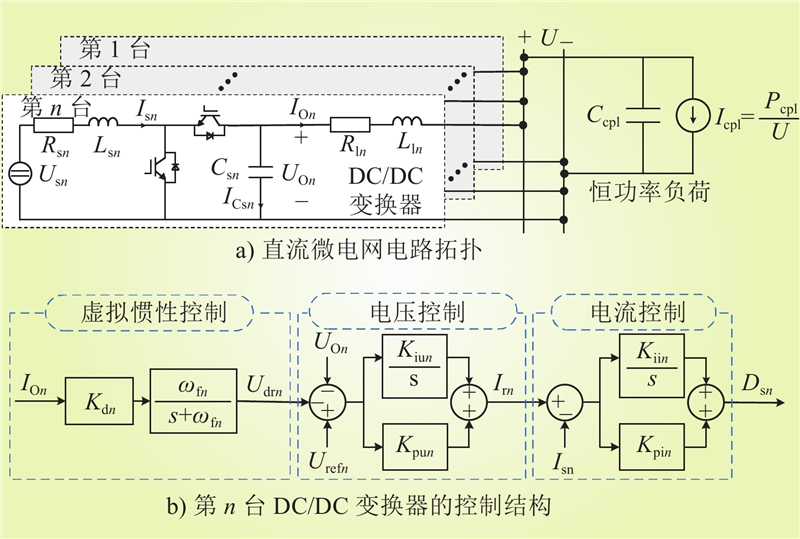
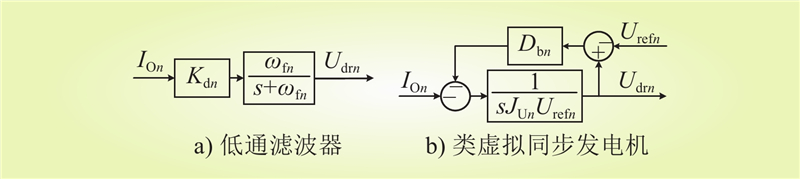
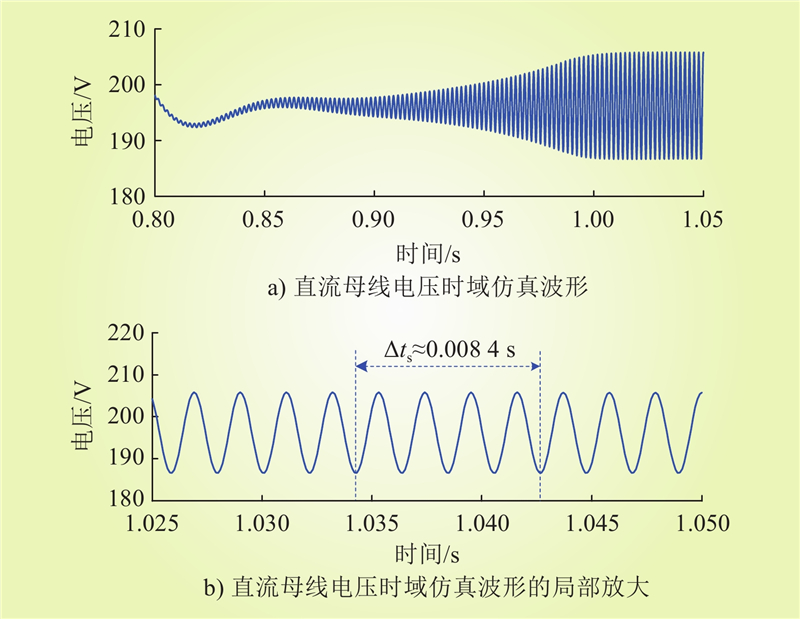
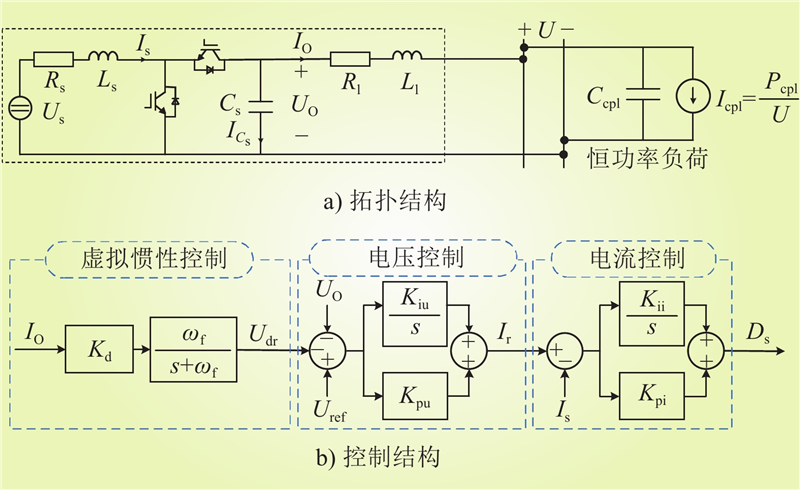
