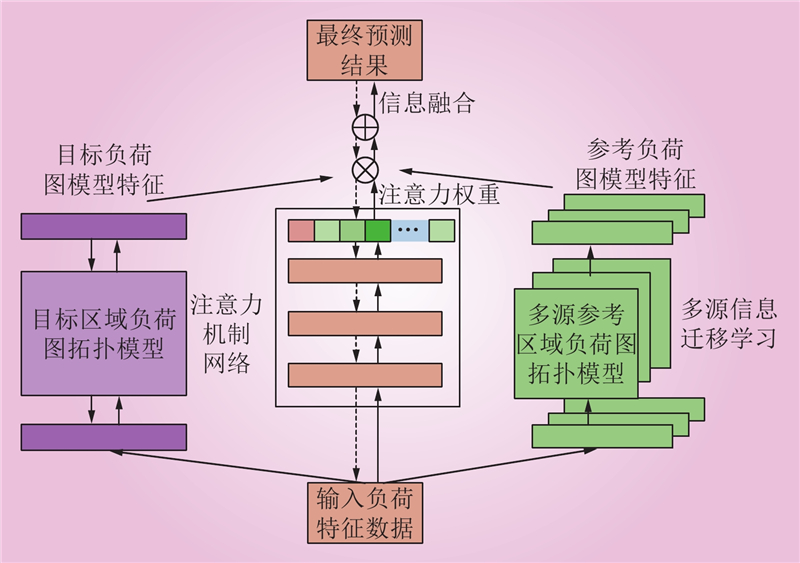
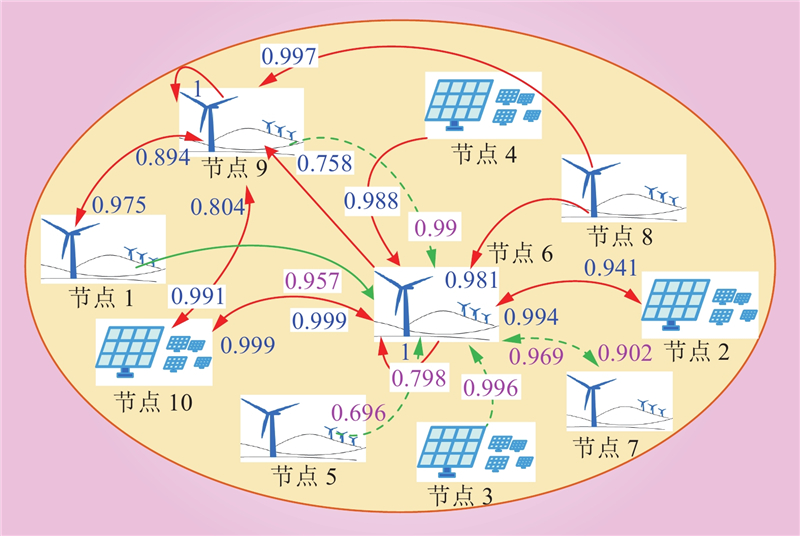
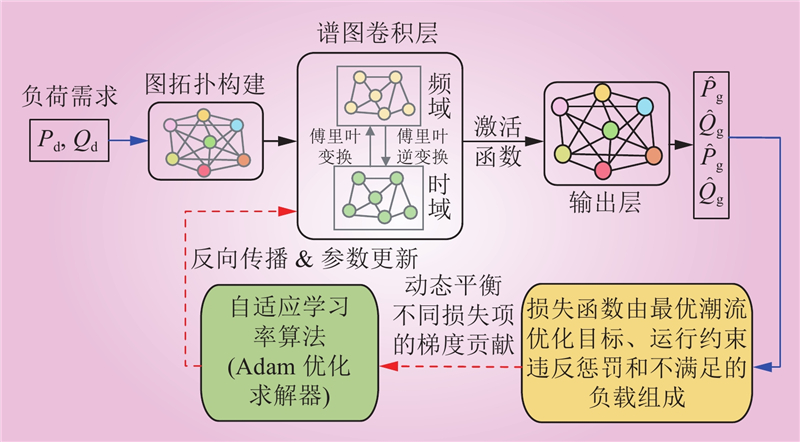
| 1 |
WITZE A. Extreme heatwaves: surprising lessons from the record warmth[J]. Nature, 2022, 608 (7923): 464- 465.
|
| 2 |
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). The paris agreement[Z], 2015. https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/englis{\boldsymbol h}_paris_agreement.pdf.
|
| 3 |
汤广福, 周静, 庞辉, 等. 能源安全格局下新型电力系统发展战略框架[J]. 中国工程科学, 2023, 25 (2): 79- 88.
