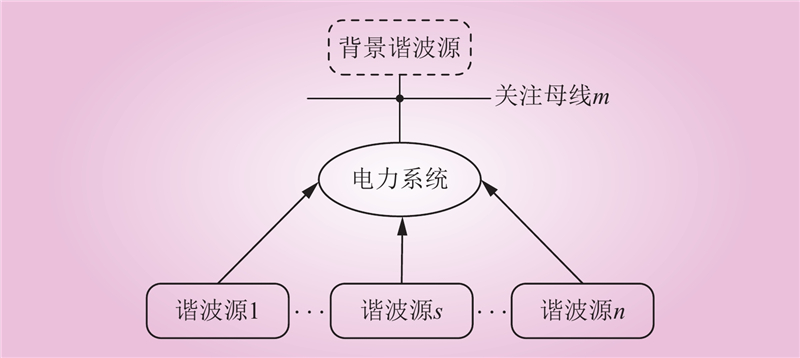
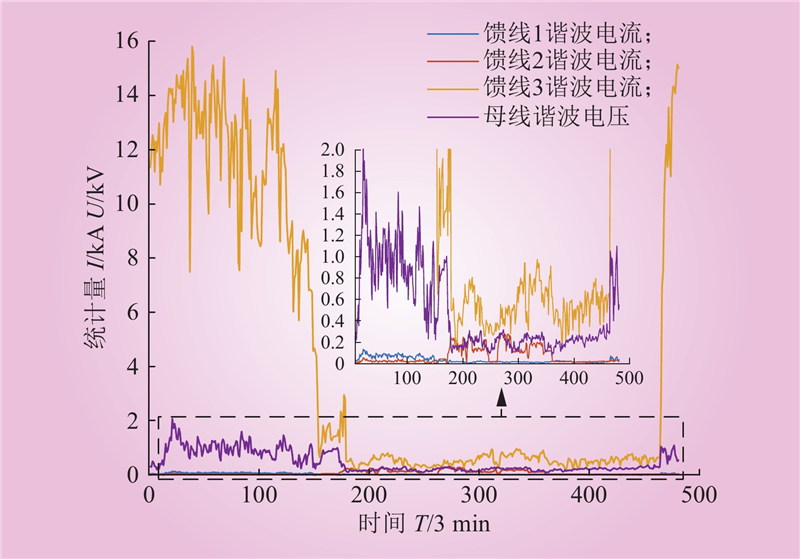
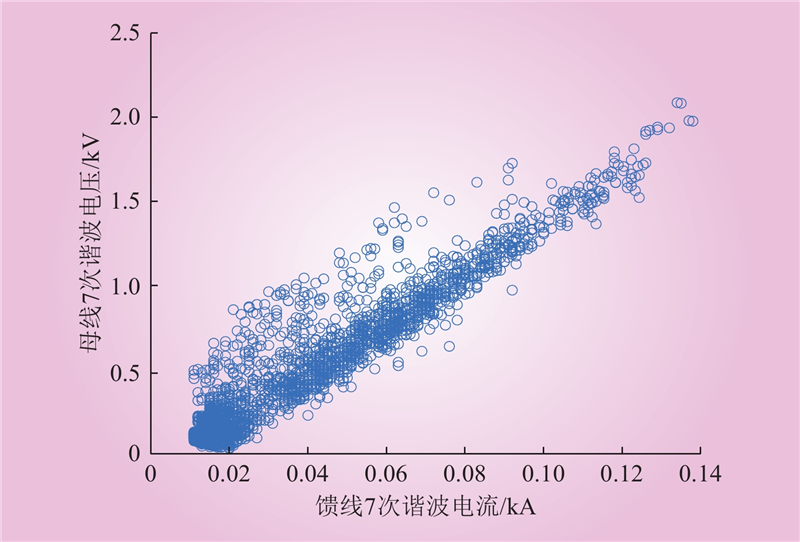
