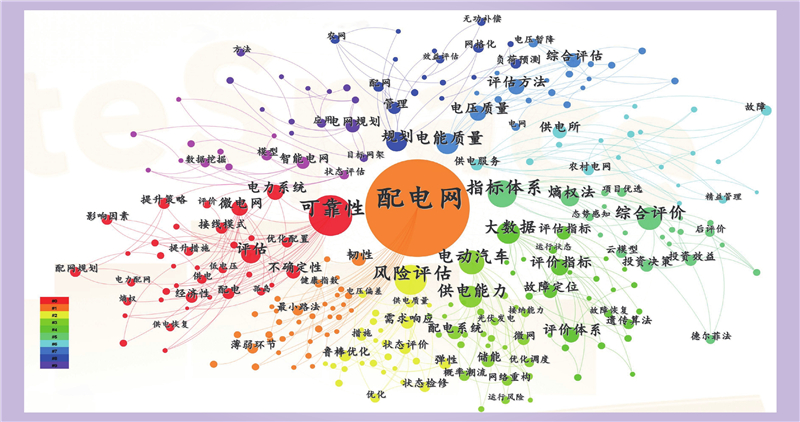
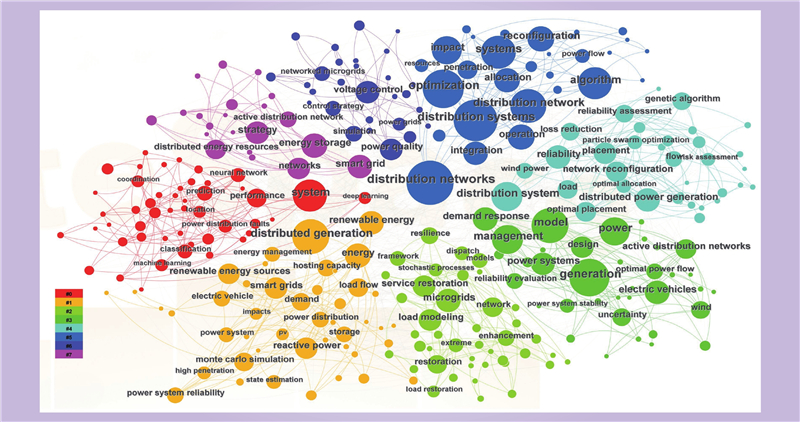
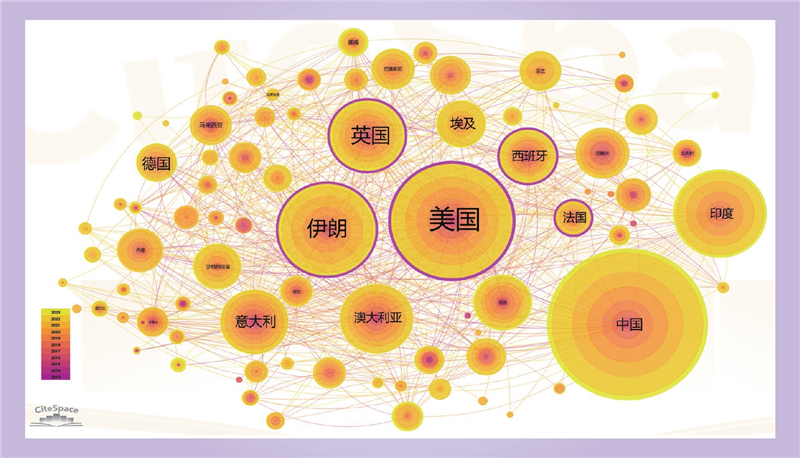
| 1 |
ECKSTEIN D, KÜNZEL V, SCHÄFER L. The global climate risk index 2021[R]. Bonn: Germanwatch, 2021.
|
| 2 |
胡源, 薛松, 张寒, 等. 近30年全球大停电事故发生的深层次原因分析及启示[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (10): 204- 210.
|
|
HU Yuan, XUE Song, ZHANG Han, et al. Cause analysis and enlightenment of global blackouts in the past 30 years[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (10): 204- 210.
|
| 3 |
梁海平, 石皓岩, 王岩, 等. 基于提升韧性的输电网灾后应急维修策略优化[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (3): 142- 151.