|
|
TANG Guangfu, ZHOU Jing, PANG Hui, et al. Strategic framework for new electric power system development under the energy security pattern[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2023, 25 (2): 79- 88.
|
| 4 |
舒印彪, 陈国平, 贺静波, 等. 构建以新能源为主体的新型电力系统框架研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2021, 23 (6): 61- 69.
|
|
SHU Yinbiao, CHEN Guoping, HE Jingbo, et al. Building a new electric power system based on new energy sources[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2021, 23 (6): 61- 69.
|
| 5 |
叶林. 大规模风电并网运行调度和主动控制策略[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2024.
|
| 6 |
JAFARISHIADEH F, MOHAMMADI F, SAHRAEI-ARDAKANI M. Preventive dispatch for transmission de-icing[C]//2021 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM). Washington, DC, USA. IEEE, 2021: 1.
|
| 7 |
LU P, ZHANG N, YE L, et al. Advances in model predictive control for large-scale wind power integration in power systems[J]. Advances in Applied Energy, 2024, 14, 100177.
|
| 8 |
KOHLHEPP P, HARB H, WOLISZ H, et al. Large-scale grid integration of residential thermal energy storages as demand-side flexibility resource: a review of international field studies[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019, 101, 527- 547.
|
| 9 |
马伟明. 关于电工学科前沿技术发展的若干思考[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36 (22): 4627- 4636.
|
|
MA Weiming. Thoughts on the development of frontier technology in electrical engineering[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36 (22): 4627- 4636.
|
| 10 |
刘俊, 王勇, 杨胜春, 等. 新一代调控系统预调度架构及关键技术[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (22): 201- 208.
|
|
LIU Jun, WANG Yong, YANG Shengchun, et al. Pre-dispatching architecture and key technologies of new generation dispatching and control system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (22): 201- 208.
|
| 11 |
叶林, 裴铭, 李卓, 等. 风电和光伏发电功率联合预测与预调度框架[J]. 高电压技术, 2024, 50 (9): 3823- 3836.
|
|
YE Lin, PEI Ming, LI Zhuo, et al. Framework for joint wind and photovoltaic power forecasting and pre-dispatch[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2024, 50 (9): 3823- 3836.
|
| 12 |
GERS F A, SCHMIDHUBER J, CUMMINS F. Learning to forget: continual prediction with LSTM[C]//1999 Ninth International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks ICANN 99. Edinburgh, UK. London: IET, 2002: 850–855.
|
| 13 |
YUAN L, ZHANG H, XU M, et al. A multiscale CNN framework for wireless technique classification in Internet of Things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9 (12): 10366- 10367.
|
| 14 |
JIN X B, GONG W T, KONG J L, et al. PFVAE: a planar flow-based variational auto-encoder prediction model for time series data[J]. Mathematics, 2022, 10 (4): 610.
|
| 15 |
GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[J]. MIT Press, 2014, 2, 2672- 2680.
|
| 16 |
KHODAYAR M, LIU G Y, WANG J H, et al. Deep learning in power systems research: a review[J]. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, 2021, 7 (2): 209- 220.
|
| 17 |
YANG L X, ZHANG Z J. A deep attention convolutional recurrent network assisted by K-shape clustering and enhanced memory for short term wind speed predictions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2022, 13 (2): 856- 867.
|
| 18 |
THIRUNAVUKKARASU M, SAWLE Y, LALA H. A comprehensive review on optimization of hybrid renewable energy systems using various optimization techniques[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2023, 176, 113192.
|
| 19 |
LIAO W L, BAK-JENSEN B, PILLAI J R, et al. A review of graph neural networks and their applications in power systems[J]. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy, 2022, 10 (2): 345- 360.
|
| 20 |
SCARSELLI F, GORI M, TSOI A C, et al. The graph neural network model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2009, 20 (1): 61- 80.
|
| 21 |
OWERKO D, GAMA F, RIBEIRO A. Predicting power outages using graph neural networks[C]//2018 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP). Anaheim, CA, USA, 2018: 743–747.
|
| 22 |
徐冰冰, 岑科廷, 黄俊杰, 等. 图卷积神经网络综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2020, 43 (5): 755- 780.
|
|
XU Bingbing, CEN Keting, HUANG Junjie, et al. A survey on graph convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43 (5): 755- 780.
|
| 23 |
WU Z H, PAN S R, CHEN F W, et al. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32 (1): 4- 24.
|
| 24 |
RAHMANI S, BAGHBANI A, BOUGUILA N, et al. Graph neural networks for intelligent transportation systems: a survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24 (8): 8846- 8885.
