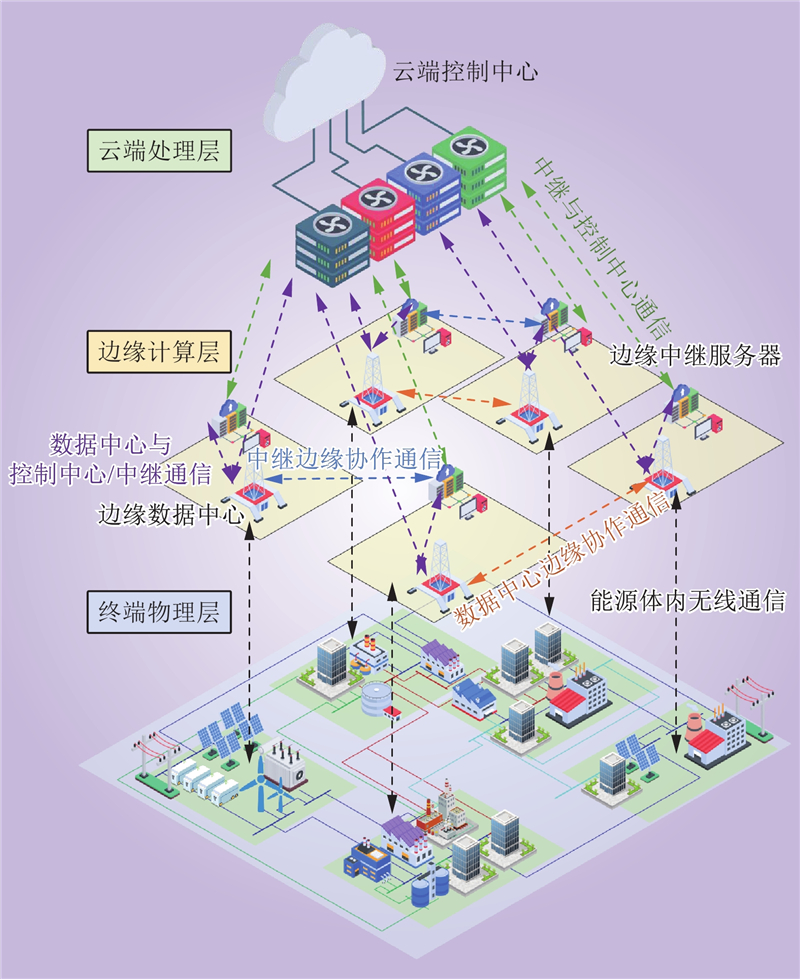
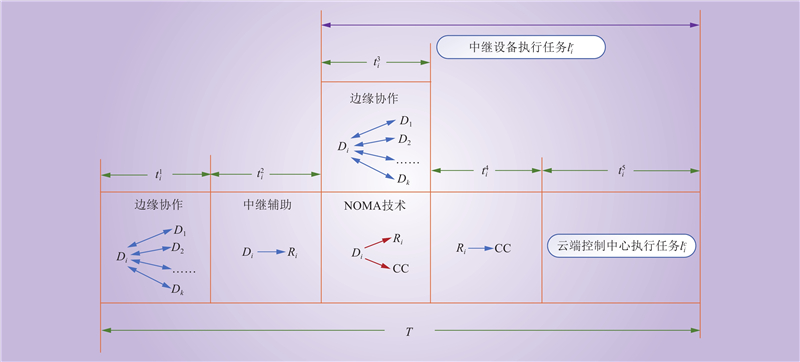
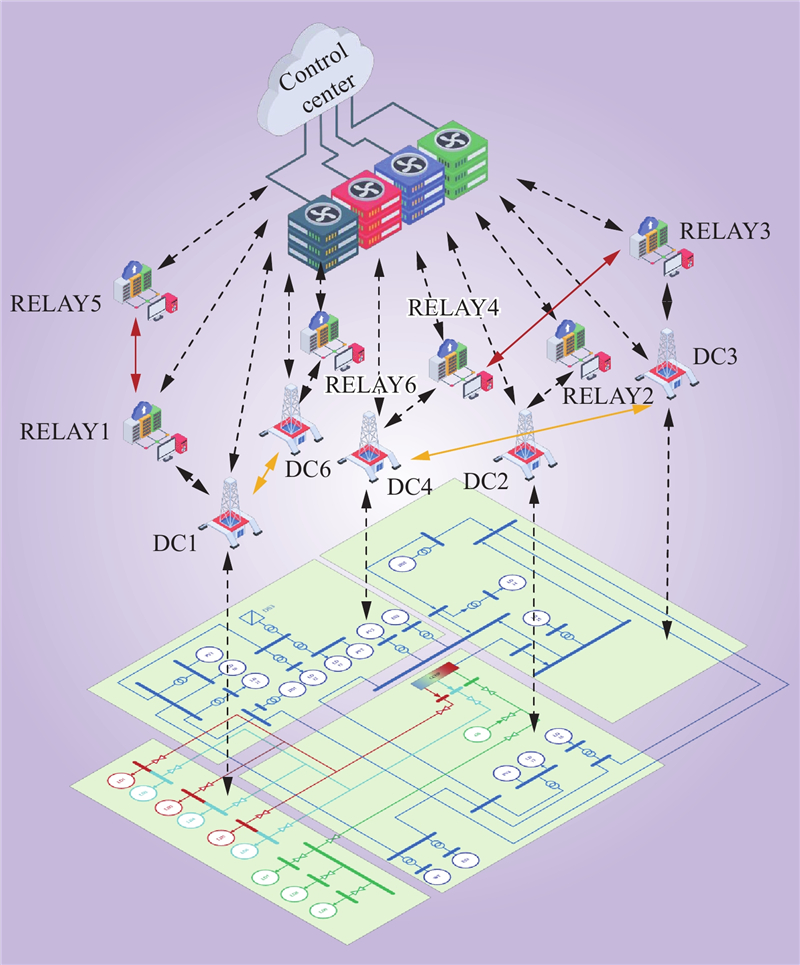
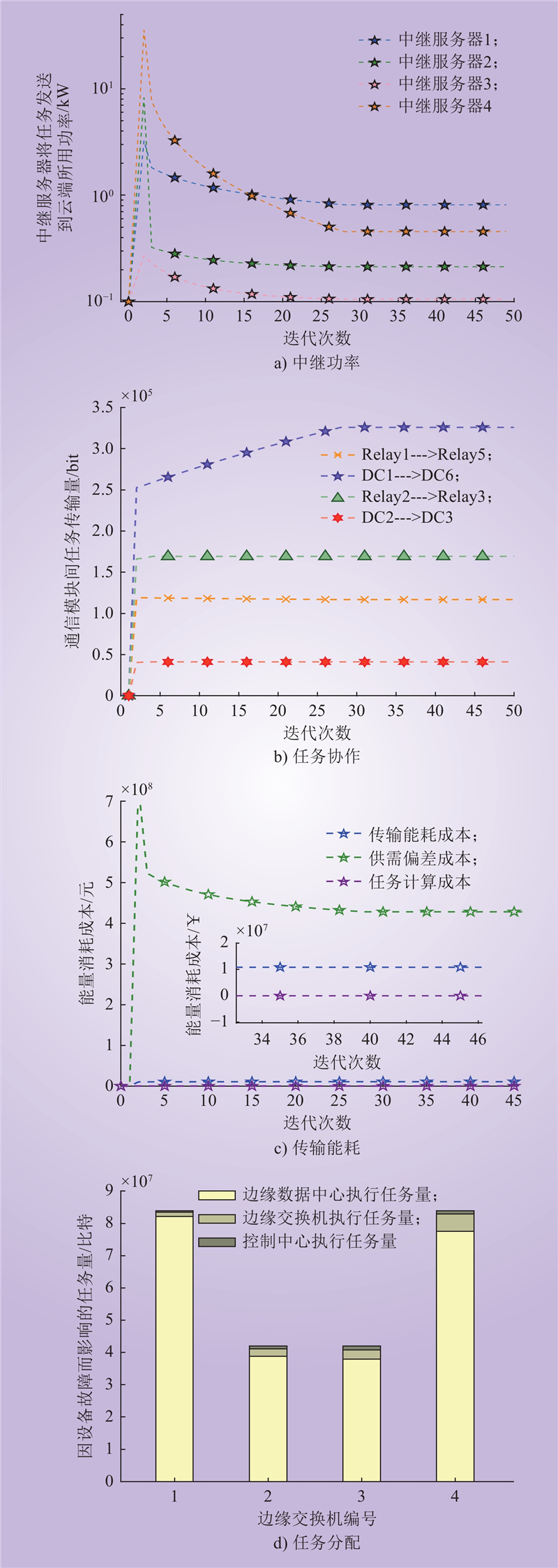
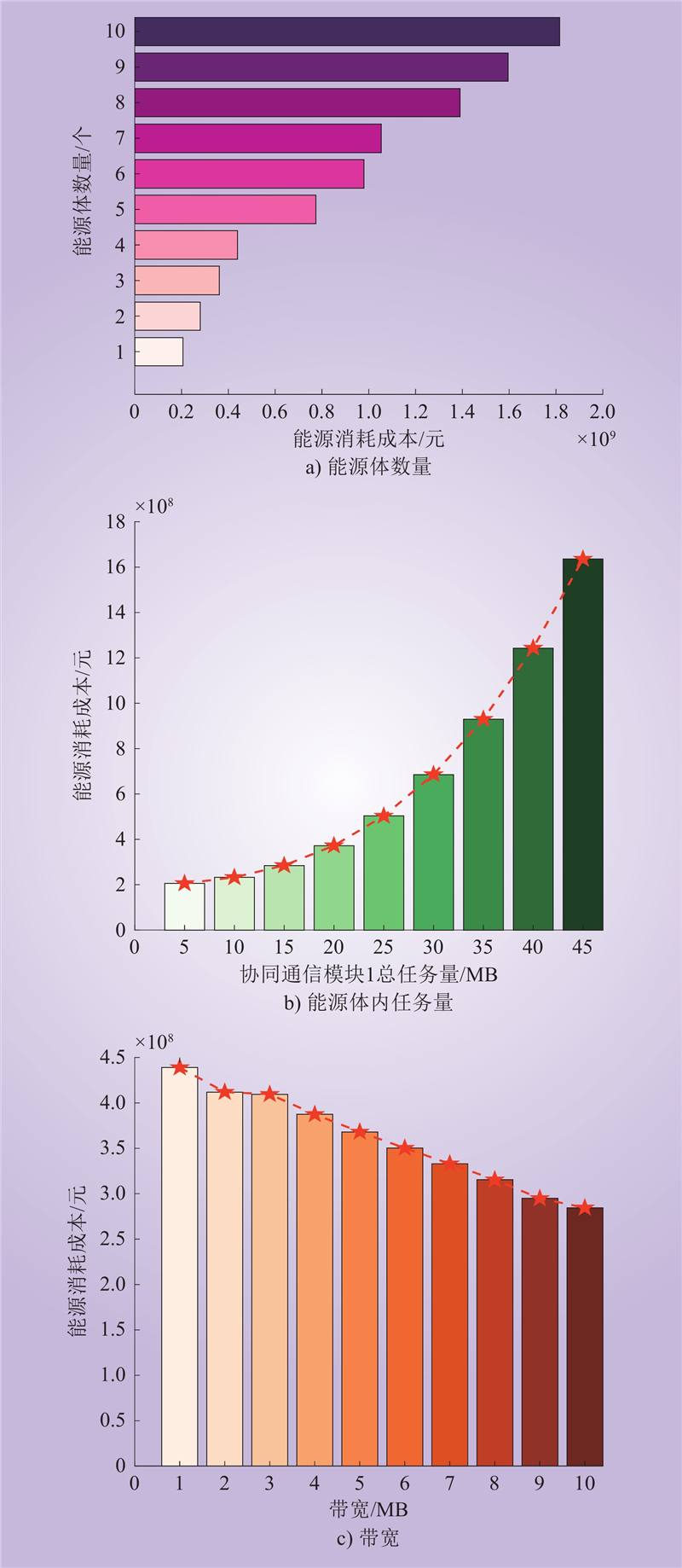
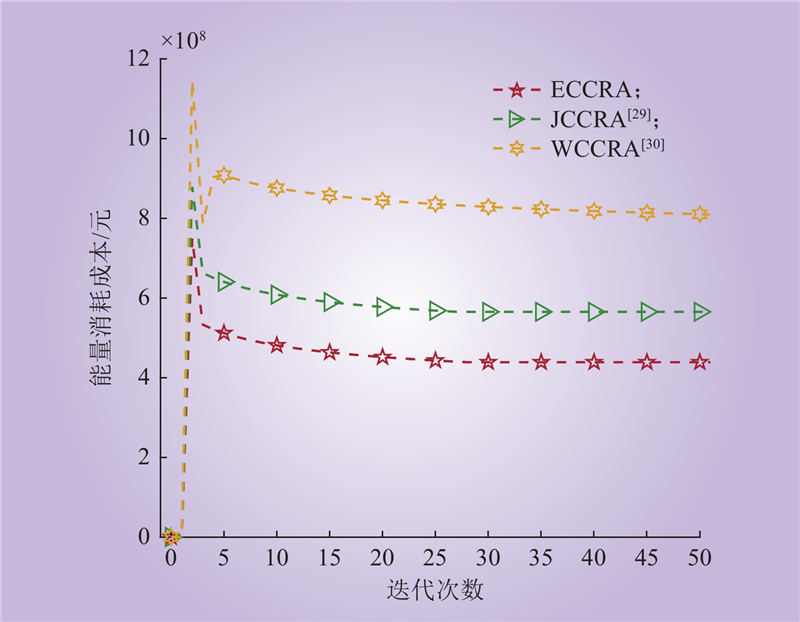
| 1 |
谭青博, 潘伟, 王竹宁, 等. 新型电力系统下综合能源系统的投资决策模型[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (8): 46- 52.
|
|
TAN Qingbo, PAN Wei, WANG Zhuning, et al. Investment decision model for comprehensive energy system under new power system[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (8): 46- 52.
