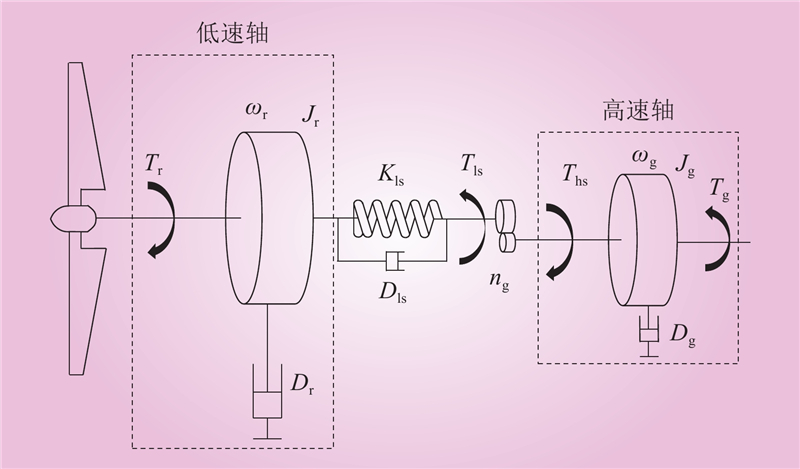
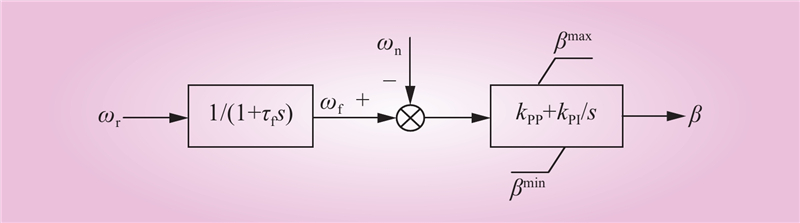
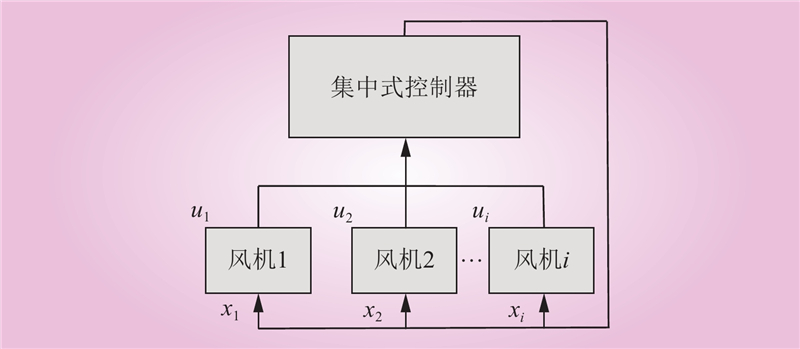
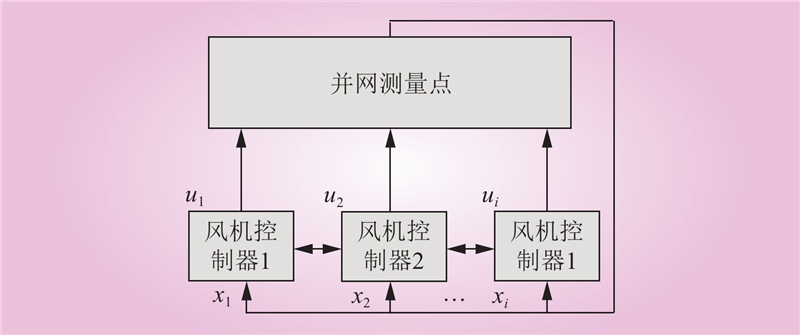
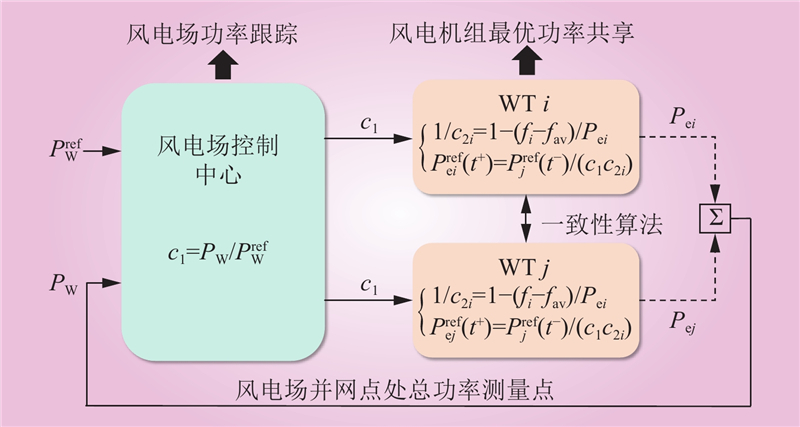
