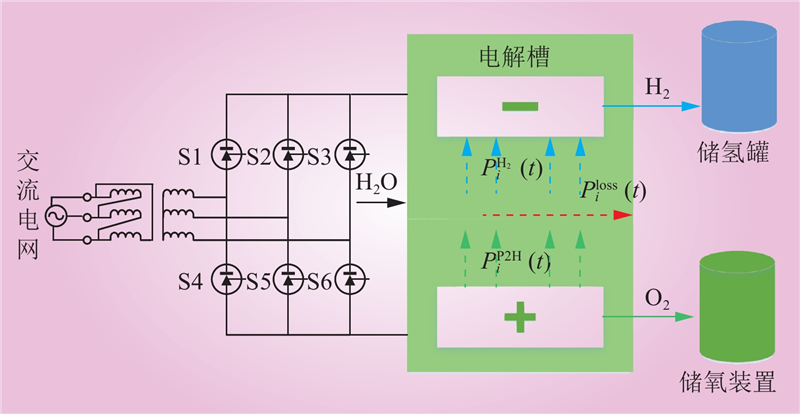
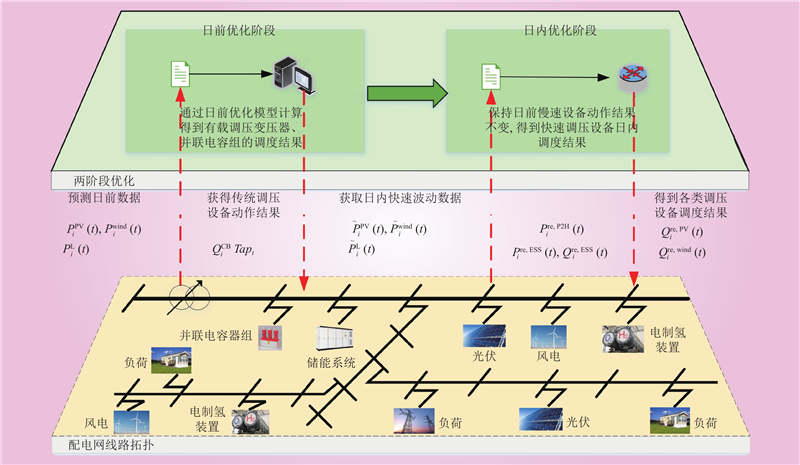
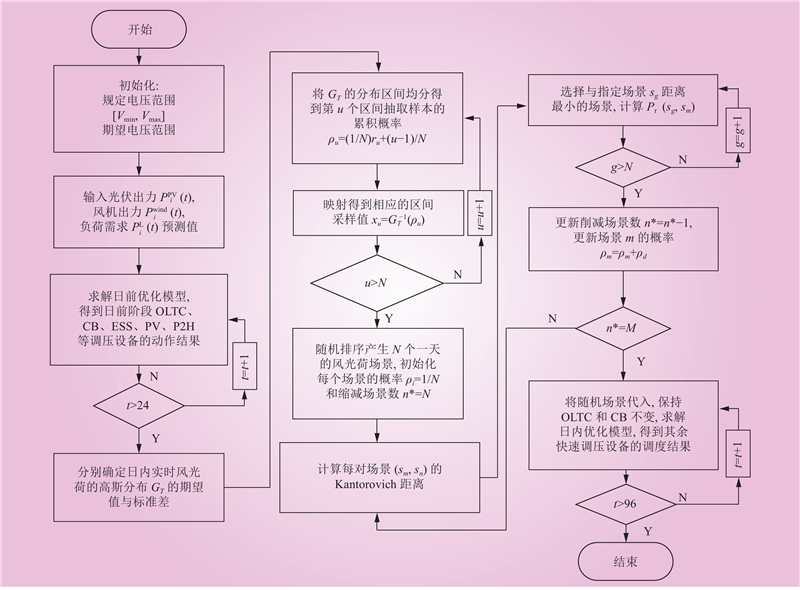
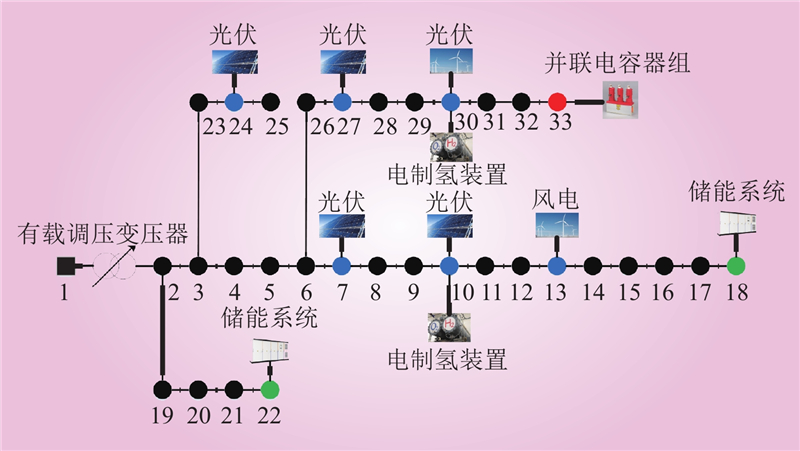
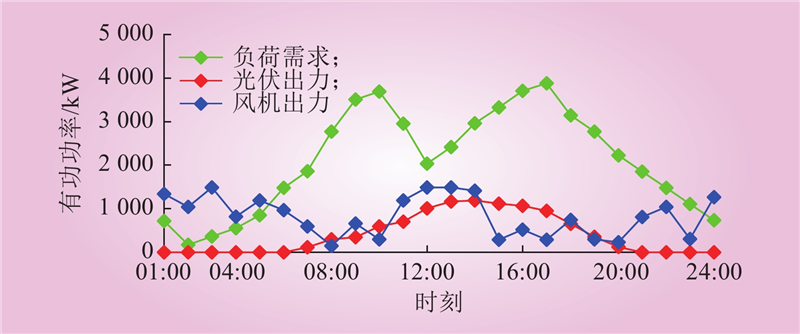
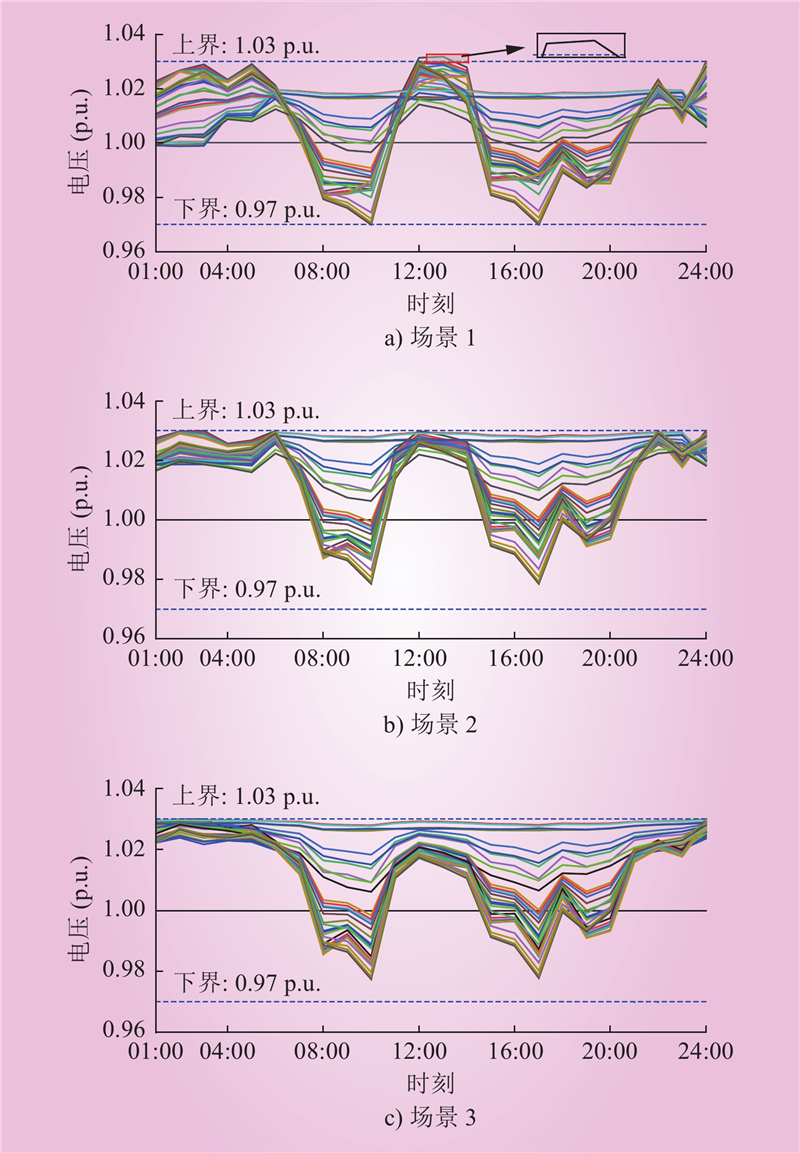
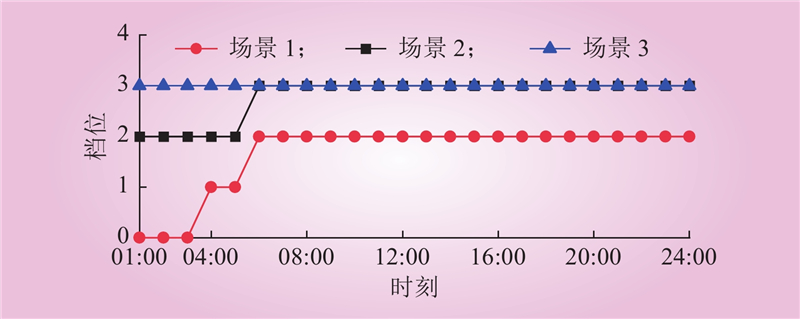
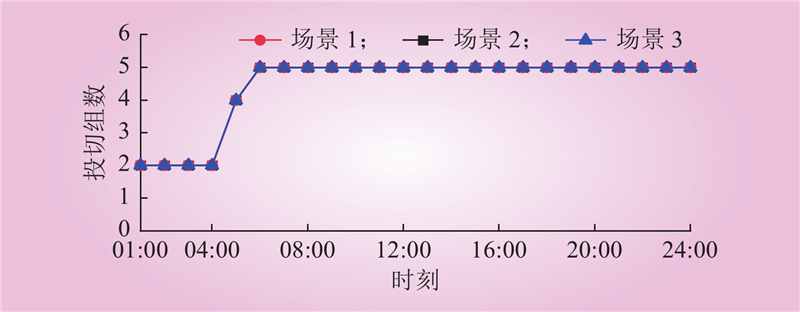
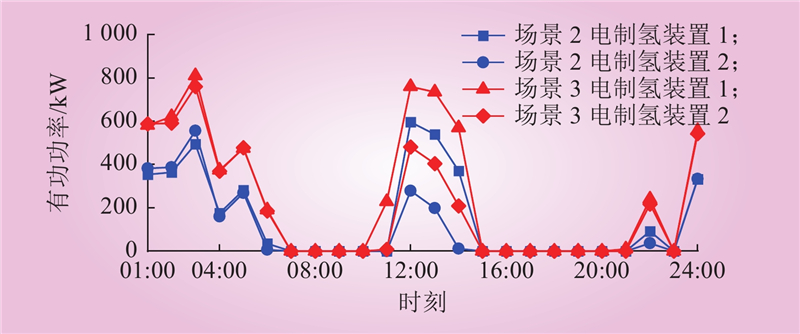
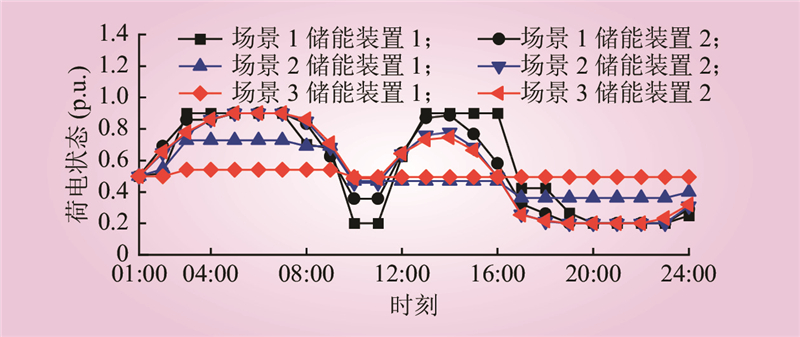
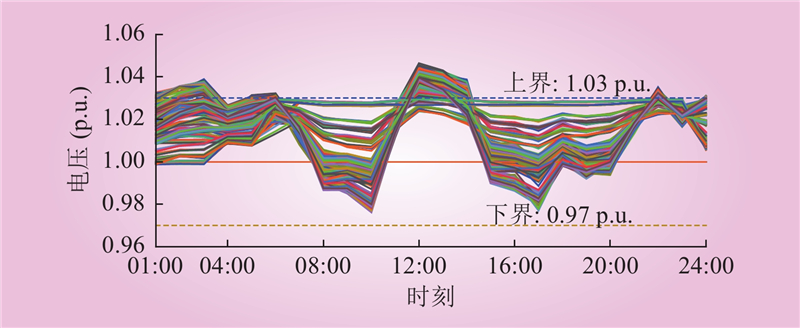
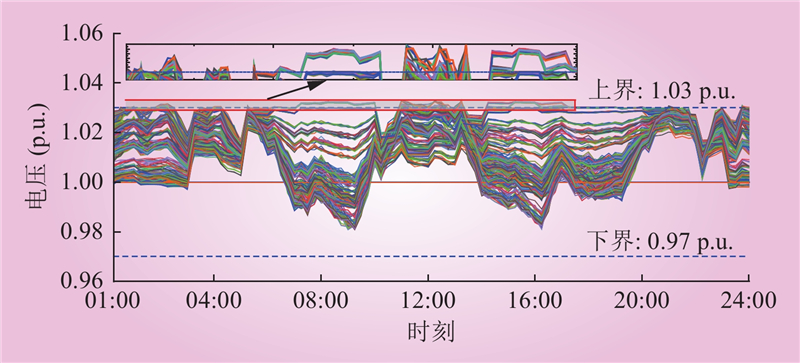
| 1 |
汪泽州, 张明明, 钱峰强, 等. 含光伏接入的中压配电网集中调控优化策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (2): 14- 22.
|
|
WANG Zezhou, ZHANG Mingming, QIAN Fengqiang, et al. Centralized regulation and optimization strategy for MV distribution network with PV integration[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (2): 14- 22.
|