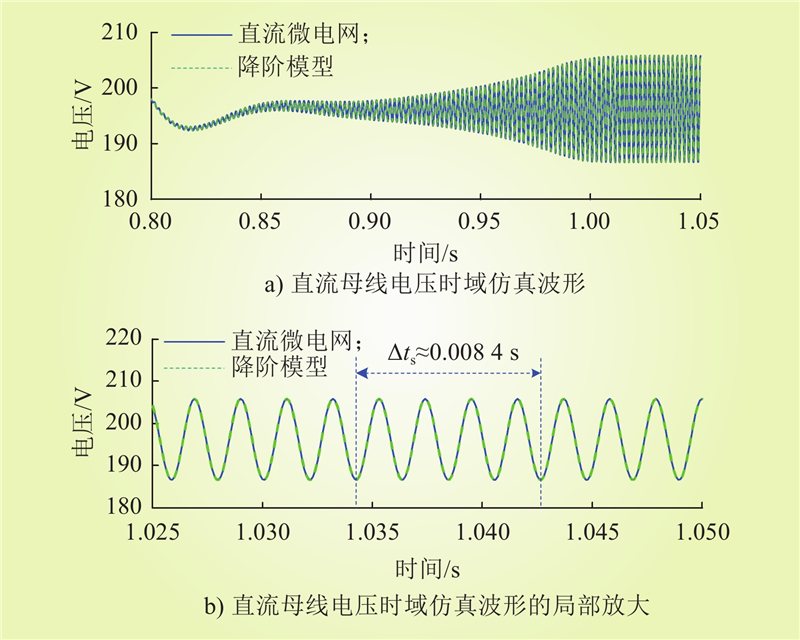
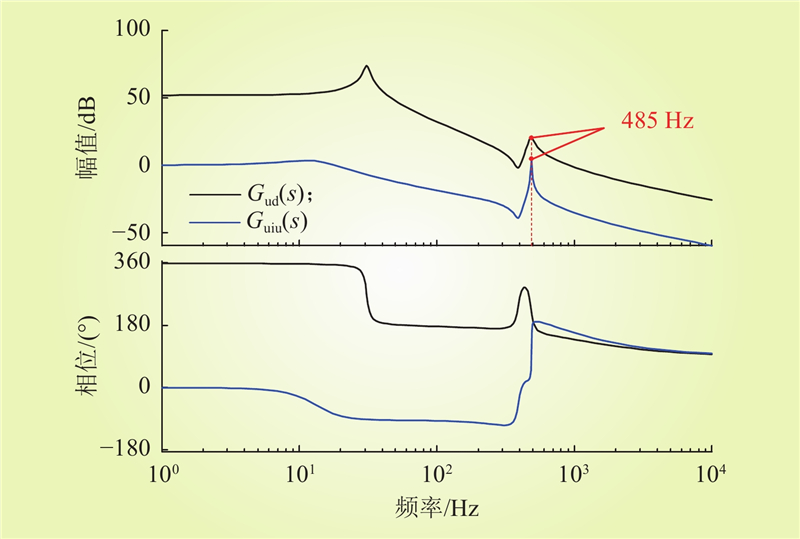
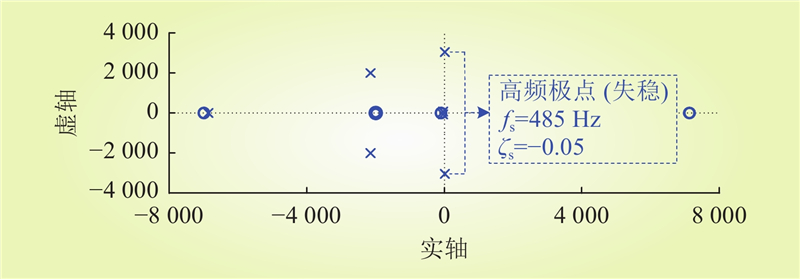
