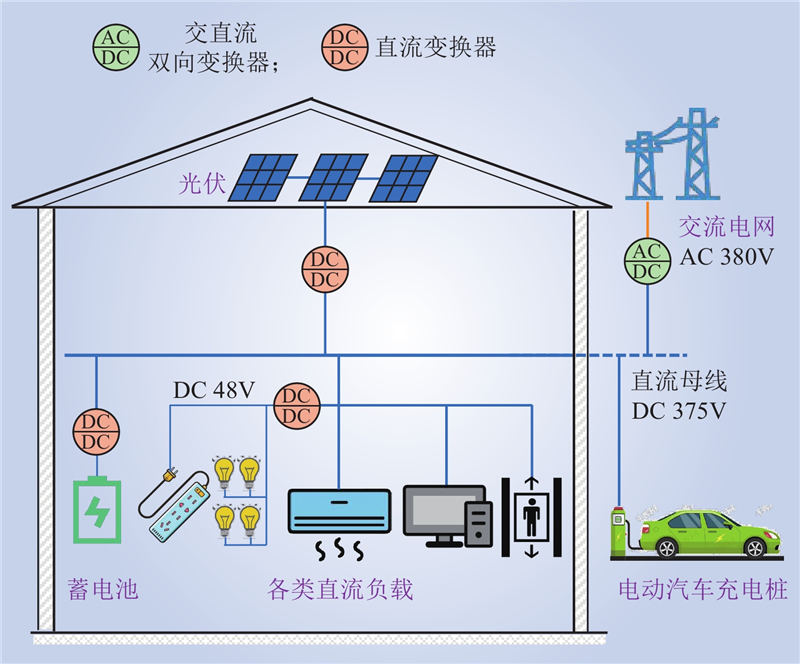
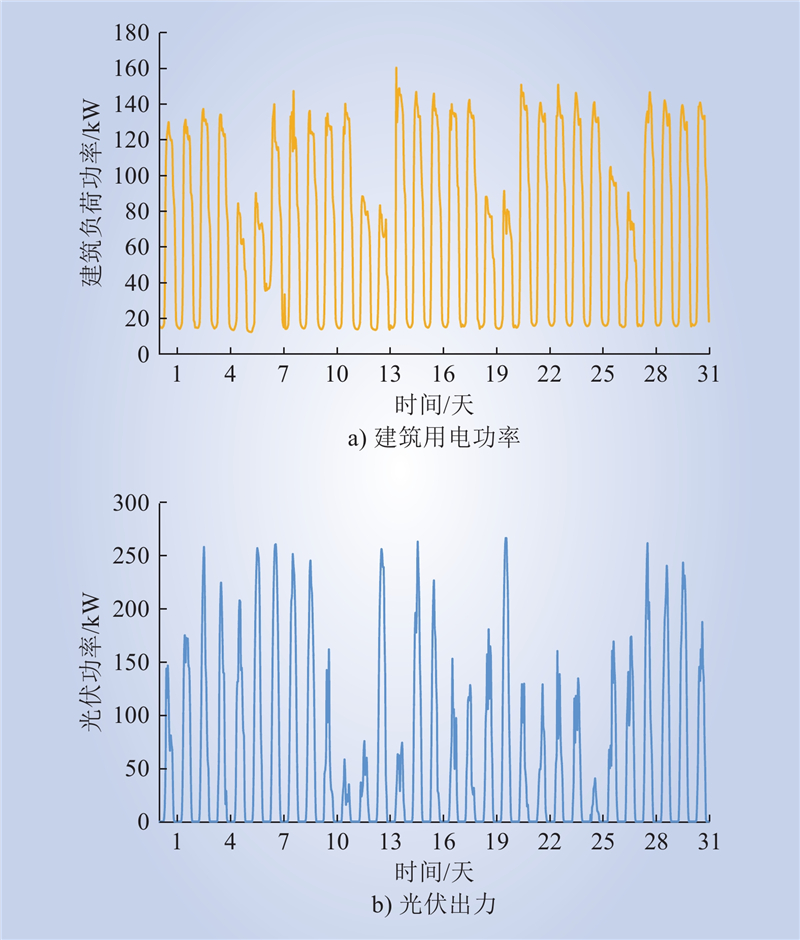
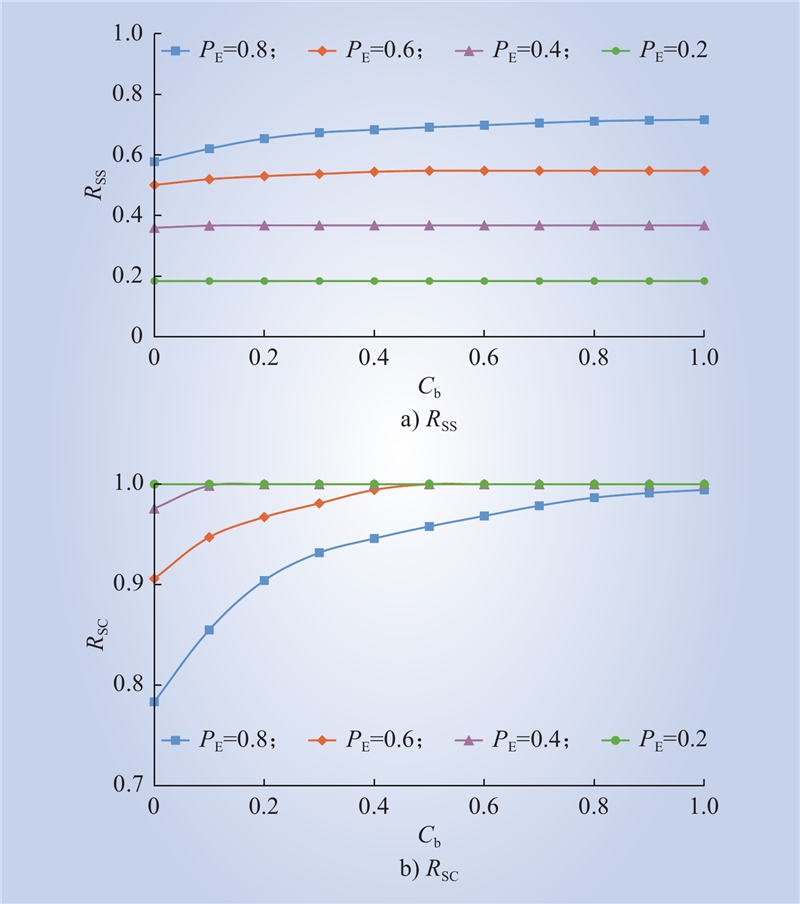
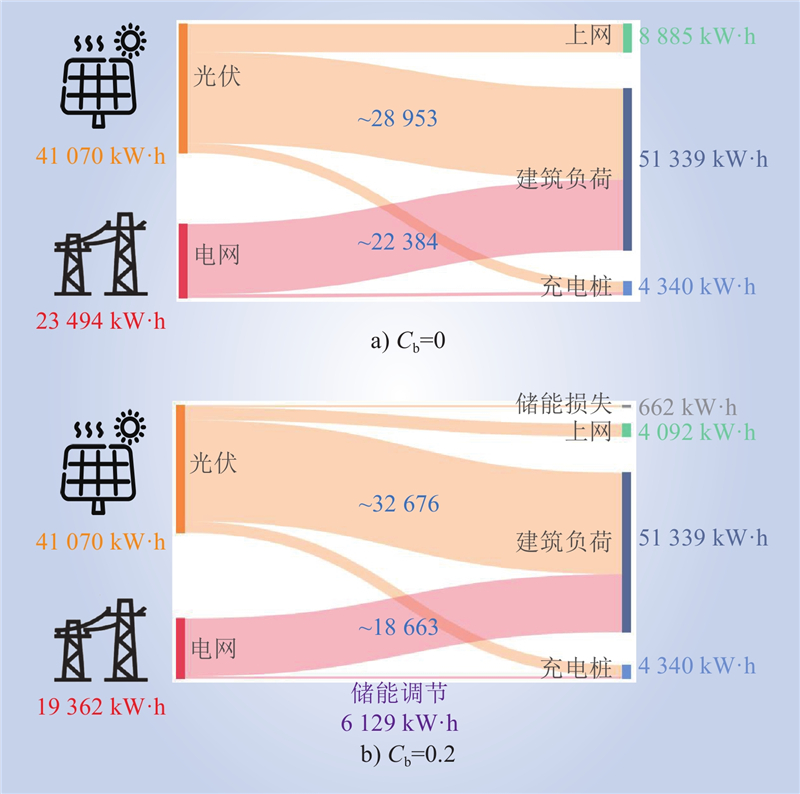
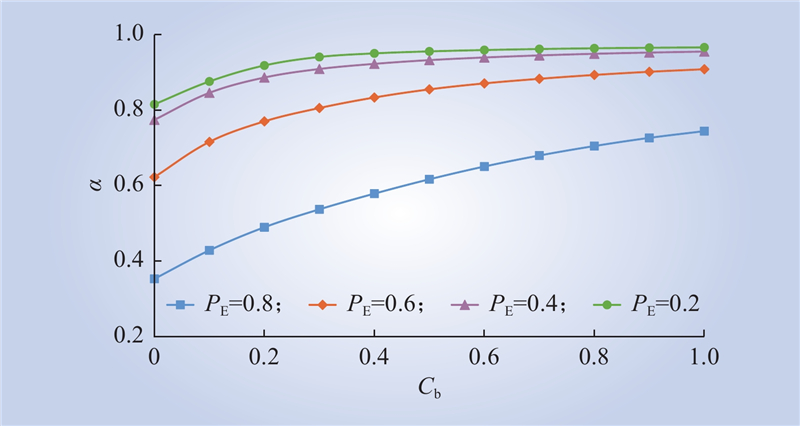
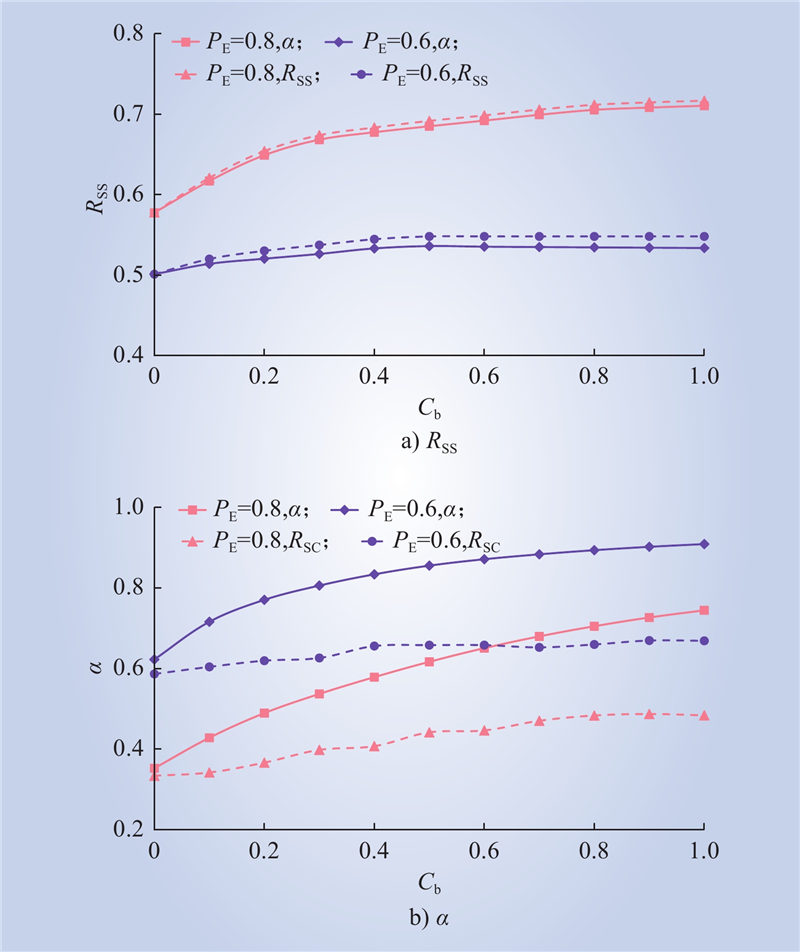
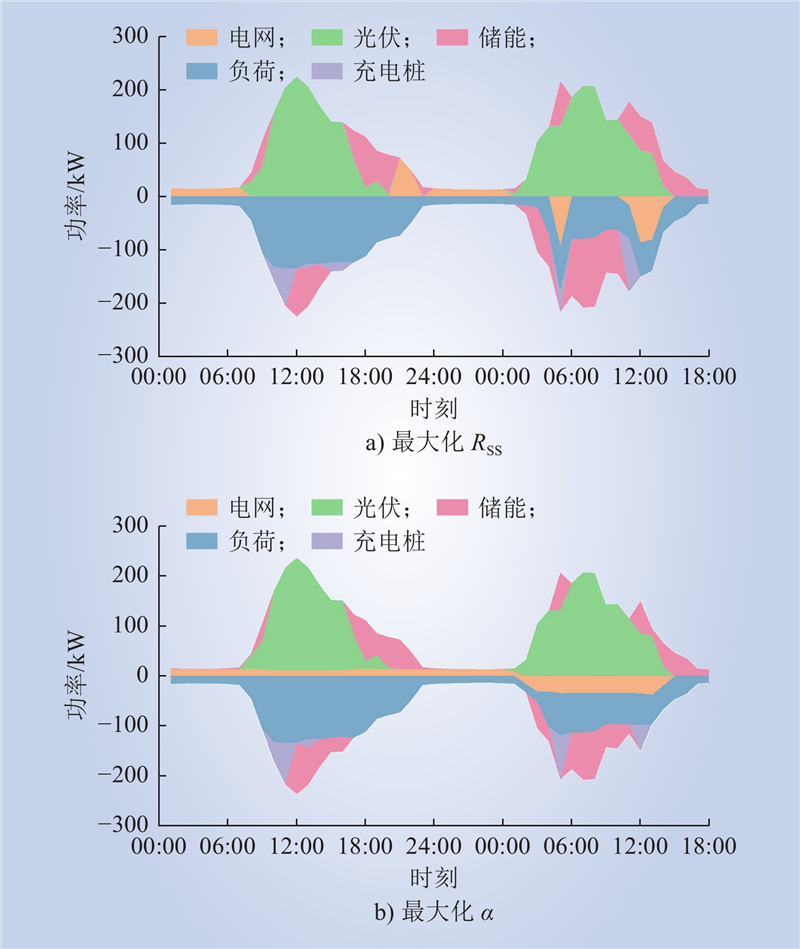
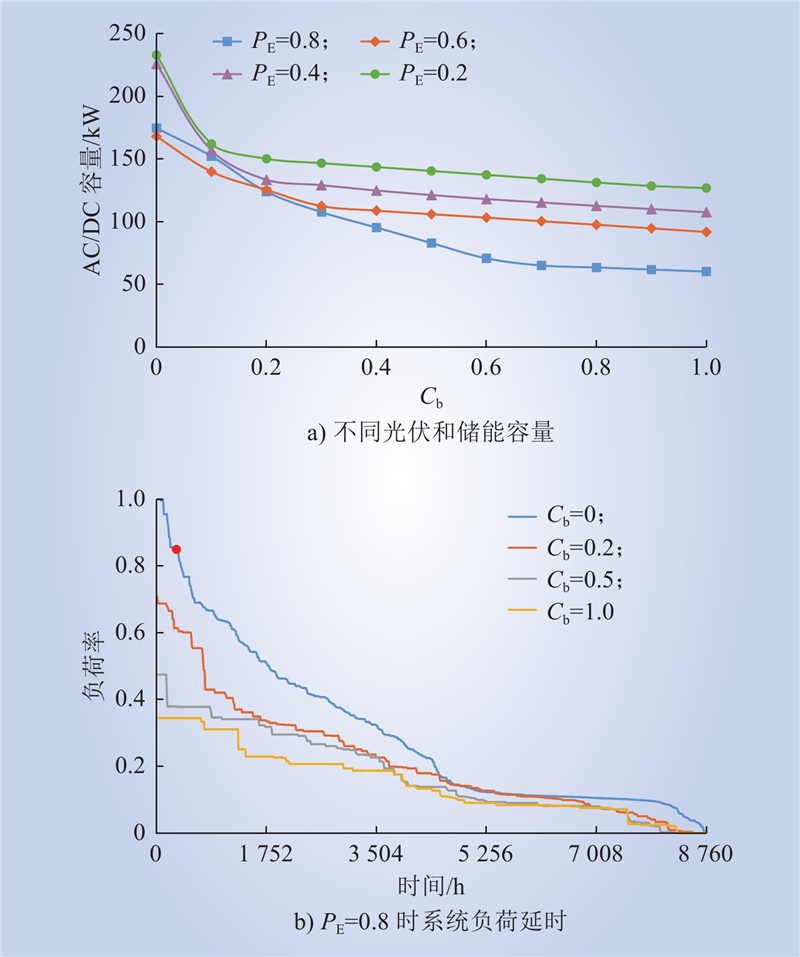
| 1 |
金晨, 任大伟, 肖晋宇, 等. 支撑碳中和目标的电力系统源-网-储灵活性资源优化规划[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (8): 164- 174.
