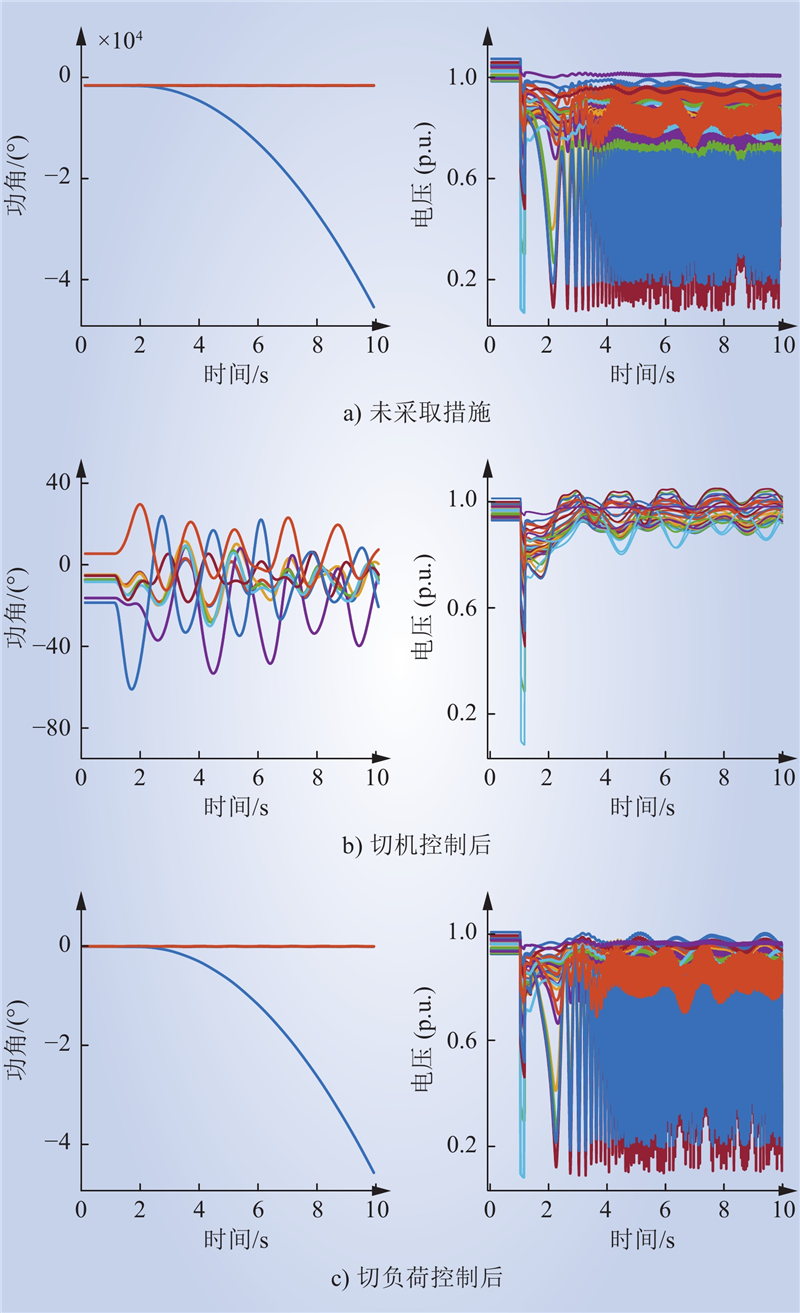
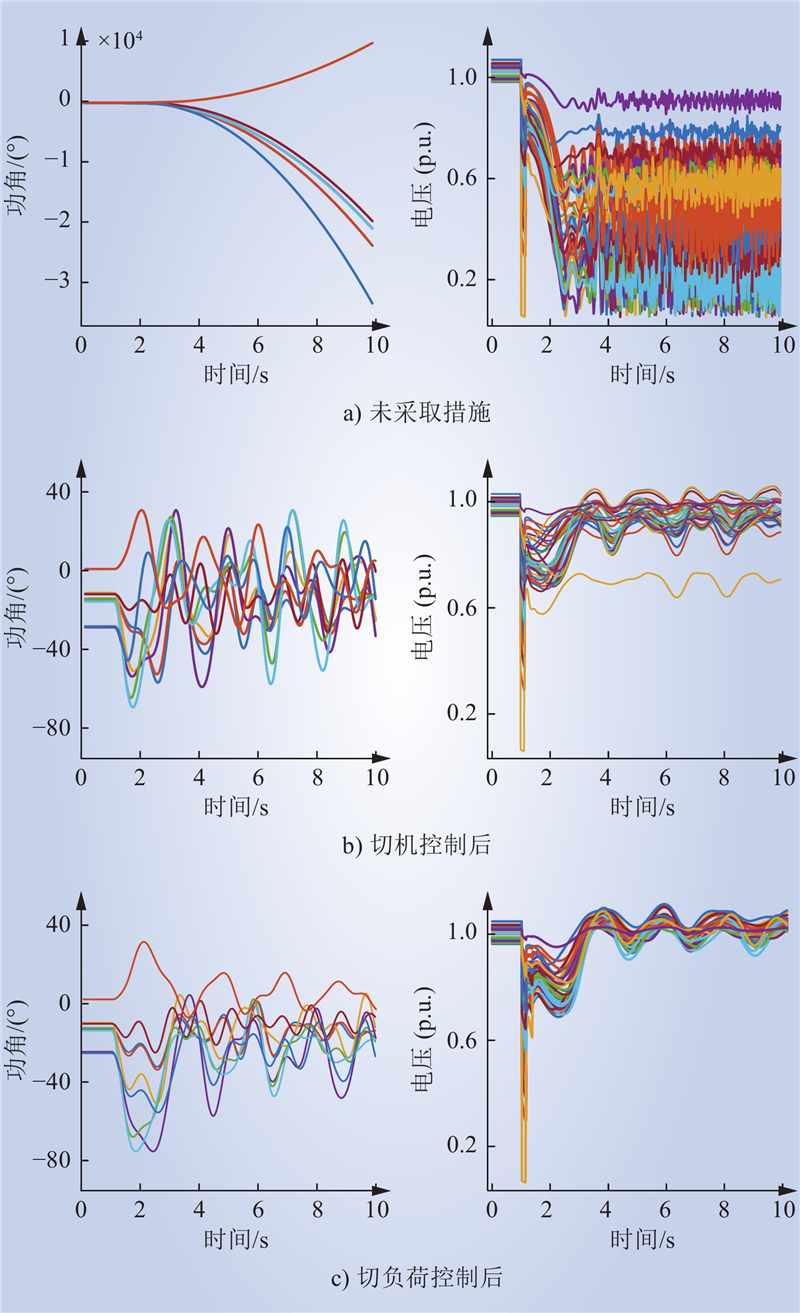
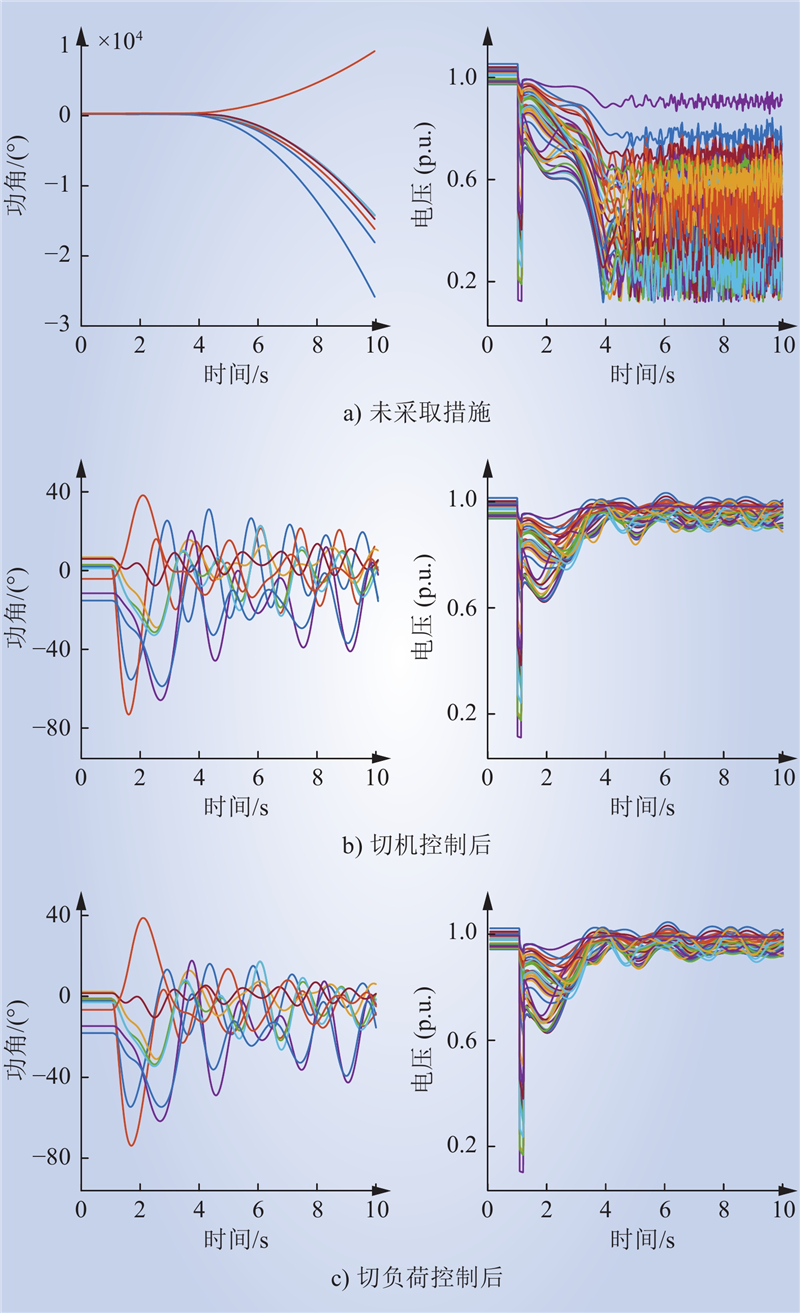
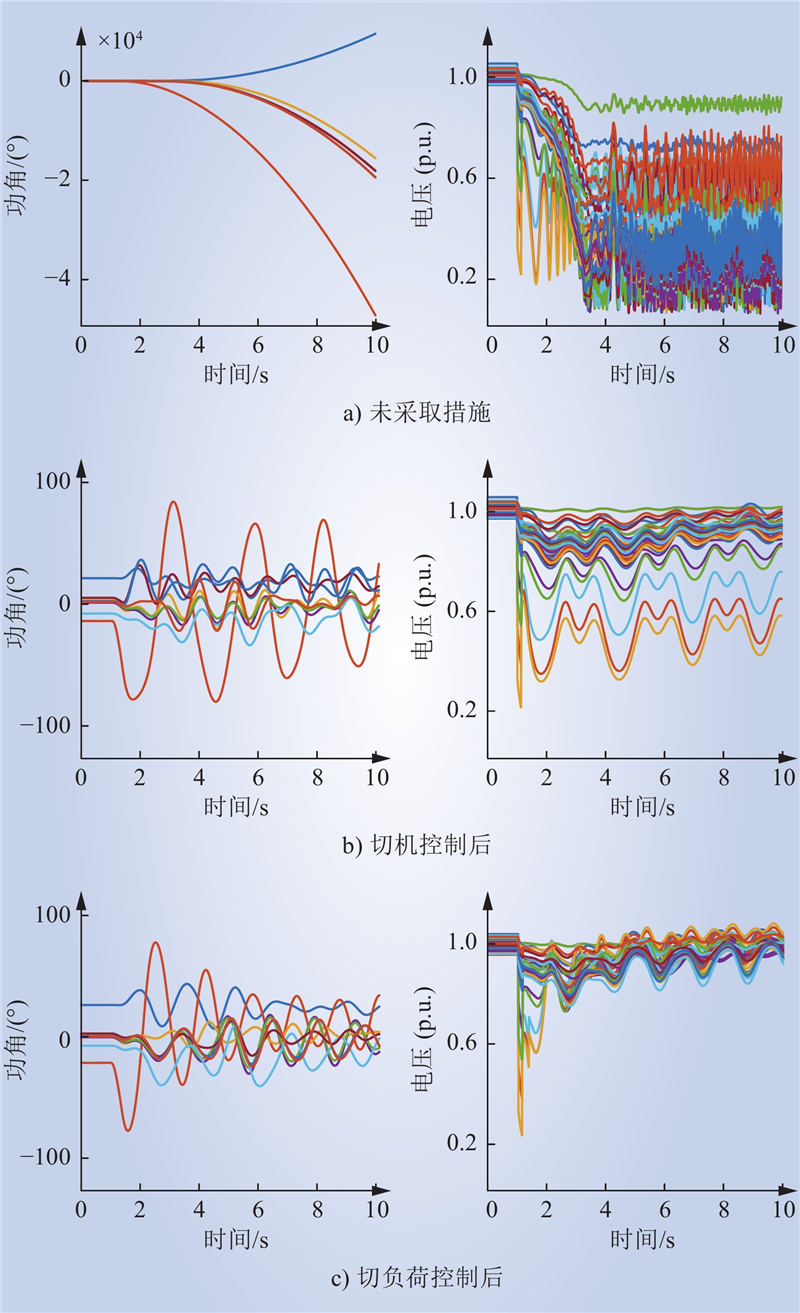
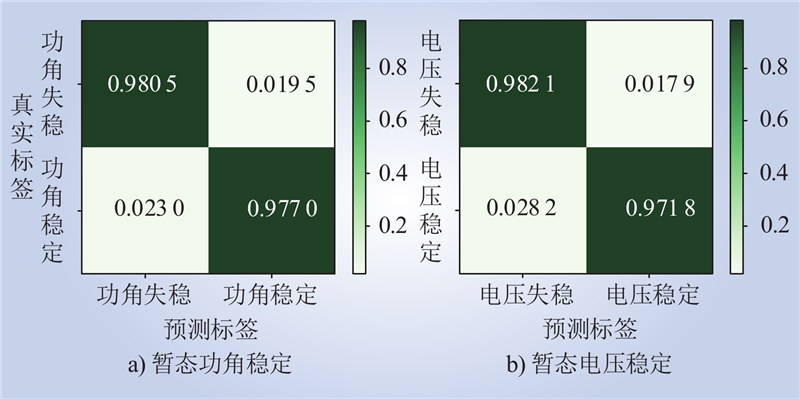
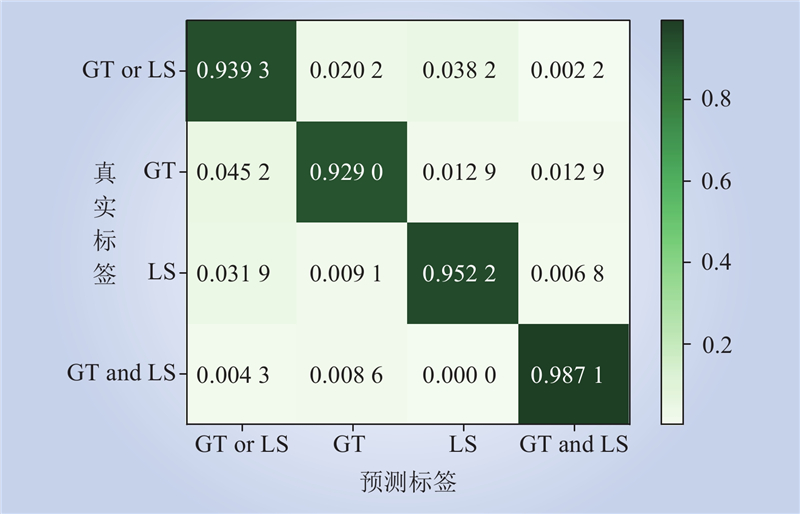
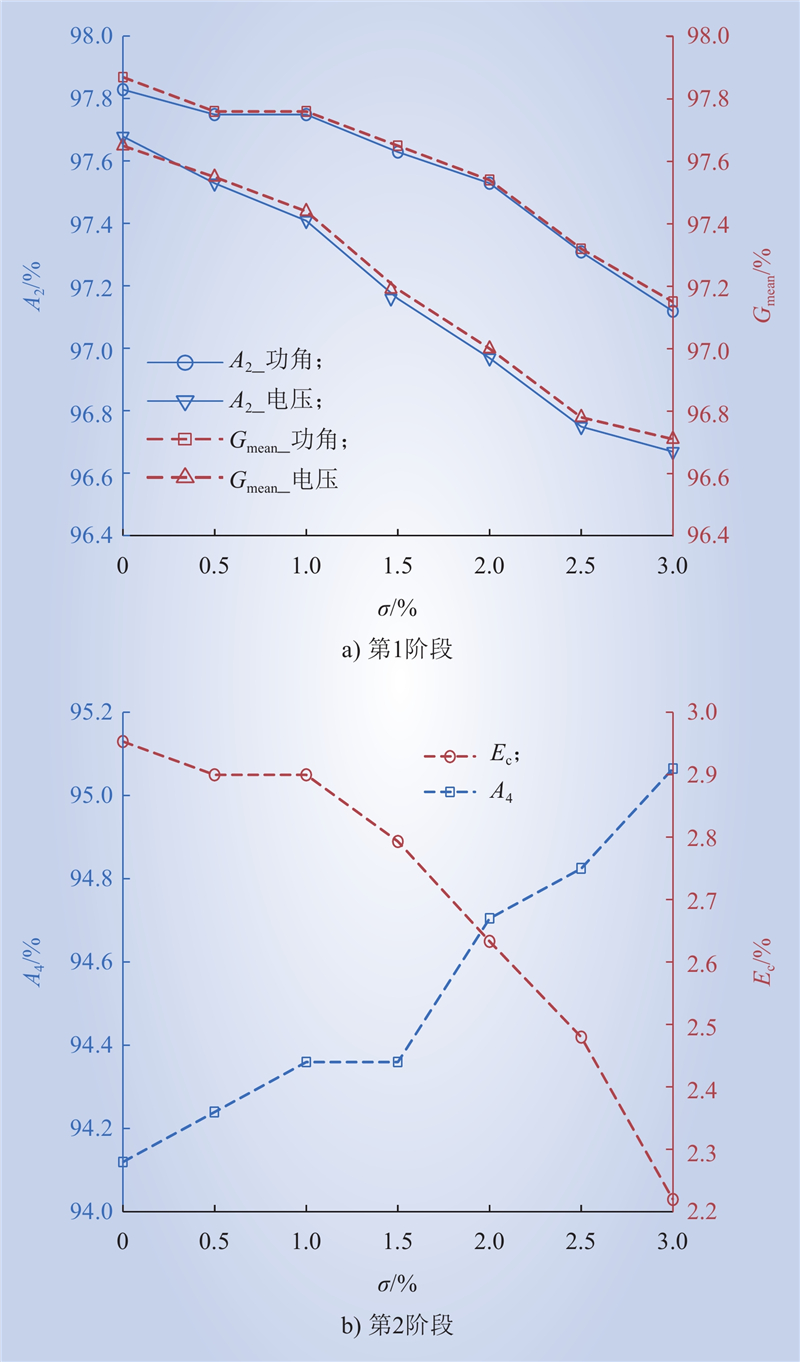
| 1 |