|
| 2 |
张程, 曾崟琳, 匡宇. 考虑需求响应和碳捕集电厂灵活运行方式的综合能源系统调度[J]. 智慧电力, 2024, 52 (9): 88- 95.
|
|
ZHANG Cheng, ZENG Yinlin, KUANG Yu. Integrated energy system scheduling considering demand response and flexible operation of carbon capture power plant[J]. Smart Power, 2024, 52 (9): 88- 95.
|
| 3 |
康渭滨, 寇明鑫, 张文文, 等. 光伏储能电站不同储能形式经济性对比分析[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2024, 40 (3): 276- 285.
|
|
KANG Weibin, KOU Mingxin, ZHANG Wenwen, et al. Economic comparison analysis of different energy storage forms for photovoltaic energy storage power stations[J]. Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection, 2024, 40 (3): 276- 285.
|
| 4 |
吕昊, 何益鸣, 田浩, 等. 基于物联网的园区综合能源系统快速通信网络建模与仿真[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (5): 166- 173.
|
|
LV Hao, HE Yiming, TIAN Hao, et al. Modeling and simulation of fast communication network for park integrated energy system based on IoT[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (5): 166- 173.
|
| 5 |
孙秋野, 刘广亮, 王一帆. 能源互联网中能源终端的研究综述及展望[J]. 电网技术, 2025, 49 (5): 1792- 1805.
|
|
SUN Qiuye, LIU Guangliang, WANG Yifan. Review and prospect of energy terminal in energy Internet[J]. Power System Technology, 2025, 49 (5): 1792- 1805.
|
| 6 |
王杰, 郑飞, 张鹏城, 等. 基于数据驱动的高比例新能源配电网规划模型[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (3): 175- 182.
|
|
WANG Jie, ZHENG Fei, ZHANG Pengcheng, et al. Model of high-proportion new energy distribution network planning based on data-driven approach[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (3): 175- 182.
|
| 7 |
孙秋野, 于潇寒, 王靖傲. “双高”配电系统的挑战与应对措施探讨[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (18): 7115- 7136.
