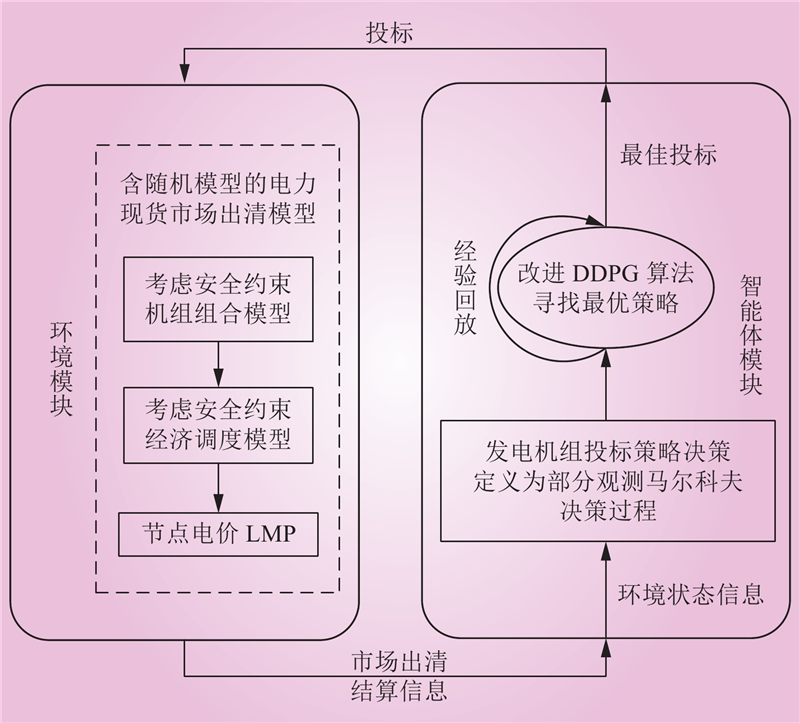
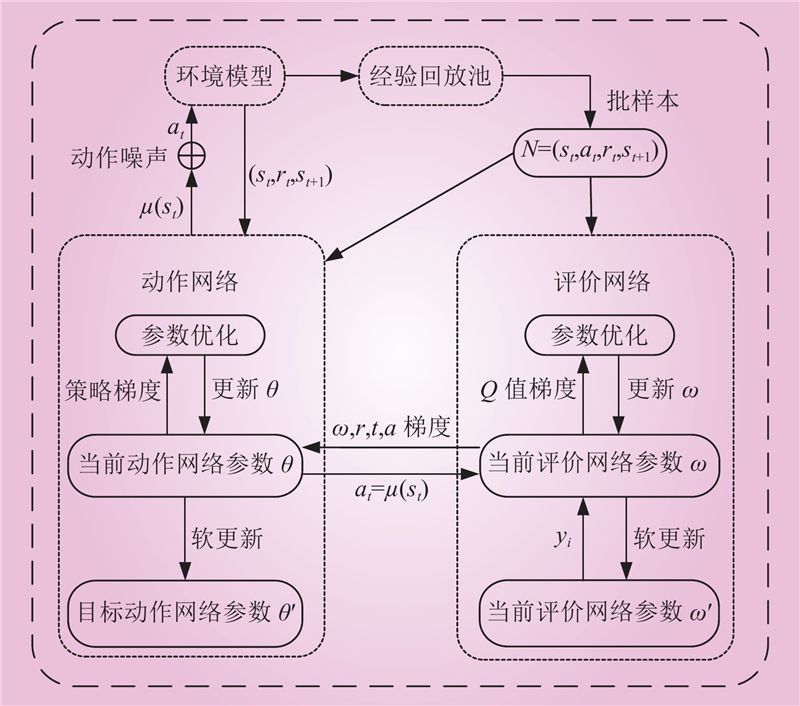
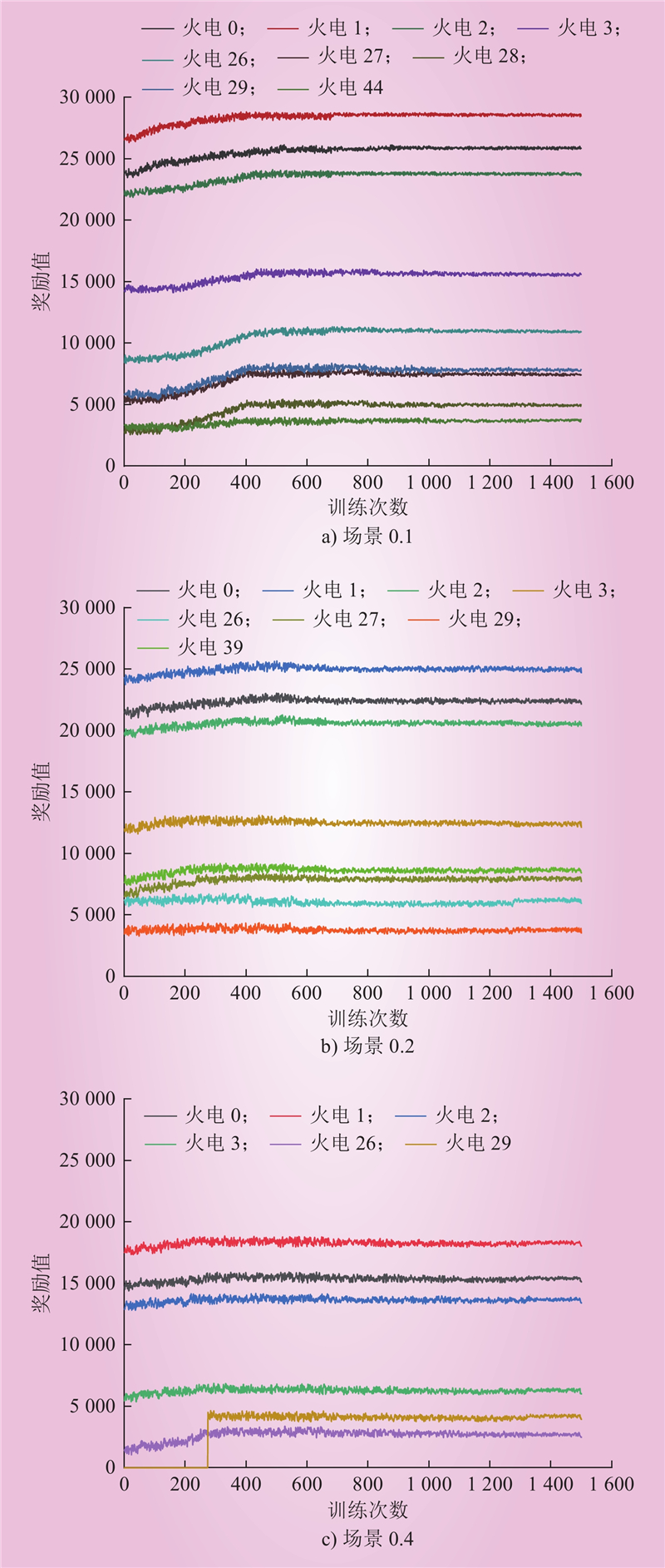
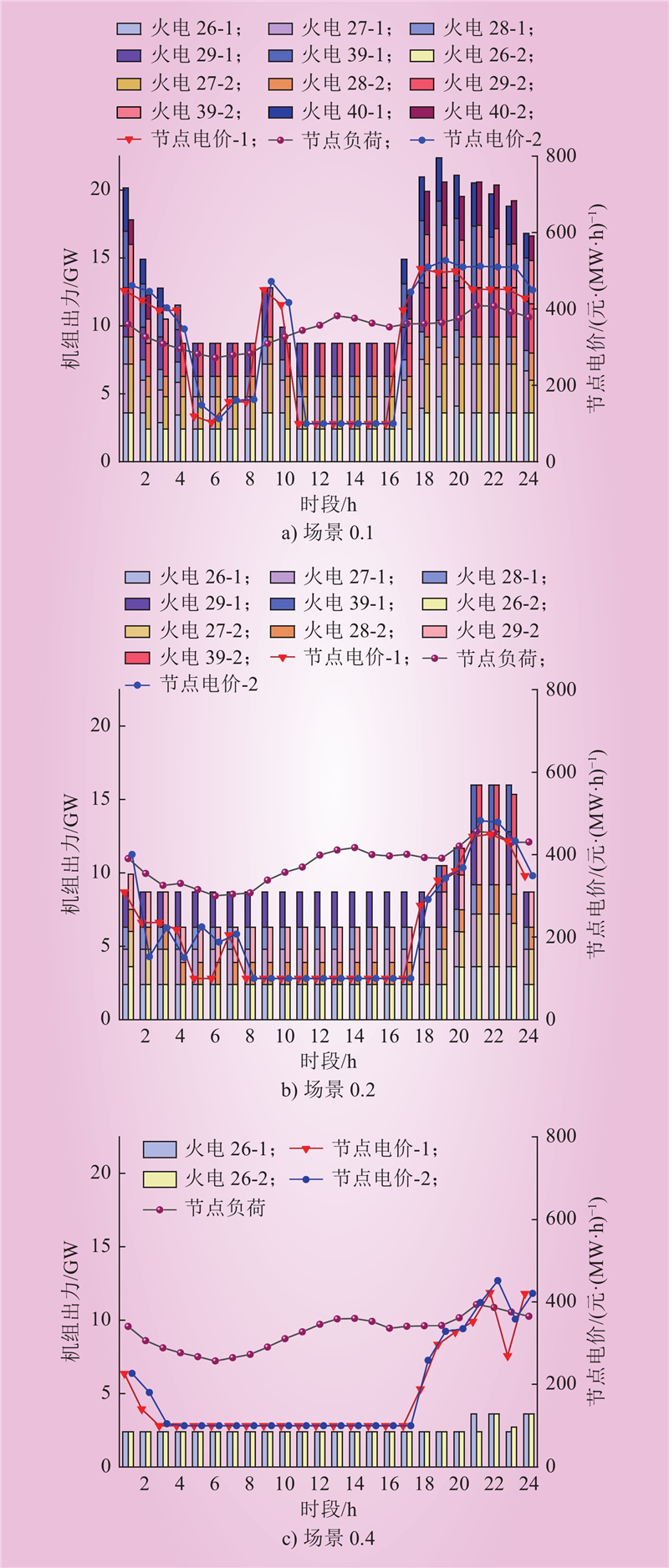
| 1 |
HAO S Y. A study of basic bidding strategy in clearing pricing auctions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2000, 15 (3): 975- 980.
