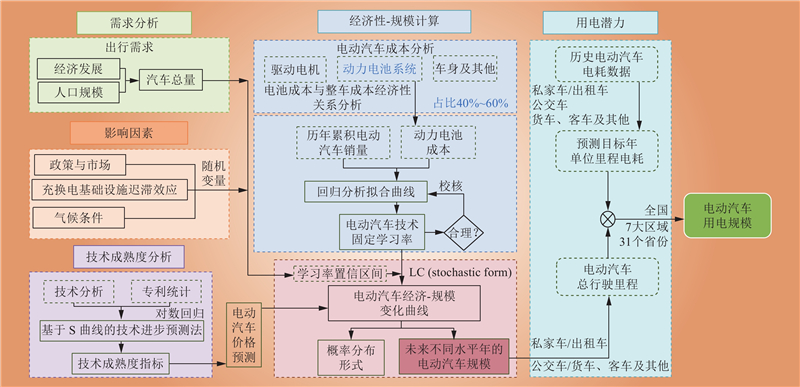
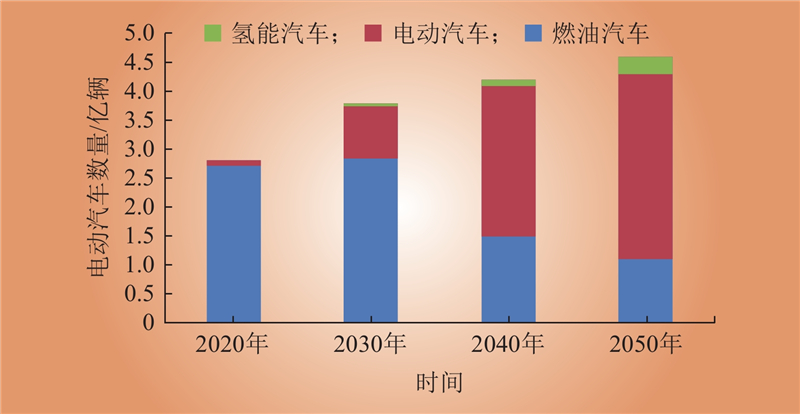
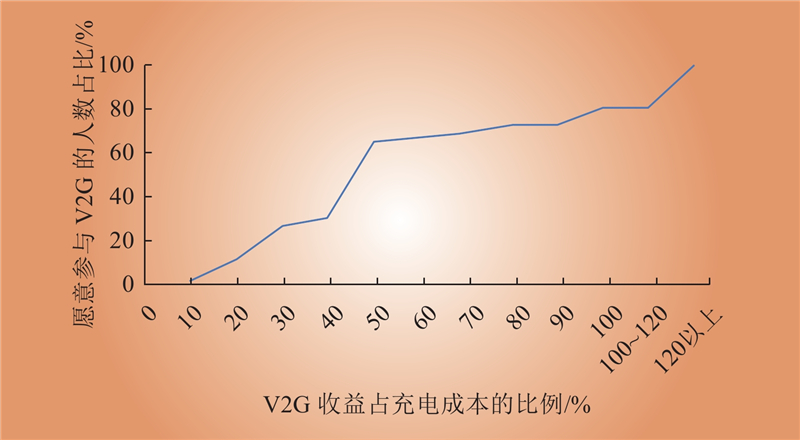
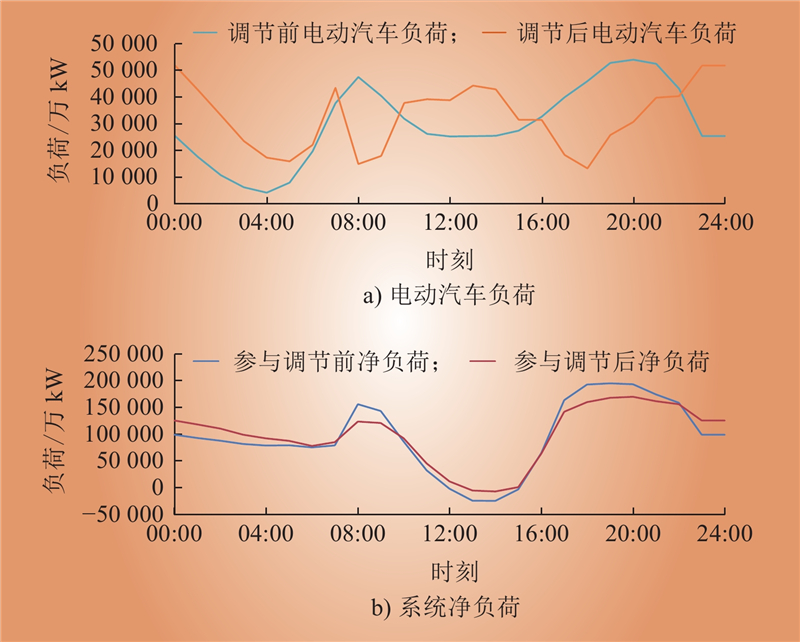
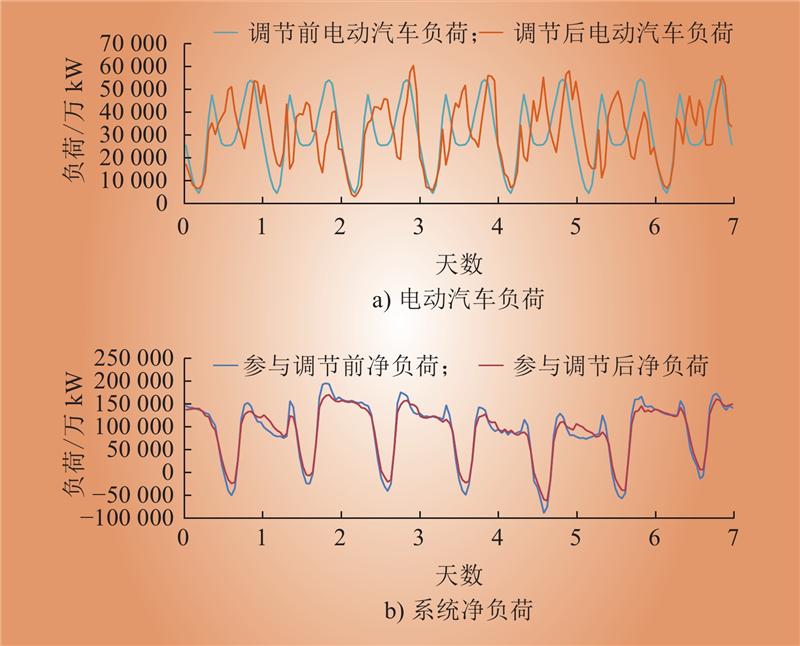
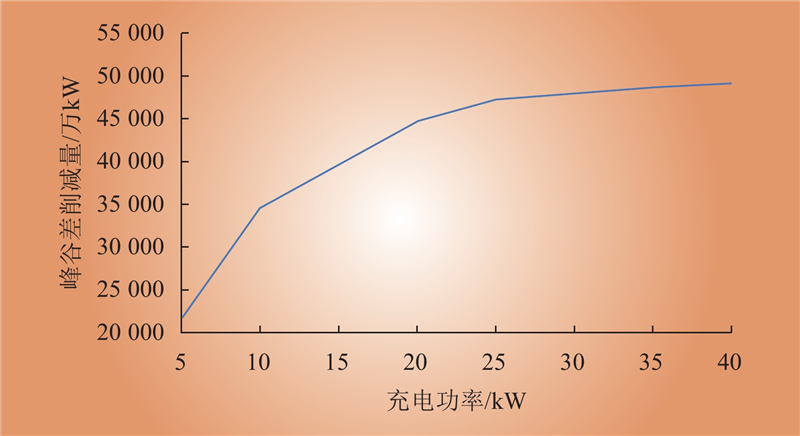
| 1 |
辛保安, 新型电力系统与新型能源体系[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2023.
|
| 2 |
周原冰, 张士宁, 侯方心, 等. 电力行业碳达峰及促进全社会碳减排影响分析[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (9): 1- 9.
|
|
ZHOU Yuanbing, ZHANG Shining, HOU Fangxin, et al. Analysis of carbon peaking in power sector and its impact on promoting whole-society carbon emissions reduction[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (9): 1- 9.
|
| 3 |
崔杨, 安宁, 付小标, 等. 面向高比例新能源电力系统调峰需求的储能容量配置方法综述[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (1): 1- 8.