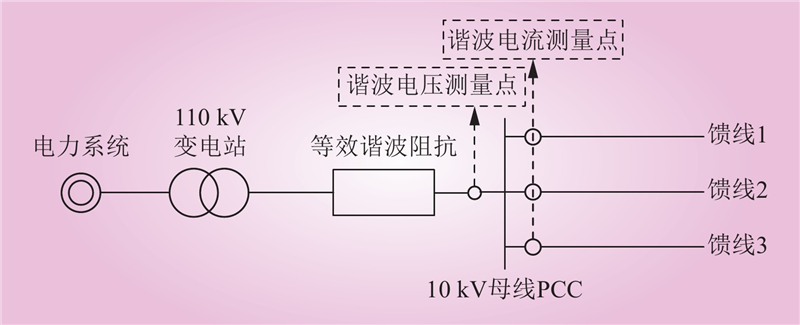
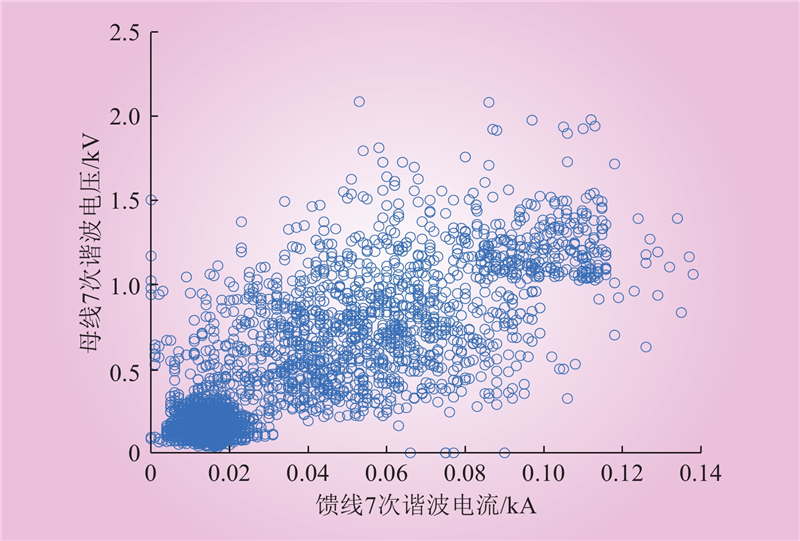
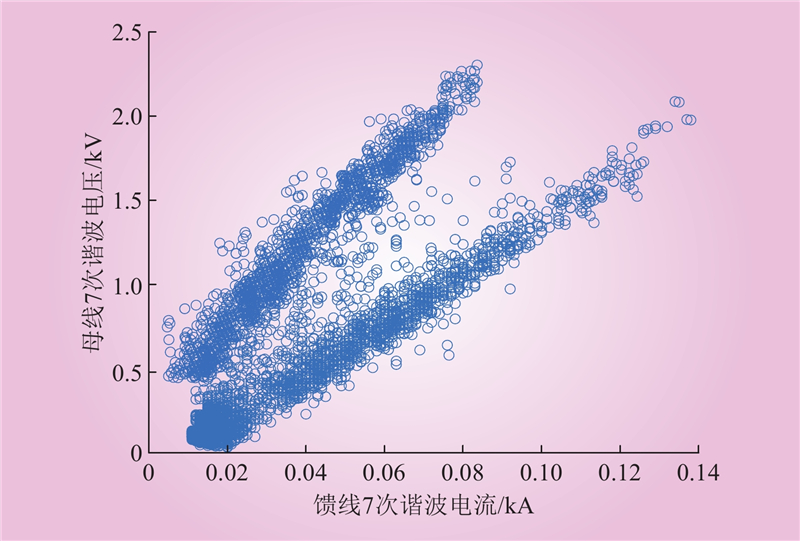
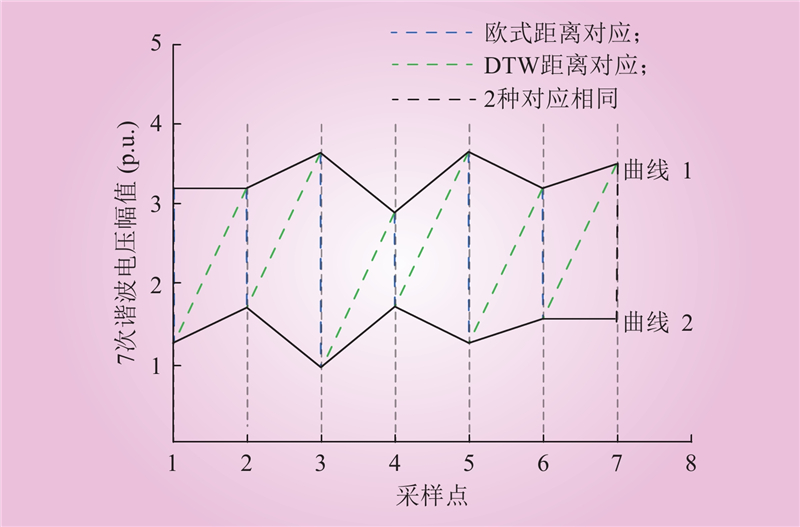