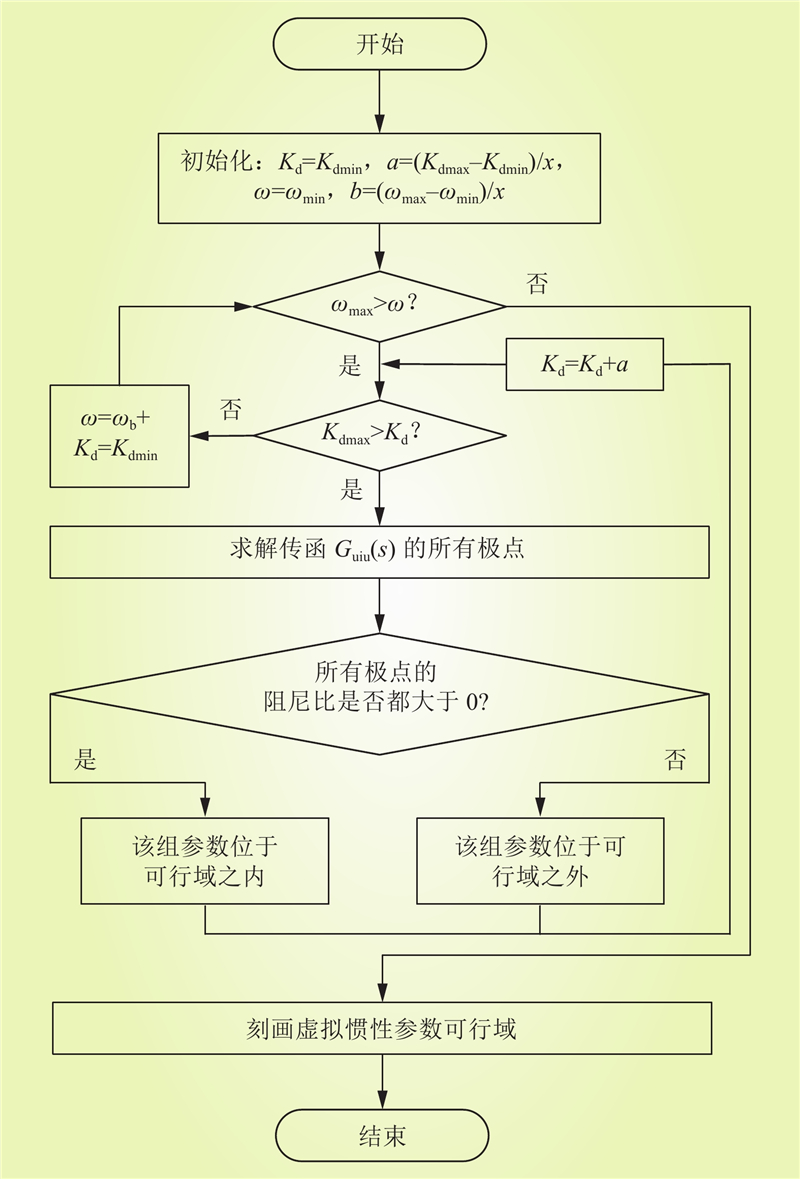
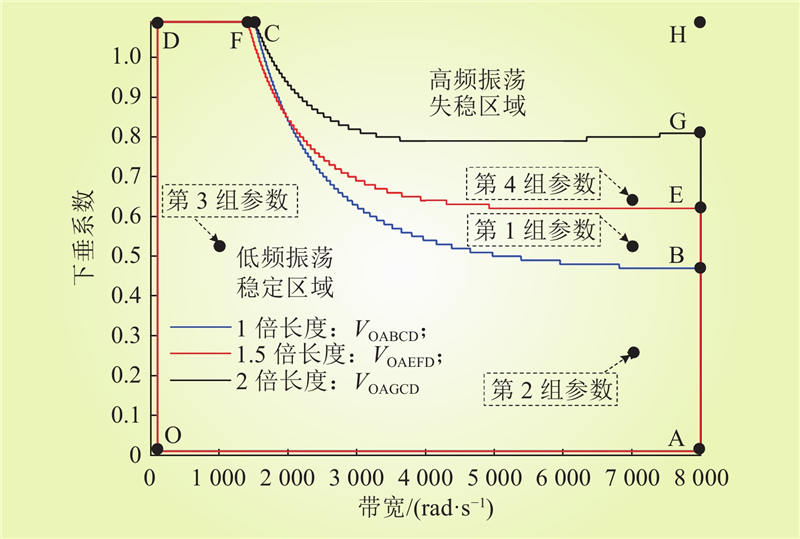
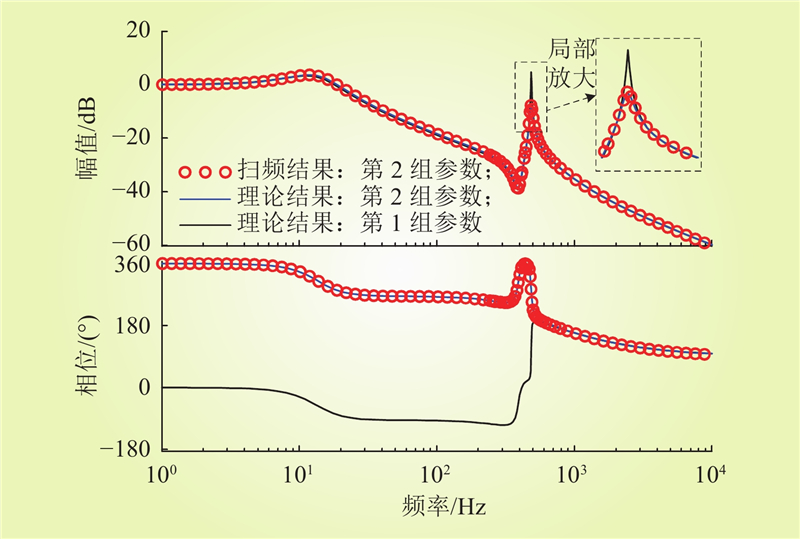
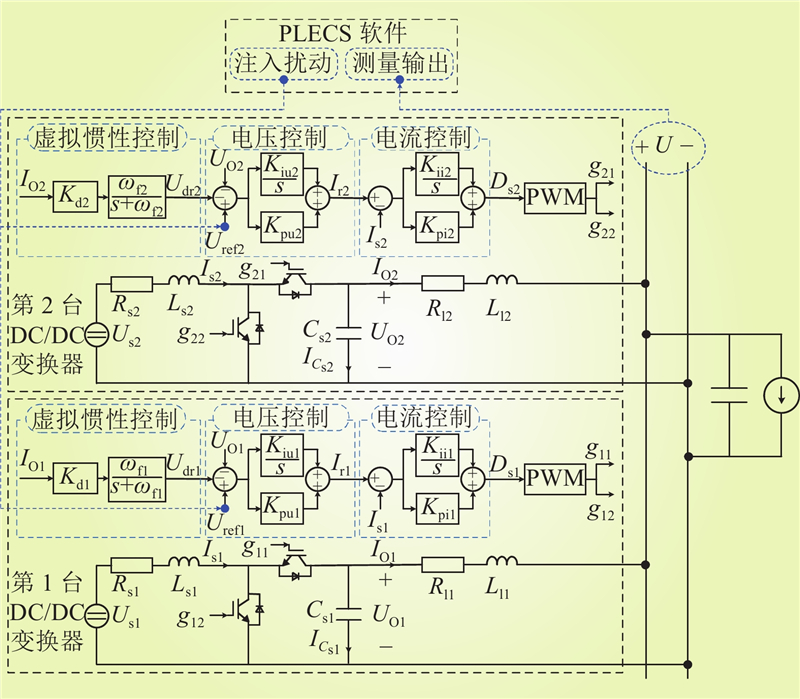
