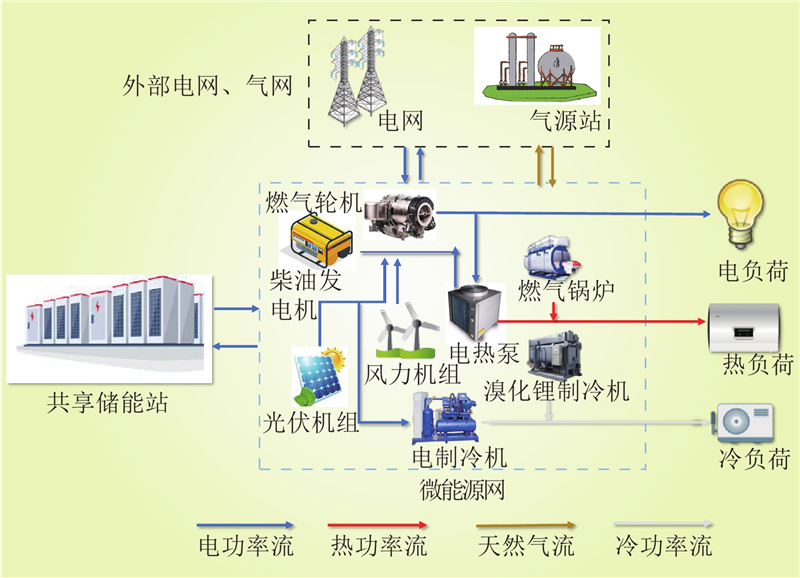
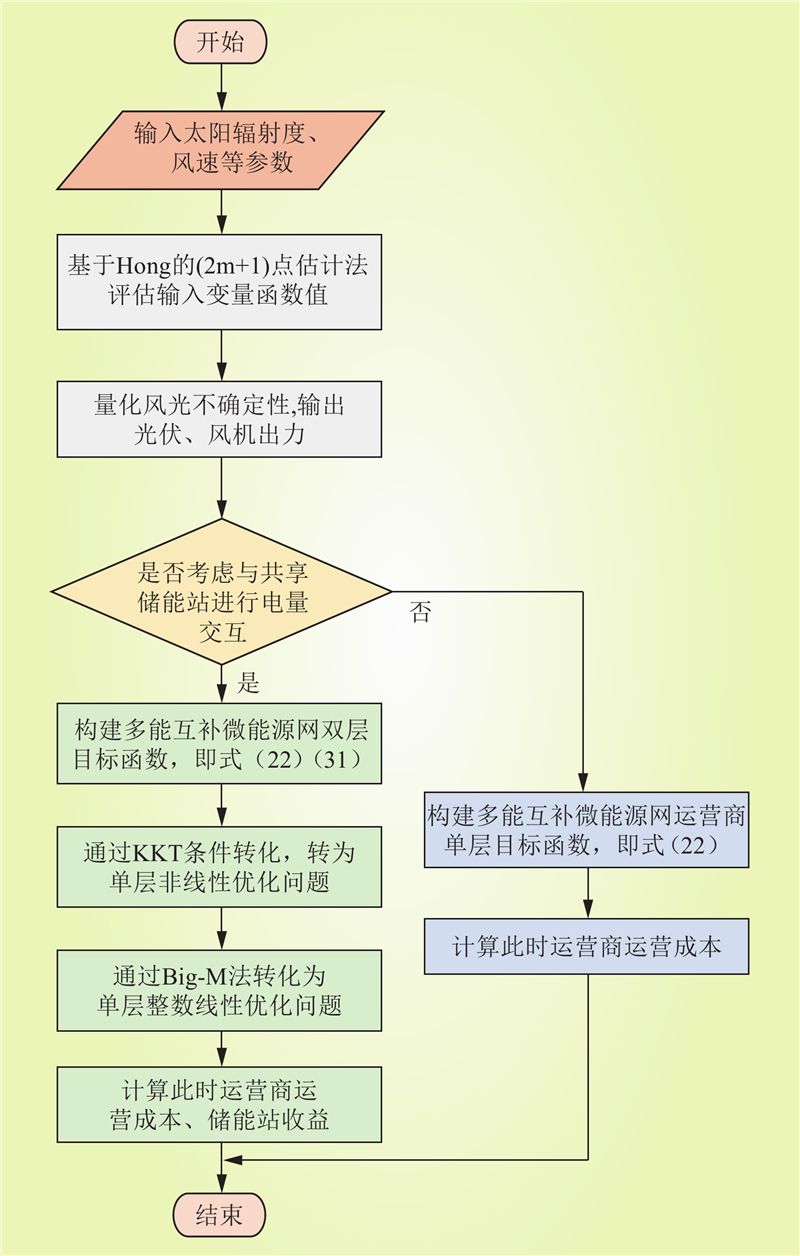
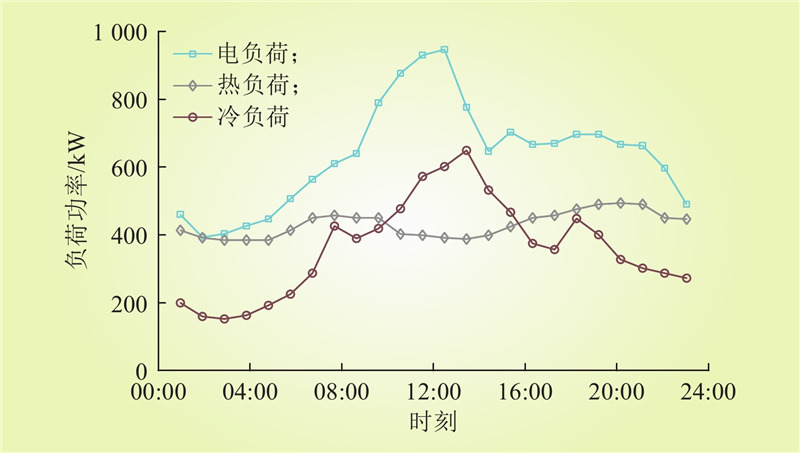
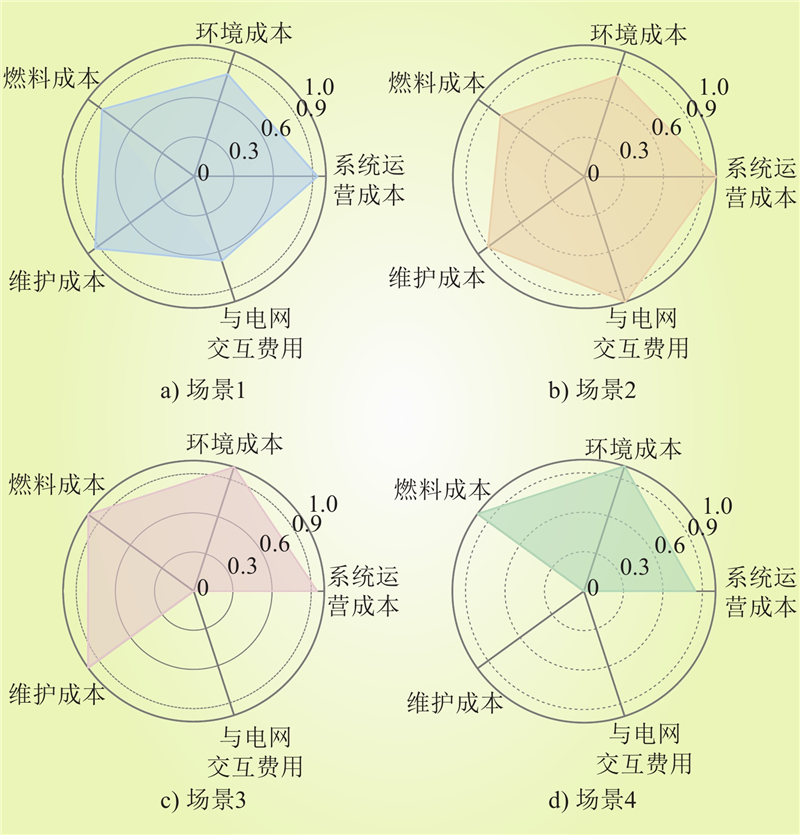
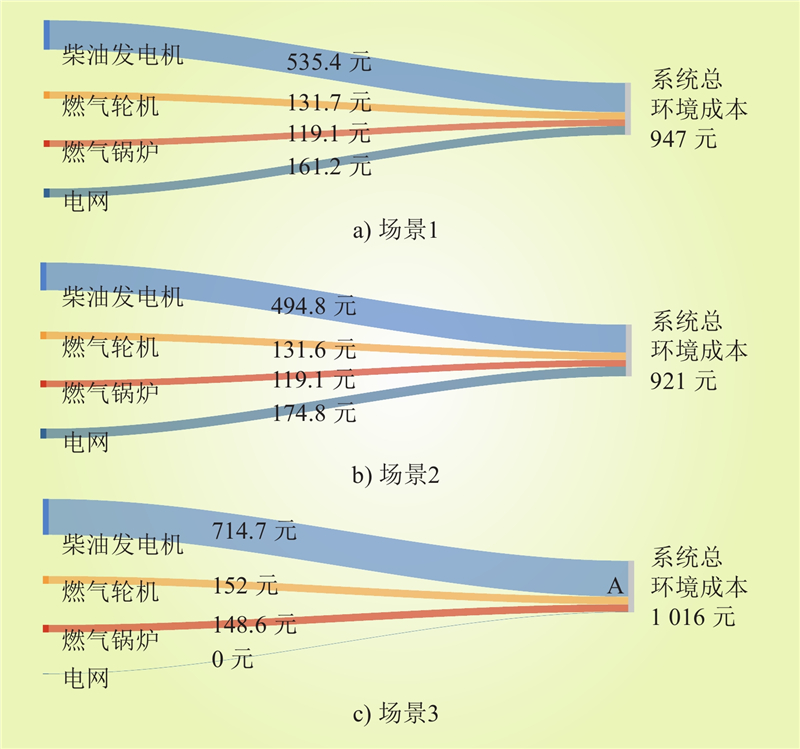