董武, 张健, 周勤勇, 等. 中国电力系统安全稳定性演化综述[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (1): 115- 127.
|
|
DONG Wu, ZHANG Jian, ZHOU Qinyong, et al. An overview of the evolution of security and stability of China’s power system[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (1): 115- 127.
|
| 2 |
AMJADY N. A framework of reliability assessment with consideration effect of transient and voltage stabilities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2004, 19 (2): 1005- 1014.
|
| 3 |
叶小宁, 王彩霞, 李琼慧, 等. 国外新能源高占比电力系统电力供应保障措施及启示[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (4): 61- 67.
|
|
YE Xiaoning, WANG Caixia, LI Qionghui, et al. Power supply ensuring measures and implications of foreign countries' power systems with high proportion of new energy[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (4): 61- 67.
|
| 4 |
CARRERAS B A, NEWMAN D E, DOBSON I. North American blackout time series statistics and implications for blackout risk[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2016, 31 (6): 4406- 4414.
|
| 5 |
OBUZ S, AYAR M, TREVIZAN R D, et al. Renewable and energy storage resources for enhancing transient stability margins: a PDE-based nonlinear control strategy[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2020, 116, 105510.
|
| 6 |
汤奕, 崔晗, 李峰, 等. 人工智能在电力系统暂态问题中的应用综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (1): 2- 13, 315.