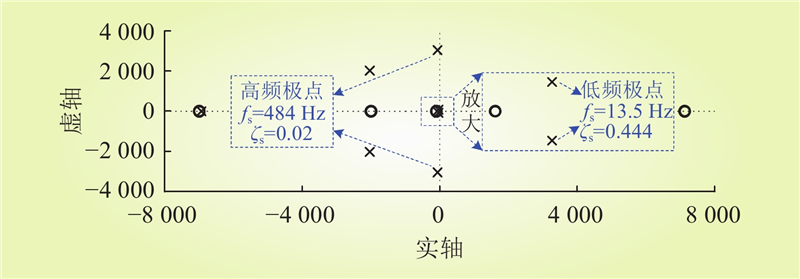
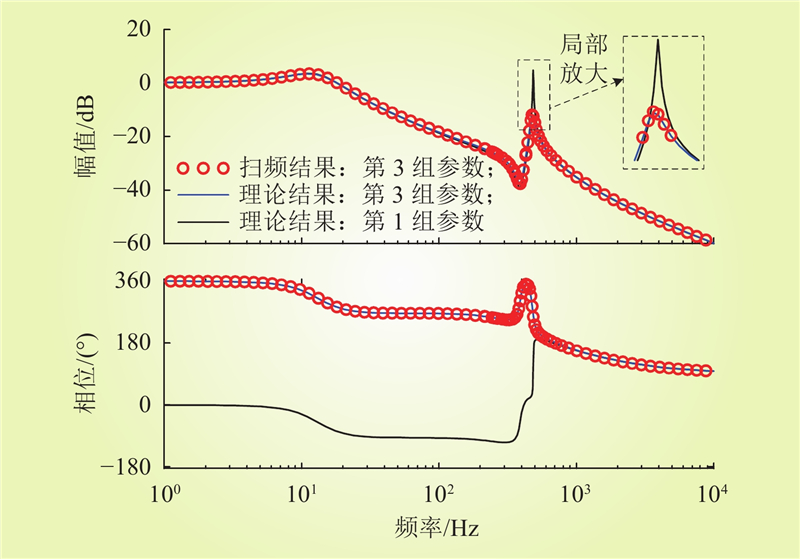
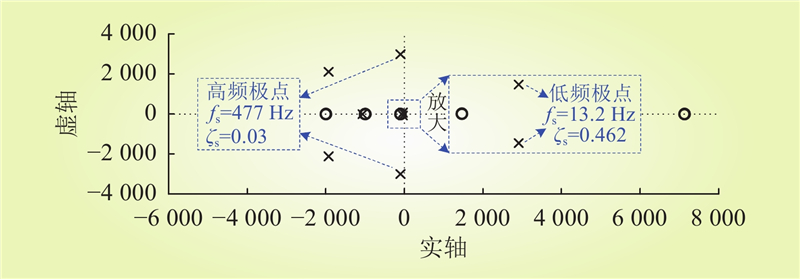
