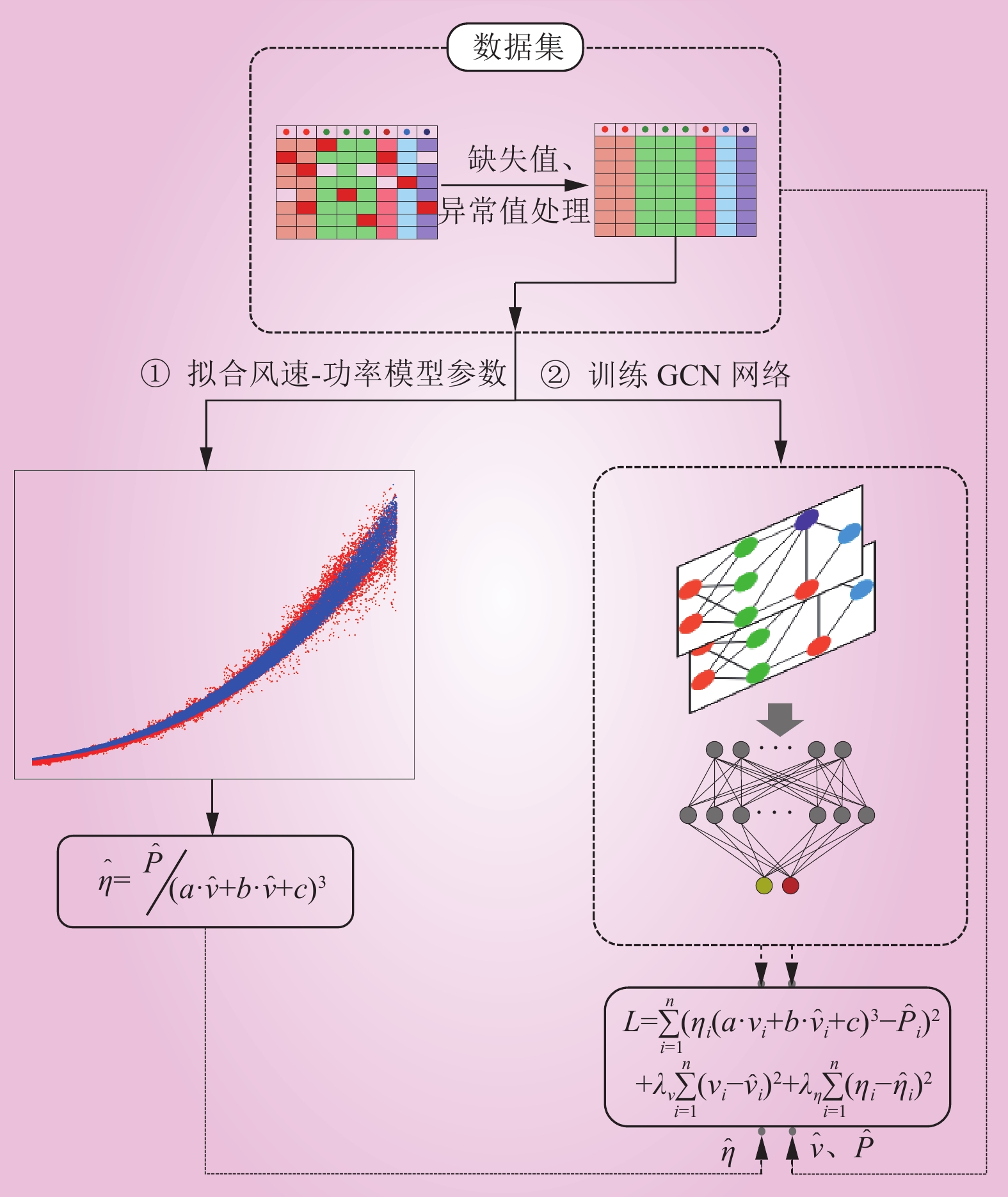
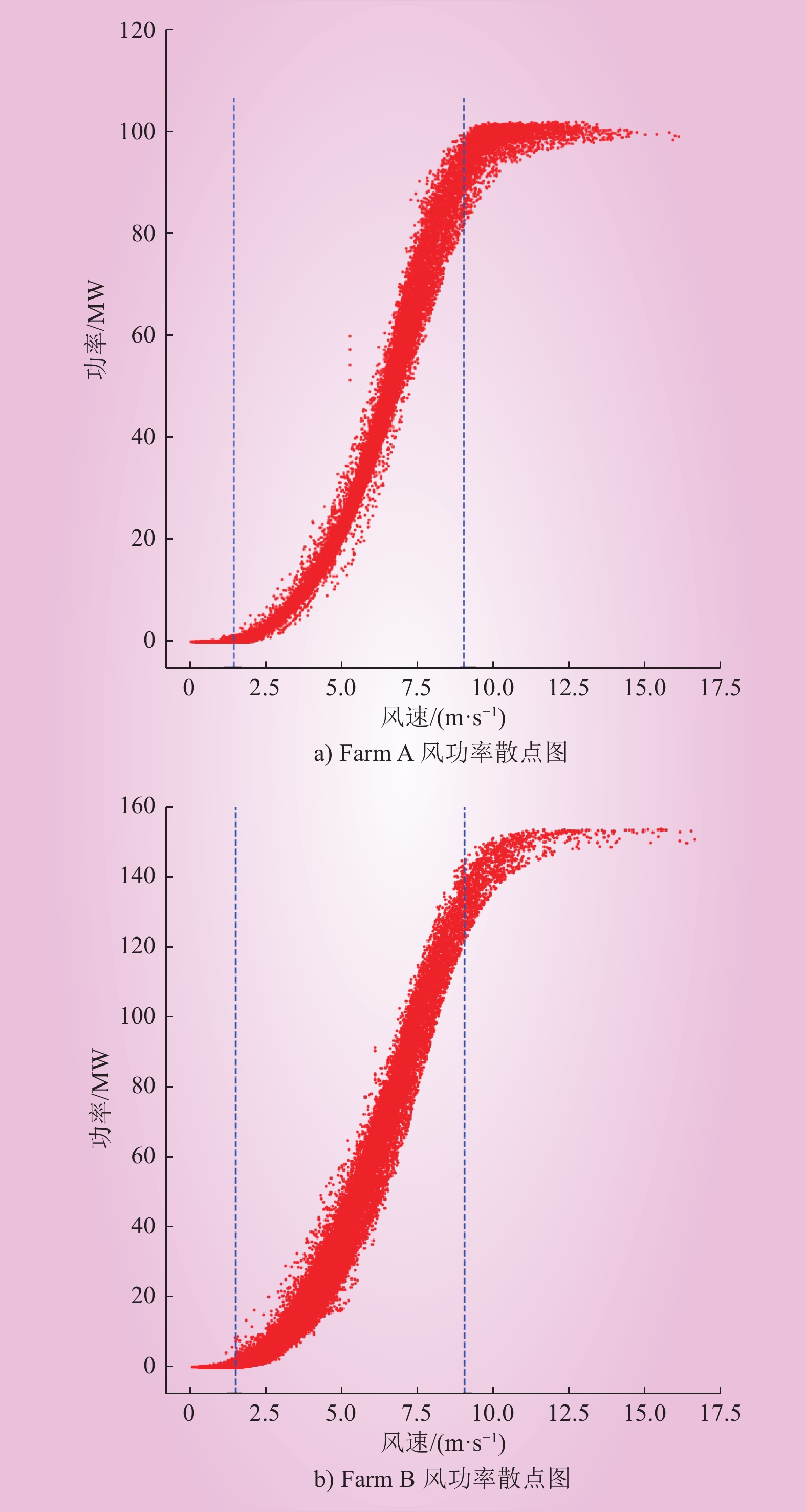
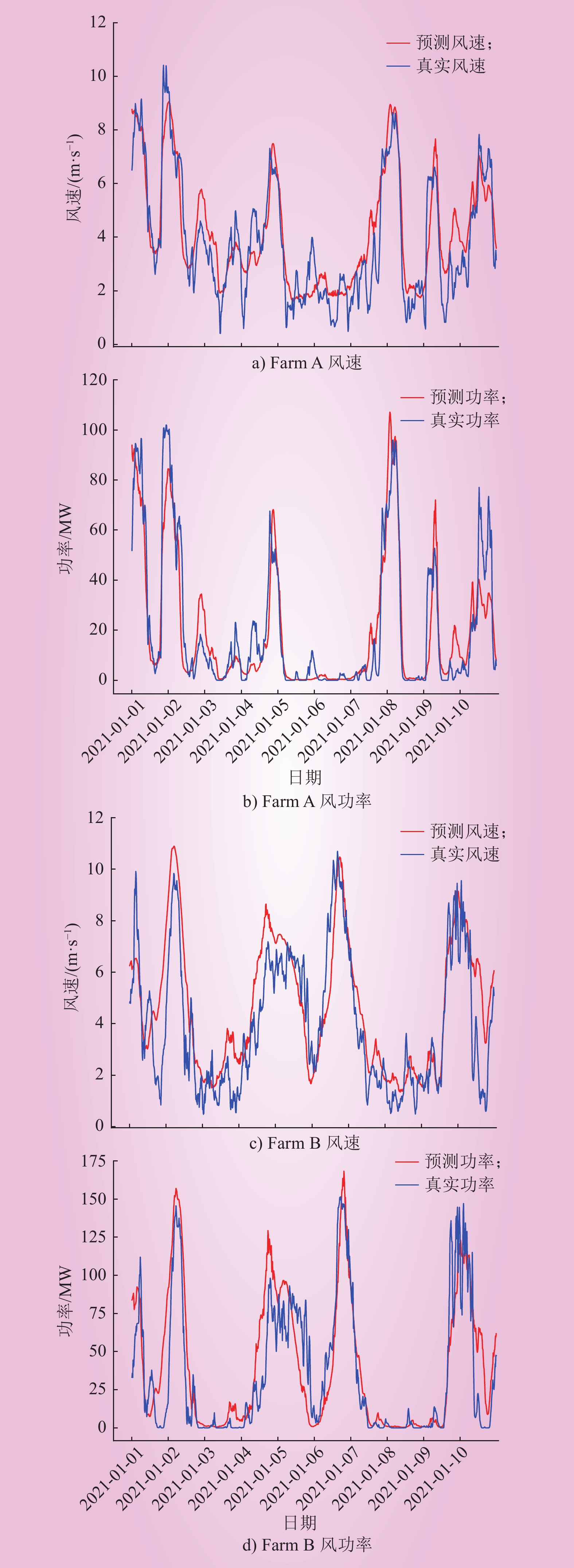
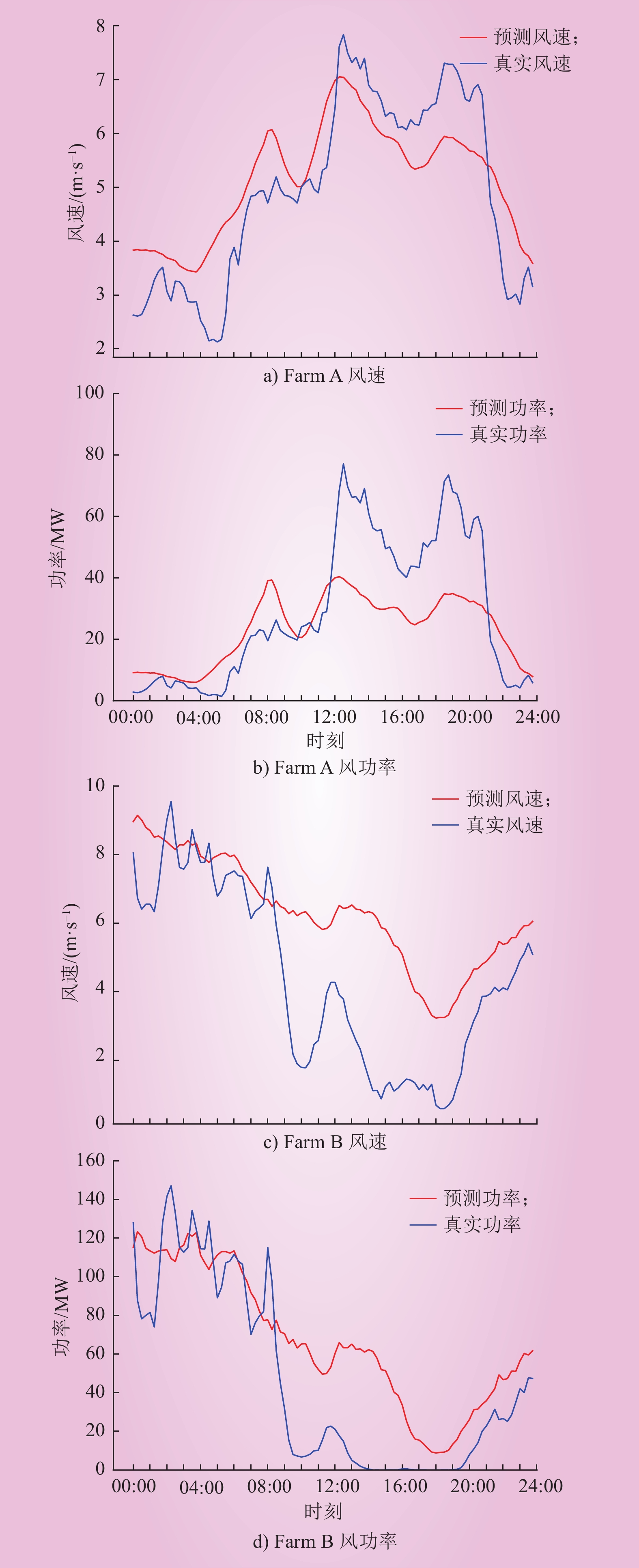
| 1 |
曹钰, 房磊. “双碳”背景下热电机组-储热联合运行消纳弃风策略[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 142- 149, 160.
|
|
CAO Yu, FANG Lei. Combined operation strategy of CHP unit and heat accumulator for eliminate abandoned wind under "double carbon" background[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 142- 149, 160.
|
| 2 |