|
|
SUN Qiuye, YU Xiaohan, WANG Jing'ao. Discussion on challenges and countermeasures of "double high" power distribution system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (18): 7115- 7136.
|
| 8 |
陈智雄, 刘宗山, 金鑫, 等. 基于协作通信的电力线通信关键技术研究综述[J]. 电网技术, 2025, 49 (4): 1668- 1680.
|
|
CHEN Zhixiong, LIU Zongshan, JIN Xin, et al. Research review and prospect of power line communication technology based on collaborative communication[J]. Power System Technology, 2025, 49 (4): 1668- 1680.
|
| 9 |
仝杰, 齐子豪, 蒲天骄, 等. 电力物联网边缘智能: 概念、架构、技术及应用[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (14): 5473- 5496.
|
|
TONG Jie, QI Zihao, PU Tianjiao, et al. Edge intelligence to power Internet of Things: concept, architecture, technology and application[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (14): 5473- 5496.
|
| 10 |
王睿, 孙秋野, 张化光, 等. 基于信-能复合调制的多母线直流微电网电流边缘控制策略[J]. 控制与决策, 2023, 38 (10): 2783- 2794.
|
|
WANG Rui, SUN Qiuye, ZHANG Huaguang, et al. Current edge-control strategy of multi-bus DC microgrids based on information-energy dual modulation[J]. Control and Decision, 2023, 38 (10): 2783- 2794.
|
| 11 |
WANG R, LI J D, SUN Q Y, et al. Current edge-control strategy for multiple energy routers based on cyber-energy dual modulations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71 (4): 4079- 4088.
|
| 12 |
聂涌泉, 彭超逸, 胡亚平, 等. 基于边缘计算的高渗透率微电网并行分布式优化经济调度[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (1): 114- 124.
|
|
NIE Yongquan, PENG Chaoyi, HU Yaping, et al. Parallel distributed optimal economic dispatch of high penetration microgrid based on edge computing[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (1): 114- 124.
|
| 13 |
陆旭, 陈影, 许中平, 等. 面向5G边缘计算网络的联合需求响应与任务卸载策略[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 209- 218.
|
|
LU Xu, CHEN Ying, XU Zhongping, et al. Joint demand response and task offloading strategy for 5G edge computing network[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 209- 218.
|
| 14 |
CHEN X J, WEN H F, NI W, et al. Distributed online optimization of edge computing with mixed power supply of renewable energy and smart grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70 (1): 389- 403.
|
| 15 |
PERVEZ F, SULTANA A, YANG C G, et al. Energy and latency efficient joint communication and computation optimization in a multi-UAV-assisted MEC network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23 (3): 1728- 1741.
|
| 16 |
CONSUL P, BUDHIRAJA I, GARG D, et al. A hybrid task offloading and resource allocation approach for digital twin-empowered UAV-assisted MEC network using federated reinforcement learning for future wireless network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2024, 70 (1): 3120- 3130.
|
| 17 |
ZHANG Z R, WANG N F, WU H M, et al. MR-DRO: a fast and efficient task offloading algorithm in heterogeneous edge/cloud computing environments[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10 (4): 3165- 3178.
|
| 18 |
YIN F F, ZENG M Y, ZHANG Z L, et al. Coded caching for smart grid enabled HetNets with resource allocation and energy cooperation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69 (10): 12058- 12071.
|
| 19 |
司羽飞, 谭阳红, 汪沨, 等. 面向电力物联网的云边协同结构模型[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (24): 7973- 7979, 8234.
|
|
SI Yufei, TAN Yanghong, WANG Feng, et al. Cloud-edge collaborative structure model for power Internet of Things[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (24): 7973- 7979, 8234.
|
| 20 |
孙毅, 陈恺, 左强, 等. 考虑5G通信负荷协同优化的云边计算网络能量管理模型[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (23): 9020- 9033.
|
|
SUN Yi, CHEN Kai, ZUO Qiang, et al. Energy management model of cloud-edge computing network considering the coordinated optimization of 5G communication load[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (23): 9020- 9033.