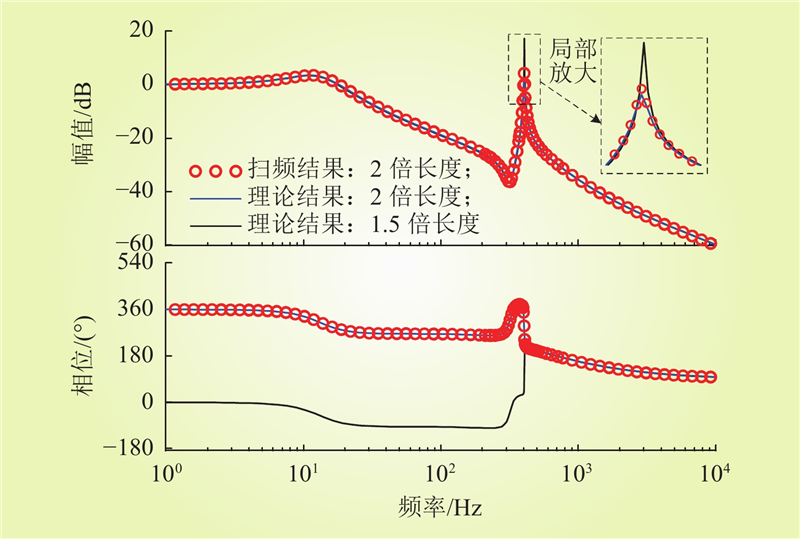
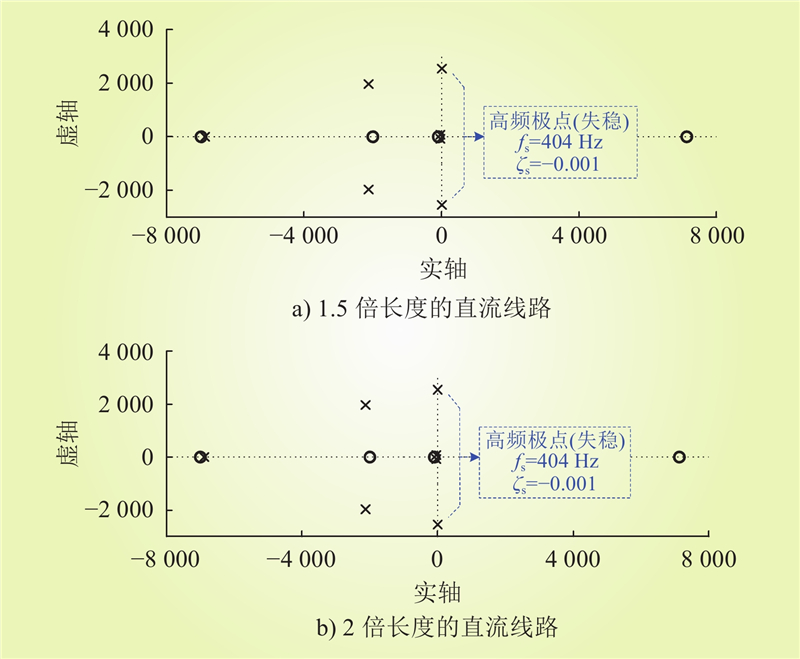
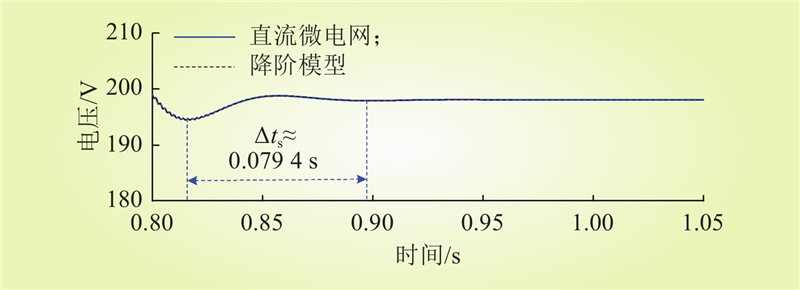
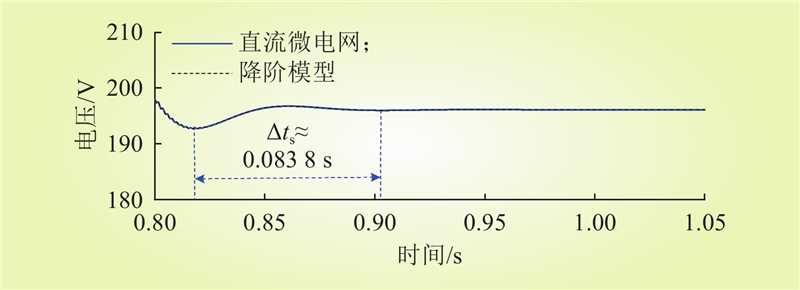