吴晓刚, 阎洁, 葛畅, 等. 基于改进GRU-CNN的风光水一体化超短期功率预测方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (9): 178- 186, 205.
|
|
WU Xiaogang, YAN Jie, GE Chang, et al. Ultra-short-term power forecasting method for wind-solar-hydro integration based on improved GRU-CNN[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (9): 178- 186, 205.
|
| 3 |
赵永宁, 李卓, 叶林, 等. 基于时空相关性的风电功率超短期自适应预测方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (6): 94- 105.
|
|
ZHAO Yongning, LI Zhuo, YE Lin, et al. A very short-term adaptive wind power forecasting method based on spatio-temporal correlation[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (6): 94- 105.
|
| 4 |
赵倩, 黄景涛. 基于EMD-SA-SVR的超短期风电功率预测研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48 (4): 89- 96.
|
|
ZHAO Qian, HUANG Jingtao. On ultra-short-term wind power prediction based on EMD-SA-SVR[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48 (4): 89- 96.
|
| 5 |
苗长新, 王霞, 李昊, 等. 基于数值天气预报风速误差修正的风电功率日前预测[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (9): 3455- 3464.
|
|
MIAO Changxin, WANG Xia, LI Hao, et al. Day-ahead prediction of wind power based on NWP wind speed error correction[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (9): 3455- 3464.
|
| 6 |
陆秋贤, 马刚, 涂孟夫. 基于IEWT-FE-BO-LSTM模型的超短期风功率预测[J]. 水电能源科学, 2023, 41 (1): 217- 220.
|
|
LU Qiuxian, MA Gang, TU Mengfu. Ultra-short-term wind power prediction based on IEWT-FE-BO-LSTM model[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2023, 41 (1): 217- 220.
|
| 7 |
姜明洋, 徐丽, 张开军, 等. 基于季节指数调整的循环神经网络风速时间序列预测[J]. 太阳能学报, 2022, 43 (2): 444- 450.