|
| 21 |
胡安妮, 张天策, 李庚银, 等. 考虑电动汽车参数一致性的虚拟电厂云边协同调度方法[J/OL]. 电力系统自动化, 2025: 1–13. (2025-03-13). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1180.TP.20250313.1106.002.html.
|
|
HU Anni, ZHANG Tiance, LI Gengyin, et al. Cloud-edge collaborative scheduling method for virtual power plants considering consistency of electric vehicle parameters[J/OL]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2025: 1–13. (2025-03-13). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1180.TP.20250313.1106.002.html.
|
| 22 |
金涛, 王万豪, 黄钦瑜, 等. 一种利用轻量级多通道注意力融合网络的窃电检测边缘计算方法[J/OL]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025: 1–13. (2025-01-23). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2107.TM.20250123.1535.010.html.
|
|
JIN Tao WANG Wanhao HUANG Qinyu, et al. An edge computing approach for electricity theft detection utilizing lightweight multi-channel attention fusion network[J/OL]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025: 1–13. (2025-01-23). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2107.TM.20250123.1535.010.html.
|
| 23 |
张爱军, 刘紫玉, 邢华栋, 等. 基于GM估计的电-气-热综合能源系统分解协调鲁棒状态估计方法[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (10): 9- 14, 53.
|
|
ZHANG Aijun, LIU Ziyu, XING Huadong, et al. Decomposition and coordination robust state estimation method for electric-gas-heat integrated energy system based on GM estimation[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (10): 9- 14, 53.
|
| 24 |
曹旺斌, 唐宏凯, 谢志远, 等. 下行NOMA-PLC系统最优功率分配方法研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025, 45 (3): 834- 846.
|
|
CAO Wangbin, TANG Hongkai, XIE Zhiyuan, et al. Research on optimal power allocation method in downlink NOMA-PLC system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025, 45 (3): 834- 846.
|
| 25 |
蒲红红, 刘晓胜, 徐殿国. 基于深度强化学习的协作非正交多址接入网络鲁棒安全传输[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (13): 4760- 4775.
|
|
PU Honghong, LIU Xiaosheng, XU Dianguo. Deep reinforcement learning based robust secure transmission for cooperative non-orthogonal multiple access networks[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (13): 4760- 4775.
|
| 26 |
佘蕊, 张宁池, 王艳茹, 等. 面向电力物联网的5G通信认知无线电NOMA系统研究[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (5): 35- 45.
|
|
SHE Rui, ZHANG Ningchi, WANG Yanru, et al. Research on cognitive radio non-orthogonal multiple access system in 5G communications oriented to ubiquitous power Internet of Things[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (5): 35- 45.
|
| 27 |
LI X W, ZHANG J Y, HAN C Z, et al. Reliability and security of CR-STAR-RIS-NOMA-assisted IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11 (17): 27969- 27980.
|
| 28 |
CHEN Y, ZHAO J, HU J T, et al. Distributed task offloading and resource purchasing in NOMA-enabled mobile edge computing: hierarchical game theoretical approaches[J]. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems, 2024, 23 (1): 1- 28.
|
| 29 |
CHEN G J, WU Q Q, CHEN W, et al. IRS-aided wireless powered MEC systems: TDMA or NOMA for computation offloading?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22 (2): 1201- 1218.
|
| 30 |
MOHAJER A, SAM DALIRI M, MIRZAEI A, et al. Heterogeneous computational resource allocation for NOMA: toward green mobile edge-computing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2023, 16 (2): 1225- 1238.
|
| 31 |
LIU P, MA K, YANG J, et al. Optimization of relay power and load control period based on cost-sharing contract in smart grid communications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8 (22): 16559- 16570.
|
| 32 |
CHUNG H M, MAHARJAN S, ZHANG Y, et al. Optimal energy trading with demand responses in cloud computing enabled virtual power plant in smart grids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2022, 10 (1): 17- 30.
|
| 33 |
LIU P, WANG J X, MA K, et al. Joint cooperative computation and communication for demand-side NOMA-MEC systems with relay assistance in smart grid communications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11 (19): 30594- 30606.
|