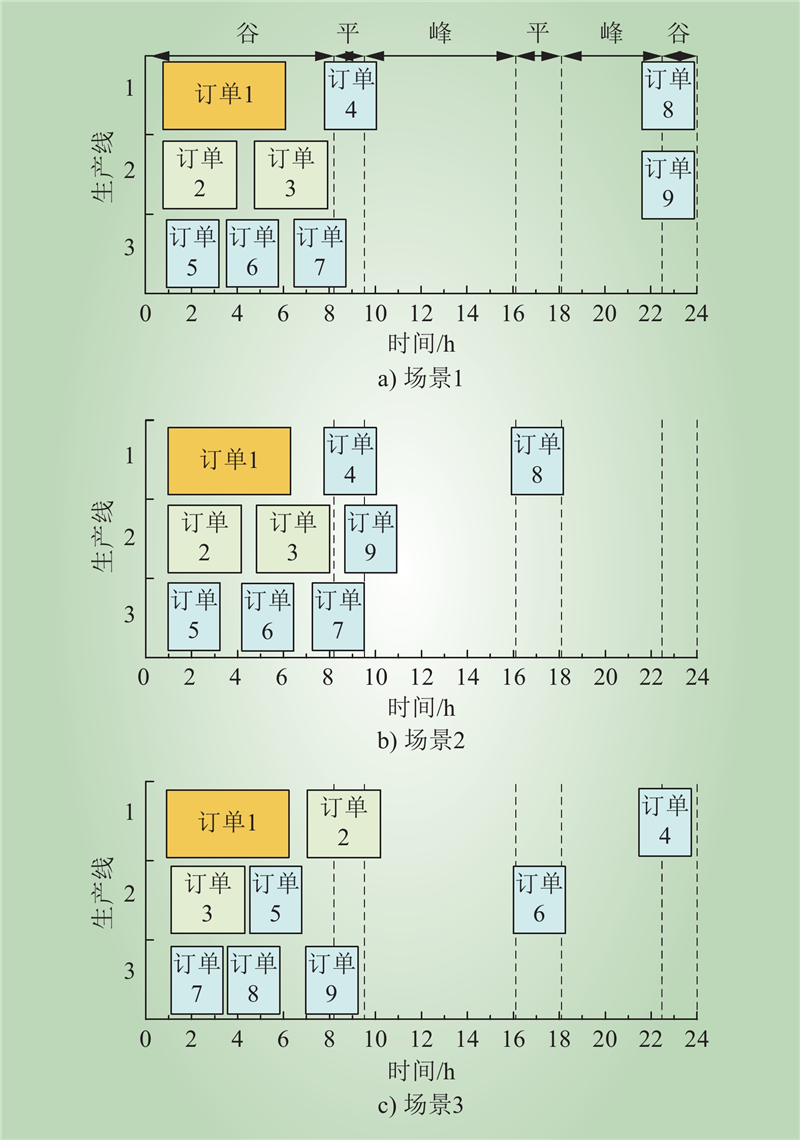
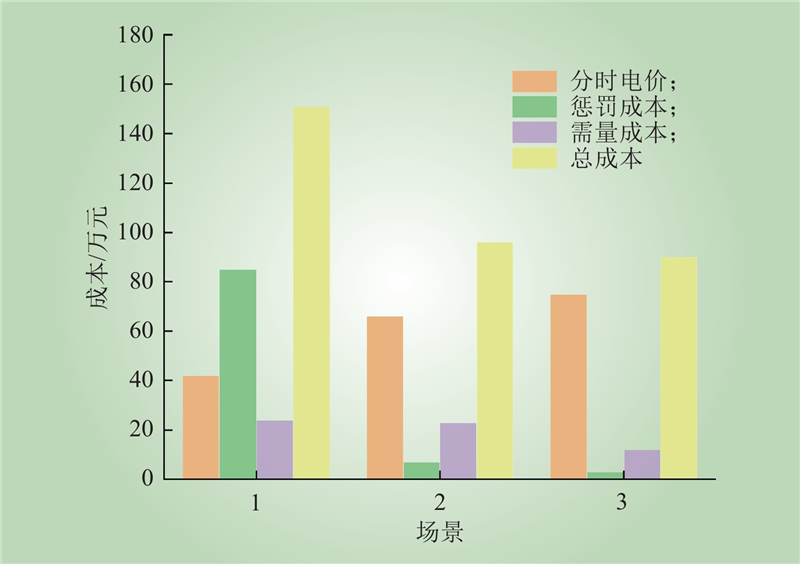
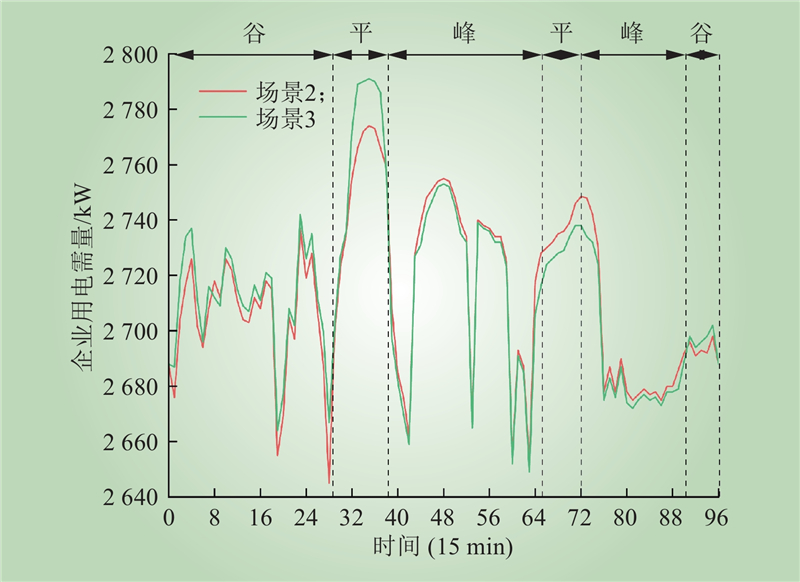
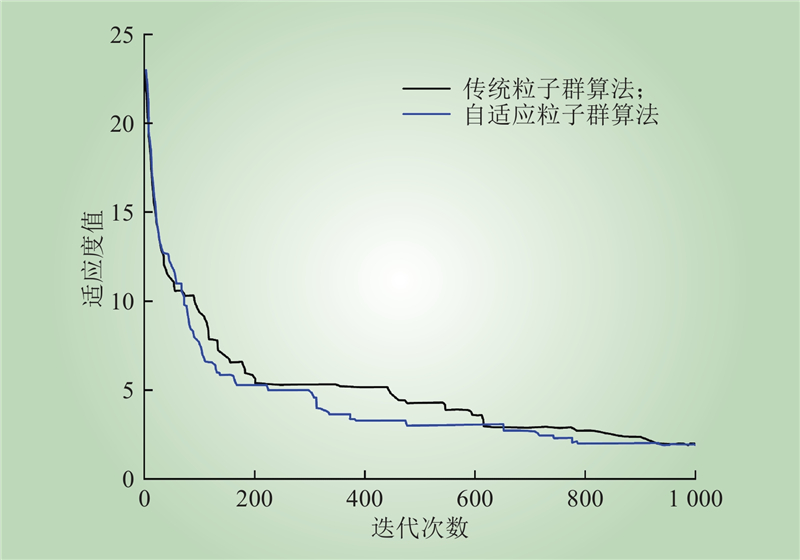
| 1 |
孙浩男, 杜鹏, 刘念, 等. 大规模风光储场站群功率跟踪优化控制实时仿真[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (8): 62- 74.
|
|
SUN Haonan, DU Peng, LIU Nian, et al. Real-time simulation of optimal power tracking control for large-scale wind-photovoltaic-storage power station clusters[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (8): 62- 74.
|
| 2 |
梁珩, 黄耕, 侯宾, 等. 工业用户连续参与需求响应的用户基线负荷精准计算方法[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (3): 34- 42.
|
|
LIANG Heng, HUANG Geng, HOU Bin, et al. Accurate estimation method of customer baseline load for continuous participation of industrial users in demand response[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (3): 34- 42.
|
| 3 |
刘晓琳, 王兆杰, 高峰, 等. 分时电价下的高耗能企业发用电响应[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2014, 38 (8): 41- 49.
|
|
LIU Xiaolin, WANG Zhaojie, GAO Feng, et al. Response behaviors of power generation and consumption in energy intensive enterprise under time-of-use price[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2014, 38 (8): 41- 49.
|
| 4 |
黄蔚亮, 苏志鹏, 梁欣怡, 等. 考虑可调市场和外部需求响应的虚拟电厂优化运行策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 156- 163.
|
|
HUANG Weiliang, SU Zhipeng, LIANG Xinyi, et al. Optimal operation strategy for virtual power plant considering regulation market and external demand response[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 156- 163.
|
| 5 |
CHEN R Z, SUN H B, GUO Q L, et al. Profit-seeking energy-intensive enterprises participating in power system scheduling: Model and mechanism[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 158, 263- 274.
|
| 6 |
ORCAJO G A, DIEZ J R, CANO J M, et al. Coordinated management of electrical energy in a steelworks and a wind farm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2022, 58 (4): 5488- 5502.
|
| 7 |
GAJIC D, HADERA H, ONOFRI L, et al. Implementation of an integrated production and electricity optimization system in melt shop[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 155, 39- 46.
