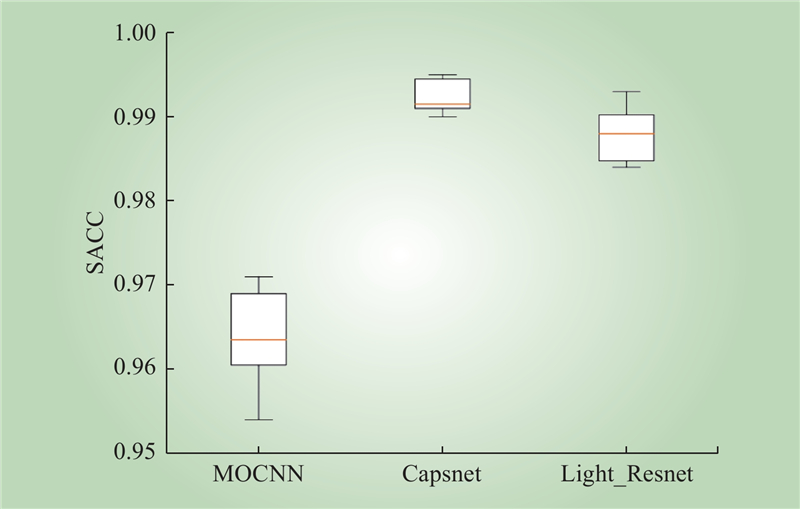
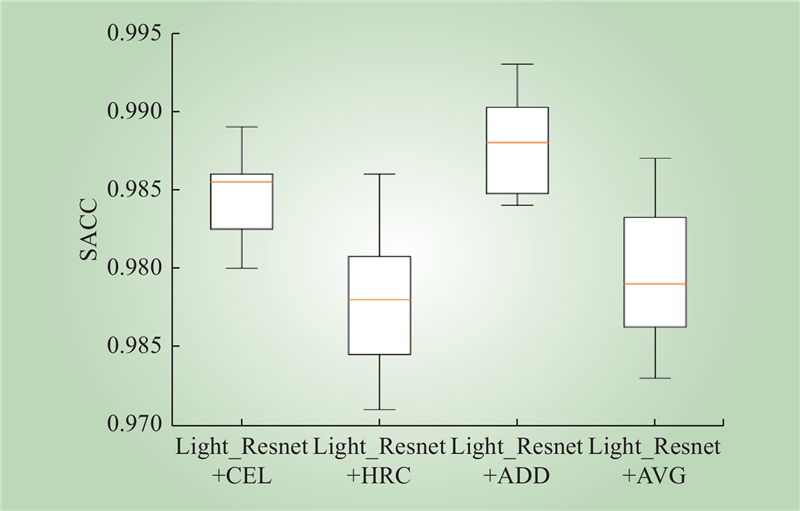
| 1 |
李博, 高志远. 人工智能技术在智能电网中的应用分析和展望[J]. 中国电力, 2017, 50 (12): 136- 140.
|
|
LI Bo, GAO Zhiyuan. Analysis and prospect on the application of artificial intelligence technologies in smart grid[J]. Electric Power, 2017, 50 (12): 136- 140.
|
| 2 |
白钒, 胡杰, 何鹏, 等. 基于物联网技术的智能电网基础设施建设数字化管理平台研究[J]. 机械与电子, 2022, 40 (10): 77- 80.
|
|
BAI Fan, HU Jie, HE Peng, et al. Research on digital management platform for smart grid infrastructure construction based on Internet of Things technology[J]. Machinery & Electronics, 2022, 40 (10): 77- 80.
|
| 3 |
ZHAO S T, LI B S, YUAN J S, et al. Research on remote meter automatic reading based on computer vision[C]//2005 IEEE/PES Transmission & Distribution Conference & Exposition: Asia and Pacific. Dalian, China. IEEE, 2005: 1–4.
|
| 4 |
EDWARD V C P. Support vector machine based automatic electric meter reading system[C]//2013 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research. Enathi, India. IEEE, 2013: 1–5.
|
| 5 |
RODRİGUEZ M, BERDUGO G, JABBA D, et al. HD_MR: a new algorithm for number recognition in electrical meters[J]. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences, 2014, 22, 87- 96.