| 2 |
杨宇, 文福拴, 周星龙, 等. 高光伏渗透率配电系统电压协同控制研究综述[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43 (10): 48- 58.
|
|
YANG Yu, WEN Fushuan, ZHOU Xinglong, et al. Research review of voltage cooperative control in distribution system with high photovoltaic penetration[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43 (10): 48- 58.
|
| 3 |
朱星旭, 韩学山, 杨明, 等. 含分布式光伏与储能配电网时变最优潮流追踪的分布式算法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (9): 2644- 2657.
|
|
ZHU Xingxu, HAN Xueshan, YANG Ming, et al. A distributed algorithm for time-varying optimal power flow tracking in distribution networks with photovoltaics and energy storage[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (9): 2644- 2657.
|
| 4 |
李世辉, 王琪, 贾晓卜, 等. 考虑热泵负荷和分布式光伏的配微网协调调度[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (9): 29- 37.
|
|
LI Shihui, WANG Qi, JIA Xiaobu, et al. Coordinated scheduling of distribution networks and microgrids considering heat pump load and distributed photovoltaic[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (9): 29- 37.
|
| 5 |
姜涛, 张东辉, 李雪, 等. 含分布式光伏的主动配电网电压分布式优化控制[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (9): 102- 109, 125.
|
|
JIANG Tao, ZHANG Donghui, LI Xue, et al. Distributed optimal control of voltage in active distribution network with distributed photovoltaic[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (9): 102- 109, 125.
|
| 6 |
田宇, 黄婧, 谢枭, 等. 主动配电网无功补偿和OLTC鲁棒多目标优化配置[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (3): 94- 99.
|
|
TIAN Yu, HUANG Jing, XIE Xiao, et al. Multi-objective optimal allocation of reactive compensation and OLTC in active distribution network[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (3): 94- 99.
|
| 7 |
ZHANG C, XU Y, DONG Z Y, et al. Three-stage robust inverter-based voltage/var control for distribution networks with high-level PV[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10 (1): 782- 793.
|
| 8 |
LI P, JI H R, WANG C S, et al. Coordinated control method of voltage and reactive power for active distribution networks based on soft open point[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2017, 8 (4): 1430- 1442.
|
| 9 |
SUN X Z, QIU J, YI Y, et al. Cost-effective coordinated voltage control in active distribution networks with photovoltaics and mobile energy storage systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2022, 13 (1): 501- 513.
|
| 10 |
严思韵, 王晨, 周登极. 含氢能气网掺混输运的综合能源系统优化研究[J]. 电力工程技术, 2021, 40 (1): 10- 16, 49.
