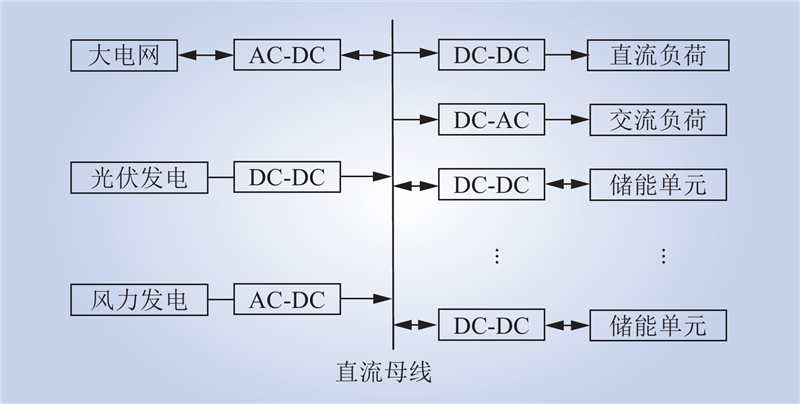
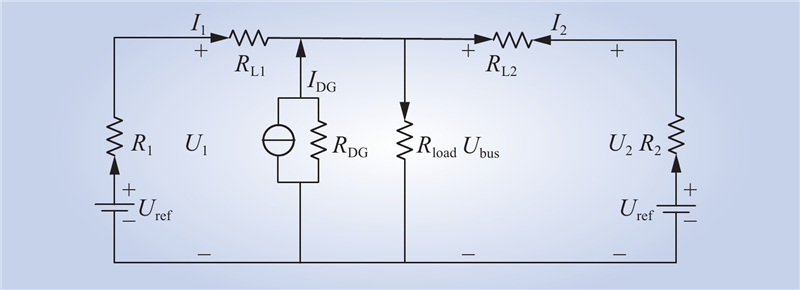
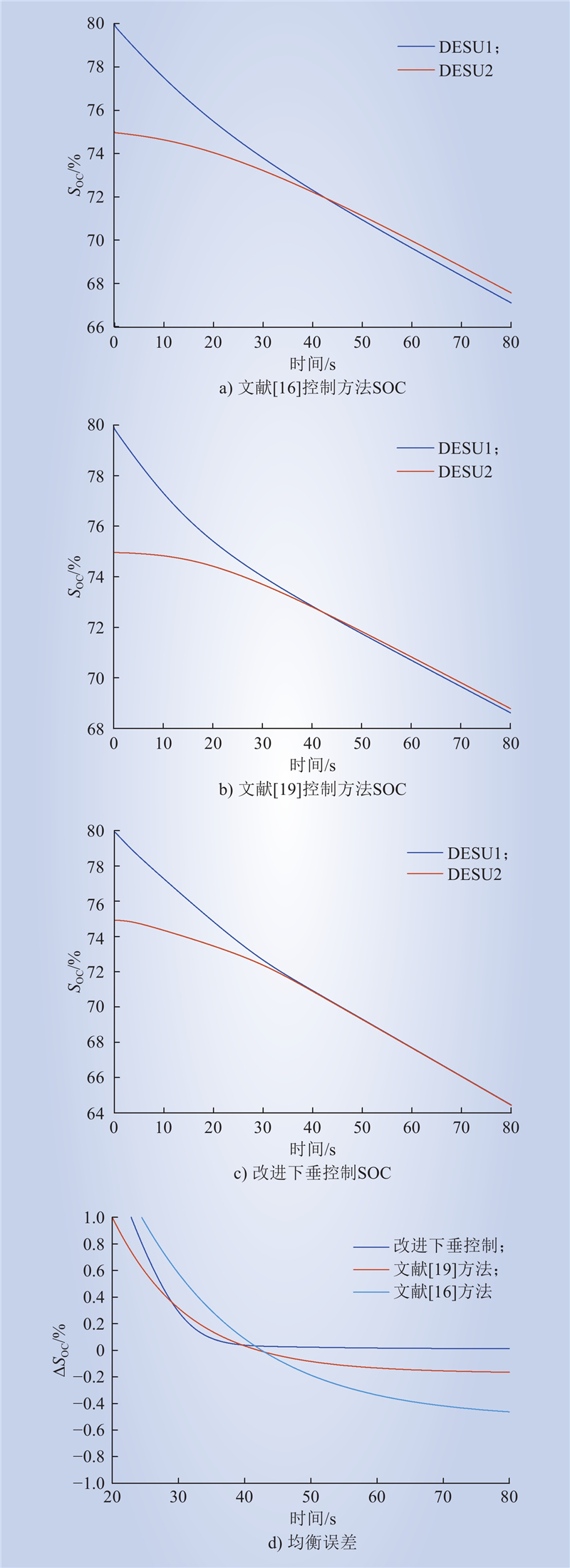
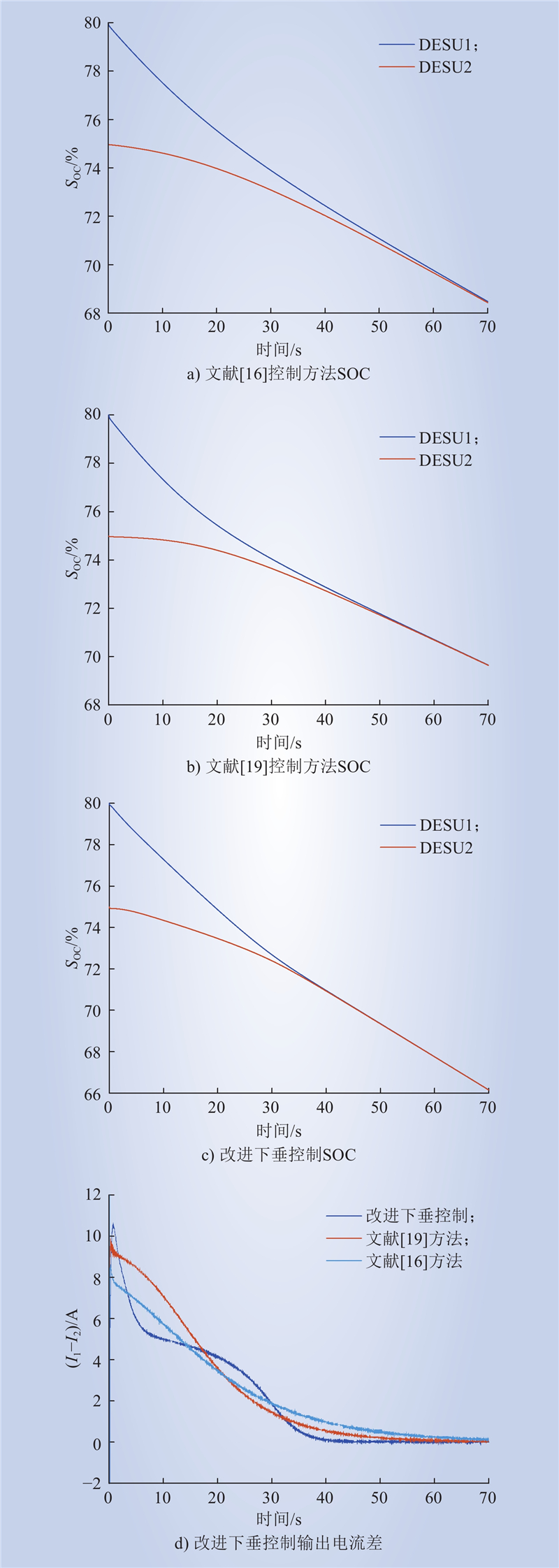