|
|
CUI Yang, AN Ning, FU Xiaobiao, et al. Overview of energy storage capacity allocation methods for high-proportion new energy power system peak shaving demand[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (1): 1- 8.
|
| 4 |
朱静慧, 高佳, 余欣梅, 等. 碳中和背景下我国生态碳汇发展形势及建议[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2022, 40 (6): 1- 8.
|
|
ZHU Jinghui, GAO Jia, YU Xinmei, et al. Developmengt situation and suggestions for ecological carbon sink in China under background of carbon neutralization[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2022, 40 (6): 1- 8.
|
| 5 |
李吉峰, 唐克, 王孜航, 等. 计及多源互补特性的新型电力系统分布式电源承载能力评估[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (1): 62- 68.
|
|
LI Jifeng, TANG Ke, WANG Zihang, et al. Assessment of distributed power generations bearing capacity of modern power systems with multi-sources complementary characteristics[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (1): 62- 68.
|
| 6 |
岳昊. 中国构建新型电力系统面临的问题、风险与建议[N]. 电力决策与舆情参考, 2021(16): 26–36.
|
| 7 |
余潇潇, 宋福龙, 周原冰, 等. “新基建” 对中国 “十四五” 电力需求和电网规划的影响分析[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (7): 11- 17.
|
|
YU Xiaoxiao, SONG Fulong, ZHOU Yuanbing, et al. Investigations on the impact of new infrastructure on electricity forecast and power system planning during the 14th five-year plan period[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (7): 11- 17.
|
| 8 |
任大伟, 侯金鸣, 肖晋宇, 等. 支撑双碳目标的新型储能发展潜力及路径研究[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (8): 17- 25.
|
|
REN Dawei, HOU Jinming, XIAO Jinyu, et al. Research on development potential and path of new energy storage supporting carbon peak and carbon neutrality[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (8): 17- 25.
|
| 9 |
中国化学与物理电源行业协会. 2024年中国新型储能产业发展白皮书[R]. 天津: 中国化学与物理电源行业协会, 2024.
|
| 10 |
中国能源研究会储能专委会, 中关村储能产业技术联盟. 储能产业研究白皮书2024[R]. 北京: 中关村储能产业技术联盟, 2024.
|
| 11 |
刘坚. 我国新型储能发展问题分析与政策建议[J]. 中国能源, 2022, 44 (6): 6- 10, 35.
|
|
LIU Jian. Analysis and policy suggestions on the development of new energy storage in China[J]. Energy of China, 2022, 44 (6): 6- 10, 35.
|
| 12 |
李更丰, 孙少华, 别朝红, 等. 面向新型电力系统弹性提升的储能优化配置与灵活调度研究综述[J]. 高电压技术, 2023, 49 (10): 4084- 4095.
|
|
LI Gengfeng, SUN Shaohua, BIE Zhaohong, et al. Review on optimal configuration and flexible scheduling research of energy storage for resilience improvement of new power system[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2023, 49 (10): 4084- 4095.
|
| 13 |
李丰, 姚韵, 张会娟, 等. 新型储能经济性及价格机制研究[J]. 价格理论与实践, 2022, (4): 66- 70, 204.
|
|
LI Feng, YAO Yun, ZHANG Huijuan, et al. Research on new energy storage price mechanism and economic[J]. Price: Theory & Practice, 2022, (4): 66- 70, 204.
|
| 14 |
刘洪波, 刘永发, 任阳, 等. 高风电渗透率下考虑系统风电备用容量的储能配置[J]. 发电技术, 2024, (2): 260- 272.
|
|
LIU Hongbo, LIU Yongfa, REN Yang, et al. Energy storage configuration considering the system wind power reserve capacity under high wind power permeability[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2024, (2): 260- 272.
|
| 15 |
任子俊, 曲小慧, 王敏之, 等. 新型电力系统中电化学储能应用与关键技术综述[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (6): 1- 7, 78.
|
|
REN Zijun, QU Xiaohui, WANG Minzhi, et al. A review of electrochemical energy storage applications and key technologies in new-type power systems[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (6): 1- 7, 78.
|
| 16 |
赵添辰, 张弓, 张云飞, 等. “双碳” 目标下抽水蓄能提升系统保供能力的技术经济性研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13 (3): 1059- 1073.
