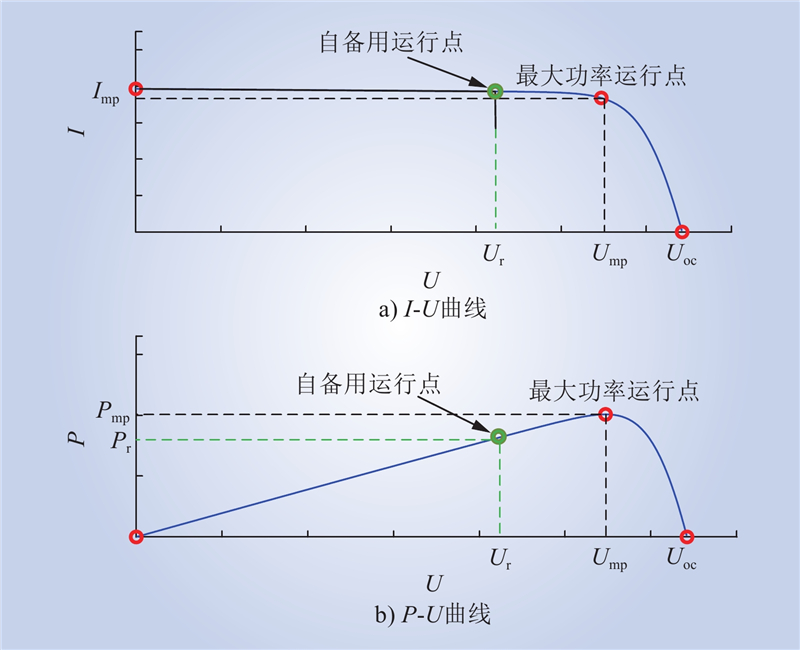
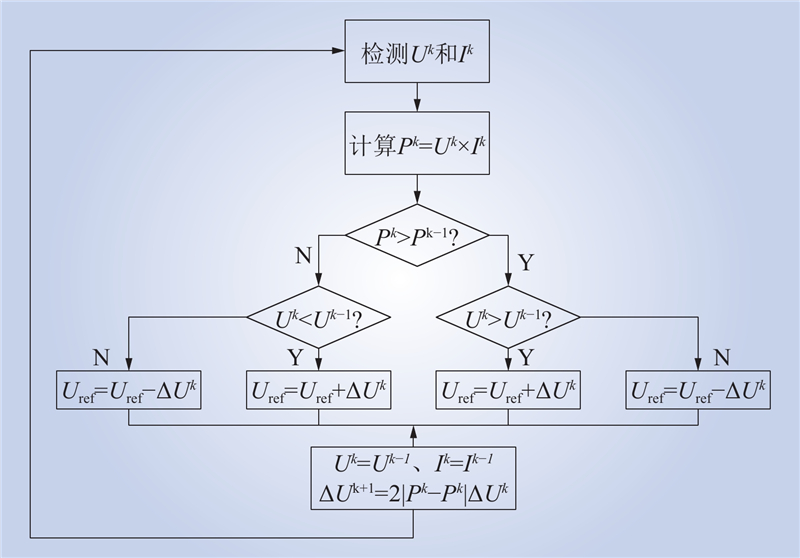
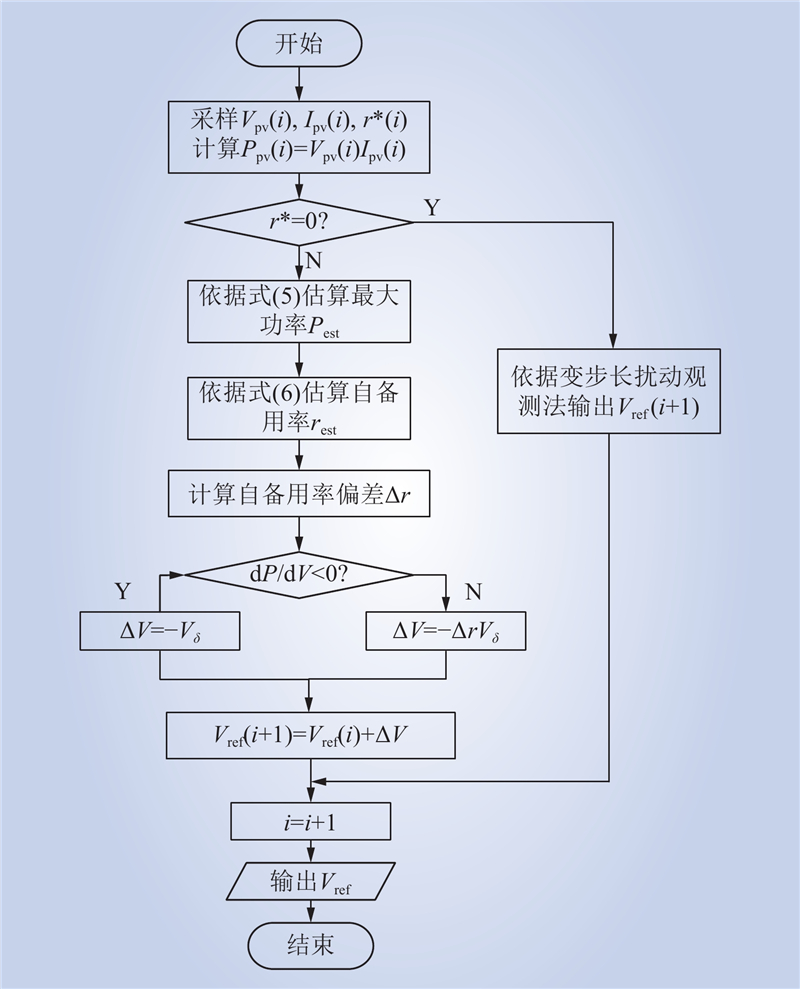
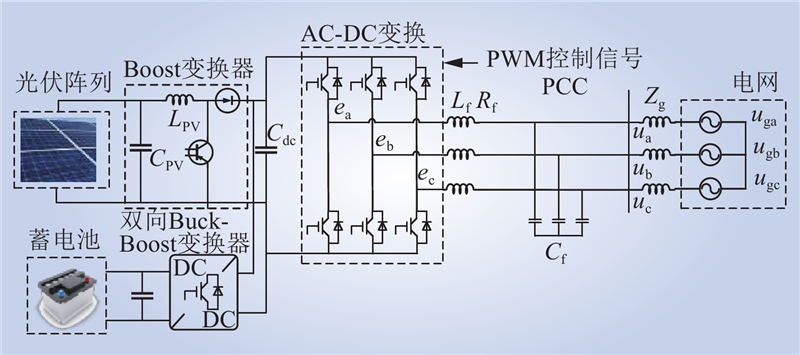
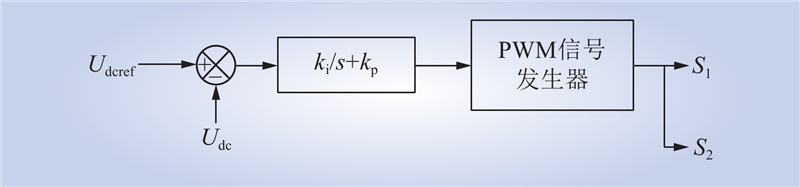
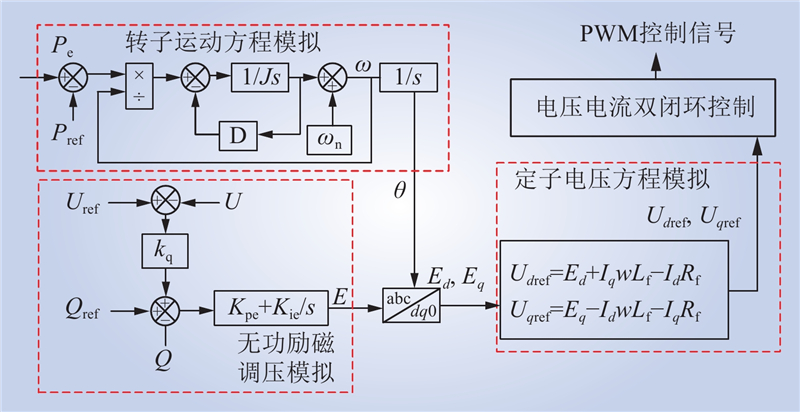
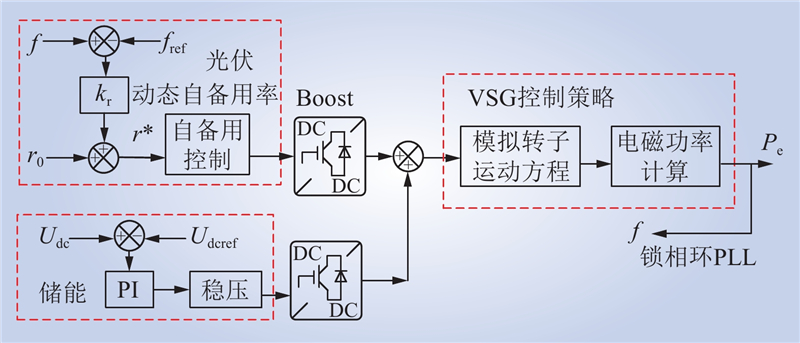
