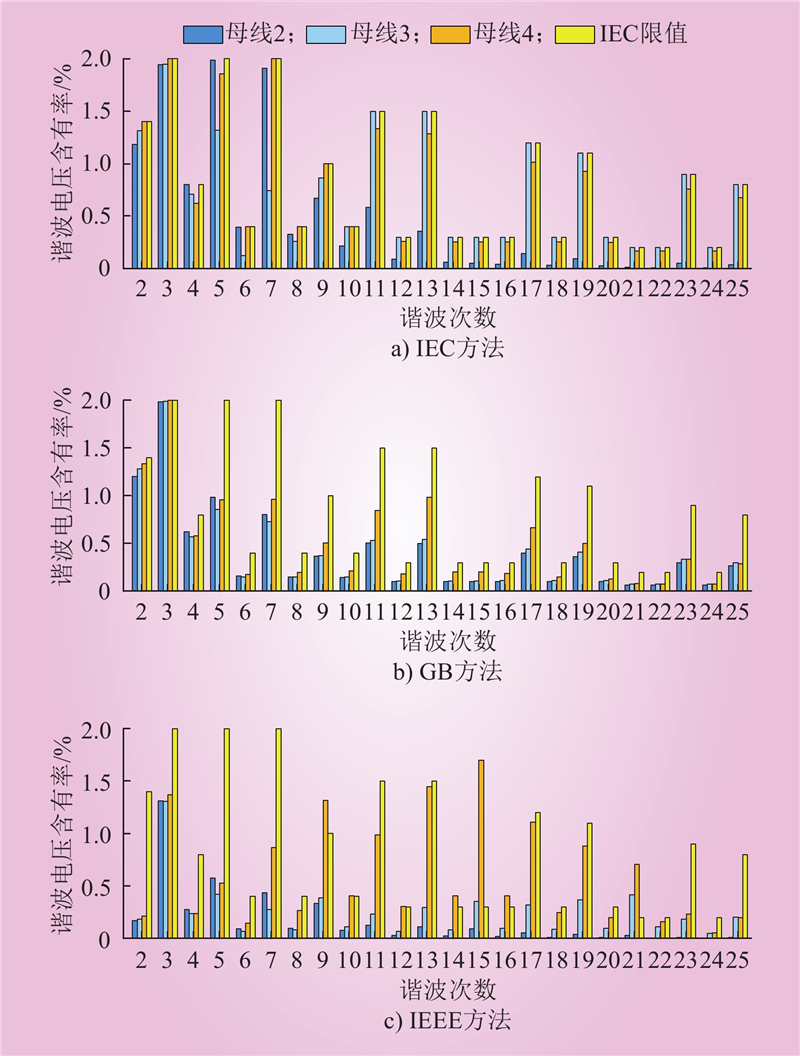
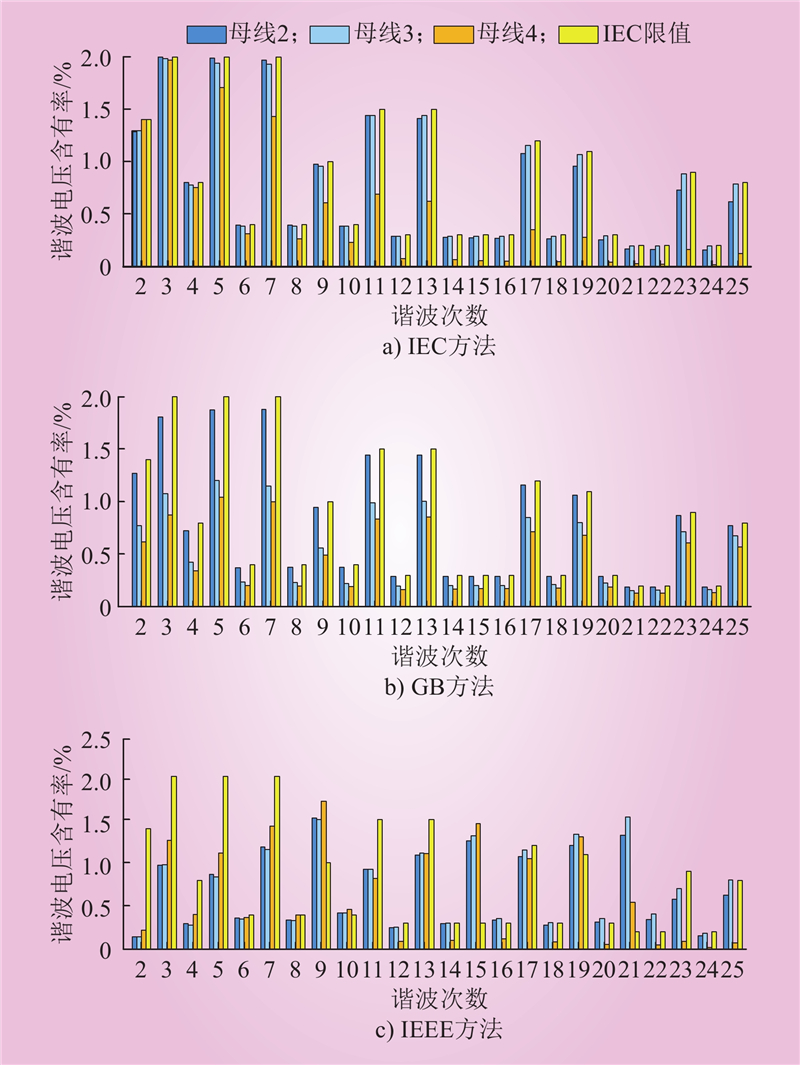
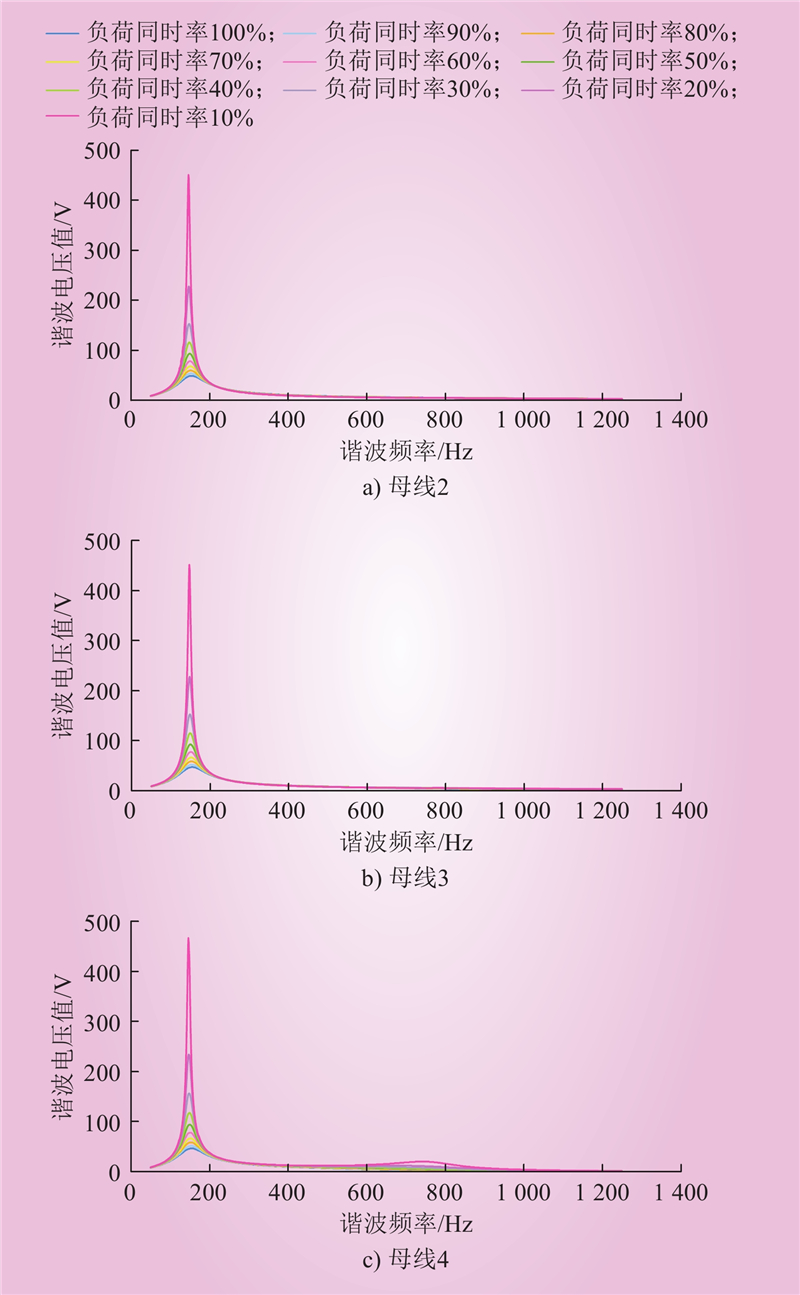
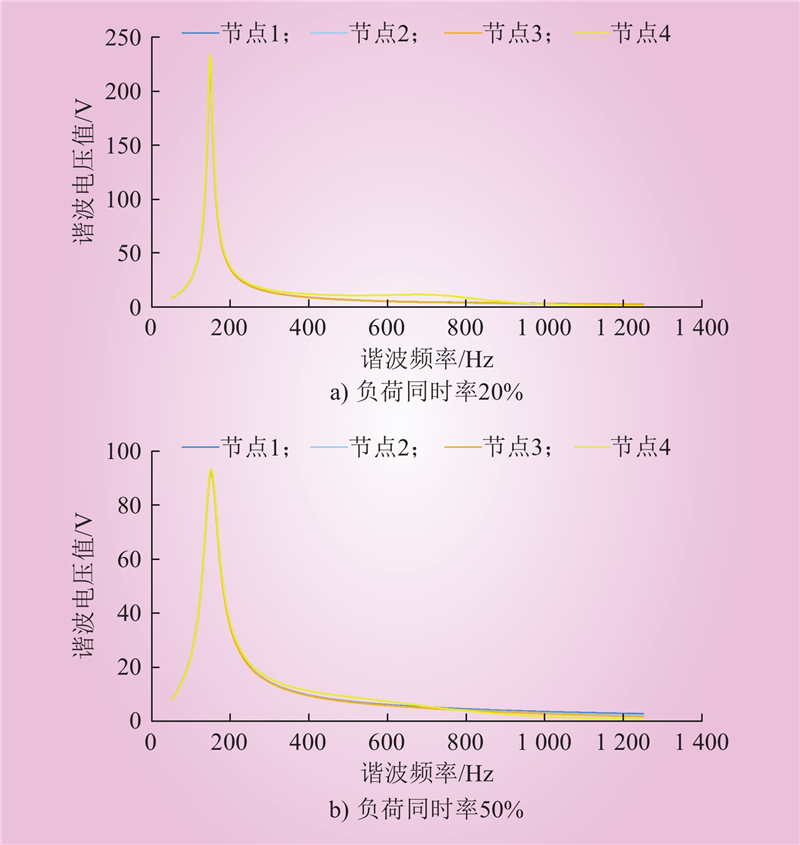
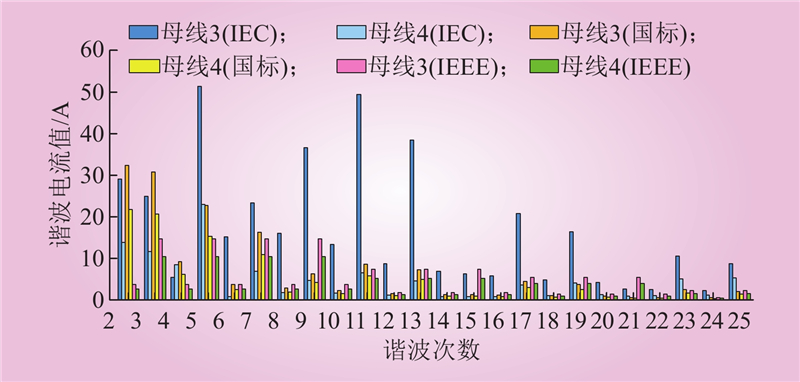
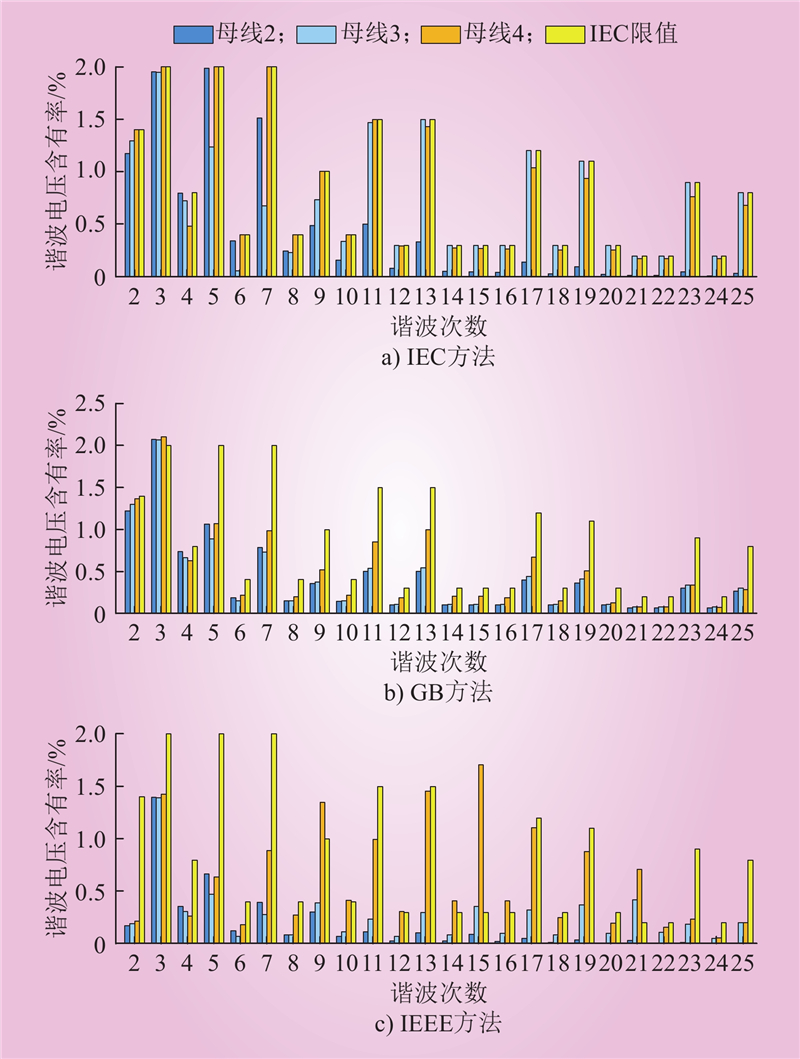
| 1 |
孙秋野, 隋政麒, 王睿, 等. “双高” 电力系统非经典稳定性分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (S1): 1- 13.
|
| 2 |
成和祥. 基于双馈风机短路特性的风电场集电线路继电保护整定方法研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48 (16): 93- 99.
|
|
CHENG Hexiang. Discussion on setting scheme of collecting line relay protection in wind farm based on a DFIG short-circuit characteristic[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48 (16): 93- 99.
|
| 3 |
