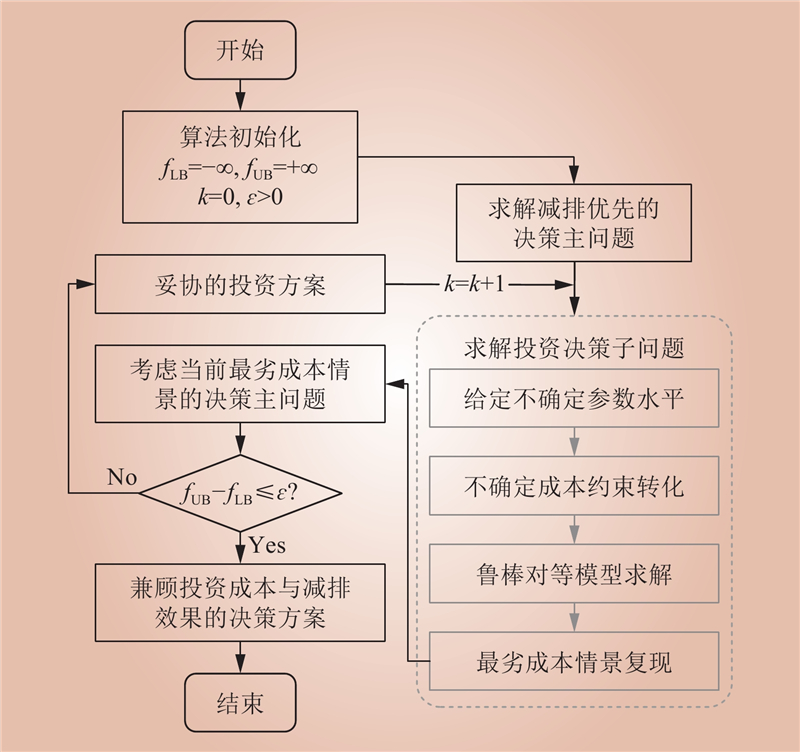
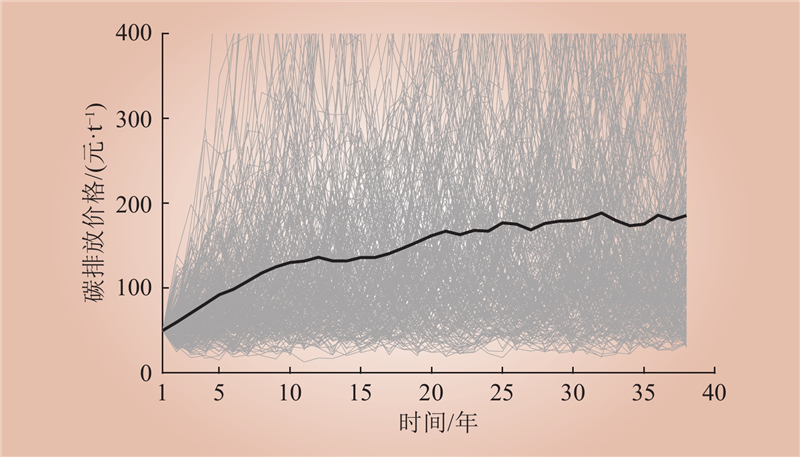
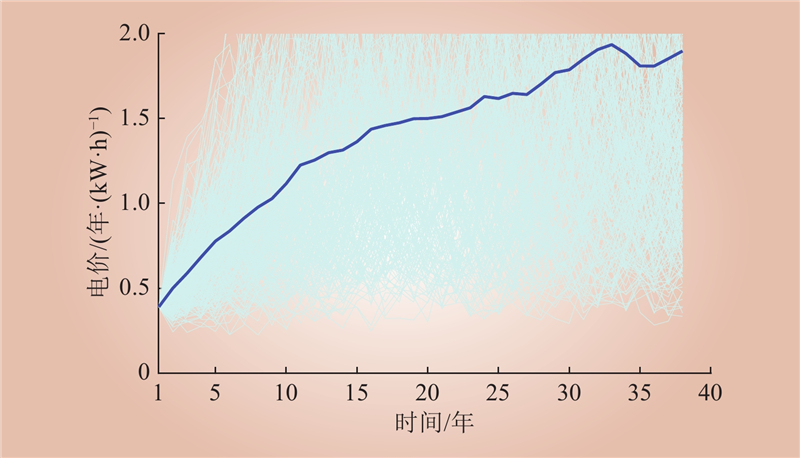
| 1 |
中国碳核算数据库. 新兴经济体二氧化碳排放报告2022[R]. 2022.