|
| 25 |
冯双, 彭祥佳, 陈佳宁, 等. 基于时空图卷积神经网络的强迫振荡定位与传播预测[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (4): 1298- 1310.
|
|
FENG Shuang, PENG Xiangjia, CHEN Jianing, et al. Forced oscillation location and propagation prediction based on temporal graph convolutional network[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (4): 1298- 1310.
|
| 26 |
SIMEUNOVIĆ J, SCHUBNEL B, ALET P J, et al. Interpretable temporal-spatial graph attention network for multi-site PV power forecasting[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 327, 120127.
|
| 27 |
ZHUANG W, FAN J L, XIA M, et al. A multi-scale spatial–temporal graph neural network-based method of multienergy load forecasting in integrated energy system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2024, 15 (3): 2652- 2666.
|
| 28 |
ZHAO Y N, YE L, PINSON P, et al. Correlation-constrained and sparsity-controlled vector autoregressive model for spatio-temporal wind power forecasting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33 (5): 5029- 5040.
|
| 29 |
HOSSAIN R R, HUANG Q H, HUANG R K. Graph convolutional network-based topology embedded deep reinforcement learning for voltage stability control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2021, 36 (5): 4848- 4851.
|
| 30 |
王渝红, 沈靖, 曾琦, 等. 基于谱图论和图卷积神经网络的直流电网节点电压估计研究[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (2): 521- 531.
|
|
WANG Yuhong, SHEN Jing, ZENG Qi, et al. Voltage estimation for DC grid nodes based on spectral theory and graph convolutional neural network[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (2): 521- 531.
|
| 31 |
李佳玮, 王小君, 和敬涵, 等. 基于图注意力网络的配电网故障定位方法[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (6): 2113- 2121.
|
|
LI Jiawei, WANG Xiaojun, HE Jinghan, et al. Distribution network fault location based on graph attention network[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (6): 2113- 2121.
|
| 32 |
杨梅, 刘俊勇, 刘挺坚, 等. 节点图和边图切换卷积驱动的快速静态安全分析方法[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (6): 2070- 2080.
|
|
YANG Mei, LIU Junyong, LIU Tingjian, et al. Switching convolution of node graph and line graph-driven method for fast static security analysis[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (6): 2070- 2080.
|
| 33 |
陈立帆, 张琳琳, 宋辉, 等. 基于图卷积神经网络的输电线路自然灾害事故预测[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (6): 2549- 2557.
|
|
CHEN Lifan, ZHANG Linlin, SONG Hui, et al. Natural disaster accident prediction of transmission line based on graph convolution network[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (6): 2549- 2557.
|
| 34 |
LIAO W L, FANG J N, YE L, et al. Can we trust explainable artificial intelligence in wind power forecasting?[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 376, 124273.
|
| 35 |
LU P, YE L, ZHAO Y N, et al. Review of meta-heuristic algorithms for wind power prediction: methodologies, applications and challenges[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 301, 117446.
|
| 36 |
LIN W X, WU D, BOULET B. Spatial-temporal residential short-term load forecasting via graph neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12 (6): 5373- 5384.
|
| 37 |
WU D, LIN W X. Efficient residential electric load forecasting via transfer learning and graph neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2023, 14 (3): 2423- 2431.
|
| 38 |
KHODAYAR M, WANG J H. Spatio-temporal graph deep neural network for short-term wind speed forecasting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2019, 10 (2): 670- 681.
|
| 39 |
LI Z, YE L, ZHAO Y N, et al. A spatiotemporal directed graph convolution network for ultra-short-term wind power prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2023, 14 (1): 39- 54.
|
| 40 |
BEINERT D, HOLZHÜTER C, THOMAS J M, et al. Power flow forecasts at transmission grid nodes using graph neural networks[J]. Energy and AI, 2023, 14, 100262.
|
| 41 |
LOPEZ-GARCIA T B, DOMÍNGUEZ-NAVARRO J A. Power flow analysis via typed graph neural networks[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 117, 105567.
|
| 42 |
GAO M S, YU J, YANG Z F, et al. A physics-guided graph convolution neural network for optimal power flow[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2024, 39 (1): 380- 390.
|
| 43 |
OWERKO D, GAMA F, RIBEIRO A. Unsupervised optimal power flow using graph neural networks[C]//ICASSP 2024 - 2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Seoul, Korea, 2024: 6885–6889.
|
| 44 |
CHATZOS M, MAK T W K, HENTENRYCK P V. Spatial network decomposition for fast and scalable AC-OPF learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2022, 37 (4): 2601- 2612.
|