刘可, 王轩, 王杨, 等. 静止无功发生器谐波模型及其对谐振影响分析[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (9): 174- 182.
|
|
LIU Ke, WANG Xuan, WANG Yang, et al. Harmonic model of static var generator and analysis of its resonance influence[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (9): 174- 182.
|
| 4 |
曾令华, 程亮, 张靖宗. 交流变频调速系统仿真建模及谐波特性分析[J]. 发电技术, 2019, 40 (3): 294- 299.
|
|
ZENG Linghua, CHENG Liang, ZHANG Jingzong. Simulation model of AC variable frequency speed regulation system and harmonic characteristics analysis[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2019, 40 (3): 294- 299.
|
| 5 |
付豪, 杨星磊, 张斌, 等. 考虑大规模新能源接入的变压器热寿命损失分析[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2020, 35 (6): 53- 60.
|
|
FU Hao, YANG Xinglei, ZHANG Bin, et al. Analysis of transformer thermal life loss considering large-scale new energy resources access[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2020, 35 (6): 53- 60.
|
| 6 |
苏寅生, 周挺辉, 赵利刚, 等. 电力电子设备谐波对主网的影响分析与对策探索[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (2): 47- 56.
|
|
SU Yinsheng, ZHOU Tinghui, ZHAO Ligang, et al. Impact analysis and countermeasure exploration of power electronic equipment harmonics on main network[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (2): 47- 56.
|
| 7 |
解绍锋, 李群湛, 赵丽平. 谐波国家标准有关问题的探讨[J]. 电网技术, 2006, 30 (13): 94- 97.
|
|
XIE Shaofeng, LI Qunzhan, ZHAO Liping. Some discussion of state standard of harmonics[J]. Power System Technology, 2006, 30 (13): 94- 97.
|
| 8 |
李嘉彬, 杨建华, 张涛, 等. 电力电子设备谐波对配电网电压骤升的影响研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2021, 49 (5): 35- 41, 84.
|
|
LI Jiabin, YANG Jianhua, ZHANG Tao, et al. Harmonic impact of power electronic devices upon voltage swell in distribution networks[J]. Smart Power, 2021, 49 (5): 35- 41, 84.
|
| 9 |
安小宇, 张涛, 李琰琰, 等. 电容分裂式变换器模型预测三相不平衡治理策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48 (13): 142- 148.
|
|
AN Xiaoyu, ZHANG Tao, LI Yanyan, et al. Model predictive three phase unbalance controlling strategy for split capacitor converter[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48 (13): 142- 148.
|
| 10 |
林海雪. 美国谐波标准IEEE Std. 519中电流限值的介绍[J]. 供用电, 2012, 29 (6): 11- 14.