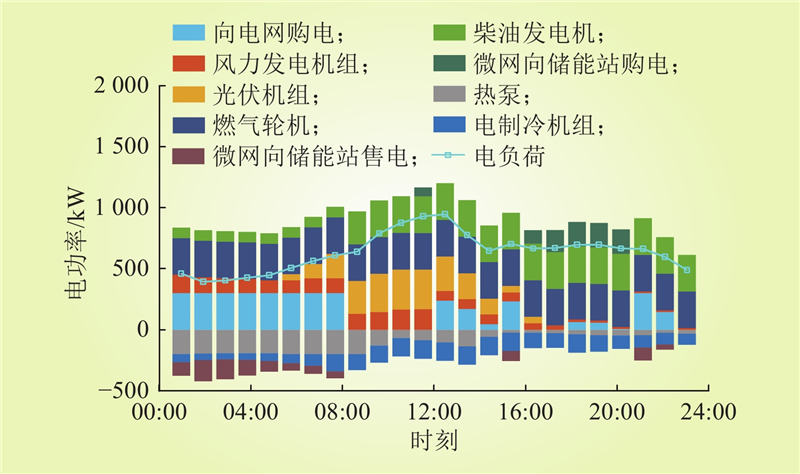
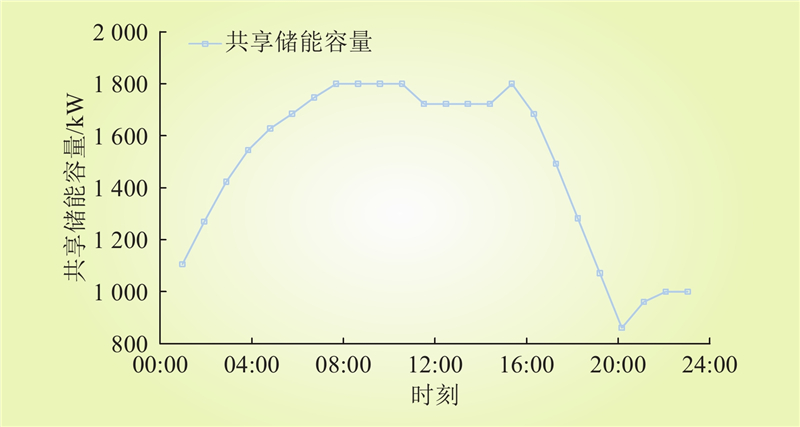
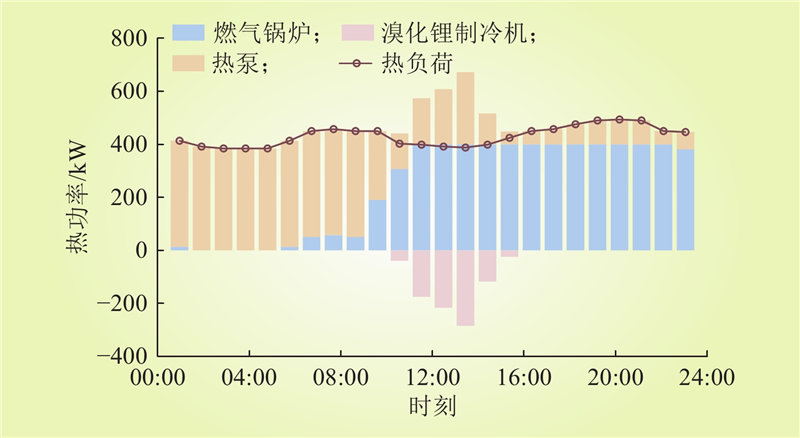
| 1 |
SHANG Y P, SANG S H, TIWARI A K, et al. Impacts of renewable energy on climate risk: a global perspective for energy transition in a climate adaptation framework[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 362, 122994.