|
| 2 |
TSAY M T, GOW H J. Congestion influence on bidding strategies in an electricity market[C]//2005 IEEE/PES Transmission & Distribution Conference & Exposition: Asia and Pacific. Dalian, China. IEEE, 2005: 1–6.
|
| 3 |
SINGH K, PADHY N P, SHARMA J. Influence of price responsive demand shifting bidding on congestion and LMP in pool-based day-ahead electricity markets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2011, 26 (2): 886- 896.
|
| 4 |
PRABAVATHI M, GNANADASS R. Energy bidding strategies for restructured electricity market[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2015, 64, 956- 966.
|
| 5 |
蒲勇健, 余沙, 黄毅祥. 基于独立售电公司双角色的Stackelberg博弈模型分析[J]. 中国管理科学, 2022, 30 (12): 317- 326.
|
|
PU Yongjian, YU Sha, HUANG Yixiang, et al. A Stackelberg game model based on the dual role of independent electricity sale company[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2022, 30 (12): 317- 326.
|
| 6 |
李章溢, 马昕, 裴玮, 等. 含用户聚合代理的工业园区需求响应主从博弈机制与策略[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (8): 40- 49.
|
|
LI Zhangyi, MA Xin, PEI Wei, et al. Leader-follower game mechanism and strategy of industrial park demand response with user aggregator[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (8): 40- 49.
|
| 7 |
田福银, 马骏, 王灿, 等. 基于双层主从博弈的综合能源系统多主体低碳经济运行策略[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (11): 184- 193.
|
|
TIAN Fuyin, MA Jun, WANG Can, et al. Multi-agent low-carbon and economy operation strategy of integrated energy system based on bi-level master-slave game[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (11): 184- 193.
|
| 8 |
鲁鹏, 冯春贤, 武伟鸣, 等. 园区能源供需价量双层Stackelberg博弈模型[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (6): 74- 79.
|
|
LU Peng, FENG Chunxian, WU Weiming, et al. Two-layer Stackelberg game model for energy supply and demand in the park[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (6): 74- 79.
|
| 9 |
崔明勇, 宣名阳, 卢志刚, 等. 基于合作博弈的多综合能源服务商运行优化策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (10): 3548- 3564.
|
|
CUI Mingyong, XUAN Mingyang, LU Zhigang, et al. Operation optimization strategy of multi integrated energy service companies based on cooperative game theory[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (10): 3548- 3564.
|
| 10 |
武昭原, 周明, 姚尚润, 等. 基于合作博弈论的风储联合参与现货市场优化运行策略[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (8): 2815- 2824.
|
|
WU Zhaoyuan, ZHOU Ming, YAO Shangrun, et al. Optimization operation strategy of wind-storage coalition in spot market based on cooperative game theory[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (8): 2815- 2824.
|
| 11 |
EPSTEIN J M. Generative social science: studies in agent-based computational modeling[M]. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2006.
|
| 12 |
RINGLER P, KELES D, FICHTNER W. Agent-based modelling and simulation of smart electricity grids and markets - a literature review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 57, 205- 215.
|
| 13 |
SANTOS G, PINTO T, MORAIS H, et al. Multi-agent simulation of competitive electricity markets: autonomous systems cooperation for European market modeling[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2015, 99, 387- 399.
|
| 14 |
ALIABADI D E, KAYA M, ŞAHIN G. An agent-based simulation of power generation company behavior in electricity markets under different market-clearing mechanisms[J]. Energy Policy, 2017, 100, 191- 205.