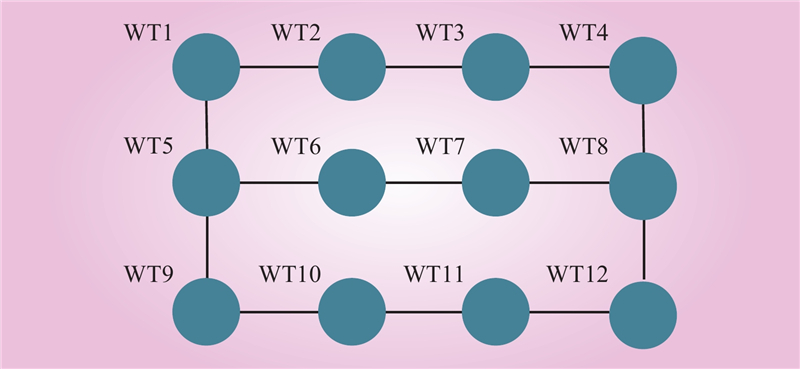
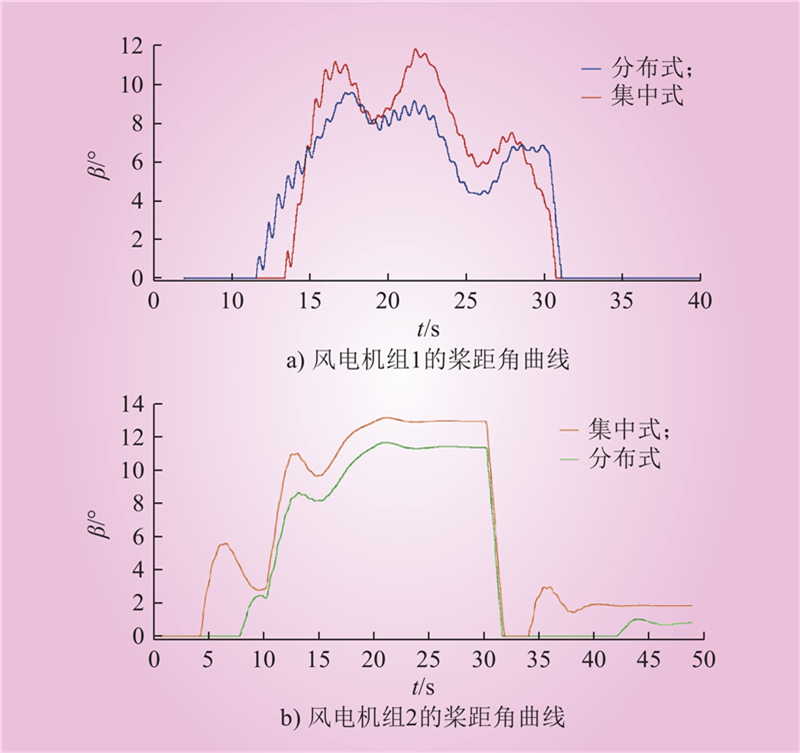
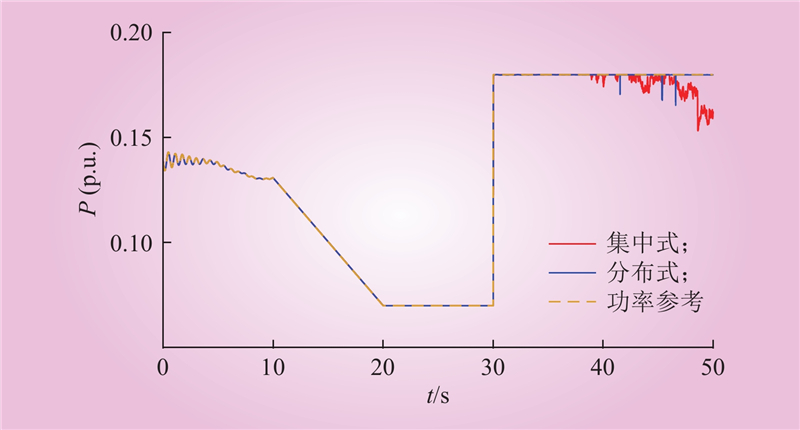
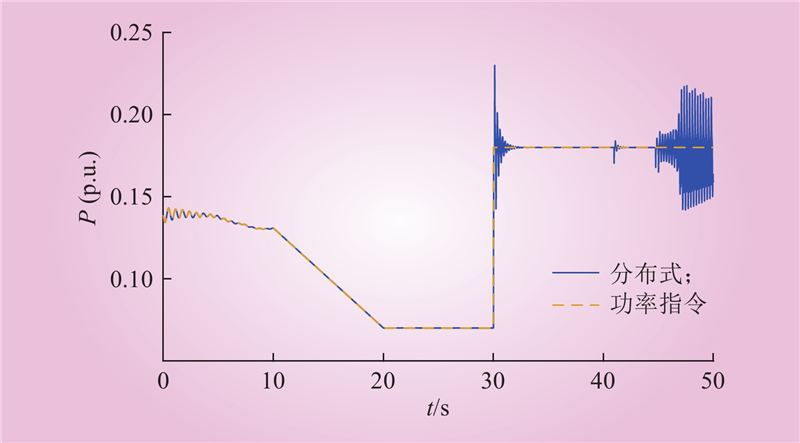
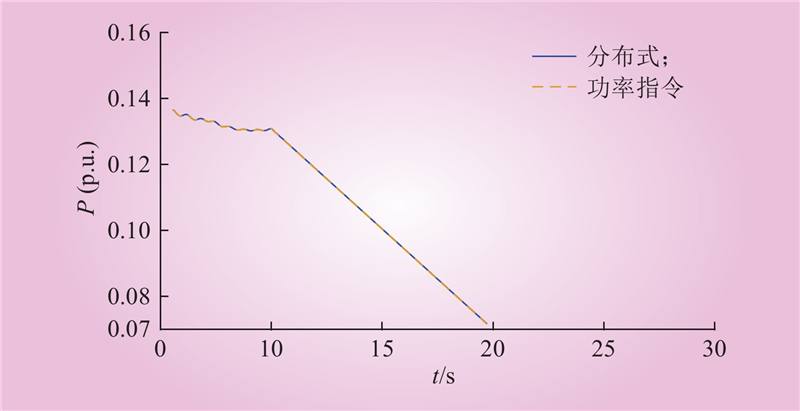