|
| 2 |
LIU Y, XU L, SUN H P, et al. Optimization of carbon performance evaluation and its application to strategy decision for investment of green technology innovation[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 325, 116593.
|
| 3 |
刘朝蓬, 王海云, 王维庆, 等. 基于多运行场景与富氧燃烧捕集技术的低碳能源系统容量优化配置[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (23): 115- 129.
|
|
LIU Zhaopeng, WANG Haiyun, WANG Weiqing, et al. Capacity optimization of low carbon energy systems based on multiple operating scenarios and oxygen-enriched combustion capture technology[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (23): 115- 129.
|
| 4 |
张文伟, 王维庆, 樊小朝, 等. 利用风电制氧的富氧燃煤电厂低碳能源系统容量优化配置[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (5): 70- 83.
|
|
ZHANG Wenwei, WANG Weiqing, FAN Xiaochao, et al. Optimal capacity configuration of a low carbon energy system of oxygen-enriched coal-firedpower plant using wind power to produce oxygen[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (5): 70- 83.
|
| 5 |
杨丰任, 王鸿, 王致杰. 基于碳排放生产优先级的综合能源虚拟电厂优化运行策略[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2024, 39 (5): 192- 202.
|
|
YANG Fengren, WANG Hong, WANG Zhijie. Optimal operation strategy of integrated energy virtual power plant based on production priority of carbon emission[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2024, 39 (5): 192- 202.
|
| 6 |
胡康, 徐飞, 陈磊, 等. 利用相变储热提升电力系统可再生能源消纳[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2018, 39 (1): 1- 7.
|
|
HU Kang, XU Fei, CHEN Lei, et al. Improve the integration of renewable energy sources into power system by the usage of phase-change heat storage[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2018, 39 (1): 1- 7.
|
| 7 |
刘雨佳, 樊艳芳, 郝俊伟, 等. 基于碱性电解槽宽功率适应模型的风光氢热虚拟电厂容量配置与调度优化[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (10): 48- 60.
|
|
LIU Yujia, FAN Yanfang, HAO Junwei, et al. Capacity configuration and optimal scheduling of a wind-photovoltaic-hydrogen-thermal virtual power plant based on a wide range power adaptation strategy for an alkaline electrolyzer[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (10): 48- 60.
|
| 8 |
张俊涛, 程春田, 于申, 等. 水电支撑新型电力系统灵活性研究进展、挑战与展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (10): 3862- 3885.
|
|
ZHANG Juntao, CHENG Chuntian, YU Shen, et al. Progress, challenges and prospects of research on hydropower supporting the flexibility of new power systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (10): 3862- 3885.
|
| 9 |
顾永正. 煤基能源碳捕集利用与封存技术研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2023, 43 (9): 38- 41, 46.
|
|
GU Yongzheng. Research progress on carbon dioxide capture, utilization and storage technology for coal-based energy industry[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2023, 43 (9): 38- 41, 46.
|
| 10 |
ZHANG Y Z, ZHANG X P, LAN L H. Robust optimization-based dynamic power generation mix evolution under the carbon-neutral target[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2022, 178, 106103.
|
| 11 |
袁铁江, 孙传帅, 谭捷, 等. 考虑氢负荷的新型电力系统电源规划[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (17): 6316- 6326.
|
|
YUAN Tiejiang, SUN Chuanshuai, TAN Jie, et al. Generation planning of new power system considering hydrogen load[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (17): 6316- 6326.
|
| 12 |
黄远明, 张玉欣, 夏赞阳, 等. 考虑需求响应资源和储能容量价值的新型电力系统电源规划方法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023, 57 (4): 432- 441.
|
|
HUANG Yuanming, ZHANG Yuxin, XIA Zanyang, et al. Power system planning considering demand response resources and capacity value of energy storage[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2023, 57 (4): 432- 441.
|
| 13 |
王斯娴, 刘文霞, 王丽娜, 等. 容量电价与风光火配比相协调的电源规划[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (8): 3217- 3229.
|
|
WANG Sixian, LIU Wenxia, WANG Lina, et al. Generation expansion planning based on coordination of capacity prices and wind, solar and fire ratios[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (8): 3217- 3229.
|
| 14 |
ZHANG X Y, HUANG G H, XIE Y L, et al. A coupled non-deterministic optimization and mixed-level factorial analysis model for power generation expansion planning–A case study of Jing-Jin-Ji metropolitan region, China[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 311, 118621.
|
| 15 |
周健, 冯楠, 季怡萍, 等. 考虑源网协同支撑作用的含新能源电力系统网架重构决策优化方法[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (10): 150- 157.
