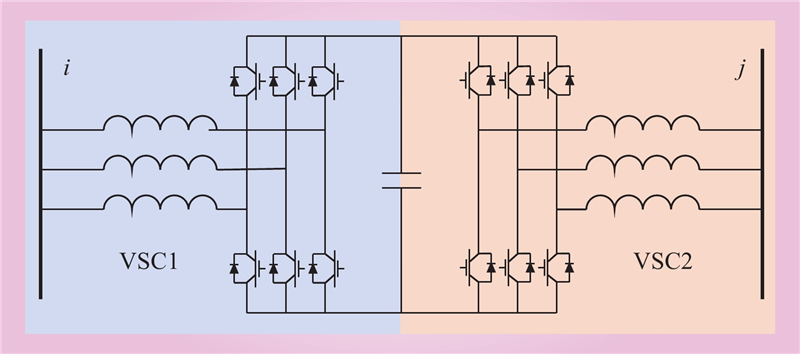
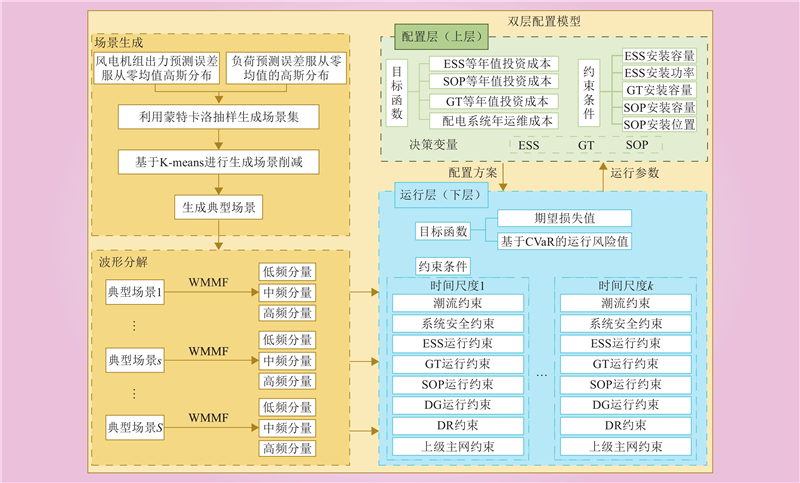
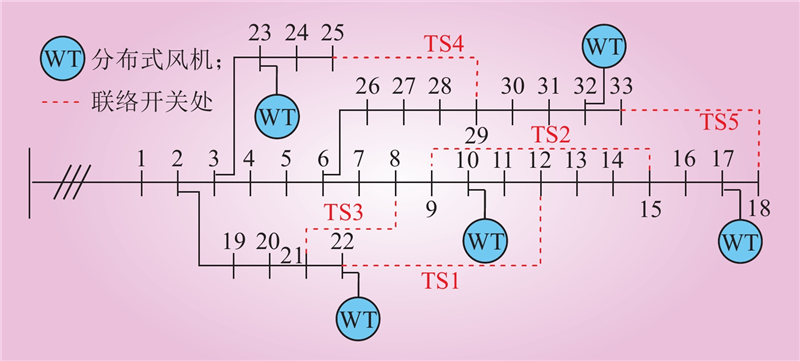