|
|
JIN Chen, REN Dawei, XIAO Jinyu, et al. Optimization planning on power system supply-grid-storage flexibility resource for supporting the "carbon neutrality" target of China[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (8): 164- 174.
|
| 2 |
詹天津, 谢玉荣. 国内分布式光伏发展形势分析及思考[J]. 华电技术, 2021, 43 (12): 60- 65.
|
|
ZHAN Tianjin, XIE Yurong. Development status analysis and consideration on domestic distributed PV energy[J]. Huadian Technology, 2021, 43 (12): 60- 65.
|
| 3 |
金国. 分布式光伏技术在商业写字楼建筑中的应用[J]. 光源与照明, 2022, (11): 83- 85.
|
| 4 |
谢敏, 高浩睿, 胡海峰. 分布式光伏+储能在民用建筑应用研究与探讨[J]. 建筑电气, 2022, 41 (12): 62- 66.
|
|
XIE Min, GAO Haorui, HU Haifeng. Research and discussion on application of distributed PV+energy storage in civil buildings[J]. Building Electricity, 2022, 41 (12): 62- 66.
|
| 5 |
唐哲. 寒冷地区钢结构工业建筑与太阳能光伏一体化设计研究[D]. 济南: 山东建筑大学, 2015.
|
|
TANG Zhe. Cold region steel structure industrial building and the integration of solar photovoltaic design research[D]. Jinan: Shandong Jianzhu University, 2015.
|
| 6 |
丁明, 王伟胜, 王秀丽, 等. 大规模光伏发电对电力系统影响综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34 (1): 1- 14.
|
|
DING Ming, WANG Weisheng, WANG Xiuli, et al. A review on the effect of large-scale PV generation on power systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34 (1): 1- 14.
|
| 7 |
李叶茂, 郝斌, 李雨桐. 直流建筑技术展望[J]. 建筑科学, 2022, 38 (2): 40- 49, 98.
|
|
LI Yemao, HAO Bin, LI Yutong. Technological outlook on DC buildings[J]. Building Science, 2022, 38 (2): 40- 49, 98.
|
| 8 |
江亿. 光储直柔: 助力实现零碳电力的新型建筑配电系统[J]. 暖通空调, 2021, 51 (10): 1- 12.
|
|
JIANG Yi. PSDF(photovoltaic, storage, DC, flexible)—a new type of building power distribution system for zero carbon power system[J]. Heating Ventilating & Air Conditioning, 2021, 51 (10): 1- 12.