|
| 15 |
HAGHIGHAT H, SEIFI H, KIAN A R. Pay-as-bid versus marginal pricing: the role of suppliers strategic behavior[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2012, 42 (1): 350- 358.
|
| 16 |
KELES D, BUBLITZ A, ZIMMERMANN F, et al. Analysis of design options for the electricity market: the German case[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 183, 884- 901.
|
| 17 |
BARAZZA E, STRACHAN N. The impact of heterogeneous market players with bounded-rationality on the electricity sector low-carbon transition[J]. Energy Policy, 2020, 138, 111274.
|
| 18 |
WANG J H, BOTTERUD A, CONZELMANN G, et al. Market power analysis in the EEX electricity market: an agent-based simulation approach[C]//2008 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting-Conversion and Delivery of Electrical Energy in the 21st Century. Pittsburgh, PA. IEEE, 2008: 1–8.
|
| 19 |
袁唯淋, 罗俊仁, 陆丽娜, 等. 智能博弈对抗方法: 博弈论与强化学习综合视角对比分析[J]. 计算机科学, 2022, 49 (8): 191- 204.
|
|
YUAN Weilin, LUO Junren, LU Lina, et al. Methods in adversarial intelligent game: a comparative analysis from perspective of game theory and reinforcement learning[J]. Computer Science, 2022, 49 (8): 191- 204.
|
| 20 |
PURUSHOTHAMAN K, CHANDRAKALA V. Roth-erev reinforcement learning approach for smart generator bidding towards long term electricity market operation using agent based dynamic modeling[J]. Electric Power Components and Systems, 2020, 48 (3): 256- 267.
|
| 21 |
ESMAEILI ALIABADI D, KAYA M, SAHIN G. Competition, risk and learning in electricity markets: an agent-based simulation study[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 195, 1000- 1011.
|
| 22 |
孙庆凯, 王小君, 王怡, 等. 基于多智能体Nash-Q强化学习的综合能源市场交易优化决策[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (16): 124- 133.
|
|
SUN Qingkai, WANG Xiaojun, WANG Yi, et al. Optimal trading decision-making for integrated energy market based on multi-agent nash-Q reinforcement learning[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (16): 124- 133.
|
| 23 |
LIU D N, WANG W Y, WANG L X, et al. Dynamic pricing strategy of electric vehicle aggregators based on DDPG reinforcement learning algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 21556- 21566.
|
| 24 |
LIANG Y C, GUO C L, DING Z H, et al. Agent-based modeling in electricity market using deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2020, 35 (6): 4180- 4192.
|
| 25 |
周斌, 崔雪, 邹晨露, 等. 基于合作博弈的风水火联合运营研究[J]. 电测与仪表, 2019, 56 (6): 69- 75.
|
|
ZHOU Bin, CUI Xue, ZOU Chenlu, et al. Research on wind-hydro-thermal power joint operation based on cooperative game theory[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2019, 56 (6): 69- 75.
|
| 26 |
陆承宇, 江婷, 邓晖, 等. 基于合作博弈的含清洁能源发电商参与现货市场竞价策略及收益分配[J]. 电力建设, 2020, 41 (12): 150- 158.
|
|
LU Chengyu, JIANG Ting, DENG Hui, et al. Bidding strategy and profit distribution of power generation company with clean energy in spot market based on cooperative game theory[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2020, 41 (12): 150- 158.
|
| 27 |
邢通. 大规模风电参与电力市场交易机制及优化模型研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2020.
|
|
XING Tong. The research on the transaction mechanism and optimization mode for large scale wind power participating in the power market. [D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2020.
|
| 28 |
袁桂丽, 贾新潮, 房方, 等. 虚拟电厂源荷双侧热电联合随机优化调度[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (8): 2932- 2940.
|
|
YUAN Guili, JIA Xinchao, FANG Fang, et al. Joint stochastic optimal scheduling of heat and power considering source and load sides of virtual power plant[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (8): 2932- 2940.
|
| 29 |
肖云鹏, 张兰, 张轩, 等. 包含独立储能的现货电能量与调频辅助服务市场出清协调机制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (S1): 167- 180.
|
|
XIAO Yunpeng, ZHANG Lan, ZHANG Xuan, et al. The coordinated market clearing mechanism for spot electric energy and regulating ancillary service incorporating independent energy storage resources[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (S1): 167- 180.
|
| 30 |
LILLICRAP T P, HUNT J J, PRITZEL A, et al. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning[EB/OL]. 2015: arXiv: 1509.02971.https://arxiv.org/abs/1509.02971.pdf.
|
| 31 |
ZHUO Z Y, ZHANG N, YANG J W, et al. Transmission expansion planning test system for AC/DC hybrid grid with high variable renewable energy penetration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2020, 35 (4): 2597- 2608.
|