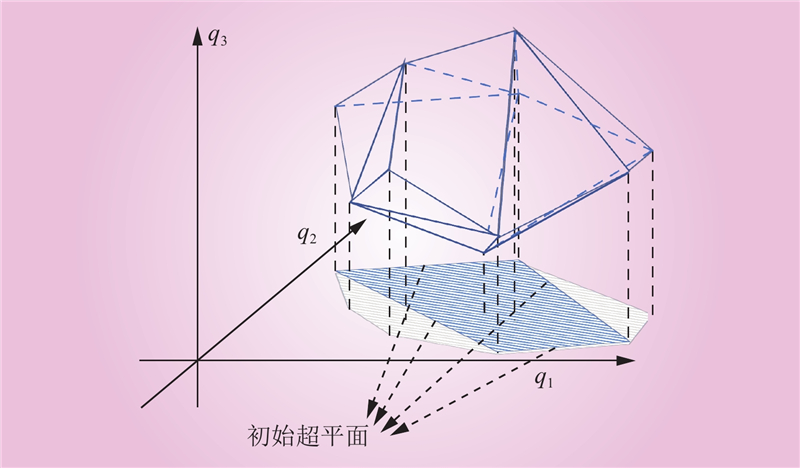
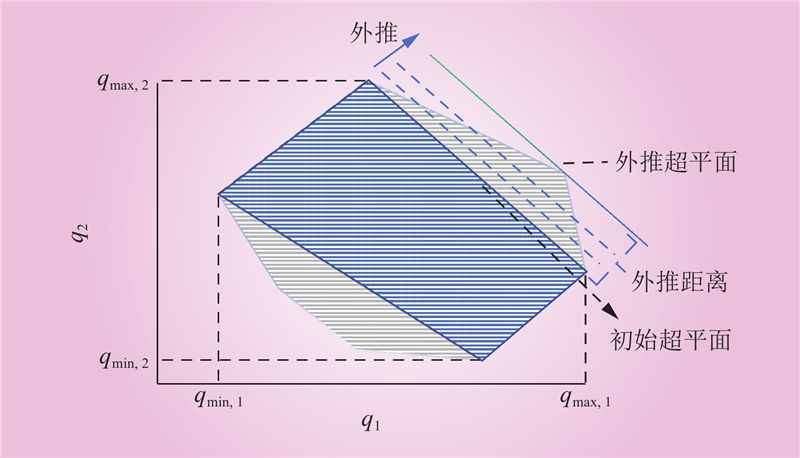
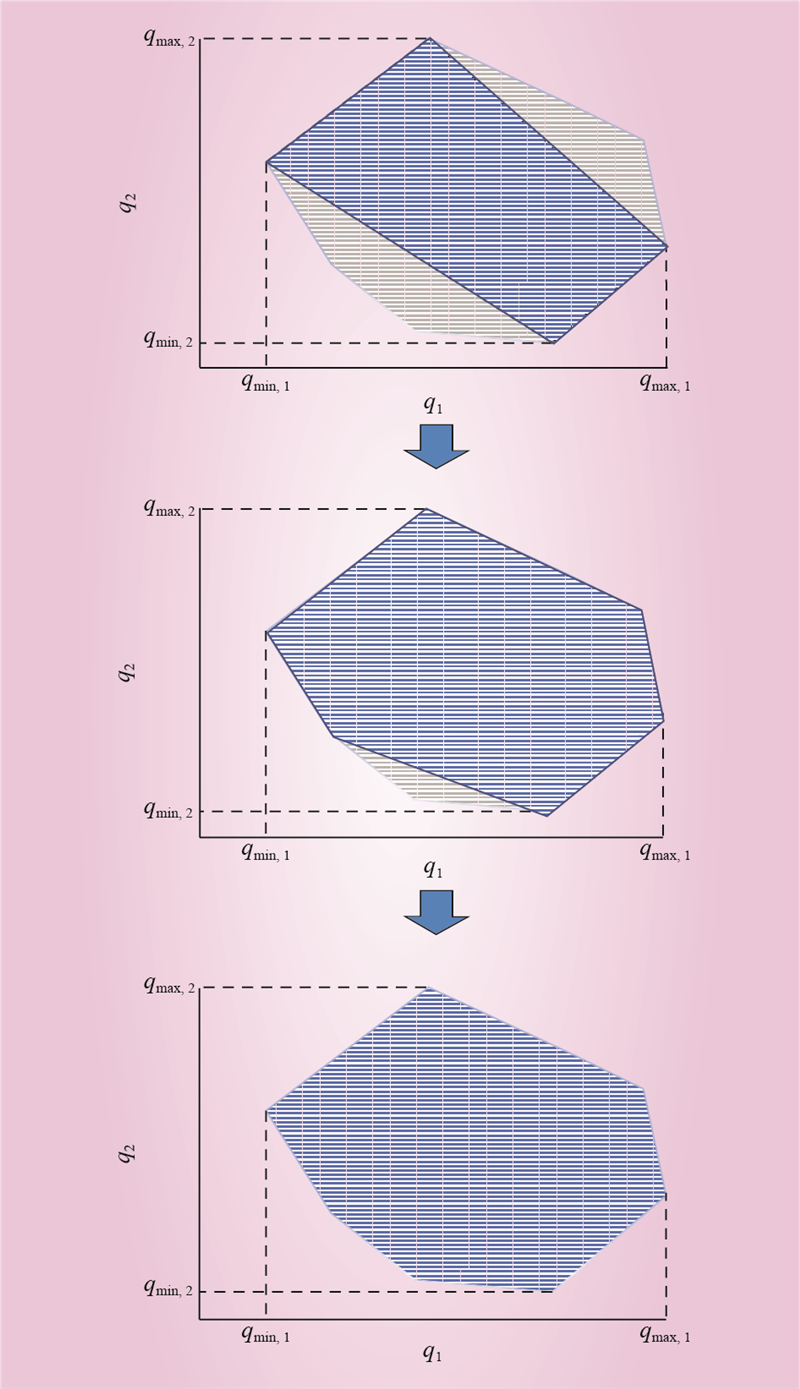
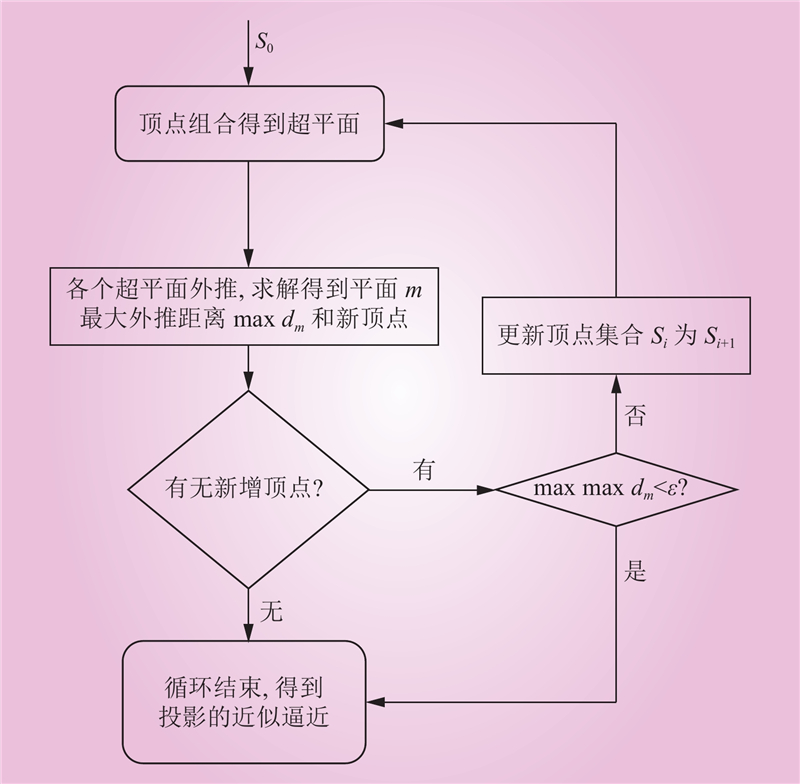
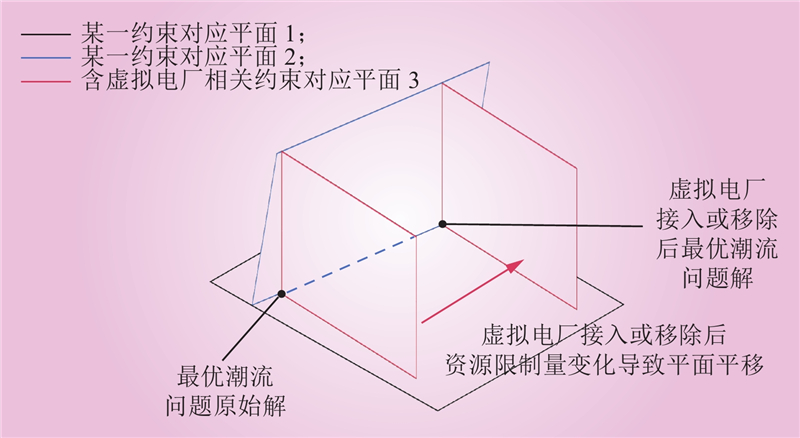
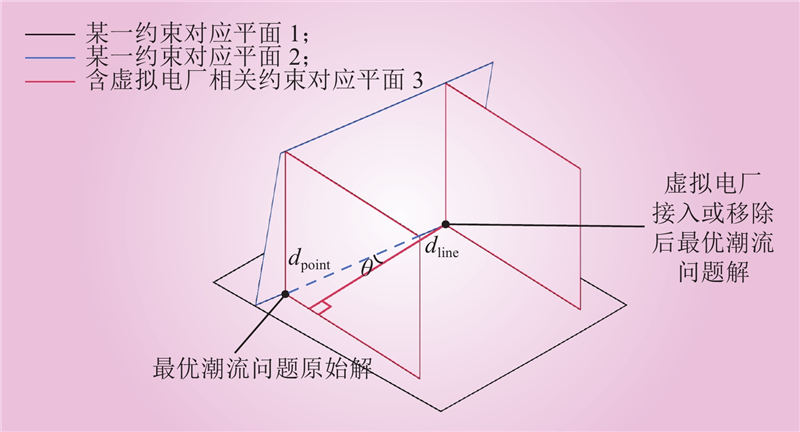
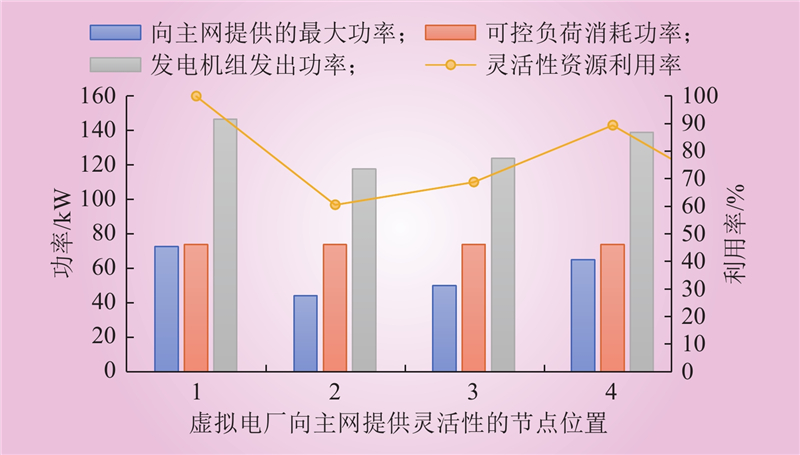
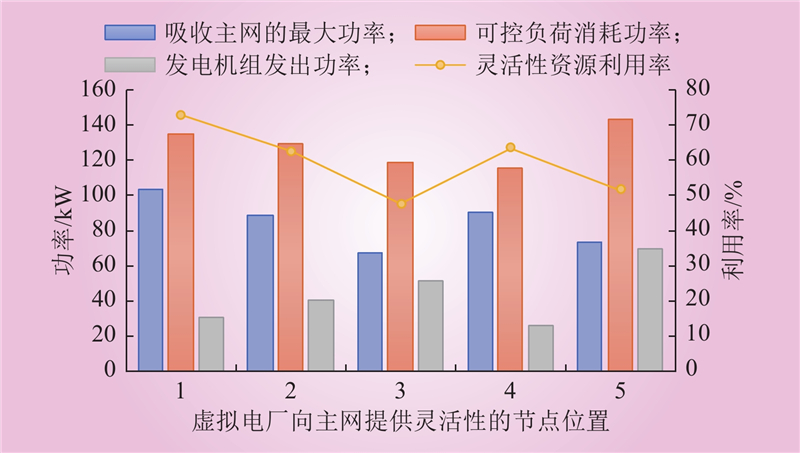
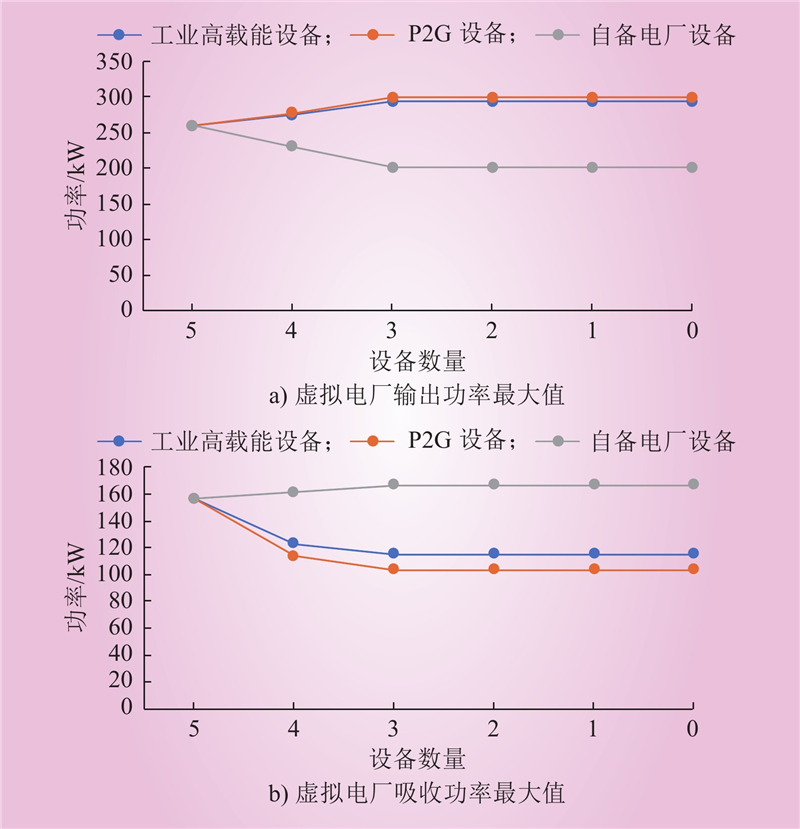