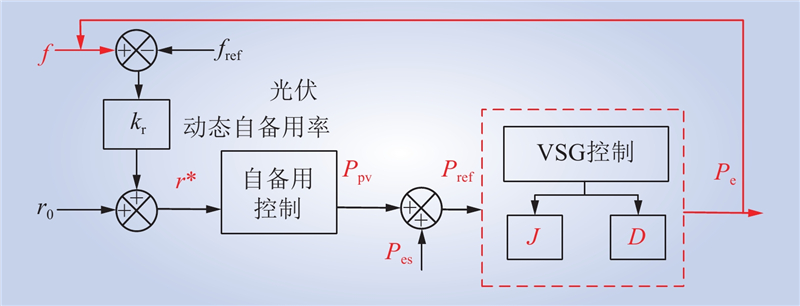
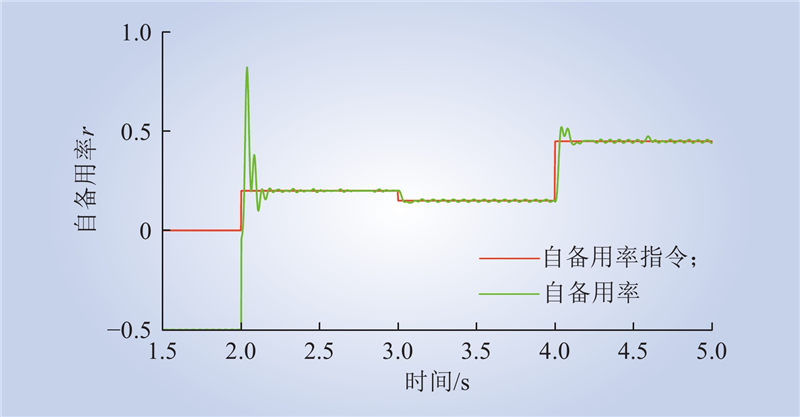
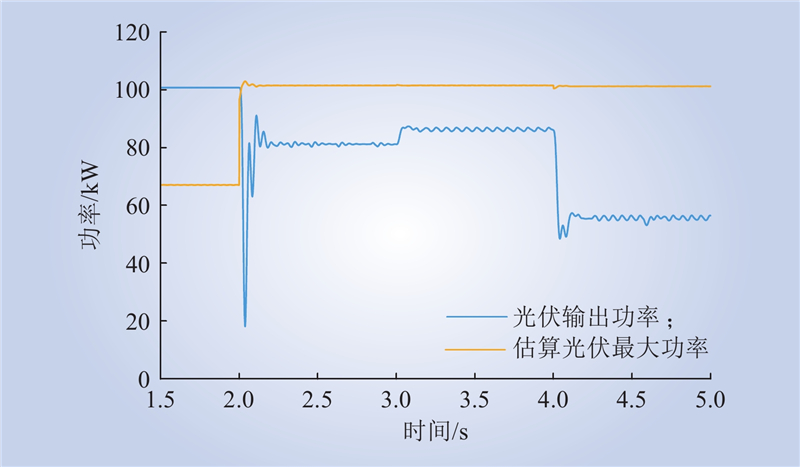
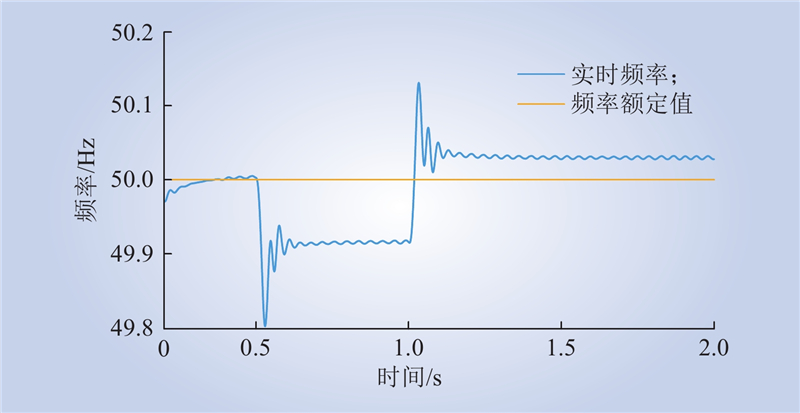
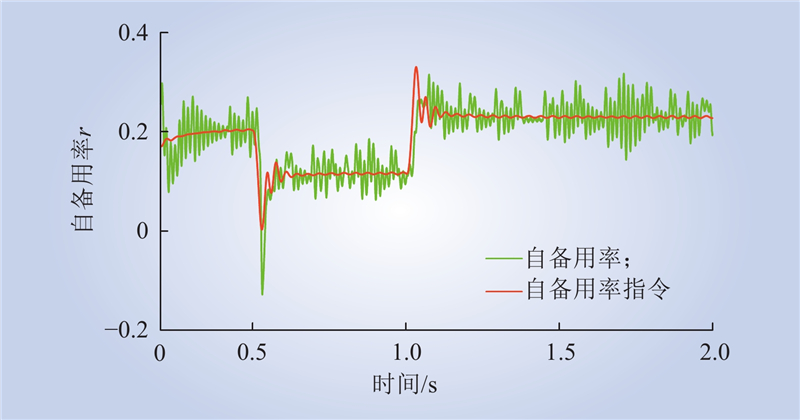
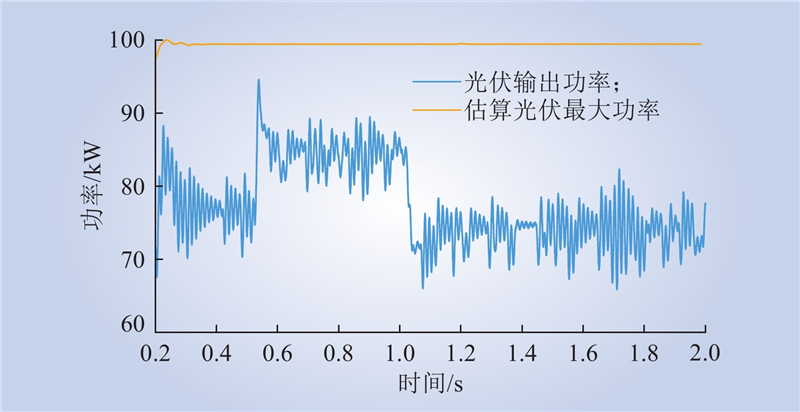
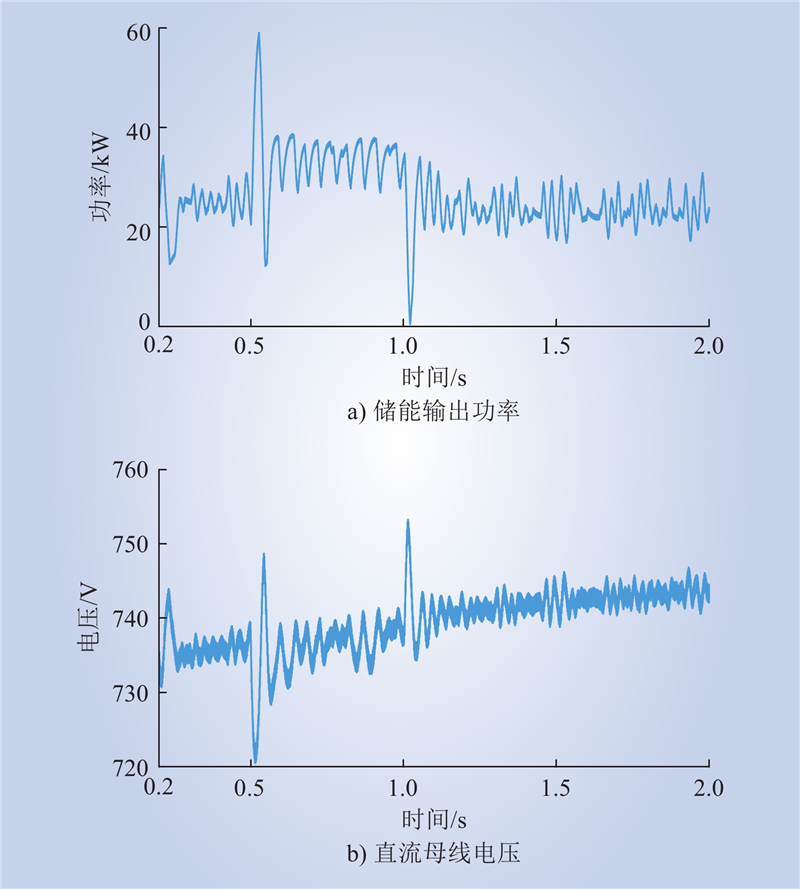