|
|
ZHAO Tianchen, ZHANG Gong, ZHANG Yunfei, et al. Technical and economic research on the capacity of supply assurance for pumped-storage systems under the target of "dual carbon"[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13 (3): 1059- 1073.
|
| 17 |
黄学良, 刘永东, 沈斐, 等. 电动汽车与电网互动: 综述与展望[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (7): 3- 23.
|
|
HUANG Xueliang, LIU Yongdong, SHEN Fei, et al. Vehicle to grid: review and prospect[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (7): 3- 23.
|
| 18 |
魏一凡, 韩雪冰, 卢兰光, 等. 面向碳中和的新能源汽车与车网互动技术展望[J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44 (4): 449- 464.
|
|
WEI Yifan, HAN Xuebing, LU Languang, et al. Technology prospects of carbon neutrality-oriented new-energy vehicles and vehicle-grid interaction[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44 (4): 449- 464.
|
| 19 |
吴佳琦, 张谦, 吴小汉, 等. 电动汽车与电网互动的关键问题研究综述[J]. 汽车工程学报, 2022, 12 (4): 411- 430.
|
|
WU Jiaqi, ZHANG Qian, WU Xiaohan, et al. A review of key issues in electric vehicle and power grid interaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Automotive Engineering, 2022, 12 (4): 411- 430.
|
| 20 |
BAE S, KWASINSKI A. Spatial and temporal model of electric vehicle charging demand[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2012, 3 (1): 394- 403.
|
| 21 |
卢慧, 谢开贵, 胡博, 等. 混合交通流下计及储能型柔性开关影响的交通-配电网联合规划[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (22): 108- 119.
|
|
LU Hui, XIE Kaigui, HU Bo, et al. Coordinated planning of transportation and distribution networks with mixed traffic flow and E-SOP[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (22): 108- 119.
|
| 22 |
于霄宇, 纪正森, 嵇灵, 等. 双碳目标下我国电动汽车碳减排贡献潜力分析[J]. 智慧电力, 2024, 52 (2): 25- 31, 39.
|
|
YU Xiaoyu, JI Zhengsen, JI Ling, et al. Analysis on carbon emission reduction potential of electric vehicles in China under goal of carbon neutrality and carbon peaking[J]. Smart Power, 2024, 52 (2): 25- 31, 39.
|
| 23 |
王斐, 李正烁, 叶萌, 等. 电动汽车充电对电网的影响及其优化调度研究述评[J]. 南方电网技术, 2016, 10 (6): 70- 80.
|
|
WANG Fei, LI Zhengshuo, YE Meng, et al. Review on research of impact of electric vehicles charging on power grids and its optimal dispatch[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2016, 10 (6): 70- 80.
|
| 24 |
杨捷, 郭凡, 曹子健. 电动汽车储能V2G模式的成本与收益分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9 (S1): 45- 51.
|
|
YANG Jie, GUO Fan, CAO Zijian. Cost and benefit analysis of EV energy storage through V2G[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9 (S1): 45- 51.
|
| 25 |
王旖旎. 中国汽车需求预测: 基于Gompertz模型的分析[J]. 财经问题研究, 2005, (11): 43- 50.
|
|
WANG Yini. CAR OWNERSHIP FORECAST IN CHINA: an analysis based on gompertz equation[J]. Research on Financial and Economic Issues, 2005, (11): 43- 50.
|
| 26 |
MA S C, FAN Y. A deployment model of EV charging piles and its impact on EV promotion[J]. Energy Policy, 2020, 146, 111777.
|
| 27 |
王慧芳. 充电基础设施对电动汽车推广的影响机制研究——基于两侧间接网络效应的分析[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2019.
|
|
WANG Huifang. Research on the influencing mechanism of charging infrastructure on the promotion of electric vehicles: based on the analysis of indirect network effect on both sides[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2019.
|
| 28 |
郭磊, 王克文, 文福拴, 等. 电动汽车充电设施规划研究综述与展望[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2019, 34 (3): 56- 70.
|
|
GUO Lei, WANG Kewen, WEN Fushuan, et al. Review and prospect of charging facility planning of electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2019, 34 (3): 56- 70.
|
| 29 |
中国汽车工程学会, 清华四川能源互联网研究院. 中国电动汽车充电基础设施发展战略与路线图研究(2021-2035)[R]. 北京: 中国汽车工程学会, 2021.
|