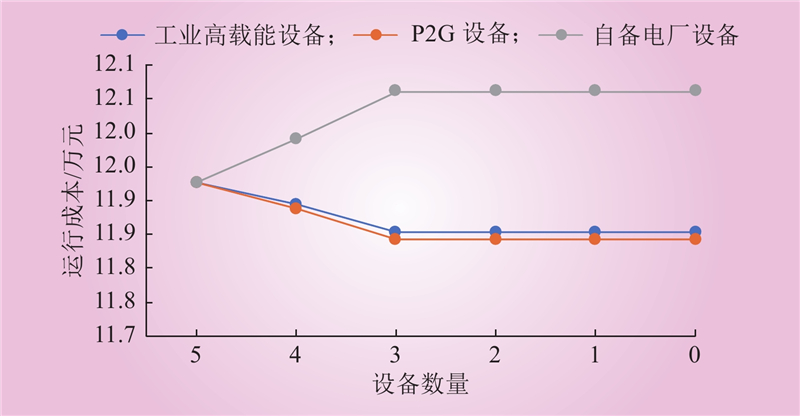
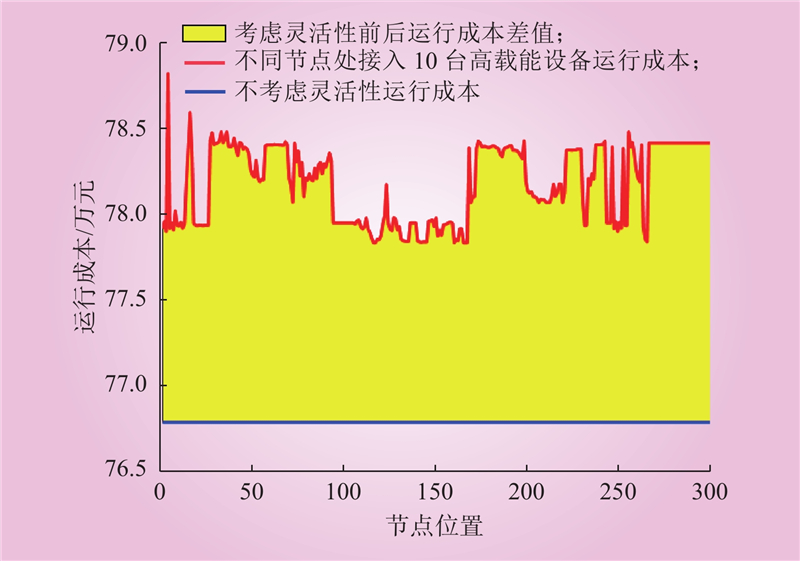
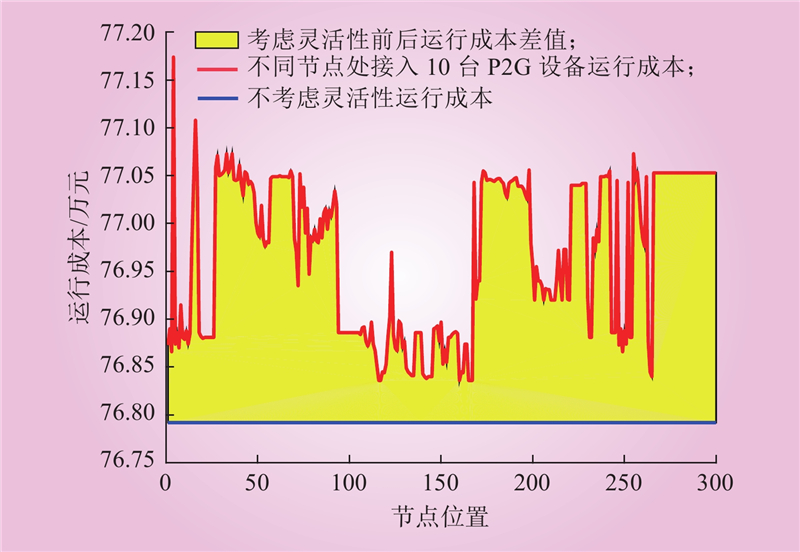
| 1 |
中共中央, 国务院. 关于完整准确全面贯彻新发展理念做好碳达峰碳中和工作的意见[EB/OL]. (2021-10-24)[2022-01-18]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-10/24/content_5644613.htm.
|
| 2 |
隋军, 金红光. 我国分布式供能关键技术研究进展[J]. 发电与空调, 2012, 33 (4): 1- 4.
|
|
SUI Jun, JIN Hongguang. Research and development on key technologies of distributed energy system in China[J]. Power Generation & Air Condition, 2012, 33 (4): 1- 4.
|
| 3 |
张燕, 乔松博, 徐奇锋, 等. 基于纳什议价理论的分布式绿色电力交易优化分析[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (12): 168- 178.
|
|
ZHANG Yan, QIAO Songbo, XU Qifeng, et al. Analysis of distributed green power transaction optimization based on Nash bargaining theory[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (12): 168- 178.
|
| 4 |
孙秋野, 滕菲, 张化光, 等. 能源互联网动态协调优化控制体系构建[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35 (14): 3667- 3677.
|
|
SUN Qiuye, TENG Fei, ZHANG Huaguang, et al. Construction of dynamic coordinated optimization control system for energy Internet[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35 (14): 3667- 3677.
|
| 5 |
白雪岩, 樊艳芳, 刘雨佳, 等. 考虑可靠性及灵活性的风光储虚拟电厂分层容量配置[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (8): 11- 24.
|
|
BAI Xueyan, FAN Yanfang, LIU Yujia, et al. Wind power storage virtual power plant considering reliability and flexibility tiered capacity configuration[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (8): 11- 24.