|
| 8 |
KONG M, PEI J, XU J, et al. A robust optimization approach for integrated steel production and batch delivery scheduling with uncertain rolling times and deterioration effect[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2020, 58 (17): 5132- 5154.
|
| 9 |
刘树, 王元超, 石山, 等. 大型工业企业生产负荷平抑优化策略[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2017, 29 (10): 138- 144.
|
|
LIU Shu, WANG Yuanchao, SHI Shan, et al. Optimization strategy of production load leveling for large industrial enterprises[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2017, 29 (10): 138- 144.
|
| 10 |
DING Y M, HONG S H, LI X H. A demand response energy management scheme for industrial facilities in smart grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2014, 10 (4): 2257- 2269.
|
| 11 |
HUANG C, ZHANG H C, SONG Y H, et al. Demand response for industrial micro-grid considering photovoltaic power uncertainty and battery operational cost[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12 (4): 3043- 3055.
|
| 12 |
DALLE AVE G, HARJUNKOSKI I, ENGELL S. A non-uniform grid approach for scheduling considering electricity load tracking and future load prediction[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2019, 129, 106506.
|
| 13 |
DING Y M, HONG S H. A model of demand response energy management system in industrial facilities[C]//2013 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm). Vancouver, BC, Canada. IEEE, 2013: 241–246.
|
| 14 |
王卿然, 谢国辉, 张粒子. 含风电系统的发用电一体化调度模型[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2011, 35 (5): 15- 18, 30.
|
|
WANG Qingran, XIE Guohui, ZHANG Lizi. An integrated generation-consumption dispatch model with wind power[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2011, 35 (5): 15- 18, 30.
|
| 15 |
梁望, 钱斌, 胡蓉, 等. 两阶段智能优化算法求解紧凑型带钢生产热轧调度问题[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2025, 31 (1): 102- 116.
|
|
LIANG Wang, QIAN Bin, HU Rong, et al. Two stage bee colony algorithm for hot rolling scheduling problem in compact strip production[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2025, 31 (1): 102- 116.
|
| 16 |
KOWALSKI M, KUGI A, STEINBOECK A. Job scheduling for a multi-line steel hot rolling mill with selectable furnaces[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2023, 56 (2): 5376- 5381.
|
| 17 |
KOWALSKI M, STEINBOECK A, KUGI A. Scheduling multiple groups of jobs for a multi-line steel hot rolling mill[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2022, 55 (21): 168- 173.
|
| 18 |
TAN M, YANG H L, DUAN B, et al. Optimizing production scheduling of steel plate hot rolling for economic load dispatch under time-of-use electricity pricing[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2017, 2017 (1): 1048081.
|
| 19 |
HU Z B, HE D F, SONG W, et al. Model and algorithm for planning hot-rolled batch processing under time-of-use electricity pricing[J]. Processes, 2020, 8 (1): 42.
|
| 20 |
齐彩娟, 陈宝生, 韦冬妮, 等. 考虑主从博弈定价模式的共享储能分布鲁棒优化配置方法研究[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (7): 40- 53.
|
|
QI Caijuan, CHEN Baosheng, WEI Dongni, et al. Distributionally robust optimal configuration for shared energy storage based on Stackelberg game pricing model[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (7): 40- 53.
|
| 21 |
黄治宁. 面向订单的钢铁企业生产成本管理优化分析[J]. 冶金与材料, 2023, 15 (6): 142- 144.
|
| 22 |
杨益, 彭涛, 许娟, 等. 基于负荷曲线的最大需量估算方法研究[J]. 安徽电气工程职业技术学院学报, 2023, 28 (4): 33- 38.
|
|
YANG Yi, PENG Tao, XU Juan, et al. Research on estimation methods of maximum demand based on load curve[J]. Journal of Anhui Electrical Engineering Professional Technique College, 2023, 28 (4): 33- 38.
|
| 23 |
张鼎衢, 钱斌, 杨路, 等. 基于模型驱动的电力系统安全稳定分析与控制策略[J/OL]. 中国电力, 2024: 1–10. (2024-11-08). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ZGDL20241106003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ.
|
|
ZHANG Dingqu, QIAN Bin, YANG Lu, et al. Data driven analysis and control of power system security and stability[J/OL]. Electric Power, 2024: 1–10. (2024-11-08). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ZGDL20241106003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ.
|
| 24 |
束娜, 江山, 刘春伶, 等. 计及灵活性资源多时间尺度协调互济的电-气-热综合能源系统优化调度[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (12): 3- 15.
|
|
SHU Na, JIANG Shan, LIU Chunling, et al. Optimal scheduling of electricity-gas-heat integrated energy system with flexible resources in multiple time scales[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (12): 3- 15.
|