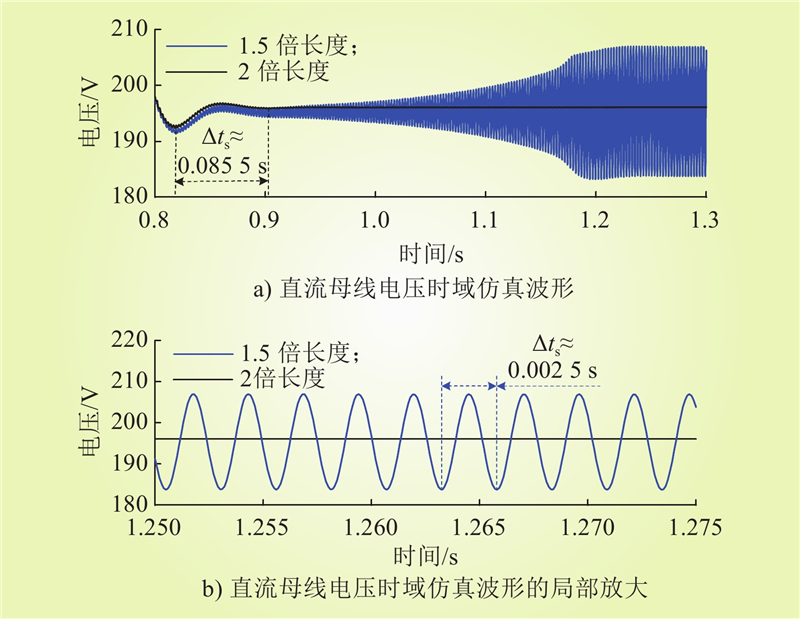
| 1 |
刘海涛, 熊雄, 季宇. 基于有限状态机转换矩阵建模的直流配电系统精细化控制[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (10): 89- 96.