|
|
JIANG Mingyang, XU Li, ZHANG Kaijun, et al. Recurrent neural network prediction of wind speed time series based on seasonal exponential adjustment[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2022, 43 (2): 444- 450.
|
| 8 |
李金龙, 王义民, 畅建霞, 等. 基于并行机器学习的风功率超短期预测[J]. 水力发电学报, 2023, 42 (1): 40- 51.
|
|
LI Jinlong, WANG Yimin, CHANG Jianxia, et al. Ultra-short-term wind power prediction based on parallel machine learning[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2023, 42 (1): 40- 51.
|
| 9 |
YUAN C, TANG Y M, MEI R, et al. A PSO-LSTM model of offshore wind power forecast considering the variation of wind speed in second-level time scale[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021, 1- 9.
|
| 10 |
ZHA W T, LIU J, LI Y L, et al. Ultra-short-term power forecast method for the wind farm based on feature selection and temporal convolution network[J]. ISA Transactions, 2022, 129, 405- 414.
|
| 11 |
陈海鹏, 李赫, 阚天洋, 等. 考虑风电时序特性的深度小波-时序卷积网络超短期风功率预测[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (4): 1653- 1665.
|
|
CHEN Haipeng, LI He, KAN Tianyang, et al. DWT-DTCNA ultra-short-term wind power prediction considering wind power timing characteristics[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (4): 1653- 1665.
|
| 12 |
武新章, 梁祥宇, 朱虹谕, 等. 基于CEEMDAN-GRA-PCC-ATCN的短期风电功率预测[J]. 山东大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52 (6): 146- 156.
|
|
WU Xinzhang, LIANG Xiangyu, ZHU Hongyu, et al. Short-term wind power forecasting based on CEEMDAN-GRA-PCC-ATCN[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2022, 52 (6): 146- 156.
|
| 13 |
马丽. 基于机器学习的中长期风功率预测方法研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2020
|
|
MA Li. Research on medium and long-term wind power prediction method based on machine learning[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2020.
|
| 14 |
何健伟, 曹渝昆. LSTM-RF的中长期风电功率组合预测方法[J]. 上海电力大学学报, 2020, 36 (4): 341- 350.
|
|
HE Jianwei, CAO Yukun. Wind power mid-long term load forecasting based on LSTM-RF combination forecasting method[J]. Journal of Shanghai University of Electric Power, 2020, 36 (4): 341- 350.
|
| 15 |
李铭. 基于风电场气象数据的风功率预测[D]. 包头: 内蒙古科技大学, 2021.
|
|
LI Ming. Wind power prediction based on meteorological data of wind farm[D]. Baotou: Inner Mongolia University of Science & Technology, 2021.
|
| 16 |
朱满庭. 基于深度学习的风电功率预测研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2021.
|
|
ZHU Manting. Research on wind power prediction based on deep learning[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021.
|
| 17 |
HAN S, QIAO Y H, YAN J, et al. Mid-to-long term wind and photovoltaic power generation prediction based on copula function and long short term memory network[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 239, 181- 191.
|
| 18 |
AHMED S I, RANGANATHAN P, SALEHFAR H. Forecasting of mid- and long-term wind power using machine learning and regression models[C]//2021 IEEE Kansas Power and Energy Conference (KPEC). Manhattan, KS, USA. IEEE, 2021: 1–6.
|
| 19 |
WU Y X, WU Q B, ZHU J Q. Data-driven wind speed forecasting using deep feature extraction and LSTM[J]. IET Renewable Power Generation, 2019, 13 (12): 2062- 2069.
|
| 20 |
WANG X X, LIU Y R, HOU J C, et al. Medium- and long-term wind-power forecasts, considering regional similarities[J]. Atmosphere, 2023, 14 (3): 430.
|
| 21 |
孙驷洲, 付敬奇, 朱峰. CGAQPSO优化LSSVM短期风电预测[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2016, 30 (11): 1718- 1725.
|
|
SUN Sizhou, FU Jingqi, ZHU Feng. Short-term wind power prediction based on LSSVM optimized by chaos Gauss attractor quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2016, 30 (11): 1718- 1725.
|