|
| 9 |
刘晓华, 张涛, 刘效辰, 等. “光储直柔” 建筑新型能源系统发展现状与研究展望[J]. 暖通空调, 2022, 52 (8): 1- 9, 82.
|
|
LIU Xiaohua, ZHANG Tao, LIU Xiaochen, et al. Development statuses and research prospects of PEDF(photovoltaics, energy storage, direct current and flexibility)building energy systems[J]. Heating Ventilating & Air Conditioning, 2022, 52 (8): 1- 9, 82.
|
| 10 |
李叶茂, 李雨桐, 郝斌, 等. 低碳发展背景下的建筑“光储直柔” 配用电系统关键技术分析[J]. 供用电, 2021, 38 (1): 32- 38.
|
|
LI Yemao, LI Yutong, HAO Bin, et al. Key technologies of building power supply and distribution system towards carbon neutral development[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2021, 38 (1): 32- 38.
|
| 11 |
贾禾, 彭晋卿, 李念平, 等. 动态电价下分布式光伏-储能系统优化与经济性分析[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42 (5): 187- 193.
|
|
JIA He, PENG Jinqing, LI Nianping, et al. Optimization and economic analysis of distributed photovoltaic-energy storage system under dynamic electricity price[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42 (5): 187- 193.
|
| 12 |
王超, 胡浩, 郑炼, 等. 基于智慧蓄电池的光伏储能系统及其控制策略[J]. 可再生能源, 2022, 40 (4): 506- 512.
|
|
WANG Chao, HU Hao, ZHENG Lian, et al. Photovoltaic energy storage system based on smart battery and its control strategy[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2022, 40 (4): 506- 512.
|
| 13 |
吴小刚, 刘宗歧, 田立亭, 等. 独立光伏系统光储容量优化配置方法[J]. 电网技术, 2014, 38 (5): 1271- 1276.
|
|
WU Xiaogang, LIU Zongqi, TIAN Liting, et al. Optimized capacity configuration of photovoltaic generation and energy storage device for stand-alone photovoltaic generation system[J]. Power System Technology, 2014, 38 (5): 1271- 1276.
|
| 14 |
王文宾, 朱燕舞, 韩天华, 等. 基于随机规划的分布式光伏并网最大准入容量计算[J]. 燕山大学学报, 2018, 42 (6): 510- 518.
|
|
WANG Wenbin, ZHU Yanwu, HAN Tianhua, et al. Maximum access capacity calculation of distributed PV grid connected based on stochastic programming[J]. Journal of Yanshan University, 2018, 42 (6): 510- 518.
|
| 15 |
赵安军, 王鹏柱, 荆竞, 等. 考虑电动汽车影响的农村家庭新能源容量优化配置方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 31- 39, 50.
|
|
ZHAO Anjun, WANG Pengzhu, JING Jing, et al. Optimal configuration method of new energy capacity for rural households considering impact of electric vehicles[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 31- 39, 50.
|
| 16 |
苏粟, 蒋小超, 王玮, 等. 计及电动汽车和光伏—储能的微网能量优化管理[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (9): 164- 171.
|
|
SU Su, JIANG Xiaochao, WANG Wei, et al. Optimal energy management for microgrids considering electric vehicles and photovoltaic-energy storage[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (9): 164- 171.
|
| 17 |
HESSE H, MARTINS R, MUSILEK P, et al. Economic optimization of component sizing for residential battery storage systems[J]. Energies, 2017, 10(7): 835.
|
| 18 |
荣秀婷, 张辉, 朱刘柱, 等. “双碳” 目标下商务楼宇 “光储直柔” 恒功率运行研究[J]. 机械制造与自动化, 2022, 51 (5): 223- 227.
|
|
RONG Xiuting, ZHANG Hui, ZHU Liuzhu, et al. Research on 'photovoltaic, storage and dc flexibility' based constant power operation in commercial buildings under targets of 'Carbon Peak' and 'Carbon Neutral'[J]. Machine Building & Automation, 2022, 51 (5): 223- 227.
|