|
|
LIANG Haiping, SHI Haoyan, WANG Yan, et al. Resilience-improving based optimization of post-disaster emergency maintenance strategy for transmission networks[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (3): 142- 151.
|
| 4 |
傅守强, 陈翔宇, 张立斌, 等. 面向韧性提升的交直流混合配电网协同恢复方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (7): 95- 106.
|
|
FU Shouqiang, CHEN Xiangyu, ZHANG Libin, et al. Coordinated restoration method of hybrid AC/DC distribution networks for resilience enhancement[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (7): 95- 106.
|
| 5 |
何维国, 王赛一, 许唐云, 等. 城市韧性配电网建设与发展路径[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (2): 680- 690.
|
|
HE Weiguo, WANG Saiyi, XU Tangyun, et al. Construction and development path of the urban resilient distribution network[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (2): 680- 690.
|
| 6 |
高海翔, 陈颖, 黄少伟, 等. 配电网韧性及其相关研究进展[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (23): 1- 8.
|
|
GAO Haixiang, CHEN Ying, HUANG Shaowei, et al. Distribution systems resilience: an overview of research progress[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (23): 1- 8.
|
| 7 |
王成山, 李鹏, 于浩. 智能配电网的新形态及其灵活性特征分析与应用[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (10): 13- 21.
|
|
WANG Chengshan, LI Peng, YU Hao. Development and characteristic analysis of flexibility in smart distribution network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42 (10): 13- 21.
|
| 8 |
邓红雷, 戴栋, 李述文. 基于层次分析-熵权组合法的架空输电线路综合运行风险评估[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2017, 45 (1): 28- 34.
|
|
DENG Honglei, DAI Dong, LI Shuwen. Comprehensive operation risk evaluation of overhead transmission line based on hierarchical analysis-entropy weight method[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2017, 45 (1): 28- 34.
|
| 9 |
李娜娜, 何正友. 主客观权重相结合的电能质量综合评估[J]. 电网技术, 2009, 33 (6): 55- 61.
|
|
LI Nana, HE Zhengyou. Power quality comprehensive evaluation combining subjective weight with objective weight[J]. Power System Technology, 2009, 33 (6): 55- 61.
|
| 10 |
高贺, 孙莹, 李可军, 等. 一种新型智能配电网风险评估模型[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2016, 36 (6): 142- 147.
|
|
GAO He, SUN Ying, LI Kejun, et al. Risk assessment model of smart distribution grid[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2016, 36 (6): 142- 147.
|
| 11 |
边疆, 王洪妤, 林子钊, 等. 城市中压配电网风险综合评估方法[J]. 电气应用, 2015, 34 (5): 130- 135.
|
| 12 |
梁朔, 秦丽文, 李春华, 等. 基于风险评估的配电设备状态检修决策方法[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2019, 31 (1): 47- 52.
|
|
LIANG Shuo, QIN Liwen, LI Chunhua, et al. Condition-based maintenance decision-making method for distribution equipment based on risk assessment[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2019, 31 (1): 47- 52.
|
| 13 |
王增平, 戴志辉. 含风力发电的配网电流保护运行风险评估[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2013, 33 (6): 7- 12.
|
|
WANG Zengping, DAI Zhihui. Operation risk assessment for current protection of distribution network with wind farm[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2013, 33 (6): 7- 12.
|
| 14 |
李强, 赵健, 王磊, 等. 配电网馈线负荷预测及风险评估预警分析方法[J]. 供用电, 2020, 37 (5): 50- 55.
|
|
LI Qiang, ZHAO Jian, WANG Lei, et al. Distribution network feeder load forecasting and risk assessment warning analysis method[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2020, 37 (5): 50- 55.
|
| 15 |
刘科研, 盛万兴, 张东霞, 等. 智能配电网大数据应用需求和场景分析研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35 (2): 287- 293.
|
|
LIU Keyan, SHENG Wanxing, ZHANG Dongxia, et al. Big data application requirements and scenario analysis in smart distribution network[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35 (2): 287- 293.
|
| 16 |
秦丽文, 梁朔, 高立克, 等. 全面数据质量管理框架在配电网领域的应用分析[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2020, 32 (4): 62- 68.