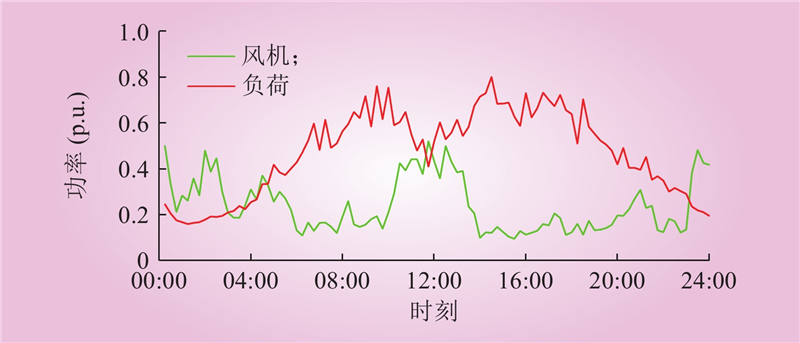
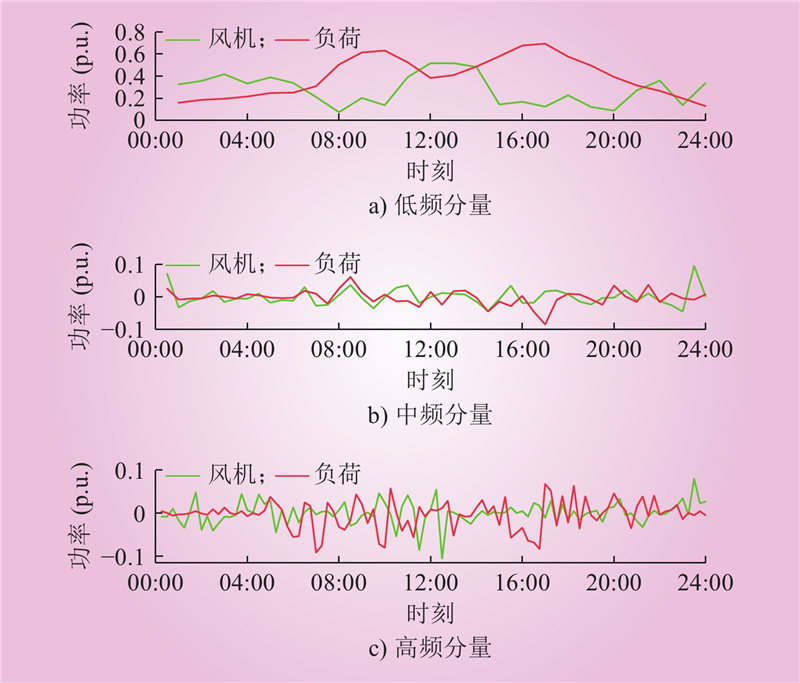
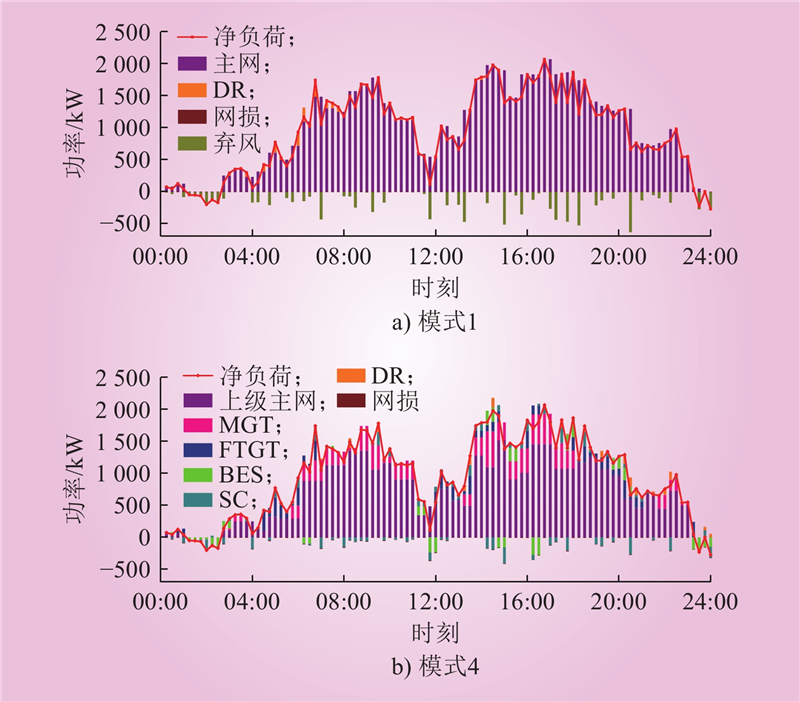