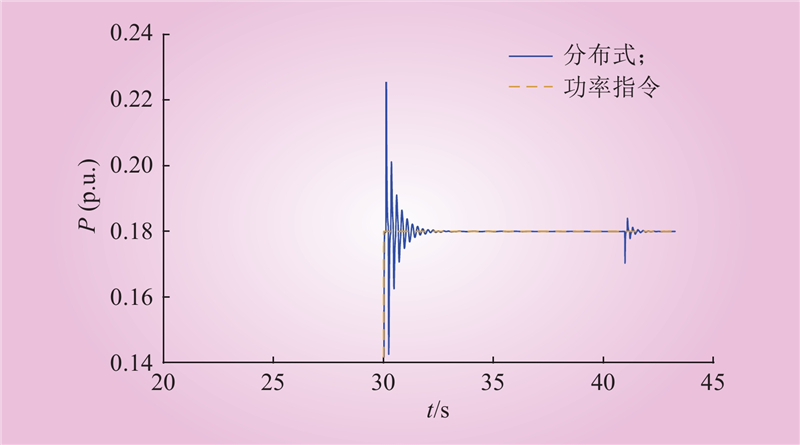
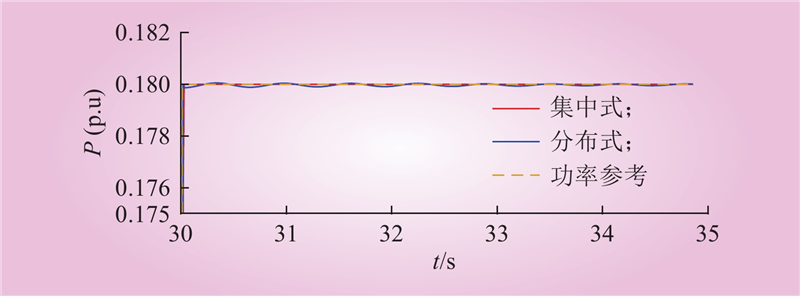
| 1 |
田刚领, 武鸿鑫, 李娟, 等. 风电场多功能储能电站功率分配策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (9): 247- 256.