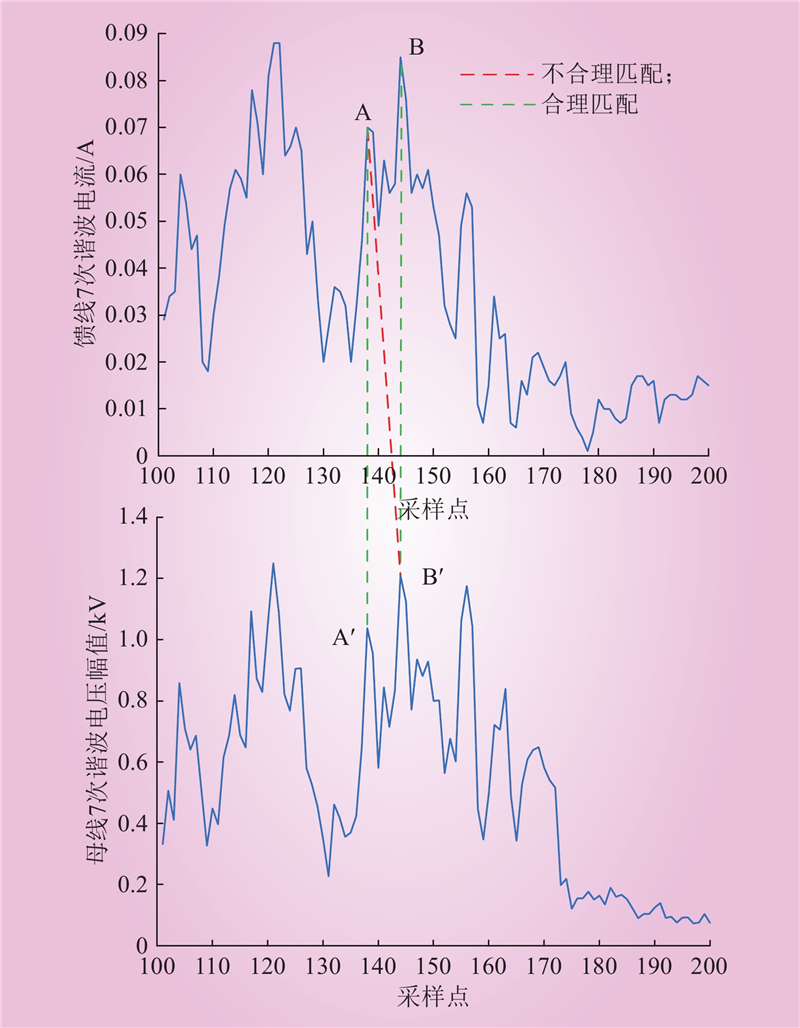
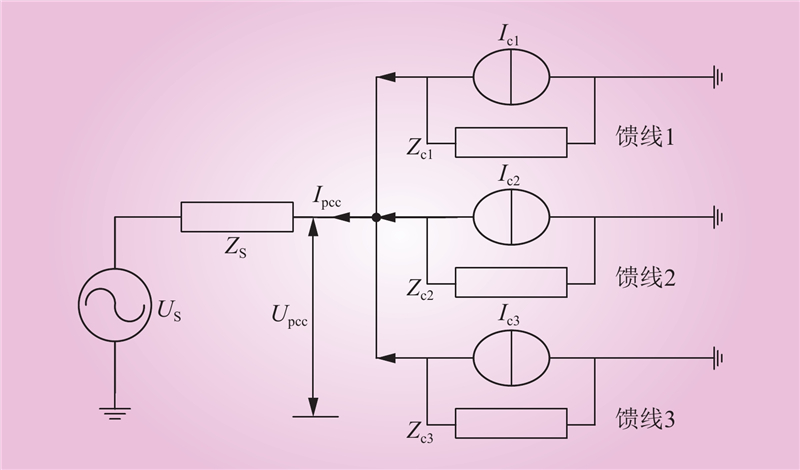
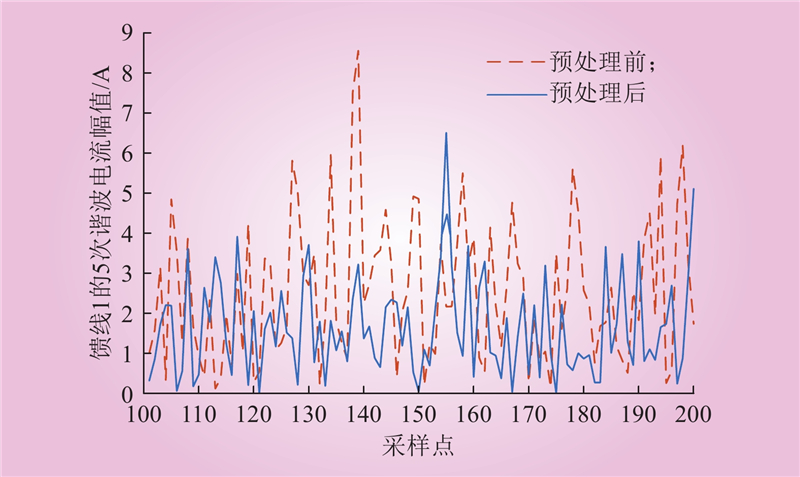