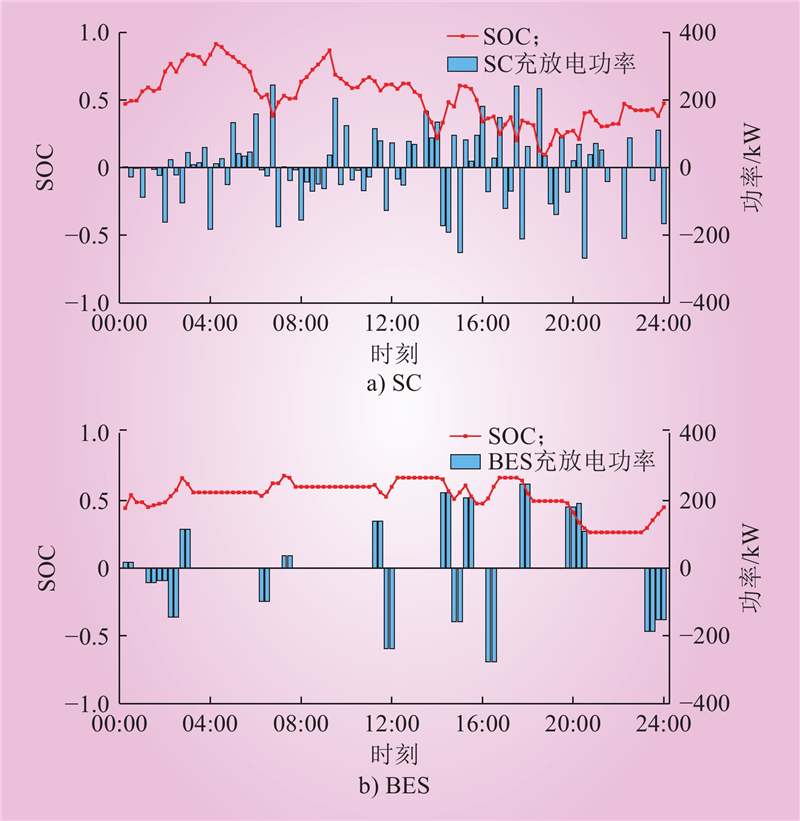
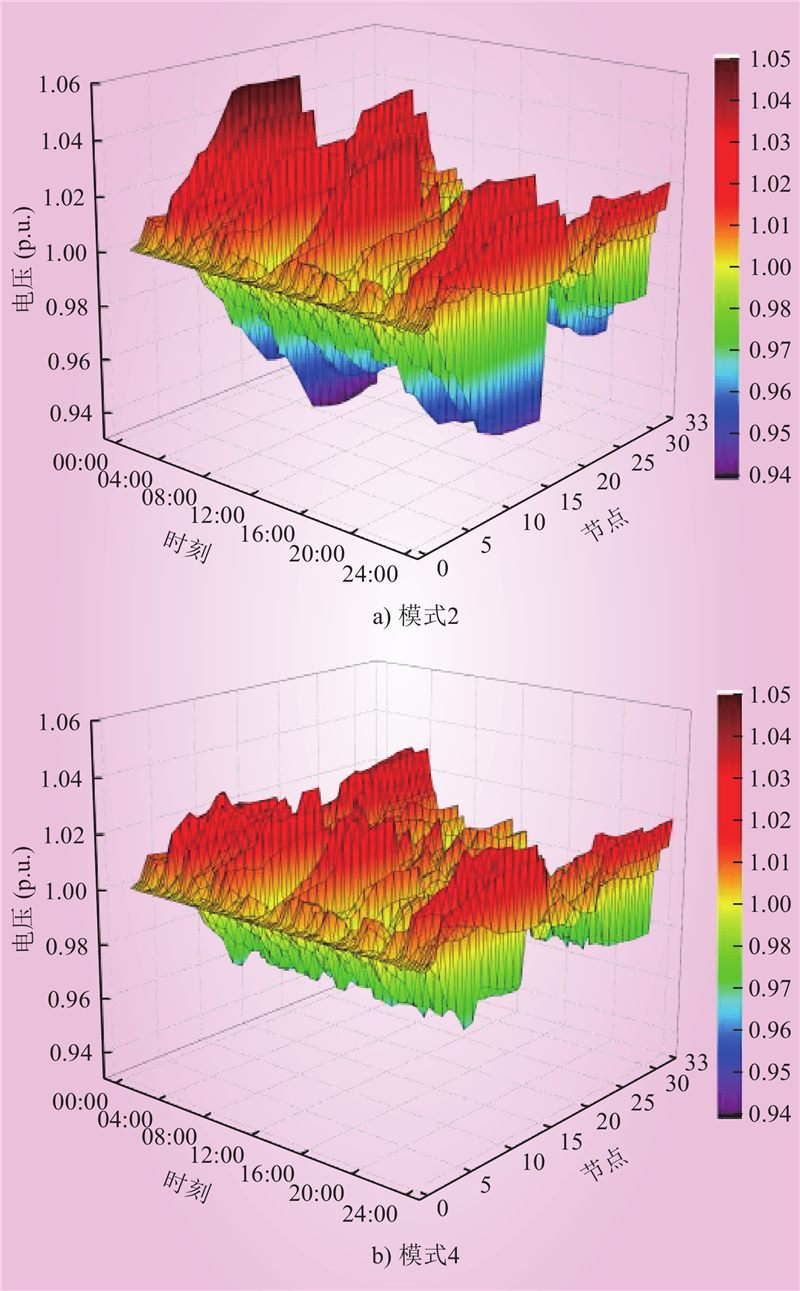
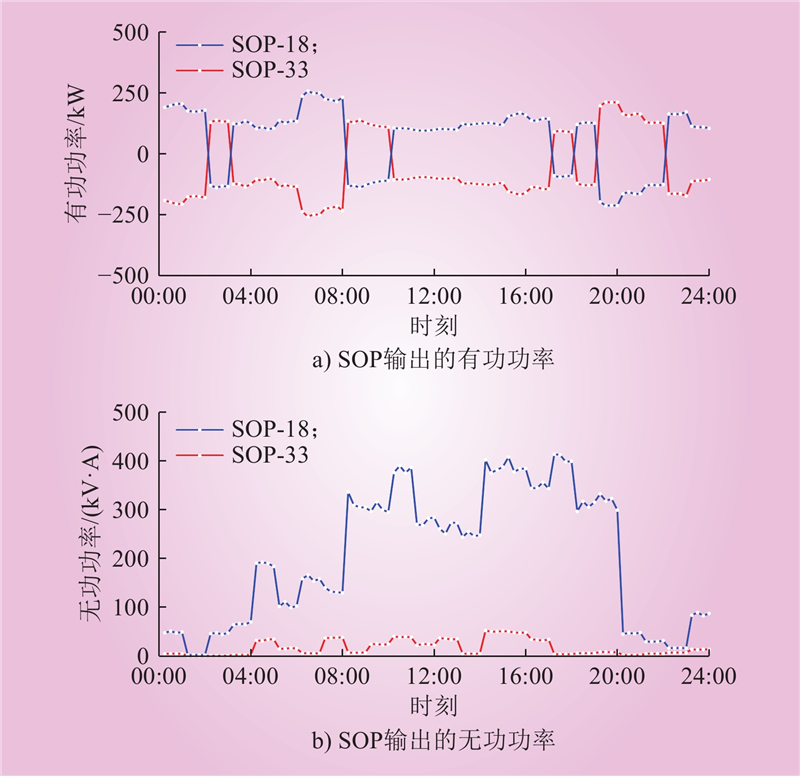