|
| 2 |
华昊辰, 吴浩星, 陈星莺, 等. 考虑用能经济性与用户满意度灵活协同的综合能源系统双层优化[J/OL]. 电网技术, 2024, 1–14 [2024-06-13]. https://doi.org/10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2024.0108.
|
|
HUA Haochen, WU Haoxing, CHEN Xingying, et al. Double layer optimization of integrated energy systems considering flexible collaboration between energy economy and user satisfaction[J/OL]. Power System Technology, 2024, 1–14 [2024-06-13]. https://doi.org/10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2024.0108.
|
| 3 |
CHEN H P, WU H, KAN T Y, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatch of integrated energy system containing electric hydrogen production based on VMD-GRU short-term wind power prediction[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems, 2023, 154, 109420.
|
| 4 |
华昊辰, 辛世禹, 陈星莺, 等. 基于“虚拟碳储存”的需求侧电-碳耦合交易机制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (6): 2131- 2144.
|
|
HUA Haochen, XIN Shiyu, CHEN Xingying, et al. Demand side electricity-carbon coupling trading mechanism based on "virtual carbon storage"[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (6): 2131- 2144.
|
| 5 |
陈湘元, 吴公平, 龙卓, 等. 考虑源荷不确定性及用户侧需求响应的综合能源系统多时间尺度优化调度[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2024, 39 (3): 217- 227.
|
|
CHEN Xiangyuan, WU Gongping, LONG Zhuo, et al. Multi-time scale optimal dispatch of integrated energy systems considering source-load uncertainty and user-side demand response[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2024, 39 (3): 217- 227.
|
| 6 |
YANG Z M, PENG X S, SONG J J, et al. Short-term wind power prediction based on multi-parameters similarity wind process matching and weighed-voting-based deep learning model selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2023, 39 (1): 2129- 2142.
|
| 7 |
李军徽, 尤宏飞, 李翠萍, 等. 基于模型预测控制的风光储黑启动功率协调策略[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (10): 3700- 3708.
|
|
LI Junhui, YOU Hongfei, LI Cuiping, et al. Power coordination strategy based on model predictive control for black start with PV-wind-battery system[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (10): 3700- 3708.
|
| 8 |
赵振宇, 包格日乐图, 李炘薪. 基于信息间隙决策理论的含碳捕集-电转气综合能源系统优化调度[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45 (4): 651- 665.
|
|
ZHAO Zhenyu, BAO Geriletu, LI Xinxin. Optimization and scheduling of integrated energy systems with carbon capture and storage-power to gas based on information gap decision theory[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2024, 45 (4): 651- 665.
|
| 9 |
YANG S B, FANG J P, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Two-stage coordinated optimal dispatching model and benefit allocation strategy for rural new energy microgrid[J]. Energy, 2024, 292, 130274.
|
| 10 |
韩佶, 苗世洪, 李超, 等. 计及相关性的电-气-热综合能源系统概率最优能量流[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34 (5): 1055- 1067.
|
|
HAN Ji, MIAO Shihong, LI Chao, et al. Probabilistic optimal energy flow of electricity-gas-heat integrated energy system considering correlation[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34 (5): 1055- 1067.
|
| 11 |
ZHAO C F, WAN C, SONG Y H. An adaptive bilevel programming model for nonparametric prediction intervals of wind power generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2019, 35 (1): 424- 439.