|
|
QIN Liwen, LIANG Shuo, GAO Like, et al. Application analysis of comprehensive data quality management framework in distribution network[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2020, 32 (4): 62- 68.
|
| 17 |
杨凤生, 曾惜, 王元峰, 等. 面向大数据应用的配电网运行状态评估方法探讨[J]. 科技与创新, 2018, (17): 4- 6.
|
| 18 |
陈磊, 邓欣怡, 陈红坤, 等. 电力系统韧性评估与提升研究综述[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (13): 11- 22.
|
|
CHEN Lei, DENG Xinyi, CHEN Hongkun, et al. Review of the assessment and improvement of power system resilience[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (13): 11- 22.
|
| 19 |
李娜, 佟春生. 基于DPSIR模型的城市配电网规划评价指标体系研究[J]. 电气工程学报, 2016, 11 (2): 28- 32.
|
|
LI Na, TONG Chunsheng. Study of assessment index system of urban distribution network planning based on DPSIR model[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2016, 11 (2): 28- 32.
|
| 20 |
欧阳森, 刘丽媛. 配电网用电可靠性指标体系及综合评估方法[J]. 电网技术, 2017, 41 (1): 215- 222.
|
|
OUYANG Sen, LIU Liyuan. Reliability index system of distribution network for power consumer and its comprehensive assessment method[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41 (1): 215- 222.
|
| 21 |
董明, 徐恩, 王文强, 等. 基于风险决策矩阵的配电网项目储备库管理[J]. 湖北电力, 2017, 41 (1): 14- 19.
|
|
DONG Ming, XU En, WANG Wenqiang, et al. Management of distribution network repository based on risk-decision matrix[J]. Hubei Electric Power, 2017, 41 (1): 14- 19.
|
| 22 |
李舰. 农网改造升级工程管理的问题与措施分析[J]. 通讯世界, 2017, (15): 215- 216.
|
| 23 |
杨蕴华, 陈杰, 程刚, 等. 标准化在配电网工程建设及造价管理中的应用[J]. 中国电力企业管理, 2016, (12): 14- 17.
|
| 24 |
马丽, 张建华, 刘念, 等. 城市配电网规划方案的多阶段综合评估方法[J]. 中国电力, 2013, 46 (11): 150- 154, 159.
|
|
MA Li, ZHANG Jianhua, LIU Nian, et al. Multistage comprehensive evaluation of urban power distribution network planning[J]. Electric Power, 2013, 46 (11): 150- 154, 159.
|
| 25 |
李鹏, 王瑞, 冀浩然, 等. 低碳化智能配电网规划研究与展望[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (24): 10- 21.
|
|
LI Peng, WANG Rui, JI Haoran, et al. Research and prospect of planning for low-carbon smart distribution network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (24): 10- 21.
|
| 26 |
曹华珍, 王天霖, 陈沛东, 等. 考虑城市场景需求的中压直流配电网规划选优分析方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (2): 77- 83.
|
|
CAO Huazhen, WANG Tianlin, CHEN Peidong, et al. Optimal selection analysis method of MVDC distribution network planning considering urban scenario demand[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (2): 77- 83.
|
| 27 |
韦涛, 马钊, 苏剑, 等. 配电网规划计算分析软件研发与应用[J]. 南方电网技术, 2016, 10 (5): 38- 44.
|
|
WEI Tao, MA Zhao, SU Jian, et al. Development and application of distribution network planning calculation and analysis software[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2016, 10 (5): 38- 44.
|
| 28 |
李辉. 城市供电可靠性提升措施探讨[J]. 技术与市场, 2015, 22 (12): 297.
|
| 29 |
赵渊, 何媛, 宿晓岚, 等. 分布式电源对配网可靠性的影响及优化配置[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2014, 34 (9): 13- 20.
|
|
ZHAO Yuan, HE Yuan, SU Xiaolan, et al. Effect of distributed generation on power distribution system reliability and its optimal allocation[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2014, 34 (9): 13- 20.
|
| 30 |
杨金涛, 乐健, 刘开培, 等. 基于LCC的配电网供电电压质量改善措施的优化[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2015, 35 (8): 59- 64.
|
|
YANG Jintao, LE Jian, LIU Kaipei, et al. Improvement measure optimization based on LCC for voltage quality of distribution network[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2015, 35 (8): 59- 64.