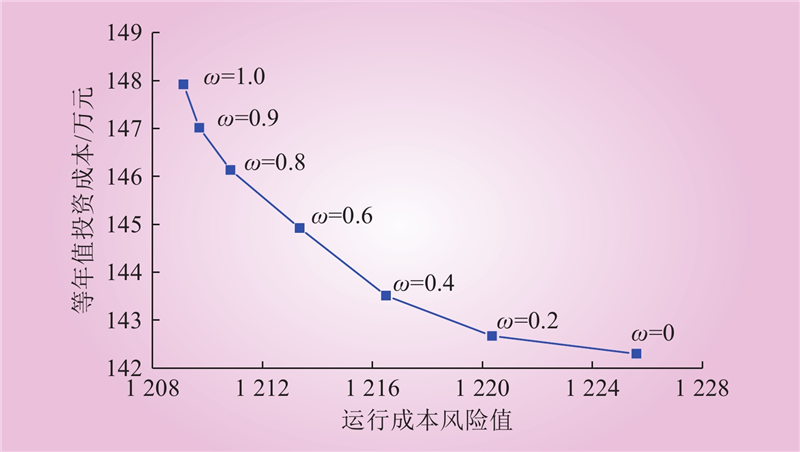
| 1 |
舒印彪, 汤涌, 张正陵, 等. 新型配电网构建及其关键技术[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (17): 6721- 6733.