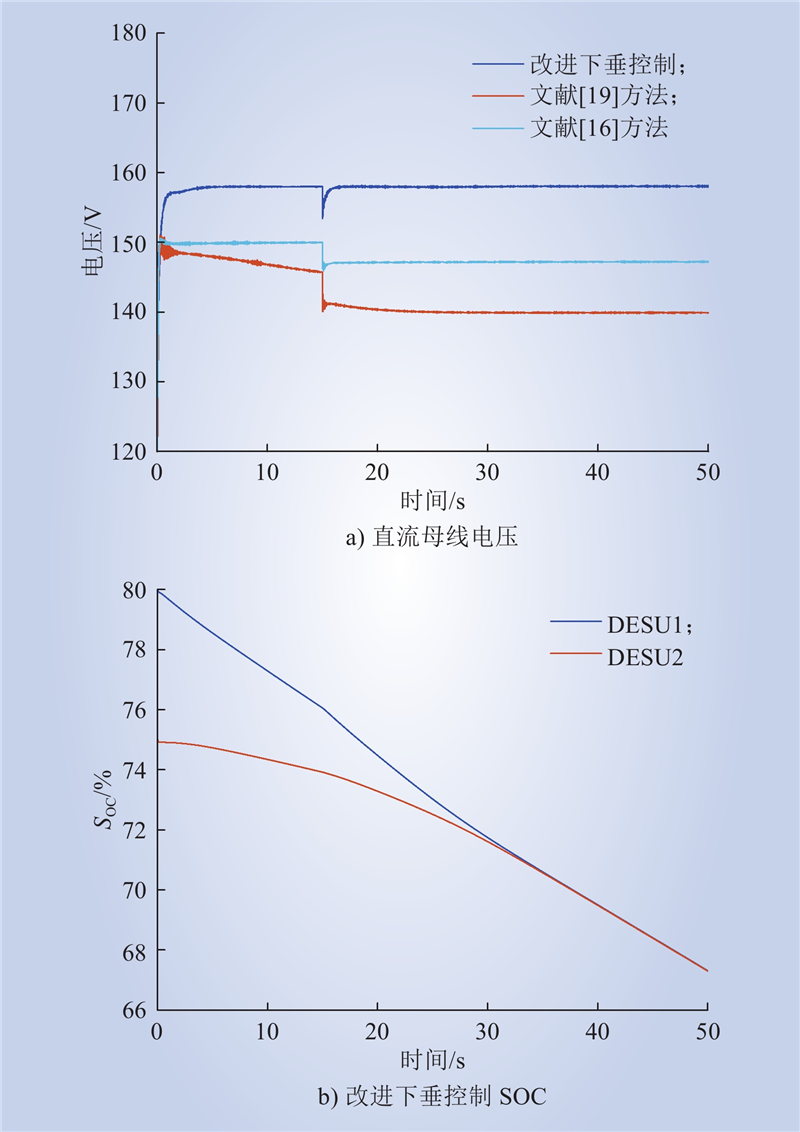
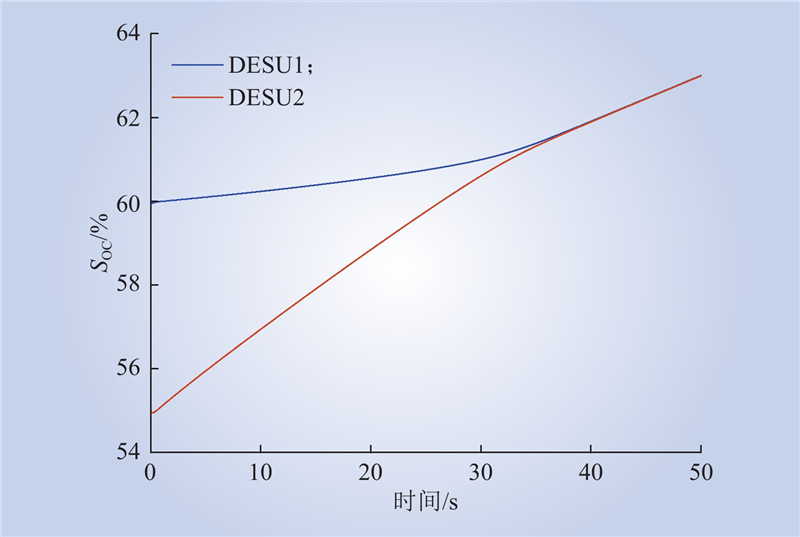
| 1 |
MOHAMED Y A R I, EL-SAADANY E F. Adaptive decentralized droop controller to preserve power sharing stability of paralleled inverters in distributed generation microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2008, 23 (6): 2806- 2816.
