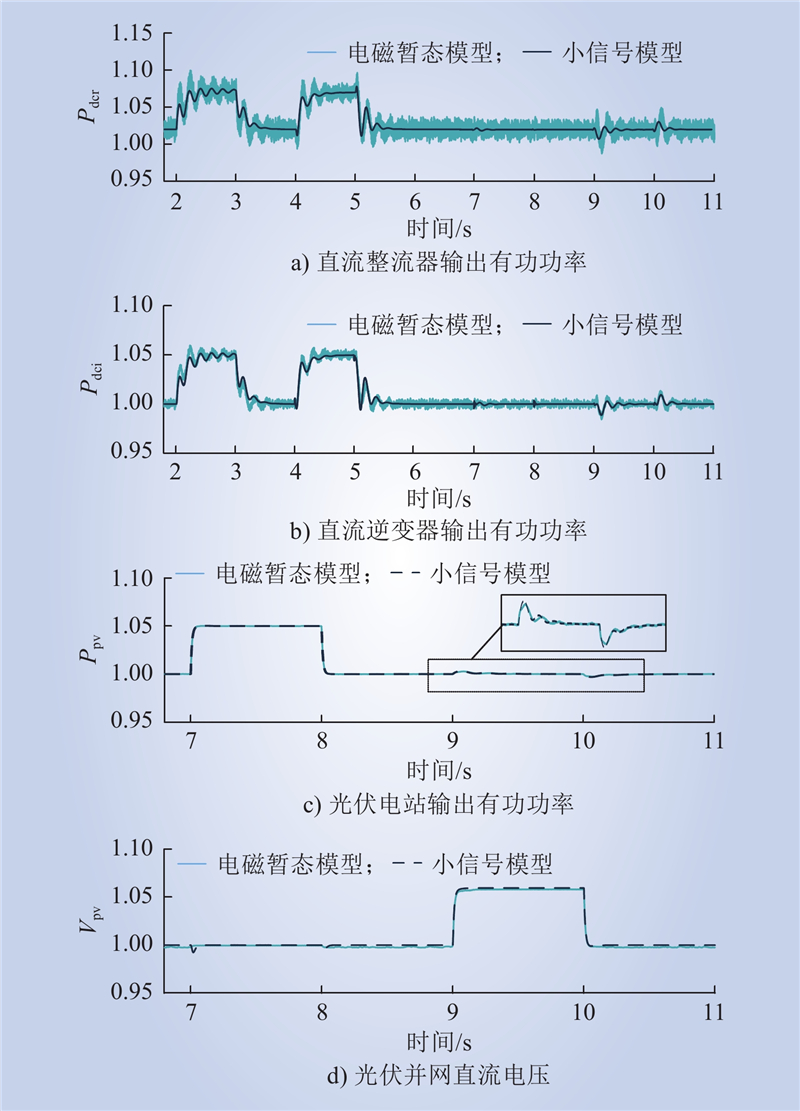
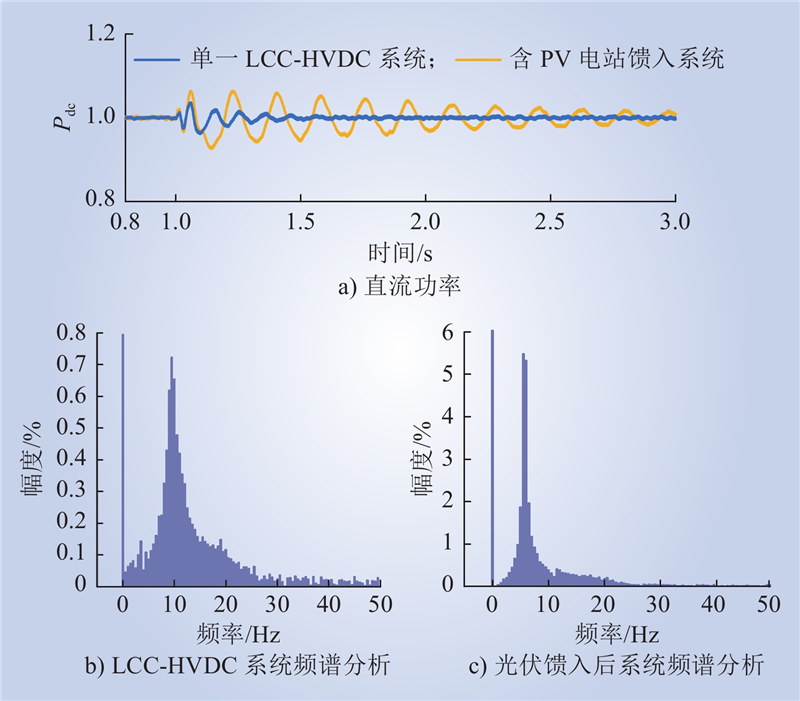
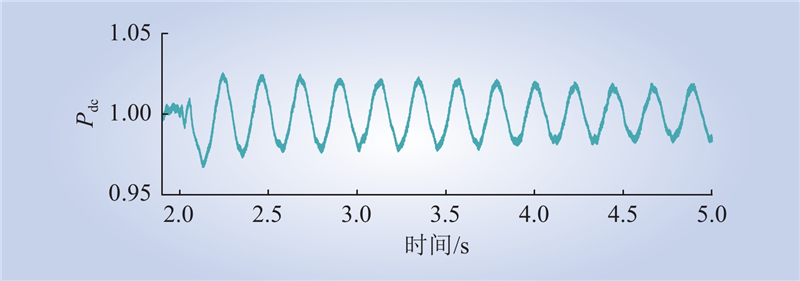
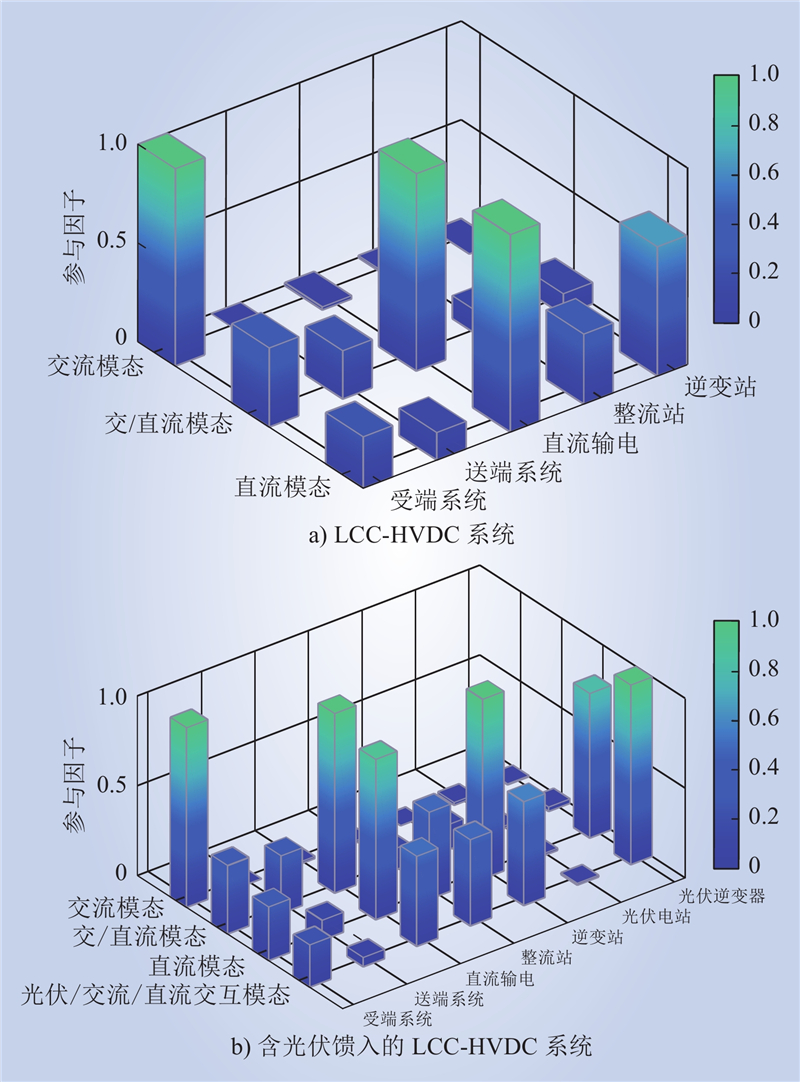
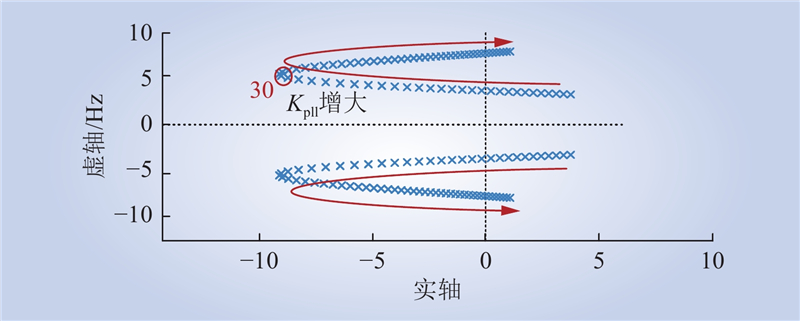
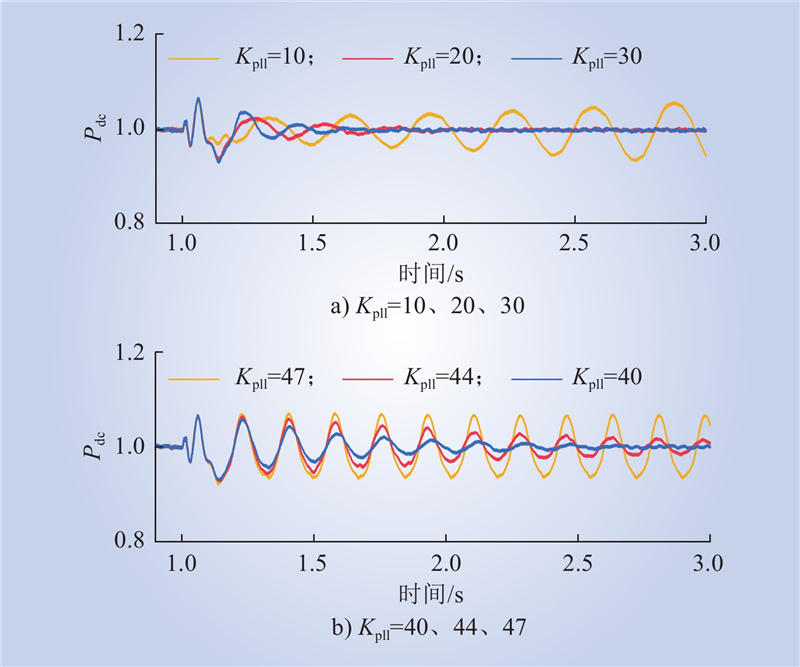
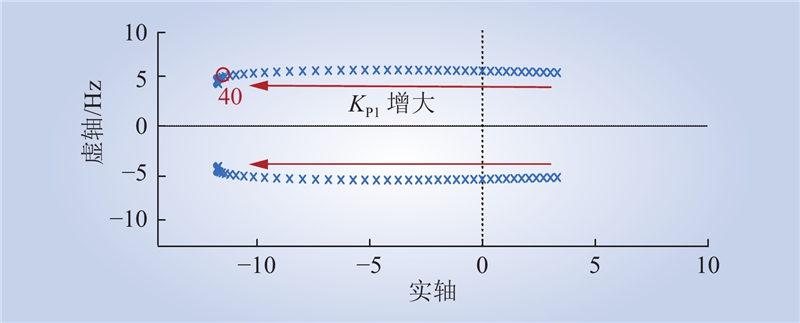
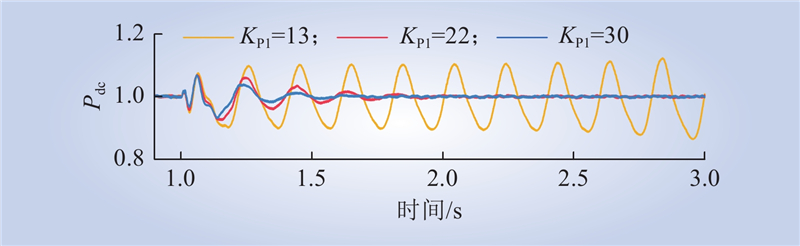
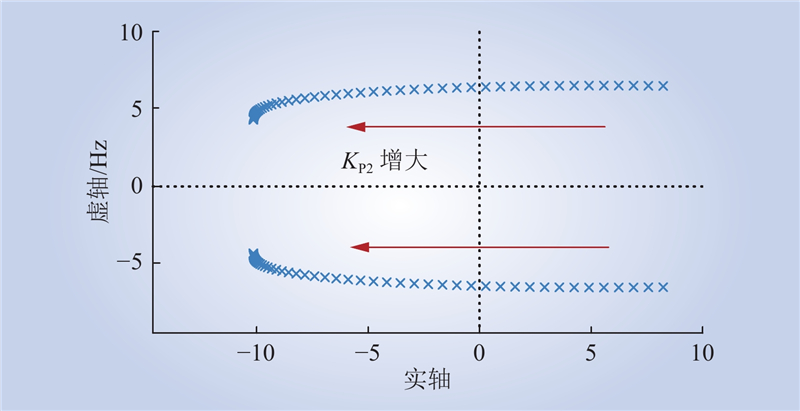