|
|
SHU Yinbiao, TANG Yong, ZHANG Zhengling, et al. Construction of new distribution network and its key technologies[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (17): 6721- 6733.
|
| 2 |
王伟, 朱江, 魏兴慎, 等. 面向新型配电系统的网络安全脆弱性评估[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (8): 37- 44.
|
|
WANG Wei, ZHU Jiang, WEI Xingshen, et al. Network security vulnerability assessment for new distribution systems[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (8): 37- 44.
|
| 3 |
WANG K, WANG C F, ZHANG Z W, et al. Multi-timescale active distribution network optimal dispatching based on SMPC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2022, 58 (2): 1644- 1653.
|
| 4 |
ZAMZAM T, SHABAN K, GAOUDA A, et al. Performance assessment of two-timescale multi-objective volt/var optimization scheme considering EV charging stations, BESSs, and RESs in active distribution networks[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2022, 207, 107843.
|
| 5 |
韩宇, 周前, 李勇, 等. 户用光伏接入的低压配电网电能质量问题分析与附加损耗量化评估[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2024, 39 (3): 177- 186.
|
|
HAN Yu, ZHOU Qian, LI Yong, et al. Analysis of power quality issues and quantitative evaluation of additional losses in low voltage distribution networks connected to household photovoltaics[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2024, 39 (3): 177- 186.
|
| 6 |
AZIZI A, VAHIDI B, NEMATOLLAHI A F. Reconfiguration of active distribution networks equipped with soft open points considering protection constraints[J]. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy, 2023, 11 (1): 212- 222.
|
| 7 |
HE Y, WU H, BI R, et al. Coordinated planning of distributed generation and soft open points in active distribution network based on complete information dynamic game[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2022, 138, 107953.
|
| 8 |
王洪坤, 王守相, 潘志新, 等. 含高渗透分布式电源配电网灵活性提升优化调度方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (15): 86- 93.
|
|
WANG Hongkun, WANG Shouxiang, PAN Zhixin, et al. Optimized dispatching method for flexibility improvement of distribution network with high-penetration distributed generation[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42 (15): 86- 93.
|
| 9 |
米伟铭, 叶鹏, 张明理, 等. 基于云模型的新型配电系统灵活性评估方法[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (6): 2532- 2540.
|
|
MI Weiming, YE Peng, ZHANG Mingli, et al. Novel flexibility evaluation for distribution systems based on cloud models[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (6): 2532- 2540.
|
| 10 |
高万胜, 蔺红. 考虑配电网灵活性不足风险的分布鲁棒低碳优化调度[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (16): 49- 61.
|
|
GAO Wansheng, LIN Hong. Distributionally robust low-carbon optimal scheduling considering flexibility deficiency risk in a distribution network[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (16): 49- 61.
|
| 11 |
OIKONOMOU K, PARVANIA M, KHATAMI R. Deliverable energy flexibility scheduling for active distribution networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11 (1): 655- 664.
|
| 12 |
徐维炜, 陈红坤, 汤骏, 等. 计及配电网灵活性的峰谷电价分布鲁棒定价策略[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2024, 44 (12): 178- 186.
|
|
XU Weiwei, CHEN Hongkun, TANG Jun, et al. Distributionally robust pricing strategy of peak-valley electricity price[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2024, 44 (12): 178- 186.
|
| 13 |
ANWAR M B, QAZI H W, BURKE D J, et al. Harnessing the flexibility of demand-side resources[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10 (4): 4151- 4163.
|
| 14 |
HARTWIG K, KOCKAR I. Impact of strategic behavior and ownership of energy storage on provision of flexibility[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2016, 7 (2): 744- 754.
|
| 15 |
温丰瑞, 李华强, 温翔宇, 等. 主动配电网中计及灵活性不足风险的储能优化配置[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (11): 3952- 3962.