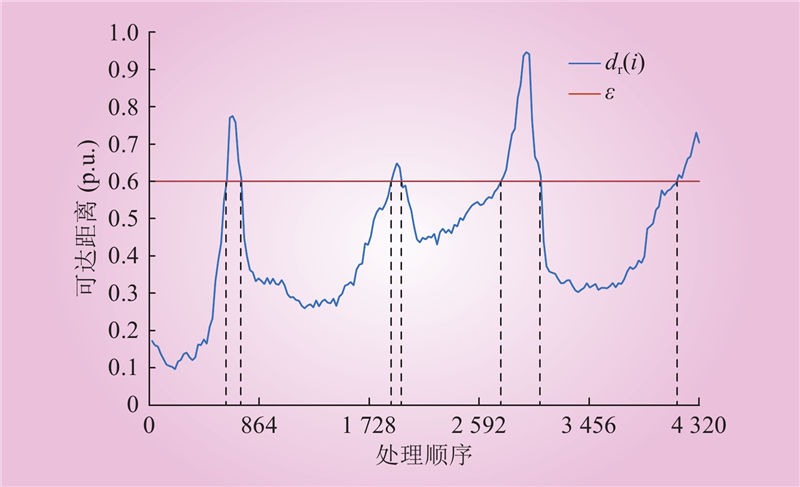
| 1 |
丁同, 陈红坤, 吴斌, 等. 多谐波源定位及谐波责任量化区分方法综述[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2020, 40 (1): 19- 30.