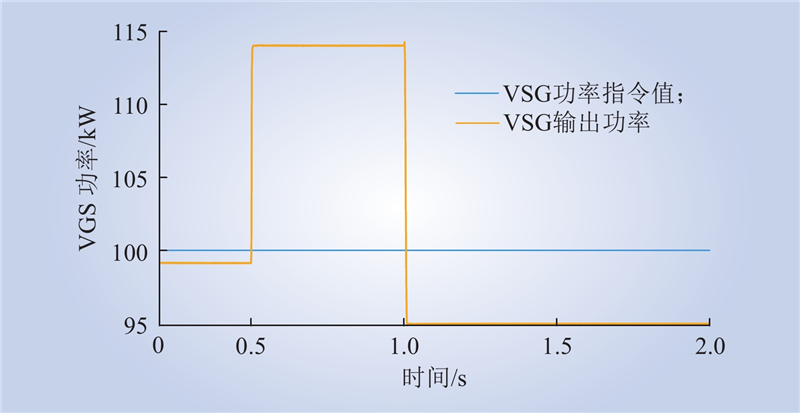
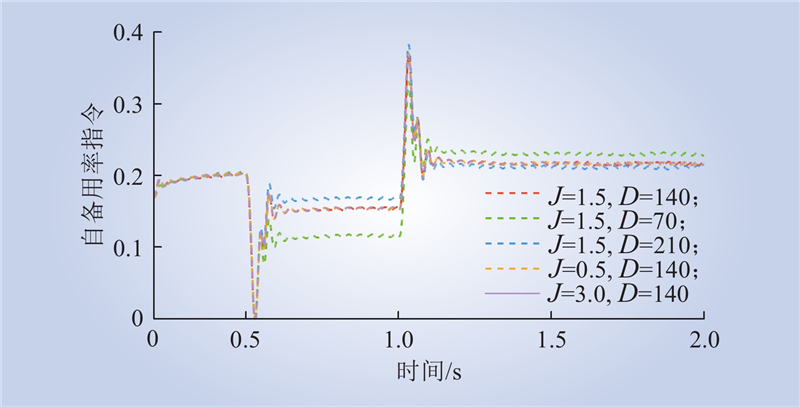
| 1 |
谭显东, 刘俊, 徐志成, 等. “双碳” 目标下 “十四五” 电力供需形势[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (5): 1- 6.
|
|
TAN Xiandong, LIU Jun, XU Zhicheng, et al. Power supply and demand balance during the 14th five-year plan period under the goal of carbon emission peak and carbon neutrality[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (5): 1- 6.
|
| 2 |
张武其, 文云峰, 迟方德, 等. 电力系统惯量评估研究框架与展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (20): 6842- 6855.
|
|
ZHANG Wuqi, WEN Yunfeng, CHI Fangde, et al. Research framework and prospect on power system inertia estimation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (20): 6842- 6855.
|
| 3 |
张子扬, 张宁, 杜尔顺, 等. 双高电力系统频率安全问题评述及其应对措施[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (1): 1- 24.