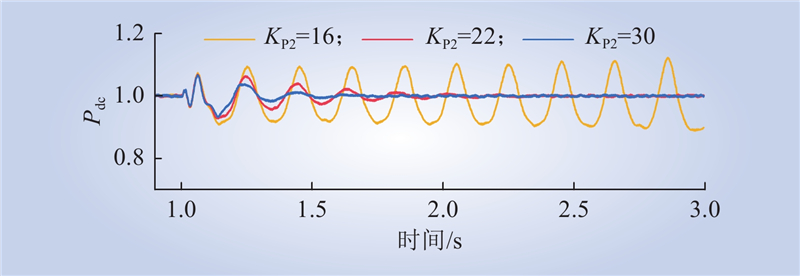
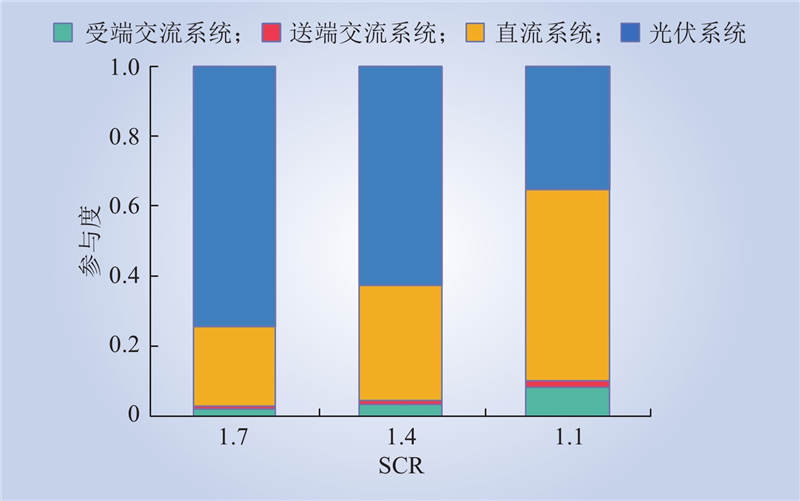
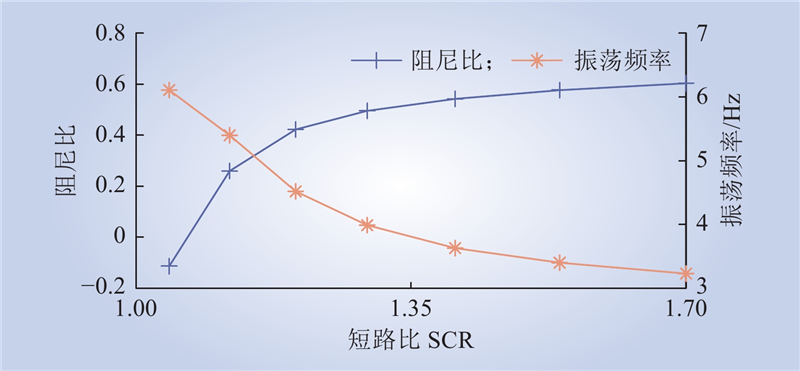
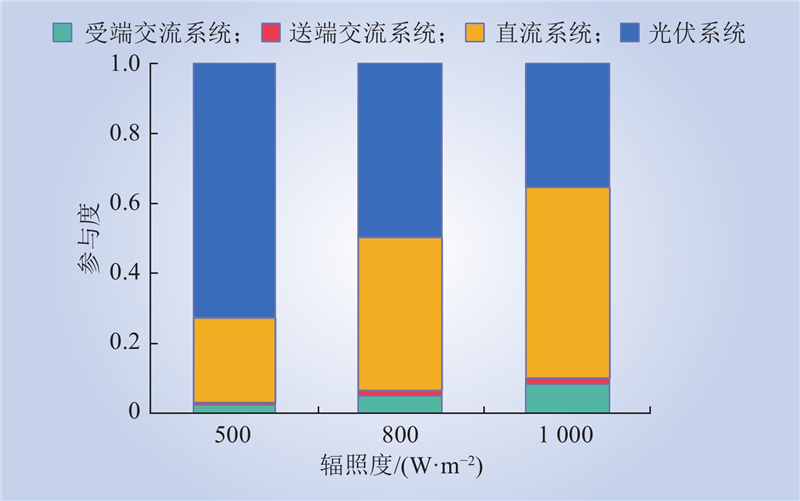
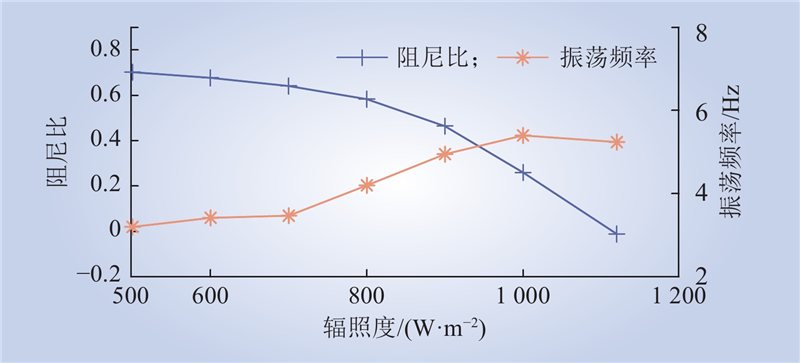
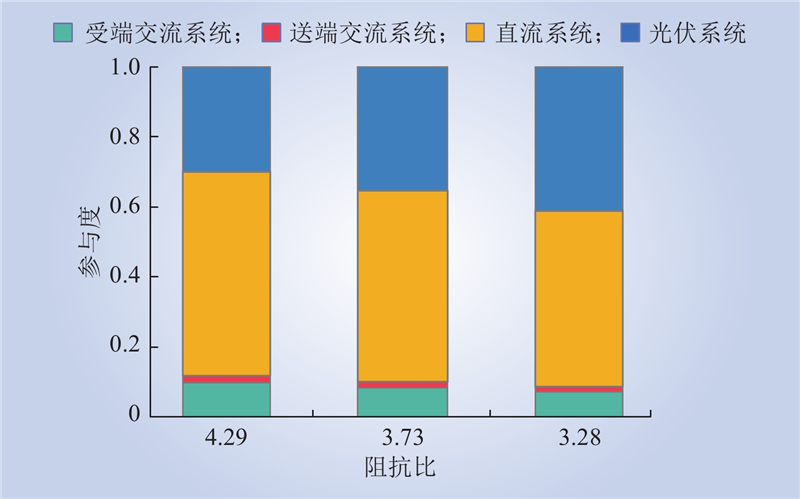
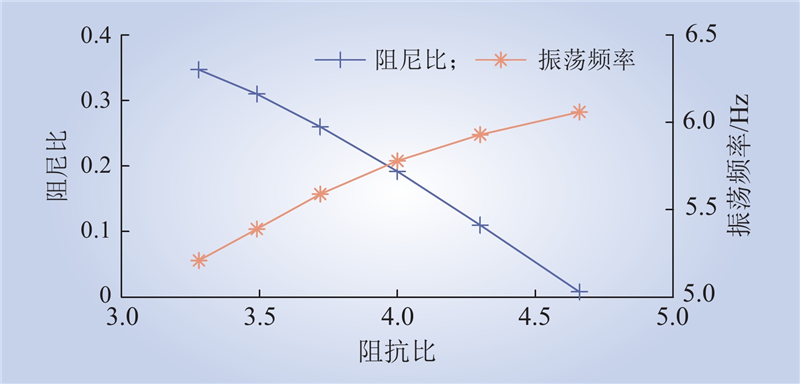
| 1 |
郭小龙, 张江飞, 亢朋朋, 等. 含基于PI控制受端二次调频的特高压直流虚拟同步控制策略[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (11): 66- 72.