|
|
DING Tong, CHEN Hongkun, WU Bin, et al. Overview on location and harmonic responsibility quantitative determination methods of multiple harmonic sources[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2020, 40 (1): 19- 30.
|
| 2 |
朱武, 刘雅娟. 大型光伏电站谐波谐振机理研究[J]. 中国电力, 2018, 51 (3): 121- 130.
|
|
ZHU Wu, LIU Yajuan. Harmonic resonance mechanism study of large-scale photovoltaic power plants[J]. Electric Power, 2018, 51 (3): 121- 130.
|
| 3 |
MCEACHERN A, GRADY W M, MONCRIEF W A, et al. Revenue and harmonics: an evaluation of some proposed rate structures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 1995, 10 (1): 474- 482.
|
| 4 |
马思棋, 王忠. 基于贝叶斯优化弹性网络回归的谐波状态估计方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 104- 112.
|
|
MA Siqi, WANG Zhong. Harmonic state estimation method based on Bayesian optimized elastic network regression[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 104- 112.
|
| 5 |
孙媛媛, 李树荣, 石访, 等. 含分布式谐波源的配电网多谐波源责任划分[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (18): 5389- 5398.
|
|
SUN Yuanyuan, LI Shurong, SHI Fang, et al. Multiple harmonic source contribution determination in the active distribution network with distributed harmonic sources[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (18): 5389- 5398.
|
| 6 |
孙媛媛, 李佳奇, 尹志明. 基于实测数据的集中式多谐波源责任评估[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34 (13): 2164- 2171.
|
|
SUN Yuanyuan, LI Jiaqi, YIN Zhiming. Quantifying harmonic impacts for concentrated multiple harmonic sources using actual data[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34 (13): 2164- 2171.
|
| 7 |
龚华麟, 肖先勇, 刘亚梅, 等. 基于主导波动量筛选原理的用户谐波发射水平估计方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2010, 30 (4): 22- 27.
|
|
GONG Hualin, XIAO Xianyong, LIU Yamei, et al. A method for assessing customer harmonic emission level based on the dominant fluctuation filtering principle[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2010, 30 (4): 22- 27.
|
| 8 |
林顺富, 颜昕昱, 钟良亮, 等. 基于子带分量分解与独立分量分析的系统谐波阻抗估计方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (1): 179- 185.
|
|
LIN Shunfu, YAN Xinyu, ZHONG Liangliang, et al. System harmonic impedance estimation method based on sub-band component decomposition and independent component analysis[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (1): 179- 185.
|
| 9 |
吴雅玥, 徐方维, 张伟骏, 等. 基于修正独立随机矢量的系统侧谐波阻抗估计[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (20): 146- 152.
|
|
WU Yayue, XU Fangwei, ZHANG Weijun, et al. System-side harmonic impedance estimation based on modified independent random vectors[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (20): 146- 152.
|
| 10 |
MAZIN H E, XU W, HUANG B. Determining the harmonic impacts of multiple harmonic-producing loads[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2011, 26 (2): 1187- 1195.
|
| 11 |
贾秀芳, 华回春, 曹东升, 等. 基于复线性最小二乘法的谐波责任定量划分[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2013, 33 (4): 149- 155, 前插19.
|
|
JIA Xiufang, HUA Huichun, CAO Dongsheng, et al. Determining harmonic contributions based on complex least squares method[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33 (4): 149- 155, 前插19.
|
| 12 |
孟思雨, 肖先勇, 张逸, 等. 基于有效数据段选取的多谐波源责任划分方法[J]. 电网技术, 2017, 41 (6): 2006- 2011.