|
| 12 |
贺帅佳, 高红均, 刘俊勇, 等. 计及需求响应柔性调节的分布鲁棒DG优化配置[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (8): 2253- 2264, 8.
|
|
HE Shuaijia, GAO Hongjun, LIU Junyong, et al. Distributionally robust optimal DG allocation model considering flexible adjustment of demand response[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (8): 2253- 2264, 8.
|
| 13 |
苏晨博, 刘崇茹, 李至峪, 等. 基于贝叶斯理论的考虑多维风速之间相关性的概率潮流计算[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (3): 157- 165.
|
|
SU Chenbo, LIU Chongru, LI Zhiyu, et al. Bayesian theory based calculation of probabilistic power flow considering correlation between multi-dimensional wind speed[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (3): 157- 165.
|
| 14 |
HARSH P, DAS D. Energy management in microgrid using incentive-based demand response and reconfigured network considering uncertainties in renewable energy sources[J]. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 2021, 46, 101225.
|
| 15 |
李强, 王璇, 琚诚, 等. 基于广义储能的多时间尺度综合能源系统优化调度模型[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (9): 117- 125, 137.
|
|
LI Qiang, WANG Xuan, JU Cheng, et al. Optimal scheduling model of multi-time scale integrated energy system based on generalized energy storage[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (9): 117- 125, 137.
|
| 16 |
朱文广, 王伟, 欧阳斌, 等. 面向节能降碳的冶炼企业风光储多目标协同定容方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (11): 86- 94.
|
|
ZHU Wenguang, WANG Wei, OUYANG Bin, et al. Multi-objective cooperative capacity determination method for integrated system of wind, photovoltaic and storage of smelting enterprises requiring energy saving and carbon reduction[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (11): 86- 94.
|
| 17 |
徐艳春, 刘海权, 孙思涵, 等. 计及混合能源共享站的多微网系统双层混合整数规划[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (23): 9136- 9149.
|
|
XU Yanchun, LIU Haiquan, SUN Sihan, et al. Bi-level mixed integer programming of multi-microgrid system considering the hybrid energy sharing station[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (23): 9136- 9149.
|
| 18 |
HU J J, WANG Y D, DONG L. Low carbon-oriented planning of shared energy storage station for multiple integrated energy systems considering energy-carbon flow and carbon emission reduction[J]. Energy, 2024, 290, 130139.
|
| 19 |
曹猛, 解超, 李凤婷, 等. 基于两阶段鲁棒的多综合能源微网-共享储能电站协同优化运行策略[J/OL]. 电网技术: 1–14 [2024-06-13]. https://doi.org/10.13335/j.10003673.pst.2024.0531.
|
|
CAO Meng, XIE Chao, LI Fengting, et al. Co-optimized operation of multi-integrated energy microgrids-shared energy storage plants based on two-stage robustness[J]. Power System Technology, 1–14 [2024-06-13]. https://doi.org/10.13335/j.10003673.pst.2024.0531.
|
| 20 |
LI J L, FANG Z J, WANG Q, et al. Optimal operation with dynamic partitioning strategy for centralized shared energy storage station with integration of large-scale renewable energy[J]. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy, 2024, 12 (2): 359- 370.
|
| 21 |
HUA H C, CHEN X Y, GAN L, et al. Demand-side joint electricity and carbon trading mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems, 2023, 2, 14- 25.
|
| 22 |
盛煊, 林舜江, 梁炜焜, 等. 考虑灵活性的城市综合能源系统区间优化调度[J/OL]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 1–12 [2024-06-13]. https://doi.org/10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.240167.
|
|
SHENG xuan, LIN shunjiang, LIANG Weikun, et al. Interval optimal dispatch of urban integrated energy system considering flexibility[J/OL]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 1–12 [2024-06-13]. https://doi.org/10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.240167.
|
| 23 |
HUA H C, SHI J B, CHEN X Y, et al. Carbon emission flow based energy routing strategy in energy Internet[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 20 (3): 3974- 3985.
|
| 24 |
胡福年, 张彭成, 周小博, 等. 计及灵活性资源的综合能源系统源荷协调优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (5): 2- 13.
|
|
HU Funian, ZHANG Pengcheng, ZHOU Xiaobo, et al. Coordinated optimal scheduling of source and load in integrated energy system considering flexible resources[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (5): 2- 13.