|
|
TIAN Gangling, WU Hongxin, LI Juan, et al. Power distribution strategy of multi-functional energy storage powerstation in wind farm[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (9): 247- 256.
|
| 2 |
梁伟, 吴林林, 赖启平, 等. 风电直流送出系统送端交流故障下风机过电压研究[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (4): 28- 37.
|
|
LIANG Wei, WU Linlin, LAI Qiping, et al. Study on overvoltage of wind farm under AC fault at sending end of HVDC transmission system[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (4): 28- 37.
|
| 3 |
段瑶. 考虑大规模风电对电网频率影响的快速随机潮流算法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2017, 32 (4): 44- 49.
|
|
DUAN Yao. Fast probabilistic power flow algorithm considering the impact on power frequencyof large scale wind power injection[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2017, 32 (4): 44- 49.
|
| 4 |
郑华, 伏睿, 张颖, 等. 构网型储能系统与风力发电的协同控制研究[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2023, 21 (11): 48- 54.
|
|
ZHENG Hua, FU Rui, ZHANG Ying, et al. Research on collaborative control of the grid-forming electrical storage system with the wind power plant[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2023, 21 (11): 48- 54.
|
| 5 |
李东东, 董楠, 姚寅, 等. 考虑频率响应分散性及系统分区的含风电系统等效惯量估计[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (3): 36- 45.
|
|
LI Dongdong, DONG Nan, YAO Yin, et al. Equivalent inertia estimation of a power system containing wind power considering dispersion offrequency response and system partitioning[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (3): 36- 45.
|
| 6 |
MORREN J, DE HAAN S W H, KLING W L, et al. Wind turbines emulating inertia and supporting primary frequency control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2006, 21 (1): 433- 434.
|
| 7 |
江灿. 大规模风电场群参与系统一次调频策略研究[D]. 包头: 内蒙古科技大学, 2023.
|
|
JIANG Can. Large-scale wind farm groups participate in the study of primary frequency modulation strategies[D]. Baotou: Inner Mongolia University of Science & Technology, 2023.
|
| 8 |
唐坚, 唐庆宏, 姚禹歌, 等. 风电调频能力的潜力分析[J]. 动力工程学报, 2022, 42 (11): 1138- 1145.
|
|
TANG Jian, TANG Qinghong, YAO Yuge, et al. Potential analysis of frequency regulation ability of wind power in the view of energy[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2022, 42 (11): 1138- 1145.
|
| 9 |
HENDRAWATI D, DIONOVA B W, Sahid, et al. Design of wind turbines power coefficient on wind farm based centralized control[C]//2021 International Seminar on Intelligent Technology and Its Applications (ISITIA). Surabaya, Indonesia. IEEE, 2021: 315–318.
|
| 10 |
BONALA A K, SANDEPUDI S R. Centralised model-predictive decoupled active–reactive power control for three-level neutral point clamped photovoltaic inverter with preference selective index-based objective prioritisation[J]. IET Power Electronics, 2019, 12 (4): 840- 851.
|
| 11 |
杨伟峰, 文云峰, 李立, 等. 考虑疲劳载荷的风电场分散式频率响应策略[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2022, 42 (4): 55- 62.
|
|
YANG Weifeng, WEN Yunfeng, LI Li, et al. Decentralized frequency response strategy for wind farm considering fatigue load[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022, 42 (4): 55- 62.
|
| 12 |
姚琦, 胡阳, 柳玉, 等. 考虑载荷抑制的风电场分布式自动发电控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37 (3): 697- 706.
|
|
YAO Qi, HU Yang, LIU Yu, et al. Distributed automatic generation control of wind farm considering load suppression[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37 (3): 697- 706.
|
| 13 |
杨伟峰, 文云峰, 张武其, 等. 基于风-储联合的双层频率响应控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (12): 184- 193.
|
|
YANG Weifeng, WEN Yunfeng, ZHANG Wuqi, et al. Bi-level frequency response control strategy based on wind power and energy storage[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (12): 184- 193.