|
|
MENG Siyu, XIAO Xianyong, ZHANG Yi, et al. A valid data selection method in estimating harmonic impact of individual loads[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41 (6): 2006- 2011.
|
| 13 |
贾秀芳, 张韶光, 华回春, 等. 部分线性核估计方法在谐波责任分摊问题中的应用[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (3): 63- 68.
|
|
JIA Xiufang, ZHANG Shaoguang, HUA Huichun, et al. Application of kernel estimation with partial linear method for harmonic contributions determination[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (3): 63- 68.
|
| 14 |
臧天磊. 动态条件下配电网多谐波源定位与贡献评估方法研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017.
|
| 15 |
国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 电能质量监测设备通用要求: GB/T 19862—2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.
|
|
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. General requirements for monitoring equipment of power quality: GB/T 19862—2016[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017.
|
| 16 |
国家能源局. 电能质量数据交换格式规范: DL/T 1608—2016[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2016.
|
| 17 |
林潇, 邵振国, 陈飞雄, 等. 采用线性动态聚类的谐波责任区间估计[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (11): 4284- 4294.
|
|
LIN Xiao, SHAO Zhenguo, CHEN Feixiong, et al. Harmonic responsibility interval estimation based on linear dynamic clustering[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (11): 4284- 4294.
|
| 18 |
雷达, 常潇, 刘子腾, 等. 基于DBSCAN聚类和数据筛选的系统谐波阻抗估算[J]. 电测与仪表, 2022, 59 (1): 93- 98.
|
|
LEI Da, CHANG Xiao, LIU Ziteng, et al. Estimation of system harmonic impedance based on DBSCAN clustering and data filtering[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2022, 59 (1): 93- 98.
|
| 19 |
国家能源局. 电能质量监测系统技术规范: DL/T 1297—2013[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2014.
|
| 20 |
杨挺, 李扬, 何周泽, 等. 基于矩阵填充的泛在电力物联网电能质量数据修复算法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44 (2): 13- 21.
|
|
YANG Ting, LI Yang, HE Zhouze, et al. Matrix completion theory based recovery algorithm for power quality data in ubiquitous power Internet of Things[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44 (2): 13- 21.
|
| 21 |
刘慧自, 汪颖, 胡文曦, 等. 考虑信息动态表达的异常用电模式识别云边协同方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2022, 42 (7): 59- 67.
|
|
LIU Huizi, WANG Ying, HU Wenxi, et al. Cloud-edge collaboration method for abnormal power consumption pattern recognition considering dynamic expression of information[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022, 42 (7): 59- 67.
|
| 22 |
ZHANG Z, TAVENARD R, BAILLY A, et al. Dynamic Time Warping under limited warping path length[J]. Information Sciences, 2017, 393, 91- 107.
|
| 23 |
顾伟, 邱海峰, 尹香, 等. 基于波形匹配的谐波责任划分方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41 (2): 129- 134.
|
|
GU Wei, QIU Haifeng, YIN Xiang, et al. Waveform matching based method for harmonic contribution determination[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41 (2): 129- 134.
|
| 24 |
ZHAO J P, ITTI L. shapeDTW: shape dynamic time warping[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 74, 171- 184.
|
| 25 |
TANG C H, WANG H, WANG Z W, et al. An improved OPTICS clustering algorithm for discovering clusters with uneven densities[J]. Intelligent Data Analysis, 2021, 25 (6): 1453- 1471.
|
| 26 |
宋晓庆, 徐永海, 陶顺, 等. 考虑背景波动与量测数据相位缺失的系统侧谐波阻抗估计方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43 (6): 168- 174, 210.
|
|
SONG Xiaoqing, XU Yonghai, TAO Shun, et al. System side harmonic impedance estimation method considering background fluctuation and phase angle missing of measurement data[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43 (6): 168- 174, 210.
|