|
|
TANG Yi, CUI Han, LI Feng, et al. Review on artificial intelligence in power system transient stability analysis[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (1): 2- 13, 315.
|
| 7 |
SHI Z T, YAO W, LI Z P, et al. Artificial intelligence techniques for stability analysis and control in smart grids: Methodologies, applications, challenges and future directions[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 278, 115733.
|
| 8 |
YANG H, ZHANG W, SHI F, et al. PMU-based model-free method for transient instability prediction and emergency generator-shedding control[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2019, 105, 381- 393.
|
| 9 |
DONG Y P, XIE X R, WANG K, et al. An emergency-demand-response based under speed load shedding scheme to improve short-term voltage stability[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 32 (5): 3726- 3735.
|
| 10 |
张若愚, 吴俊勇, 李宝琴, 等. 基于迁移学习的电力系统暂态稳定自适应预测[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (6): 2196- 2205.
|
|
ZHANG Ruoyu, WU Junyong, LI Baoqin, et al. Self-adaptive power system transient stability prediction based on transfer learning[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (6): 2196- 2205.
|
| 11 |
吴俊勇, 张若愚, 季佳伸, 等. 计及漏判/误判代价的两阶段电力系统暂态稳定预测方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44 (24): 44- 52.
|
|
WU Junyong, ZHANG Ruoyu, JI Jiashen, et al. Two-stage transient stability prediction method of power system considering cost of misdetection and false alarm[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44 (24): 44- 52.
|
| 12 |
刘建锋, 姚晨曦, 陈乐乐. 基于门控时空图神经网络的电力系统暂态稳定评估[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38 (2): 214- 223.
|
|
LIU Jianfeng, YAO Chenxi, CHEN Lele. Power system transient stability assessment based on gating spatial temporal graph neural network[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38 (2): 214- 223.
|
| 13 |
张建新, 蔡锱涵, 李诗旸, 等. 利用网络等值进行图降维的图注意力暂态功角稳定评估模型[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (4): 30- 40.
|
|
ZHANG Jianxin, CAI Zihan, LI Shiyang, et al. Transient power angle stability evaluation model for graph attention using network equivalence for graph dimensionality reduction[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (4): 30- 40.
|
| 14 |
张晓英, 高金, 王琨, 等. 基于电压时间序列的电力系统暂态电压稳定分析[J]. 智慧电力, 2021, 49 (3): 51- 58.
|
|
ZHANG Xiaoying, GAO Jin, WANG Kun, et al. Transient voltage stability analysis of power system based on voltage time series[J]. Smart Power, 2021, 49 (3): 51- 58.
|
| 15 |
SU H Y, LIU T Y. Enhanced-online-random-forest model for static voltage stability assessment using wide area measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33 (6): 6696- 6704.
|
| 16 |
周挺, 杨军, 詹祥澎, 等. 一种数据驱动的暂态电压稳定评估方法及其可解释性研究[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (11): 4416- 4425.
|
|
ZHOU Ting, YANG Jun, ZHAN Xiangpeng, et al. Data-driven method and interpretability analysis for transient voltage stability assessment[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (11): 4416- 4425.
|
| 17 |
朱林, 张健, 陈达, 等. 面向暂态电压稳定评估的卷积神经网络输入特征构建方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (1): 85- 93.
|
|
ZHU Lin, ZHANG Jian, CHEN Da, et al. Construction method for input features of convolutional neural network for transient voltage stability assessment[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (1): 85- 93.
|
| 18 |
黎晓, 刘崇茹, 辛蜀骏, 等. 暂态功角稳定与暂态电压稳定的耦合机理分析与耦合强度评估指标[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (15): 5091- 5107.
|
|
LI Xiao, LIU Chongru, XIN Shujun, et al. Coupling mechanism analysis and coupling strength evaluation index of transient power angle stability and transient voltage stability[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (15): 5091- 5107.
|
| 19 |
吴为, 汤涌, 孙华东, 等. 电力系统暂态功角失稳与暂态电压失稳的主导性识别[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34 (31): 5610- 5617.
|
|
WU Wei, TANG Yong, SUN Huadong, et al. The recognition of principal mode between rotor angle instability and transient voltage instability[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34 (31): 5610- 5617.