|
| 14 |
侯婷. 考虑疲劳优化的风电场分布式有功功率分配策略研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2021.
|
|
HOU Ting. Research on wind farm distributed active power allocation strategy considering fatigue optimization. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021.
|
| 15 |
姚琦. 风电场有功调度与频率支撑优化控制研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2020.
|
|
YAO Qi. Research on active power dispatching and frequency optimization control of wind farm[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2020.
|
| 16 |
王瑞田. 基于MPC的风电场有功分配策略研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2021.
|
|
WANG Ruitian. Research on active power distribution strategy of wind farm based on MPC[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021.
|
| 17 |
KONG X B, MA L L, WANG C, et al. Large-scale wind farm control using distributed economic model predictive scheme[J]. Renewable Energy, 2022, 181, 581- 591.
|
| 18 |
刘肖杰. 基于分布式模型预测控制的孤岛微电网电压协调优化控制策略研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2022.
|
|
LIU Xiaojie. Coordinated Optimization Control Strategy of Voltagefor Islanded Microgrid Based on Distributed ModelPredictive Control[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2022.
|
| 19 |
薛帅. 大规模海上风电场有功功率的分层分布式控制[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2021.
|
|
XUE Shuai. Hierarchical distributed active power control for large-scale wind farm[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2021.
|
| 20 |
黄鑫, 王婕, 邢侃. 双馈风力发电系统的MPPT自适应滑模控制[J]. 水电能源科学, 2021, 39 (12): 214- 218.
|
|
HUANG Xin, WANG Jie, XING Kan. Adaptive sliding mode control for maximum power point tracking of doubly-fed wind turbine[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2021, 39 (12): 214- 218.
|
| 21 |
陈载宇, 沈春, 殷明慧, 等. 面向AGC的变速变桨风电机组有功功率控制策略[J]. 电力工程技术, 2017, 36 (1): 9- 14.
|
|
CHEN Zaiyu, SHEN Chun, YIN Minghui, et al. Review of active power control strategy for variable-speed variable-pitch wind turbine participating in AGC[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2017, 36 (1): 9- 14.
|
| 22 |
张继勇, 嵇仁君, 马一鸣, 等. 风力发电变桨距模糊自适应PID控制[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2022, 12 (33): 16- 19.
|
|
ZHANG Jiyong, JI Renjun, MA Yiming, et al. Fuzzy adaptive PID control of variable pitch for wind power generation[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2022, 12 (33): 16- 19.
|
| 23 |
曹俊伟, 张硕望, 黄凌翔, 等. 基于自适应桨距角控制策略的风电机组发电性能优化方法[J]. 太阳能, 2024, (5): 52- 61.
|
|
CAO Junwei, ZHANG Shuowang, HUANG Lingxiang, et al. Optimization method for wind turbine power generation performance based on self-adaption pitch angle control strategy[J]. Solar Energy, 2024, (5): 52- 61.
|
| 24 |
陈载宇. 低风速风力机最大功率点跟踪控制的性能分析与改进方法[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2019.
|
|
CHEN Zaiyu. Performance analysis and improvements for maximum power point tracking control of low wind speed wind turbines[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2019.
|
| 25 |
李斌, 张镇麒, 于浩辉, 等. 风力发电机组泵控液压系统变桨距控制研究[J]. 液压与气动, 2023, 47 (4): 27- 35.
|
|
LI Bin, ZHANG Zhenqi, YU Haohui, et al. Study on variable pitch control of pump controlled hydraulic system of wind turbine[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2023, 47 (4): 27- 35.
|
| 26 |
卢奭瑄, 史航. 风力发电机组的桨距角控制技术分析[J]. 集成电路应用, 2023, 40 (9): 70- 72.
|
|
LU Shixuan, SHI Hang. Analysis of pitch angle control technology for wind turbine generators[J]. Application of IC, 2023, 40 (9): 70- 72.
|
| 27 |
王东风, 张鹏, 黄宇, 等. 针对风机变桨距控制系统隐蔽攻击的防御方法研究[J]. 电力科学与工程, 2024, 40 (5): 47- 54.
|
|
WANG Dongfeng, ZHANG Peng, HUANG Yu, et al. Research on the defense method of covert attack for variable pitch control system of wind turbine[J]. Electric Power Science and Engineering, 2024, 40 (5): 47- 54.
|