|
|
GUO Xiaolong, ZHANG Jiangfei, KANG Pengpeng, et al. Virtual synchronization control strategy for UHVDC with secondary frequency modulation based on PI control[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (11): 66- 72.
|
| 2 |
于琳琳, 严格, 晏昕童, 等. 考虑电网支撑能力约束的直流落点及定容优化规划[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (8): 175- 185.
|
|
YU Linlin, YAN Ge, YAN Xintong, et al. Optimal planning of terminal locations and capacity of UHVDC considering constraints of receiving-end power grid support capability[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (8): 175- 185.
|
| 3 |
张振兴. 湖北电网新能源出力首破千万千瓦大关[N]. 新华网, 2022-03-10.
|
| 4 |
蔡维正, 郭昆丽, 刘璐雨, 等. 基于一阶LADRC控制的直驱风机次同步振荡抑制策略[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (4): 175- 184.
|
|
CAI Weizheng, GUO Kunli, LIU Luyu, et al. Subsynchronous oscillation mitigation strategy based on first-order LADRC for direct-drive wind turbines[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (4): 175- 184.
|
| 5 |
金标, 余一平, 樊陈, 等. 基于宽频量测间谐波潮流计算的次/超同步振荡溯源方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2022, 42 (8): 221- 228.
|
|
JIN Biao, YU Yiping, FAN Chen, et al. Tracing method of sub-/ super-synchronous oscillation based on interharmonic power flow calculation of wide frequency measurement[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022, 42 (8): 221- 228.
|
| 6 |
王晓宇, 杨杰, 吴亚楠, 等. 渝鄂背靠背柔性直流对系统次同步振荡特性的影响分析[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2019, 39 (7): 188- 194, 202.