|
| 31 |
黄德华, 余涛, 张水平. 配网电能质量监测与高级分析软件平台的设计与实现[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2013, 41 (3): 128- 133.
|
|
HUANG Dehua, YU Tao, ZHANG Shuiping. Design and implementation of a power quality monitoring and advanced analysis software in distribution network[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2013, 41 (3): 128- 133.
|
| 32 |
左伟杰, 马钊, 周莉梅, 等. 基于配电网电能质量健康评估策略的分布式光伏接入方法[J]. 电网技术, 2015, 39 (12): 3442- 3448.
|
|
ZUO Weijie, MA Zhao, ZHOU Limei, et al. Grid-connection of distributed photovoltaic generation method based on the power quality health status of distribution system[J]. Power System Technology, 2015, 39 (12): 3442- 3448.
|
| 33 |
李琼林, 刘书铭, 温佳静, 等. 计及电能质量影响的10 kV配电网损耗计算模型及其实验验证[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2022, 42 (1): 212- 220.
|
|
LI Qionglin, LIU Shuming, WEN Jiajing, et al. Calculation model of 10 kV distribution network loss considering power quality impact and its experimental verification[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022, 42 (1): 212- 220.
|
| 34 |
陈厚合, 刘丽娜, 姜涛, 等. 提升配电网电压质量的分布式储能经济优化配置方法[J]. 电网技术, 2018, 42 (7): 2127- 2135.
|
|
CHEN Houhe, LIU Lina, JIANG Tao, et al. Optimal economic configuration of distributed energy storage systems for improving voltage quality in distribution network[J]. Power System Technology, 2018, 42 (7): 2127- 2135.
|
| 35 |
管永高, 许文超, 汤奕, 等. 基于有向图和序贯蒙特卡洛法的含电动汽车配电网可靠性评估[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2019, 35 (3): 49- 57.
|
|
GUAN Yonggao, XU Wenchao, TANG Yi, et al. Reliability evaluation of distribution network with electric vehicles based on digraph and sequential Monte Carlo method[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2019, 35 (3): 49- 57.
|
| 36 |
赵胜霞, 刘俊勇, 向月, 等. 考虑配电网接纳能力的电动汽车充换电服务网基础设施配置方案分析与评估[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2016, 36 (6): 94- 101.
|
|
ZHAO Shengxia, LIU Junyong, XIANG Yue, et al. Analysis and assessment considering accommodation capability of distribution network for infrastructure deployment of EV charging/swapping service network[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2016, 36 (6): 94- 101.
|
| 37 |
李振坤, 钱晋, 宋治儒. 考虑电动汽车停泊概率的配电网接纳电动汽车能力评估方法[J]. 智慧电力, 2021, 49 (11): 31- 37.
|
|
LI Zhenkun, QIAN Jin, SONG Zhiru. Evaluation Method of Electric Vehicle Hosting Capacity in Distribution Network Considering Electric Vehicle Parking Probability[J]. Smart Power, 2021, 49 (11): 31- 37.
|
| 38 |
王龙宇, 刘灿, 王丙东, 等. 考虑微网充电站影响的输电网风险评估方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46 (5): 114- 121.
|
|
WANG Longyu, LIU Can, WANG Bingdong, et al. Risk based assessment method for transmission system considering the influence of micro-grid charging station[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2018, 46 (5): 114- 121.
|
| 39 |
杨昕然, 吕林, 向月, 等. “车-路-网”耦合下电动汽车恶劣充电场景及其对城市配电网电压稳定性影响[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2019, 39 (10): 102- 108, 122.
|
|
YANG Xinran, LÜ Lin, XIANG Yue, et al. Degradation charging scenarios and impacts on voltage stability of urban distribution network under "EV-road-grid" coupling[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2019, 39 (10): 102- 108, 122.
|
| 40 |
王婷, 陈晨, 谢海鹏. 配电网对分布式电源和电动汽车的承载力评估及提升方法综述[J]. 电力建设, 2022, 43 (9): 12- 24.
|
|
WANG Ting, CHEN Chen, XIE Haipeng. Review on evaluation and promotion methods of carrying capacity for distributed generation and electric vehicles in distribution network[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2022, 43 (9): 12- 24.