|
| 25 |
韩子娇, 那广宇, 董鹤楠, 等. 考虑灵活性供需平衡的含电转氢综合能源系统鲁棒优化调度[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (6): 161- 169.
|
|
HAN Zijiao, NA Guangyu, DONG Henan, et al. Robust optimal operation of integrated energy system with P2H considering flexibility balance[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (6): 161- 169.
|
| 26 |
邓倩文, 李奇, 邱宜彬, 等. 考虑多类型灵活性资源联合运行的综合能源系统优化配置方法[J/OL]. 上海交通大学学报: 1–24 [2024-06-13]. https://doi.org/10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2023.457.
|
|
DENG Qianwen, LI Qi, QIU Yibin, et al. Optimal allocation method of integrated energy system considering joint operation of multi-type Flexible resources[J/OL]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 1–24 [2024-06-13]. https://doi.org/10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2023.457.
|
| 27 |
KAYAL P, CHANDA C K. Optimal mix of solar and wind distributed generations considering performance improvement of electrical distribution network[J]. Renewable Energy, 2015, 75, 173- 186.
|
| 28 |
HUA H C, QIN Y C, HAO C T, et al. Optimal energy management strategies for energy Internet via deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 239, 598- 609.
|
| 29 |
李贻涛, 高鹏飞, 邢晓敏. 多园区综合能源系统接入主动配电网双层优化调度研究[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2024, 44 (2): 88- 98.
|
|
LI Yitao, GAO Pengfei, XING Xiaomin. Research on two-layer optimal dispatching of multi-park integrated energy system connected to active distribution network[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2024, 44 (2): 88- 98.
|
| 30 |
孙雯, 陈紫薇, 张玉琼, 等. 基于动态规划的SOFC冷热电三联供综合能源系统日前经济调度[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (21): 7775- 7784.
|
|
SUN Wen, CHEN Ziwei, ZHANG Yuqiong, et al. Economic day-ahead scheduling of SOFC-based integrated tri-generation energy system using dynamic programming[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (21): 7775- 7784.
|
| 31 |
WANG T H, HUA H C, SHI T Y, et al. A bi-level dispatch optimization of multi-microgrid considering green electricity consumption willingness under renewable portfolio standard policy[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 356, 122428.
|
| 32 |
彭宇文, 李瑞, 周永旺, 等. 基于IGDT和PSO-SA的综合能源系统鲁棒优化调度方法[J]. 广东电力, 2023, 36 (9): 60- 71.
|
|
PENG Yuwen, LI Rui, ZHOU Yongwang, et al. Robust optimal scheduling method for integrated energy system based on IGDT and PSO-SA[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2023, 36 (9): 60- 71.
|
| 33 |
华昊辰, 翟家祥, 陈星莺, 等. 基于增强精英保留遗传算法的虚拟微网群动态划分及能量局域自治[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (12): 4652- 4666.
|
|
HUA Haochen, ZHAI Jiaxiang, CHEN Xingying, et al. Dynamical partitioning and local energy autonomy of virtual microgrid groups based on strengthen elitist genetic algorithm[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (12): 4652- 4666.
|
| 34 |
帅轩越, 马志程, 王秀丽, 等. 基于主从博弈理论的共享储能与综合能源微网优化运行研究[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (2): 679- 690.
|
|
SHUAI Xuanyue, MA Zhicheng, WANG Xiuli, et al. Optimal operation of shared energy storage and integrated energy microgrid based on leader-follower game theory[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (2): 679- 690.
|
| 35 |
聂永辉, 李宗锴. 基于纳什谈判和主从博弈的多园区综合能源系统优化调度[J]. 智慧电力, 2024, 52 (5): 37- 43, 104.
|
|
NIE Yonghui, LI Zongkai. Optimal scheduling of multi-park integrated energy system based on Nash negotiation and master-slave game[J]. Smart Power, 2024, 52 (5): 37- 43, 104.
|
| 36 |
吴盛军, 李群, 刘建坤, 等. 基于储能电站服务的冷热电多微网系统双层优化配置[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (10): 3822- 3832.
|
|
WU Shengjun, LI Qun, LIU Jiankun, et al. Bi-level optimal configuration for combined cooling heating and power multi-microgrids based on energy storage station service[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (10): 3822- 3832.
|