|
|
WANG Xiaoyu, YANG Jie, WU Yanan, et al. Effect analysis of back-to-back flexible HVDC connecting Chongqing and Hubei Power Grid on sub-synchronous oscillation characteristics[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2019, 39 (7): 188- 194, 202.
|
| 7 |
戴礼国, 杨浩, 陈力, 等. 基于深度强化学习的风电柔直并网系统次同步振荡抑制方法[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (4): 1- 7, 91.
|
|
DAI Liguo, YANG Hao, CHEN Li, et al. Subsynchronous oscillation suppression method for flexible direct grid-connected wind power system based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Smart Grid, 2023, 51 (4): 1- 7, 91.
|
| 8 |
杨硕, 郭春义, 张加卿, 等. LCC-HVDC系统整流–逆变交互振荡模式稳定变化特征及机理研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(16): 6181–6192.
|
|
YANG Shuo, GUO Chunyi, ZHANG Jiaqin, et al. Study on characteristics and mechanism of the stability moving trend of rectifier-inverter interactive oscillation mode for LCC-HVDC system[J/OL]. Proceedings of the CSEE: 2023, 43(16): 6181–6192.
|
| 9 |
莫泽, 汪娟娟, 丁天皓, 等. 基于改进开关函数的LCC-HVDC直流阻抗建模及小扰动稳定性分析[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (11): 4491- 4505.
|
|
MO Ze, WANG Juanjuan, DING Tianhao, et al. LCC-HVDC impedance modeling and small disturbance stability analysis based on improved switching function[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (11): 4491- 4505.
|
| 10 |
高本锋, 姚磊, 李忍, 等. 大规模光伏电站并网的振荡模式分析[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2017, 37 (8): 123- 130.
|
|
GAO Benfeng, YAO Lei, LI Ren, et al. Analysis on oscillation modes of large-scale grid-connected PV power plant[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2017, 37 (8): 123- 130.
|
| 11 |
汪洋. 大型光伏并网系统的复杂振荡问题研究[D]. 保定: 华北电力大学(保定), 2018.
|
|
WANG Yang. Research on complex oscillation problems of large photovoltaic grid-connected systems[D]. Baoding: North China Electric Power University (Baoding), 2018.
|
| 12 |
赵书强, 李忍, 高本锋, 等. 光伏并入弱交流电网次同步振荡机理与特性分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (24): 7215- 7225, 7448.
|
|
ZHAO Shuqiang, LI Ren, GAO Benfeng, et al. Analysis of mechanism and characteristics in sub synchronous oscillation between PV and weak AC networks[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (24): 7215- 7225, 7448.
|
| 13 |
苗淼, 何维, 张祥成, 等. 串联补偿线路对光伏发电系统稳定性影响[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2016, 36 (9): 106- 113.
|
|
MIAO Miao, HE Wei, ZHANG Xiangcheng, et al. Influence of series compensation lines on PV system stability[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2016, 36 (9): 106- 113.
|
| 14 |
庞博, 郭春义, 王潇, 等. 风电接入对柔性直流电网站间耦合振荡模式的影响及站间交互作用的定量评估[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (8): 3206- 3220.
|
|
PANG Bo, GUO Chunyi, WANG Xiao, et al. Influence of wind power access on coupling oscillation modes between converter stations in MMC-based HVDC grid and quantitative evaluation of interaction[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (8): 3206- 3220.
|
| 15 |
高本锋, 刘毅, 宋瑞华, 等. 双馈风电场经LCC-HVDC送出的次同步振荡特性研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (11): 3477- 3489.
|
|
GAO Benfeng, LIU Yi, SONG Ruihua, et al. Study on subsynchronous oscillation characteristics of DFIG-based wind farm integrated with LCC-HVDC system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (11): 3477- 3489.