|
|
YAN Siyun, WANG Chen, ZHOU Dengji. Optimization of integrated electricity and gas system considering hydrogen-natural-gas mixture transportation[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2021, 40 (1): 10- 16, 49.
|
| 11 |
岳大为, 赵文体, 袁行行, 等. 计及电-氢混合储能的孤岛直流微电网可靠性评估[J]. 电力工程技术, 2023, (3): 27- 35.
|
|
YUE Dawei, ZHAO Wenti, YUAN Hanghang, et al. Reliability evaluation of islanded DC microgrid considering electric-hydrogen hybrid energy storage[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2023, (3): 27- 35.
|
| 12 |
希望·阿不都瓦依提, 吕海鹏, 晁勤. 基于非合作博弈的风-光-氢微电网容量优化配置[J]. 电力工程技术, 2022, 41 (2): 110- 118.
|
|
XIWANG·Abuduwayiti, LYU Haipeng, CHAO Qin. Optimal capacity configuration of wind-photovoltaic-hydrogen microgrid based on non-cooperative game theory[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2022, 41 (2): 110- 118.
|
| 13 |
张长云, 黄景光, 李振兴, 等. 极地环境含风氢储混合微电网容量优化配置[J]. 电力工程技术, 2022, 41 (1): 108- 116.
|
|
ZHANG Changyun, HUANG Jingguang, LI Zhenxing, et al. Optimal configuration of wind-hydrogen-storage hybrid microgrid capacity in polar environment[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2022, 41 (1): 108- 116.
|
| 14 |
LI J R, LIN J, SONG Y H, et al. Operation optimization of power to hydrogen and heat (P2HH) in ADN coordinated with the district heating network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2019, 10 (4): 1672- 1683.
|
| 15 |
张昊天, 韦钢, 袁洪涛, 等. 考虑氢-电混合储能的直流配电网优化调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (14): 72- 81.
|
|
ZHANG Haotian, WEI Gang, YUAN Hongtao, et al. Optimal scheduling of DC distribution network considering hydrogen-power hybrid energy storage[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (14): 72- 81.
|
| 16 |
朱俊澎, 袁越, 吴涵. 考虑移动氢储能和高密度可再生能源的主动配电网优化调度[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2020, 40 (12): 42- 48.
|
|
ZHU Junpeng, YUAN Yue, WU Han. Optimal dispatch of active distribution network considering mobile hydrogen energy storage and high-density renewable energy sources[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2020, 40 (12): 42- 48.
|
| 17 |
ZHANG Y X, CHEN J, ZHAO H R, et al. Coordinated voltage control of active distribution networks with photovoltaic and power to hydrogen[J]. IET Energy Systems Integration, 2023, 5 (3): 245- 260.
|
| 18 |
李佳蓉, 林今, 邢学韬, 等. 主动配电网中基于统一运行模型的电制氢(P2H)模块组合选型与优化规划[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (12): 4021- 4032.
|
|
LI Jiarong, LIN Jin, XING Xuetao, et al. Technology portfolio selection and optimal planning of power-to-hydrogen (P2H) modules in active distribution network[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (12): 4021- 4032.
|
| 19 |
ABDIN Z, WEBB C J, GRAY E M. Modelling and simulation of a proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolyser cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40 (39): 13243- 13257.
|
| 20 |
魏繁荣, 随权, 林湘宁, 等. 考虑制氢设备效率特性的煤风氢能源网调度优化策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (5): 1428- 1439.
|
|
WEI Fanrong, SUI Quan, LIN Xiangning, et al. Energy control scheduling optimization strategy for coal-wind-hydrogen energy grid under consideration of the efficiency features of hydrogen production equipment[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (5): 1428- 1439.
|
| 21 |
张春雁, 窦真兰, 王俊, 等. 电解水制氢-储氢-供氢在电力系统中的发展路线[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (3): 305- 317.
|
|
ZHANG Chunyan, DOU Zhenlan, WANG Jun, et al. Development route of hydrogen production by water electrolysis, hydrogen storage and hydrogen supply in power system[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (3): 305- 317.
|
| 22 |
RUAN H B, GAO H J, LIU Y B, et al. Distributed voltage control in active distribution network considering renewable energy: a novel network partitioning method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2020, 35 (6): 4220- 4231.