|
| 2 |
彭寒梅, 曹一家, 黄小庆. 对等控制孤岛微电网的静态安全风险评估[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36 (18): 4837- 4846, 5107.
|
|
PENG Hanmei, CAO Yijia, HUANG Xiaoqing. Static security risk assessment of islanded microgrids under peer-peer control[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36 (18): 4837- 4846, 5107.
|
| 3 |
孙佳航, 王小华, 黄景光, 等. 基于MPC-VSG的孤岛微电网频率和电压动态稳定控制策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (6): 51- 60, 81.
|
|
SUN Jiahang, WANG Xiaohua, HUANG Jingguang, et al. MPC-VSG based control strategy for dynamic stability of frequency and voltage in islanded microgrid[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (6): 51- 60, 81.
|
| 4 |
郝少飞, 邹文进, 葛浩然, 等. 基于改进鲸鱼优化算法的微电网优化运行[J]. 广东电力, 2022, 35 (1): 51- 59.
|
|
HAO Shaofei, ZOU Wenjin, GE Haoran, et al. Optimizing operation of microgrid based on improved whale optimization algorithm[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2022, 35 (1): 51- 59.
|
| 5 |
霍龙, 张誉宝, 陈欣. 人工智能在分布式储能技术中的应用[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43 (5): 707- 717.
|
|
HUO Long, ZHANG Yubao, CHEN Xin. Artificial intelligence applications in distributed energy storage technologies[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2022, 43 (5): 707- 717.
|
| 6 |
许丹莉, 顾慧杰, 何宇斌, 等. 端对端交易-云储能市场的非合作联合博弈出清模型[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (1): 85- 93.
|
|
XU Danli, GU Huijie, HE Yubin, et al. Non-cooperative joint game clearing model of peer-to-peer transaction and cloud energy stroage market[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (1): 85- 93.
|
| 7 |
邓诗蕾, 王明渝. 直流微电网潮流控制器与分布式储能协同控制策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46 (24): 40- 46.
|
|
DENG Shilei, WANG Mingyu. Cooperative control strategy of DC microgrid power flow controller and distributed energy storage system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2018, 46 (24): 40- 46.
|
| 8 |
张静炜, 朱想, 赫卫国, 等. 考虑光伏发电和储能系统调压能力的配电网储能容量优化配置[J]. 广东电力, 2018, 31 (7): 30- 35.
|
|
ZHANG Jingwei, ZHU Xiang, HE Weiguo, et al. Optimized configuration for ESS capacity of distribution network considering voltage regulation ability of photovoltaic generation and ESS[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2018, 31 (7): 30- 35.
|
| 9 |
MOKHTAR M, MAREI M I, EL-SATTAR A A. An adaptive droop control scheme for DC microgrids integrating sliding mode voltage and current controlled boost converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10 (2): 1685- 1693.
|
| 10 |
袁娜娜, 王允建, 张君, 等. 直流微网中基于SOC的改进下垂控制[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47 (15): 17- 23.
|
|
YUAN Nana, WANG Yunjian, ZHANG Jun, et al. Improved droop control based on SOC in DC microgrid[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47 (15): 17- 23.
|
| 11 |
郭昆丽, 付建哲, 闫东, 等. 考虑不同容量的储能单元荷电状态均衡研究[J]. 电源技术, 2021, 45 (9): 1202- 1204, 1226.
|
|
GUO Kunli, FU Jianzhe, YAN Dong, et al. Research on state of charge balance of energy storage units considering different capacity[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 45 (9): 1202- 1204, 1226.