|
|
ZHANG Ziyang, ZHANG Ning, DU Ershun, et al. Review and countermeasures on frequency security issues of power systems with high shares of renewables and power electronics[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (1): 1- 24.
|
| 4 |
谢小荣, 贺静波, 毛航银, 等. “双高” 电力系统稳定性的新问题及分类探讨[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (2): 461- 474.
|
|
XIE Xiaorong, HE Jingbo, MAO Hangyin, et al. New issues and classification of power system stability with high shares of renewables and power electronics[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (2): 461- 474.
|
| 5 |
国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 电力系统安全稳定导则: GB 38755—2019[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2019.
|
| 6 |
国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 并网电源一次调频技术规定及试验导则: GB/T 40595—2021[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021.
|
| 7 |
刘中建, 周明, 李昭辉, 等. 高比例新能源电力系统的惯量控制技术与惯量需求评估综述[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (12): 1- 11, 53.
|
|
LIU Zhongjian, ZHOU Ming, LI Zhaohui, et al. Review of inertia control technology and requirement evaluation in renewable-dominant power system[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (12): 1- 11, 53.
|
| 8 |
王博, 杨德友, 蔡国伟. 高比例新能源接入下电力系统惯量相关问题研究综述[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (8): 2998- 3006.
|
|
WANG Bo, YANG Deyou, CAI Guowei. Review of research on power system inertia related issues in the context of high penetration of renewable power generation[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (8): 2998- 3006.
|
| 9 |
孙骁强, 刘鑫, 程林, 等. 基于多调频资源协调控制的西北送端大电网新能源快速频率响应参数设置方案[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (5): 1760- 1765.
|
|
SUN Xiaoqiang, LIU Xin, CHENG Lin, et al. Parameter setting of rapid frequency response of renewable energy sources in northwest power grid based on coordinated control of multi-frequency regulation resources[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (5): 1760- 1765.
|
| 10 |
陆剑峰, 邹鑫, 牟晓春. 基于光伏电站的一次调频控制系统设计[J]. 电力电子技术, 2021, 55 (9): 90- 92, 102.
|
|
LU Jianfeng, ZOU Xin, MU Xiaochun. Design of a fast frequency modulation control system based on photovoltaic power station[J]. Power Electronics, 2021, 55 (9): 90- 92, 102.
|
| 11 |
刘刚, 陈海东, 孙睿哲, 等. 集群光伏电站频率主动支撑自校正控制方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (9): 156- 162.
|
|
LIU Gang, CHEN Haidong, SUN Ruizhe, et al. Self-tuning control method of active frequency support of clustering photovoltaic power plants[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (9): 156- 162.
|
| 12 |
刘畅, 卓建坤, 赵东明, 等. 利用储能系统实现可再生能源微电网灵活安全运行的研究综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (1): 1- 18.
|
|
LIU Chang, ZHUO Jiankun, ZHAO Dongming, et al. A review on the utilization of energy storage system for the flexible and safe operation of renewable energy microgrids[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (1): 1- 18.
|
| 13 |
XU H Z, YU C Z, LIU C, et al. An improved virtual inertia algorithm of virtual synchronous generator[J]. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy, 2020, 8 (2): 377- 386.
|
| 14 |
王逸超, 李湘旗, 陈仲伟, 等. 一种光储独立并网式虚拟同步发电机控制方法[J]. 太阳能学报, 2022, 43 (1): 249- 255.
|
|
WANG Yichao, LI Xiangqi, CHEN Zhongwei, et al. A virtual synchronous generator control method based on independent grid-connected structure of photovoltaic system and energy storage system[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2022, 43 (1): 249- 255.
|
| 15 |
李帅虎, 胡耀尹, 罗滇生, 等. 基于模型预测控制的光储发电系统VSG频率控制方法[J]. 全球能源互联网, 2022, 5 (4): 348- 355.
|
|
LI Shuaihu, HU Yaoyin, LUO Diansheng, et al. VSG frequency control method of photovoltaic system with storage based on model predictive control[J]. Journal of Global Energy Interconnection, 2022, 5 (4): 348- 355.
|
| 16 |
徐华电, 苏建徽, 施永, 等. 具有同步发电机特性的储能型光伏并网发电系统研究[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2018, 35 (7): 1021- 1028.