|
| 6 |
Draft document-virtual power plants: IEC 63189-DRAFT[S]. Germany: DE-DIN, 2021.
|
| 7 |
孙玲玲, 高赐威, 谈健, 等. 负荷聚合技术及其应用[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41 (6): 159- 167.
|
|
SUN Lingling, GAO Ciwei, TAN Jian, et al. Load aggregation technology and its applications[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41 (6): 159- 167.
|
| 8 |
刘向向, 张森林, 朱思乔, 等. 基于灰靶理论和谱聚类的虚拟电厂多形态柔性资源聚合模型[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (11): 104- 112.
|
|
LIU Xiangxiang, ZHANG Senlin, ZHU Siqiao, et al. Multi-form flexible resource aggregation model for virtual power plant based on grey target theory and spectral clustering[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (11): 104- 112.
|
| 9 |
姜华, 杨知方, 林伟, 等. 计及分布式新能源不确定性的虚拟电厂调度边界概率分布刻画方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (15): 5565- 5576.
|
|
JIANG Hua, YANG Zhifang, LIN Wei, et al. Probability distribution of dispatch region for a virtual power plant considering distributed renewable uncertainties[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (15): 5565- 5576.
|
| 10 |
李国庆, 王成山, 余贻鑫. 大型互联电力系统区域间功率交换能力研究综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2001, 21 (4): 20- 25.
|
|
LI Guoqing, WANG Chengshan, YU Yixin. A survey on transmission transfer capability of interconnected electric power systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2001, 21 (4): 20- 25.
|
| 11 |
TAN Z F, ZHONG H W, XIA Q, et al. Exploiting integrated flexibility from a local smart energy hub[C]//2020 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM). Montreal, QC, Canada. IEEE, 2020.
|
| 12 |
LIU Y K, WU L, CHEN Y H, et al. Integrating high DER-penetrated distribution systems into ISO energy market clearing: a feasible region projection approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2021, 36 (3): 2262- 2272.
|
| 13 |
张林, 杨高峰, 汪洋, 等. 基于多参数规划理论的互联电网直流联络线功率可行域确定方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (19): 5763- 5771, 5904.
|
|
ZHANG Lin, YANG Gaofeng, WANG Yang, et al. Determination of the DC tie-line transfer capacity region of the interconnected power grid: a multi-parametric programming approach[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (19): 5763- 5771, 5904.
|
| 14 |
MARTEN F, LOWER L, TOBERMANN J C, et al. Optimizing the reactive power balance between a distribution and transmission grid through iteratively updated grid equivalents[C]//2014 Power Systems Computation Conference. Wroclaw, Poland. IEEE, 2014.
|
| 15 |
TAN Z F, ZHONG H W, WANG J X, et al. Enforcing intra-regional constraints in tie-line scheduling: a projection-based framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2019, 34 (6): 4751- 4761.
|
| 16 |
胡俊杰, 刘雪涛, 王程. 考虑网络约束的能量枢纽灵活性价值评估[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (5): 1799- 1813.
|
|
HU Junjie, LIU Xuetao, WANG Cheng. Value evaluation of energy hub flexibility considering network constraints[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (5): 1799- 1813.
|
| 17 |
王毅, 张宁, 康重庆. 能源互联网中能量枢纽的优化规划与运行研究综述及展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35 (22): 5669- 5681.
|
|
WANG Yi, ZHANG Ning, KANG Chongqing. Review and prospect of optimal planning and operation of energy hub in energy Internet[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35 (22): 5669- 5681.
|
| 18 |
贾宏杰, 王丹, 徐宪东, 等. 区域综合能源系统若干问题研究[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (7): 198- 207.
|
|
JIA Hongjie, WANG Dan, XU Xiandong, et al. Research on some key problems related to integrated energy systems[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (7): 198- 207.
|
| 19 |
边晓燕, 孙明琦, 董璐, 等. 计及灵活性聚合功率的源-荷分布式协调调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (17): 89- 98.
|
|
BIAN Xiaoyan, SUN Mingqi, DONG Lu, et al. Distributed source-load coordinated dispatching considering flexible aggregated power[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (17): 89- 98.
|