|
|
LIN Haixue. Introducing current limits in US harmonic standard IEEE Std. 519[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2012, 29 (6): 11- 14.
|
| 11 |
International Electrotechnical Commission. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Part 3-6: limits – assessment of emission limits for the connection of distorting installations to MV, HV and EHV power systems: IEC 61000-3-6: 2008[S]. 2008.
|
| 12 |
国家技术监督局. 电能质量 公用电网谐波: GB/T 14549—1993[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1994.
|
|
State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision of the People’s Republic of China. Quality of electric energy supply-Harmonics in public supply network: GB/T 14549—1993[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1994.
|
| 13 |
IEEE Standard for Harmonic Control in Electric Power Systems: IEEE Std. 519: 2022[S]. 2022.
|
| 14 |
AMORNVIPAS C, HOFMANN L. Allocating harmonic emission limits at HV and EHV based on IEC 61000–3–6 under consideration of global and future installations[C]//2011 IEEE/PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition. Phoenix, AZ, USA. IEEE, 2011: 1–8.
|
| 15 |
林海雪. 电能质量国家标准系列讲座 第3讲 公用电网谐波标准[J]. 建筑电气, 2011, 30 (6): 3- 8.
|
|
LIN Haixue. Lectures on national standard of power quality lecture three standards of harmonics in public supply network[J]. Building Electricity, 2011, 30 (6): 3- 8.
|
| 16 |
林海雪, 周胜军. 电气化铁路的谐波标准问题[J]. 中国电力, 1999, 32 (9): 55- 58.
|
|
LIN Haixue, ZHOU Shengjun. Problems on harmonics standard for electrified railway[J]. Electric Power, 1999, 32 (9): 55- 58.
|
| 17 |
吴命利, 杨少兵, 翟铁久. 电气化铁路接入电网谐波预评估有关问题分析及谐波国家标准修订建议[J]. 铁道学报, 2016, 38 (8): 1- 7.
|
|
WU Mingli, YANG Shaobing, ZHAI Tiejiu. Analysis of problems about harmonic preliminary assessment for the connection of electric railways to the power grid and suggestions on revision of national harmonic standard[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2016, 38 (8): 1- 7.
|
| 18 |
吴命利. IEEE Std 519—2014谐波标准简介[J]. 山西电力, 2016, (5): 70- 72.
|
|
WU Mingli. An introduction to the IEEE std 519—2014 harmonic standard[J]. Shanxi Electric Power, 2016, (5): 70- 72.
|
| 19 |
HALPIN S M. Comparison of IEEE and IEC harmonic standards[C]//IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting. San Francisco, CA, USA. IEEE, 2005: 2214–2216.
|
| 20 |
CHO N, LEE H, BHAT R, et al. Analysis of harmonic hosting capacity of IEEE std. 519 with IEC 61000-3-6 in distribution systems[C]//2019 IEEE PES GTD Grand International Conference and Exposition Asia (GTD Asia). Bangkok, Thailand. IEEE, 2019: 730–734.
|
| 21 |
SCHÜTTE N, NEUFELD A, HOFMANN L, et al. Harmonic emission limit allocation using VDE AR-N 4130: application and adaptation of experiences from IEC TR 61000-3-6[C]//2021 56th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC). Middlesbrough, United Kingdom. IEEE, 2021: 1–6.
|
| 22 |
林海雪. 公用电网谐波国标中的几个问题[J]. 电网技术, 2003, 27 (1): 65- 70.
|
|
LIN Haixue. Some problems in national standard for harmonics in public supply network[J]. Power System Technology, 2003, 27 (1): 65- 70.
|
| 23 |
宋一凡, 赵贺, 沈俊言, 等. GB/T 14549—93与IEEE std. 519: 2014谐波电流限值确定方法对比[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (7): 42- 48.
|
|
SONG Yifan, ZHAO He, SHEN Junyan, et al. Comparison of harmonic current limit determination methods between GB/T 14549—93 and IEEE std. 519: 2014[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (7): 42- 48.
|
| 24 |
IEEE Standard for Harmonic Control in Electric Power Systems: IEEE Std. 519: 1992[S]. 1993.
|
| 25 |
RIBEIRO P F. Common misapplications of the IEEE 519 harmonic standard: Voltage or current limits[C]//2008 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting - Conversion and Delivery of Electrical Energy in the 21st Century. Pittsburgh, PA, USA. IEEE, 2008: 1–3.
|
| 26 |
Network modelling for harmonic studies[M]. CIGRE. 2019: 71.
|