|
|
LIU Haitao, XIONG Xiong, JI Yu. Precise control of DC distributed system based on finite state machine matrix modeling[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (10): 89- 96.
|
| 2 |
袁宇波, 易文飞, 赵学深, 等. 一种基于泰勒展开的临界降阶直流配电系统稳定控制算法[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (10): 73- 80.
|
|
YUAN Yubo, YI Wenfei, ZHAO Xueshen, et al. A stabilization control method of supercritical reduced-order medium-voltage DC distribution system based on Taylor expansion[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (10): 73- 80.
|
| 3 |
杨茂, 杨明. 高比例新能源电力系统功率预测及优化运行技术[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2024, 44 (1): 5- 6.
|
| 4 |
明远山, 胡慧慧, 刘凯旋, 等. 孤岛模式下直流微网中储能单元SOC均衡控制策略[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38 (4): 57- 64.
|
|
MING Yuanshan, HU Huihui, LIU Kaixuan, et al. Research on SOC balance control strategy of energy storage unit in DC microgrid in island mode[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38 (4): 57- 64.
|
| 5 |
李瑞, 李占凯, 张福民, 等. 基于共识算法的直流微网群分布式优化调度策略[J]. 南方电网技术, 2022, 16 (1): 49- 57.
|
|
LI Rui, LI Zhankai, ZHANG Fumin, et al. Distributed optimal scheduling strategy of DC microgrid cluster based on consensus algorithm[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2022, 16 (1): 49- 57.
|
| 6 |
李鹏飞, 李霞林, 王成山, 等. 中低压柔性直流配电系统稳定性分析模型与机理研究综述[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (5): 3- 21.
|
|
LI Pengfei, LI Xialin, WANG Chengshan, et al. Review of stability analysis model and mechanism research of medium-and low-voltage flexible DC distribution system[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (5): 3- 21.
|
| 7 |
王鑫, 杨德健, 金恩淑, 等. 双馈风电机的虚拟惯性控制优化策略[J]. 智慧电力, 2022, 50 (8): 1- 6, 81.
|
|
WANG Xin, YANG Dejian, JIN Enshu, et al. Improved virtual inertial control strategy of doubly-fed induction generator[J]. Smart Power, 2022, 50 (8): 1- 6, 81.
|
| 8 |
杨继鑫, 王久和, 王勉, 等. 基于无源控制的光储直流微网虚拟惯性控制策略研究[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42 (5): 576- 584.
|
|
YANG Jixin, WANG Jiuhe, WANG Mian, et al. Research on virtual inertial control strategy of DC microgrid with photovoltaic and storage system based on passivity-based control[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2021, 42 (5): 576- 584.
|
| 9 |
姚广增, 彭克, 李海荣, 等. 柔性直流配电系统高频振荡降阶模型与机理分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44 (20): 29- 36.
|
|
YAO Guangzeng, PENG Ke, LI Hairong, et al. Reduced-order model and mechanism analysis of high-frequency oscillation in flexible DC distribution system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44 (20): 29- 36.
|
| 10 |
李鹏飞, 郭力, 王洪达, 等. 直流微电网高频振荡稳定问题的降阶建模及分析[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (5): 65- 72.
|
|
LI Pengfei, GUO Li, WANG Hongda, et al. Reduced-order modeling and analysis of high-frequency oscillation stability in DC microgrid[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (5): 65- 72.
|
| 11 |
RASHIDIRAD N, HAMZEH M, SHESHYEKANI K, et al. High-frequency oscillations and their leading causes in DC microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2017, 32 (4): 1479- 1491.
|
| 12 |
李鲁阳, 裴玮, 邓卫, 等. 改善直流配电网中VSC与线路交互失稳的有源阻尼策略[J]. 高电压技术, 2019, 45 (9): 2884- 2894.