|
| 41 |
王守相, 陈建凯, 王洪坤, 等. 综合考虑电动汽车充电与储能及可中断负荷调度的配电网两阶段灵活性提升优化方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2020, 40 (11): 1- 10.
|
|
WANG Shouxiang, CHEN Jiankai, WANG Hongkun, et al. Two-stage flexibility improvement optimization method of distribution network considering EV charging and scheduling of energy storage and interruptible loads[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2020, 40 (11): 1- 10.
|
| 42 |
杨祺铭, 李更丰, 别朝红, 等. 台风灾害下基于V2G的城市配电网弹性提升策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (12): 130- 139.
|
|
YANG Qiming, LI Gengfeng, BIE Zhaohong, et al. Vehicle-to-grid based resilience promotion strategy for urban distribution network under typhoon disaster[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (12): 130- 139.
|
| 43 |
AVALOS R J, CAÑIZARES C, MILANO F, et al. Equivalency of continuation and optimization methods to determine saddle-node and limit-induced bifurcations in power systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 2009, 56 (1): 210- 223.
|
| 44 |
佟曦, 侯朗博, 孙昊, 等. 高比例光伏和电动汽车接入配电网的无功优化[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (10): 31- 37, 102.
|
|
TONG Xi, HOU Langbo, SUN Hao, et al. Reactive power optimization of distribution networks with high proportion of PV and EVs[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (10): 31- 37, 102.
|
| 45 |
CHEHRI A, FOFANA I, YANG X M. Security risk modeling in smart grid critical infrastructures in the era of big data and artificial intelligence[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13 (6): 3196.
|
| 46 |
RAZAVI S E, AREFI A, LEDWICH G, et al. From load to net energy forecasting: short-term residential forecasting for the blend of load and PV behind the meter[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 224343- 224353.
|
| 47 |
BOUBAKER S, BENGHANEM M, MELLIT A, et al. Deep neural networks for predicting solar radiation at hail region, Saudi Arabia[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 36719- 36729.
|
| 48 |
MOHAMMADPOURFARD M, KHALILI A, GENC I, et al. Cyber-resilient smart cities: detection of malicious attacks in smart grids[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021, 75, 103116.
|
| 49 |
ZHANG J H, YAN J, INFIELD D, et al. Short-term forecasting and uncertainty analysis of wind turbine power based on long short-term memory network and Gaussian mixture model[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 241, 229- 244.
|
| 50 |
CHEN M R, ZENG G Q, LU K D, et al. A two-layer nonlinear combination method for short-term wind speed prediction based on ELM, ENN, and LSTM[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6 (4): 6997- 7010.
|
| 51 |
BABAR M, TARIQ M U, AHMAD JAN M. Secure and resilient demand side management engine using machine learning for IoT-enabled smart grid[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2020, 62, 102370.
|
| 52 |
ISMAEL S M, ABDEL ALEEM S H E, ABDELAZIZ A Y, et al. State-of-the-art of hosting capacity in modern power systems with distributed generation[J]. Renewable Energy, 2019, 130, 1002- 1020.
|
| 53 |
DAS H S, RAHMAN M M, LI S, et al. Electric vehicles standards, charging infrastructure, and impact on grid integration: a technological review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 120, 109618.
|
| 54 |
WIDÉN J, CARPMAN N, CASTELLUCCI V, et al. Variability assessment and forecasting of renewables: a review for solar, wind, wave and tidal resources[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 44, 356- 375.
|
| 55 |
SHAUKAT N, KHAN B, ALI S M, et al. A survey on electric vehicle transportation within smart grid system[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 81, 1329- 1349.
|
| 56 |
DEO R C, WEN X H, QI F. A wavelet-coupled support vector machine model for forecasting global incident solar radiation using limited meteorological dataset[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 168, 568- 593.
|
| 57 |
ABEYSEKERA M, WU J, JENKINS N, et al. Steady state analysis of gas networks with distributed injection of alternative gas[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 164, 991- 1002.
|
| 58 |
WANG Y, XU Y, HE J H, et al. Coordinating multiple sources for service restoration to enhance resilience of distribution systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10 (5): 5781- 5793.