|
|
ZHOU Jian, FENG Nan, JI Yiping, et al. A decision-making optimization method for network reconfiguration of power system with new energy considering the synergistic support of source-grid[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (10): 150- 157.
|
| 16 |
李超英, 檀勤良. 基于智能体建模的新型电力系统下火电企业市场交易策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (2): 212- 225.
|
|
LI Chaoying, TAN Qinliang. Market trading strategy for thermal power enterprise in new power system based on agent modeling[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (2): 212- 225.
|
| 17 |
钟志鸣, 李星梅. 燃煤机组退役与技术升级的减排及经济效益研究: 基于鲁棒电源规划的方法[J]. 中国管理科学, 2021, 29 (4): 16- 25.
|
|
ZHONG Zhiming, LI Xingmei. Study on emission reduction and economic benefits of the retirement and technology upgrade of coal-fired units: a robust generation expansion planning approach[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2021, 29 (4): 16- 25.
|
| 18 |
姚力, 郑海峰, 单葆国, 等. 基于数据驱动机会约束的发电企业电煤采购及库存优化模型[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (6): 176- 184.
|
|
YAO Li, ZHENG Haifeng, SHAN Baoguo, et al. An optimization coal procurement and inventory model for power generation enterprises based on data-driven chance constraints[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (6): 176- 184.
|
| 19 |
聂鹏飞, 高哲远, 王喜平. 不同商业模式下燃煤电厂CCUS投资决策研究[J]. 热力发电, 2023, 52 (4): 63- 71.
|
|
NIE Pengfei, GAO Zheyuan, WANG Xiping. Research on CCUS investment decision of coal-fired power plant under different business modes[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2023, 52 (4): 63- 71.
|
| 20 |
王喜平, 高哲远. 基于实物期权的燃煤电厂CCUS投资决策研究[J/OL]. 洁净煤技术, 1–11[2025-01-09]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3676.TD.20230816.1054.002.html.
|
|
WANG Xiping, GAO Zheyuan. CCUS investment decisions and policy incentives for coal-fired power plants: based on different scenarios under an integrated mode[J/OL]. Clean Coal Technology, 1–11[2025-01-09]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3676.TD.20230816.1054.002.html.
|
| 21 |
LIU J F, ZHANG Q, LI H L, et al. Investment decision on carbon capture and utilization (CCU) technologies: a real option model based on technology learning effect[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 322, 119514.
|
| 22 |
丁志刚, 陈涵, 徐琪. 碳交易与碳税双重风险下供应链低碳技术采纳时机决策研究[J]. 软科学, 2020, 34 (7): 101- 107.
|
|
DING Zhigang, CHEN Han, XU Qi. Research on decision-making of low-carbon technology adoption timing in supply chain under the dual risk of carbon trading and carbon tax[J]. Soft Science, 2020, 34 (7): 101- 107.
|
| 23 |
YIN S F, WANG J H. Generation and transmission expansion planning towards a 100% renewable future[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 37(4): 3274–3285.
|
| 24 |
ZHU L, FAN Y. A real options–based CCS investment evaluation model: Case study of China's power generation sector[J]. Applied Energy, 2011, 88 (12): 4320- 4333.
|
| 25 |
何永贵, 韦淑敏, 何宸. 光储电站发电平价上网问题研究[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2019, 31 (3): 113- 121.
|
|
HE Yonggui, WEI Shumin, HE Chen. Research on gird parity of photovoltaic power station with energy storage system[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2019, 31 (3): 113- 121.
|
| 26 |
周祎, 顾阿伦. 中国风力发电成本下降和减排碳价分析[J]. 可再生能源, 2019, 37 (7): 1084- 1090.
|
|
ZHOU Yi, GU Alun. Analysis of cost reduction and abatement carbon price of wind power in China[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2019, 37 (7): 1084- 1090.
|
| 27 |
NREL. 2022 Electricity ATB Technologies and Data Overview[Z]. 2023.
|
| 28 |
BERTSIMAS D, SIM M. The price of robustness[J]. Operations Research, 2004, 52 (1): 35- 53.
|
| 29 |
ZENG B, ZHAO L. Solving two-stage robust optimization problems using a column-and-constraint generation method[J]. Operations Research Letters, 2013, 41 (5): 457- 461.
|
| 30 |
国家发展改革委办公厅. 国家发展改革委办公厅关于印发首批10个行业企业温室气体排放核算方法与报告指南(试行)的通知(发改办气候[2013]2526号)[Z]. 2013.
|