|
|
LI Luyang, PEI Wei, DENG Wei, et al. Active damping strategy for improving VSC and line interaction instability in DC distribution network[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2019, 45 (9): 2884- 2894.
|
| 13 |
LI X L, GUO L, ZHANG S H, et al. Observer-based DC voltage droop and current feed-forward control of a DC microgrid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9 (5): 5207- 5216.
|
| 14 |
郭力, 冯怿彬, 李霞林, 等. 直流微电网稳定性分析及阻尼控制方法研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36 (4): 927- 936.
|
|
GUO Li, FENG Yibin, LI Xialin, et al. Stability analysis and research of active damping method for DC microgrids[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36 (4): 927- 936.
|
| 15 |
朱晓荣, 孟凡奇. 含虚拟惯性控制的直流微电网稳定性分析[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (1): 208- 218.
|
|
ZHU Xiaorong, MENG Fanqi. Stability analysis of DC microgrid with virtual inertia control[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (1): 208- 218.
|
| 16 |
付媛, 李浩, 张祥宇. 基于振荡状态反馈的直流微网储能换流器的有源阻尼控制技术[J]. 高电压技术, 2021, 47 (3): 927- 937.
|
|
FU Yuan, LI Hao, ZHANG Xiangyu. Active damping control of energy storage converter in DC microgrid based on oscillatory state feedback[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2021, 47 (3): 927- 937.
|
| 17 |
朱晓荣, 韩丹慧. 基于虚拟惯性控制的直流微电网稳定性分析及其改进方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2019, 39 (12): 121- 127.
|
|
ZHU Xiaorong, HAN Danhui. Stability analysis of DC microgrid based on virtual inertia control and its improved method[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2019, 39 (12): 121- 127.
|
| 18 |
徐李清, 郭春义, 杨硕. 联接低惯量交流系统的MMC与发电机之间的低频交互振荡模式研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (9): 3402- 3415.
|
|
XU Liqing, GUO Chunyi, YANG Shuo. Research on low frequency interactive oscillation mode between generator and MMC connected to low inertia AC system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (9): 3402- 3415.
|
| 19 |
ZHANG Z, FANG J Y, DONG C Y, et al. Enhanced grid frequency and DC-link voltage regulation in hybrid AC/DC microgrids through bidirectional virtual inertia support[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70 (7): 6931- 6940.
|
| 20 |
许津铭, 谢少军, 肖华锋. LCL滤波器有源阻尼控制机制研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2012, 32 (9): 27- 33, 6.
|
|
XU Jinming, XIE Shaojun, XIAO Huafeng. Research on control mechanism of active damping for LCL filters[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2012, 32 (9): 27- 33, 6.
|
| 21 |
朱晓荣, 孟凡奇, 谢志云. 基于虚拟同步发电机的直流微网DC-DC变换器控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (21): 132- 140.
|
|
ZHU Xiaorong, MENG Fanqi, XIE Zhiyun. Control strategy of DC-DC converter in DC microgrid based on virtual synchronous generator[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (21): 132- 140.
|
| 22 |
沈可心, 薛博文, 朱晓荣. 直流微网中直驱风机的类虚拟同步发电机惯性控制策略[J]. 高电压技术, 2023, 49 (6): 2526- 2537.
|
|
SHEN Kexin, XUE Bowen, ZHU Xiaorong. Inertia control strategy of direct-driven wind generation system in DC microgrid based on analogous virtual synchronous generator[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2023, 49 (6): 2526- 2537.
|
| 23 |
张纯江, 暴云飞, 孟宪慧, 等. 直流微网储能DC/DC变换器的自适应虚拟直流电机控制[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (1): 12- 20.
|
|
ZHANG Chunjiang, BAO Yunfei, MENG Xianhui, et al. Adaptive virtual DC machine control for a DC microgrid energy storage DC/DC converter[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (1): 12- 20.
|
| 24 |
朱琳, 赵学深, 郭力, 等. 计及换流器间动态交互的中压直流配电系统控制参数设计[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (3): 121- 128.
|
|
ZHU Lin, ZHAO Xueshen, GUO Li, et al. Control parameter design of medium-voltage DC distribution system considering dynamic interaction between converters[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (3): 121- 128.
|
| 25 |
CUPELLI M, ZHU L, MONTI A. Why ideal constant power loads are not the worst case condition from a control standpoint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2015, 6 (6): 2596- 2606.
|