|
| 59 |
DING T, WANG Z K, JIA W H, et al. Multiperiod distribution system restoration with routing repair crews, mobile electric vehicles, and soft-open-point networked microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11 (6): 4795- 4808.
|
| 60 |
LEI S B, WANG J H, CHEN C, et al. Mobile emergency generator pre-positioning and real-time allocation for resilient response to natural disasters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016: 1.
|
| 61 |
KHALOIE H, ABDOLLAHI A, RASHIDINEJAD M, et al. Risk-based probabilistic-possibilistic self-scheduling considering high-impact low-probability events uncertainty[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2019, 110, 598- 612.
|
| 62 |
YAO S H, WANG P, ZHAO T Y. Transportable energy storage for more resilient distribution systems with multiple microgrids[C]//2019 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM). Atlanta, GA, USA. IEEE, 2019: 598–612.
|
| 63 |
RAO R S, RAVINDRA K, SATISH K, et al. Power loss minimization in distribution system using network reconfiguration in the presence of distributed generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28 (1): 317- 325.
|
| 64 |
SHAABAN M F, ATWA Y M, EL-SAADANY E F. DG allocation for benefit maximization in distribution networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28 (2): 639- 649.
|
| 65 |
CLEMENT-NYNS K, HAESEN E, DRIESEN J. The impact of charging plug-In hybrid electric vehicles on a residential distribution grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2010, 25 (1): 371- 380.
|
| 66 |
ZIMMERMAN R D, MURILLO-SANCHEZ C E, THOMAS R J. MATPOWER: steady-state operations, planning, and analysis tools for power systems research and education[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2011, 26 (1): 12- 19.
|
| 67 |
GEORGILAKIS P S, HATZIARGYRIOU N D. Optimal distributed generation placement in power distribution networks: models, methods, and future research[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28 (3): 3420- 3428.
|
| 68 |
GEORGILAKIS P S, HATZIARGYRIOU N D. A review of power distribution planning in the modern power systems era: models, methods and future research[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2015, 121, 89- 100.
|
| 69 |
WANG Z Y, WANG J H. Self-healing resilient distribution systems based on sectionalization into microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2015, 30 (6): 3139- 3149.
|
| 70 |
LI J A, MA X Y, LIU C C, et al. Distribution system restoration with microgrids using spanning tree search[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2014, 29 (6): 3021- 3029.
|
| 71 |
CAPITANESCU F, OCHOA L F, MARGOSSIAN H, et al. Assessing the potential of network reconfiguration to improve distributed generation hosting capacity in active distribution systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2015, 30 (1): 346- 356.
|
| 72 |
PANTELI M, MANCARELLA P. The grid: stronger, bigger, smarter?: presenting a conceptual framework of power system resilience[J]. IEEE Power and Energy Magazine, 2015, 13 (3): 58- 66.
|
| 73 |
WANG Y Z, CHEN C, WANG J H, et al. Research on resilience of power systems under natural disasters-a review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2016, 31 (2): 1604- 1613.
|
| 74 |
NICK M, CHERKAOUI R, PAOLONE M. Optimal allocation of dispersed energy storage systems in active distribution networks for energy balance and grid support[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2014, 29 (5): 2300- 2310.
|
| 75 |
SEDGHI M, AHMADIAN A, ALIAKBAR-GOLKAR M. Optimal storage planning in active distribution network considering uncertainty of wind power distributed generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2015, 31 (1): 304- 316.
|
| 76 |
CHEN C, WU W C, ZHANG B M, et al. An analytical adequacy evaluation method for distribution networks considering protection strategies and distributed generators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2015, 30 (3): 1392- 1400.
|
| 77 |
WANG Z Y, CHEN B K, WANG J H, et al. Robust optimization based optimal DG placement in microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2014, 5 (5): 2173- 2182.
|
| 78 |
SALMAN A M, LI Y, STEWART M G. Evaluating system reliability and targeted hardening strategies of power distribution systems subjected to hurricanes[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2015, 144, 319- 333.
|
| 79 |
FARZIN H, FOTUHI-FIRUZABAD M, MOEINI-AGHTAIE M. Enhancing power system resilience through hierarchical outage management in multi-microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 7 (6): 2869- 2879.
|