|
|
XU Huadian, SU Jianhui, SHI Yong, et al. Research on grid-connected photovoltaics-energy storage system with synchronous generator characteristics[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 35 (7): 1021- 1028.
|
| 17 |
周扬. 光伏减载参与电网频率响应策略研究[D]. 吉林: 东北电力大学, 2021.
|
|
ZHOU Yang . Photovoltaic load reduction participation in power grid frequency response strategy research [D]. Jilin: Northeast Electric Power University, 2021.
|
| 18 |
ZHONG C, ZHOU Y, YAN G G. Power reserve control with real-time iterative estimation for PV system participation in frequency regulation[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2021, 124, 106367.
|
| 19 |
钟璐, 熊俊, 张茜, 等. 基于光伏减载的电力系统紧急降风险控制方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49 (14): 157- 167.
|
|
ZHONG Lu, XIONG Jun, ZHANG Qian, et al. A risk-reduction emergency control method of a power system based on photovoltaic power reserve[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49 (14): 157- 167.
|
| 20 |
王利猛, 孙珮然, 韩凯, 等. 计及备用容量的光伏发电系统等比例减载调频控制技术研究[J]. 可再生能源, 2020, 38 (9): 1203- 1209.
|
|
WANG Limeng, SUN Peiran, HAN Kai, et al. The control strategy of frequency regulation by proportional deloading for a PV system considering available reserves[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2020, 38 (9): 1203- 1209.
|
| 21 |
马明, 包广清, 吕清泉, 等. 具有有功功率自备用能力的光伏系统虚拟同步控制研究[J]. 兰州理工大学学报, 2022, 48 (1): 71- 77.
|
|
MA Ming, BAO Guangqing, LYU Qingquan, et al. Study on PV system virtual synchronization control with active power self-reserve ability[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2022, 48 (1): 71- 77.
|
| 22 |
包广清, 谭宏涛, 丁坤, 等. 光伏系统有功功率自备用研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2020, 41 (12): 90- 96.
|
|
BAO Guangqing, TAN Hongtao, DING Kun, et al. Research on active power self-reserve of photovoltaic system[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2020, 41 (12): 90- 96.
|
| 23 |
付文启, 杨鑫, 管飞, 等. 光伏减载驱动新能源同步机参与电力系统调频的研究[J]. 电机与控制应用, 2021, 48 (5): 79- 85.
|
|
FU Wenqi, YANG Xin, GUAN Fei, et al. Research on photovoltaic driving motor-generator pair to participate in frequency regulation under load shedding control[J]. Electric Machines & Control Application, 2021, 48 (5): 79- 85.
|
| 24 |
付文启, 黄永章, 杨鑫, 等. 光伏驱动新能源同步机并网的调频能力研究[J]. 电气传动, 2022, 52 (10): 21- 27.
|
|
FU Wenqi, HUANG Yongzhang, YANG Xin, et al. Research on frequency regulation capability of photovoltaic integration via a motor-generator pair[J]. Electric Drive, 2022, 52 (10): 21- 27.
|
| 25 |
钱国明, 孟杰, 朱海东, 等. 基于调频服务的新型光-储电站容量规划及运行策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (6): 132- 138, 147.
|
|
QIAN Guoming, MENG Jie, ZHU Haidong, et al. Capacity planning and operation strategy of new PV-storage power station based on frequency modulation service[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (6): 132- 138, 147.
|
| 26 |
白晶, 金广厚, 孙鹤林, 等. 高渗透光伏配电网第三方主体调压辅助服务补偿与获取[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (4): 95- 103, 111.
|
|
BAI Jing, JIN Guanghou, SUN Helin, et al. Third-party entity voltage regulation ancillary service compensation and procurement in distribution networks with high-penetration PV[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (4): 95- 103, 111.
|
| 27 |
MANSOOR M, MIRZA A F, LING Q, et al. Novel Grass Hopper optimization based MPPT of PV systems for complex partial shading conditions[J]. Solar Energy, 2020, 198, 499- 518.
|
| 28 |
曾正, 邵伟华, 冉立, 等. 虚拟同步发电机的模型及储能单元优化配置[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (13): 22- 31.
|
|
ZENG Zheng, SHAO Weihua, RAN Li, et al. Mathematical model and strategic energy storage selection of virtual synchronous generators[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (13): 22- 31.
|