|
| 23 |
李军徽, 孙大朋, 朱星旭, 等. 光伏高渗透率下分布式储能群间协同的电压控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (10): 47- 56.
|
|
LI Junhui, SUN Dapeng, ZHU Xingxu, et al. Voltage regulation strategy for distributed energy storage considering coordination among clusters with high penetration of photovoltaics[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (10): 47- 56.
|
| 24 |
RESHIKESHAN S S M, MATTHIESEN S L, ILLINDALA M S, et al. Autonomous voltage regulation by distributed PV inverters with minimal inter-node interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2021, 57 (3): 2058- 2066.
|
| 25 |
ZERAATI M, GOLSHAN M E H, GUERRERO J M. Voltage quality improvement in low voltage distribution networks using reactive power capability of single-phase PV inverters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10 (5): 5057- 5065.
|
| 26 |
XU Y, DONG Z Y, ZHANG R, et al. Multi-timescale coordinated voltage/var control of high renewable-penetrated distribution systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 32 (6): 4398- 4408.
|
| 27 |
XU Q S, YANG Y, LIU Y J, et al. An improved Latin hypercube sampling method to enhance numerical stability considering the correlation of input variables[J]. IEEE Access, 1992, 5, 15197- 15205.
|
| 28 |
YANG Y, LI H, AICHHORN A, et al. Sizing strategy of distributed battery storage system with high penetration of photovoltaic for voltage regulation and peak load shaving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2014, 5 (2): 982- 991.
|
| 29 |
林涛, 赵丹阳, 严寒. 风电消纳下多型号制氢机组阵列优化调度研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2022, 43 (11): 466- 473.
|
|
LIN Tao, ZHAO Danyang, YAN Han. Research on optimal scheduling of multi-model hydrogen generator array under wind power consumption[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2022, 43 (11): 466- 473.
|
| 30 |
SÁNCHEZ M, AMORES E, RODRÍGUEZ L, et al. Semi-empirical model and experimental validation for the performance evaluation of a 15 kW alkaline water electrolyzer[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43 (45): 20332- 20345.
|
| 31 |
李亚莎, 张永蘅, 陈俊璋, 等. 计及氢能高效利用和热电灵活输出的综合能源系统源荷灵活运行策略[J]. 广东电力, 2024, 37 (4): 49- 61.
|
|
LI Yasha, ZHANG Yongheng, CHEN Junzhang, et al. Flexible operation strategy for source and load of integrated energy system considering efficient utilization of hydrogen energy and flexible thermal and electric output[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2024, 37 (4): 49- 61.
|
| 32 |
石梦舒, 许小峰, 张继广, 等. 考虑电-氢市场的虚拟电厂两阶段优化策略研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (5): 645- 655.
|
|
SHI Mengshu, XU Xiaofeng, ZHANG Jiguang, et al. A two-stage optimization strategy for virtual power plants considering the electricity-hydrogen market[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (5): 645- 655.
|
| 33 |
胡轶坤, 曹军文, 张文强, 等. 高温固体氧化物电解池应用研究进展[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (3): 361- 372.
|
|
HU Yikun, CAO Junwen, ZHANG Wenqiang, et al. Application research progress of high temperature solid oxide electrolysis cell[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (3): 361- 372.
|
| 34 |
谭笑, 华栋. 源荷协同下计及电转氢和电动汽车的含风电配网日前优化调度[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (4): 144- 155,166.
|
|
TAN Xiao, HUA Dong. Day-ahead optimal dispatch of wind power distribution network with P2H and EVs in consideration of source-load coordination[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (4): 144- 155,166.
|
| 35 |
欧珊珊, 江岳文. 氢能证书交易体系及其对制氢优化的影响[J]. 广东电力, 2023, 36 (10): 30- 38.
|
|
OU Shanshan, JIANG Yuewen. Hydrogen certificate trade system and its influence on hydrogen production optimization[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2023, 36 (10): 30- 38.
|
| 36 |
钱俊杰, 徐懂理, 袁乐, 等. 计及全过程碳足迹和灵活输出模型的综合能源系统低碳经济运行[J]. 广东电力, 2023, 36 (10): 19- 29.
|
|
QIAN Junjie, XU Dongli, YUAN Le, et al. Low-carbon economic operation model of integrated energy system considering the whole process carbon footprint and flexible output models[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2023, 36 (10): 19- 29.
|