|
| 16 |
高本锋, 崔意婵, 李蕴红, 等. D-PMSG经LCC-HVDC送出系统的次同步振荡特性分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (6): 2084- 2096.
|
|
GAO Benfeng, CUI Yichan, LI Yunhong, et al. Analysis of subsynchronous oscillation characteristics of D-PMSG integrated with LCC-HVDC system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (6): 2084- 2096.
|
| 17 |
邵冰冰, 赵书强, 裴继坤, 等. 直驱风电场经VSC-HVDC并网的次同步振荡特性分析[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (9): 3344- 3355.
|
|
SHAO Bingbing, ZHAO Shuqiang, PEI Jikun, et al. Subsynchronous oscillation characteristic analysis of grid-connected DDWFs via VSC-HVDC system[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (9): 3344- 3355.
|
| 18 |
高本锋, 陈淑平, 沈琳, 等. 光伏经LCC-HVDC外送系统的次同步振荡特性分析[J]. 华北电力大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 49 (2): 41- 52.
|
|
GAO Benfeng, CHEN Shuping, SHEN Lin, et al. Analysis of subsynchronous oscillation characteristics of photovoltaic power station integrated with LCC-HVDC system[J]. Journal of North China Electric Power University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 49 (2): 41- 52.
|
| 19 |
陈露洁, 徐式蕴, 孙华东, 等. 高比例电力电子电力系统宽频带振荡研究综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (7): 2297- 2310.
|
|
CHEN Lujie, XU Shiyun, SUN Huadong, et al. A survey on wide-frequency oscillation for power systems with high penetration of power electronics[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (7): 2297- 2310.
|
| 20 |
刘芳, 刘威, 汪浩东, 等. 高比例新能源电力系统振荡机理及其分析方法研究综述[J]. 高电压技术, 2022, 48 (1): 95- 114.
|
|
LIU Fang, LIU Wei, WANG Haodong, et al. Review on oscillation mechanism and analysis methods of high proportion renewable energy power system[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2022, 48 (1): 95- 114.
|
| 21 |
郭春义, 宁琳如, 王虹富, 等. 基于开关函数的LCC-HVDC换流站动态模型及小干扰稳定性[J]. 电网技术, 2017, 41 (12): 3862- 3870.
|
|
GUO Chunyi, NING Linru, WANG Hongfu, et al. Switching-function based dynamic model of LCC-HVDC station and small signal stability analysis[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41 (12): 3862- 3870.
|
| 22 |
贺杨烊, 郑晓冬, 邰能灵, 等. 交直流混联电网LCC-HVDC换流器建模方法综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (11): 3119- 3130.
|
|
HE Yangyang, ZHENG Xiaodong, TAI Nengling, et al. A review of modeling methods for LCC-HVDC converter in AC/DC hybrid power grid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (11): 3119- 3130.
|
| 23 |
任必兴, 杜文娟, 王海风, 等. 锁相环控制对永磁直驱风机并网次同步振荡稳定性的影响: 控制参数安全域[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2020, 40 (9): 142- 149.
|
|
REN Bixing, DU Wenjuan, WANG Haifeng, et al. Influence of PLL control on sub-synchronous oscillation stability of grid-connected PMSG: control parameter safety region[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2020, 40 (9): 142- 149.
|
| 24 |
王钦, 姚伟, 艾小猛, 等. 含大规模面板级直流优化器的分布式光伏并网系统动态建模[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (2): 559- 570.
|
|
WANG Qin, YAO Wei, AI Xiaomeng, et al. Dynamic modelling of distributed PV grid-connected system with large scale of panel level DC optimizers[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (2): 559- 570.
|
| 25 |
于琳, 孙华东, 徐式蕴, 等. 电力电子设备接入电压支撑强度量化评估指标综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (2): 499- 515.
|
|
YU Lin, SUN Huadong, XU Shiyun, et al. Overview of strength quantification indexes of power system with power electronic equipment[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (2): 499- 515.
|