|
| 6 |
陈英, 李磊, 汪文源, 等. 家用水表字符的识别算法研究[J]. 现代电子技术, 2018, 41 (18): 99- 103.
|
|
CHEN Ying, LI Lei, WANG Wenyuan, et al. Research on character recognition algorithm for domestic water meter[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2018, 41 (18): 99- 103.
|
| 7 |
GÓMEZ L, RUSIÑOL M, KARATZAS D. Cutting sayre’s knot: reading scene text without segmentation. application to utility meters[C]//2018 13th IAPR International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems (DAS). Vienna, Austria. IEEE, 2018: 97-102.
|
| 8 |
YANG F, JIN L W, LAI S X, et al. Fully convolutional sequence recognition network for water meter number reading[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 11679- 11687.
|
| 9 |
DA SILVA MARQUES R C, COSTA SERRA A, FERREIRA FRANÇA J V, et al. Image-based electric consumption recognition via multi-task learning[C]//2019 8th Brazilian Conference on Intelligent Systems (BRACIS). Salvador, Brazil. IEEE, 2019: 419–424.
|
| 10 |
龚安, 张洋, 唐永红. 基于YOLOv3网络的电能表示数识别方法[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2020, 29 (1): 196- 202.
|
|
GONG An, ZHANG Yang, TANG Yonghong. Automatic reading method of electric energy meter based on YOLOv3[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2020, 29 (1): 196- 202.
|
| 11 |
顾允迪, 徐望明, 何钦. 字轮式仪表智能图像抄表系统的设计[J]. 液晶与显示, 2023, 38 (7): 985- 996.
|
|
GU Yundi, XU Wangming, HE Qin. Design of image-based intelligent meter reading system for wheel meters[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2023, 38 (7): 985- 996.
|
| 12 |
吉训生, 谭凯凯. 基于卷积神经网络的水表读数识别方法[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2020, 39 (12): 130- 133.
|
|
JI Xunsheng, TAN Kaikai. Water meter character recognition method based on CNN[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2020, 39 (12): 130- 133.
|
| 13 |
HAN D, KIM H. A number recognition system with memory optimized convolutional neural network for smart metering devices[C]//2018 International Conference on Electronics, Information, and Communication (ICEIC). Honolulu, HI, USA. IEEE, 2018: 1–4.
|
| 14 |
LI C S, SU Y K, YUAN R, et al. Light-weight spliced convolution network-based automatic water meter reading in smart city[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 174359- 174367.
|
| 15 |
JUNAGADE S, JAIN P, SARANGI S, et al. Digital display recognition towards connected sensing systems for precision agriculture[C]//2021 IEEE Global Humanitarian Technology Conference (GHTC). Seattle, WA, USA. IEEE, 2021: 155–162.
|
| 16 |
XIU H, HE J, ZHANG X T, et al. HRC-mCNNs: a hybrid regression and classification multibranch CNNs for automatic meter reading with smart shell[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9 (24): 25752- 25766.
|
| 17 |
FAN Z Z, SHI L R, XI C, et al. Real time power equipment meter recognition based on deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71, 5017015.
|
| 18 |
DONG Z P, GAO Y, YAN Y H, et al. Vector detection network: an application study on robots reading analog meters in the wild[J]. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 2 (5): 394- 403.
|
| 19 |
CIPOLLA R, GAL Y, KENDALL A. Multi-task learning using uncertainty to weigh losses for scene geometry and semantics[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, UT, USA. IEEE, 2018: 7482–7491.
|
| 20 |
EVGENIOU T, PONTIL M. Regularized multi: task learning[C]//Proceedings of the tenth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining. Seattle, WA, USA. ACM, 2004: 109–117.
|
| 21 |
CARUANA R. Multitask learning[M]//Learning to Learn. Boston, MA: Springer US, 1998: 95–133.
|
| 22 |
HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA. IEEE, 2016: 770–778.
|
| 23 |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Identity mappings in deep residual networks [C]//Computer Vision – ECCV 2016. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016, 630: 45.
|
| 24 |
IOFFE S, SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning - Volume 37. Lille, France. ACM, 2015: 448–456.
|
| 25 |
GLOROT X, BORDES A, BENGIO Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 15, 315- 323.
|
| 26 |
SABOUR S, FROSST N, HINTON G E. Dynamic routing between capsules[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, California, USA. ACM, 2017: 3859–3869.
|