|
|
WEN Fengrui, LI Huaqiang, WEN Xiangyu, et al. Optimal allocation of energy storage systems considering flexibility deficiency risk in active distribution network[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (11): 3952- 3962.
|
| 16 |
程杉, 傅桐, 李沣洋, 等. 含高渗透可再生能源的配电网灵活性供需协同规划[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (22): 1- 12.
|
|
CHENG Shan, FU Tong, LI Fengyang, et al. Flexible supply demand collaborative planning for distribution networks with high penetration of renewable energy[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (22): 1- 12.
|
| 17 |
WANG C L, LIU C M, CHEN J, et al. Cooperative planning of renewable energy generation and multi-timescale flexible resources in active distribution networks[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 356, 122429.
|
| 18 |
ZHANG J R, FOLEY A, WANG S Y. Optimal planning of a soft open point in a distribution network subject to typhoons[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2021, 129, 106839.
|
| 19 |
LI J K, GE S Y, ZHANG S D, et al. A multi-objective stochastic-information gap decision model for soft open points planning considering power fluctuation and growth uncertainty[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 317, 119141.
|
| 20 |
JI H R, WANG C S, LI P, et al. Quantified flexibility evaluation of soft open points to improve distributed generator penetration in active distribution networks based on difference-of-convex programming[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 218, 338- 348.
|
| 21 |
CAO W Y, WU J Z, JENKINS N, et al. Benefits analysis of Soft Open Points for electrical distribution network operation[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 165, 36- 47.
|
| 22 |
PAMSHETTI V B, SINGH S P. Coordinated allocation of BESS and SOP in high PV penetrated distribution network incorporating DR and CVR schemes[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16 (1): 420- 430.
|
| 23 |
DA COSTA L C, THOMÉ F S, GARCIA J D, et al. Reliability-constrained power system expansion planning: A stochastic risk-averse optimization approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2021, 36 (1): 97- 106.
|
| 24 |
SABER H, HEIDARABADI H, MOEINI-AGHTAIE M, et al. Expansion planning studies of independent-locally operated battery energy storage systems (BESSs): A CVaR-based study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2020, 11 (4): 2109- 2118.
|
| 25 |
张海波, 胡玉康, 李正荣, 等. 负荷高密度地区中计及灵活性不足风险的储能优化配置[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (12): 4926- 4940.
|
|
ZHANG Haibo, HU Yukang, LI Zhengrong, et al. Optimal configuration of energy storage considering the risk of insufficient flexibility in high load density areas[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (12): 4926- 4940.
|
| 26 |
DE LIMA T D, SOARES J, LEZAMA F, et al. A risk-based planning approach for sustainable distribution systems considering EV charging stations and carbon taxes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2023, 14 (4): 2294- 2307.
|
| 27 |
MORADIJOZ M, MOGHADDAM M P, HAGHIFAM M R. A flexible active distribution system expansion planning model: a risk-based approach[J]. Energy, 2018, 145, 442- 457.
|
| 28 |
詹勋淞, 管霖, 卓映君, 等. 基于形态学分解的大规模风光并网电力系统多时间尺度灵活性评估[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (11): 3890- 3901.
|
|
ZHAN Xunsong, GUAN Lin, ZHUO Yingjun, et al. Multi-scale flexibility evaluation of large-scale hybrid wind and solar grid-connected power system based on multi-scale morphology[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (11): 3890- 3901.
|
| 29 |
ZHANG L J, XU J W, YANG J H, et al. Multiscale morphology analysis and its application to fault diagnosis[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2008, 22 (3): 597- 610.
|
| 30 |
VENZKE A, HALILBASIC L, MARKOVIC U, et al. Convex relaxations of chance constrained AC optimal power flow[C]//2018 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM). Portland, OR, USA, IEEE, 2018: 1.
|
| 31 |
ROCKAFELLAR R T, URYASEV S. Optimization of conditional value-at-risk[J]. The Journal of Risk, 2000, 2 (3): 21- 41.
|
| 32 |
BARAN M E, WU F F. Network reconfiguration in distribution systems for loss reduction and load balancing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 1989, 4 (2): 1401- 1407.
|