|
| 20 |
WANG Y H, SUN Y J, MEI S W. A method of distinguishing short-term voltage stability from rotor angle stability and its application[C]//IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies. Tianjin, China. IEEE, 2012: 1–5.
|
| 21 |
HAN T, CHEN Y B, MA J, et al. Surrogate modeling-based multi-objective dynamic VAR planning considering short-term voltage stability and transient stability[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33 (1): 622- 633.
|
| 22 |
顾卓远, 汤涌. 基于响应信息的电压与功角稳定实时紧急控制方案[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34 (28): 4876- 4885.
|
|
GU Zhuoyuan, TANG Yong. Response-information based real-time power system voltage stability and angle stability emergency control scheme[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34 (28): 4876- 4885.
|
| 23 |
孙黎霞, 彭嘉杰, 白景涛, 等. 结合图嵌入算法的电力系统多任务暂态稳定评估[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (2): 83- 91.
|
|
SUN Lixia, PENG Jiajie, BAI Jingtao, et al. Multi-task transient stability assessment of power system incorporating graph embedding algorithm[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (2): 83- 91.
|
| 24 |
史法顺, 吴俊勇, 季佳伸, 等. 基于深度学习的电力系统暂态电压与暂态功角稳定一体化超前评估[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (2): 741- 758.
|
|
SHI Fashun, WU Junyong, JI Jiashen, et al. Integrated advance assessment of power system transient voltage and transient angle stability based on deep learning[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (2): 741- 758.
|
| 25 |
史法顺, 吴俊勇, 吴昊衍, 等. 基于深度学习的电力系统暂态功角与暂态电压稳定裕度一体化评估[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (2): 731- 740.
|
|
SHI Fashun, WU Junyong, WU Haoyan, et al. Integrated evaluation of power system transient power angle and transient voltage stability margin based on deep learning[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (2): 731- 740.
|
| 26 |
石重托, 姚伟, 黄彦浩, 等. 基于SE-CNN和仿真数据的电力系统主导失稳模式智能识别[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (21): 7719- 7731.
|
|
SHI Zhongtuo, YAO Wei, HUANG Yanhao, et al. Power system dominant instability mode identification based on convolutional neural networks with squeeze and excitation block and simulation data[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (21): 7719- 7731.
|
| 27 |
ZHANG R F, YAO W, SHI Z T, et al. A graph attention networks-based model to distinguish the transient rotor angle instability and short-term voltage instability in power systems[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2022, 137, 107783.
|
| 28 |
ZHOU Y Z, XU T, YE L, et al. Transient rotor angle and voltage stability discrimination based on deep convolutional neural network with multiple inputs[C]//2021 IEEE 4th International Electrical and Energy Conference (CIEEC). Wuhan, China. IEEE, 2021: 1–6.
|
| 29 |
LASHGARI M, SHAHRTASH S M. Fast online decision tree-based scheme for predicting transient and short-term voltage stability status and determining driving force of instability[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2022, 137, 107738.
|
| 30 |
KUNDUR P, PASERBA J, AJJARAPU V, et al. Definition and classification of power system stability IEEE/CIGRE joint task force on stability terms and definitions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2004, 19 (3): 1387- 1401.
|
| 31 |
张海. 基于扩展等面积法的电力系统暂态稳定分析[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2006.
|
|
ZHANG Hai. Power system transient stability analysis based on EEAC method[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2006.
|
| 32 |
顾卓远, 汤涌, 易俊, 等. 电力系统功角失稳与局部感应电动机失稳相互影响机理分析[J]. 电网技术, 2017, 41 (8): 2499- 2505.
|
|
GU Zhuoyuan, TANG Yong, YI Jun, et al. Study on mechanism of interrelationship between power system angle stability and induction motor stability[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41 (8): 2499- 2505.
|
| 33 |
WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[M]//Computer Vision – ECCV 2018. Cham: Springer International Publishing2018: 3–19.
|
| 34 |
李宝琴, 吴俊勇, 邵美阳, 等. 基于集成深度置信网络的精细化电力系统暂态稳定评估[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44 (6): 17- 26.
|
|
LI Baoqin, WU Junyong, SHAO Meiyang, et al. Refined transient stability evaluation for power system based on ensemble deep belief network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44 (6): 17- 26.
|