|
| 12 |
郑丽君, 王子鹏, 吕世轩, 等. 基于荷电状态的直流微电网中多储能分级运行控制方法[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (3): 1006- 1015.
|
|
ZHENG Lijun, WANG Zipeng, LÜ Shixuan, et al. Hierarchical operation control of multi-energy storage in DC microgrid based on state of charge[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (3): 1006- 1015.
|
| 13 |
朱珊珊, 汪飞, 郭慧, 等. 直流微电网下垂控制技术研究综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (1): 72- 84, 344.
|
|
ZHU Shanshan, WANG Fei, GUO Hui, et al. Overview of droop control in DC microgrid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (1): 72- 84, 344.
|
| 14 |
韦佐霖, 陈民铀, 李杰, 等. 孤岛微网中分布式储能SOC和效率均衡控制策略[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2018, 38 (4): 169- 177.
|
|
WEI Zuolin, CHEN Minyou, LI Jie, et al. Balancing control strategy of SOC and efficiency for distributed energy storage in islanded microgrid[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2018, 38 (4): 169- 177.
|
| 15 |
XU D Z, XU A J, YANG C S, et al. A novel double-quadrant SoC consistent adaptive droop control in DC microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2020, 67 (10): 2034- 2038.
|
| 16 |
OLIVEIRA T R, GONÇALVES SILVA W W A, DONOSO-GARCIA P F. Distributed secondary level control for energy storage management in DC microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2017, 8 (6): 2597- 2607.
|
| 17 |
米阳, 蔡杭谊, 袁明瀚, 等. 直流微电网分布式储能系统电流负荷动态分配方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2019, 39 (10): 17- 23.
|
|
MI Yang, CAI Hangyi, YUAN Minghan, et al. Dynamic distribution method of current load for distributed energy storage system in DC microgrid[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2019, 39 (10): 17- 23.
|
| 18 |
刘勇, 雷延科, 盘宏斌. 一种直流微电网无母线电压偏移的均衡控制策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48 (12): 154- 161.
|
|
LIU Yong, LEI Yanke, PAN Hongbin. A balancing control strategy for DC microgrid without bus voltage offset[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48 (12): 154- 161.
|
| 19 |
李鹏程, 张纯江, 袁然然, 等. 改进SOC下垂控制的分布式储能系统负荷电流分配方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37 (13): 3746- 3754.
|
|
LI Pengcheng, ZHANG Chunjiang, YUAN Ranran, et al. Load current sharing method of distributed energy storage systems by improved SOC drooping control[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37 (13): 3746- 3754.
|
| 20 |
米阳, 纪宏澎, 何星瑭, 等. 多储能独立直流微电网自适应分级协调控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (7): 1980- 1989, 2213.
|
|
MI Yang, JI Hongpeng, HE Xingtang, et al. Adaptive hierarchical coordinated control of multi-energy storage in isolated DC microgrid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (7): 1980- 1989, 2213.
|
| 21 |
柴秀慧, 张纯江, 柴建国, 等. 改进互联通信荷电状态下垂控制及功率均衡优化[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36 (16): 3365- 3374.
|
|
CHAI Xiuhui, ZHANG Chunjiang, CHAI Jianguo, et al. Improved interconnected communication state of charge droop control and power balance optimization[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36 (16): 3365- 3374.
|
| 22 |
樊重阳, 何山. 电流精确分配的直流微网储能单元SOC均衡控制策略[J]. 安徽大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46 (3): 102- 108.
|
|
FAN Chongyang, HE Shan. SOC balancing control strategy of energy storage unit in DC microgrid with accurate current distribution[J]. Journal of Anhui University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 46 (3): 102- 108.
|
| 23 |
XU Y L, SHEN X W. Optimal control based energy management of multiple energy storage systems in a microgrid[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6, 32925- 32934.
|
| 24 |
LU X N, SUN K, GUERRERO J M, et al. SoC-based droop method for distributed energy storage in DC microgrid applications[C]//2012 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics. Hangzhou, China. IEEE, 2012: 1640–1645.
|