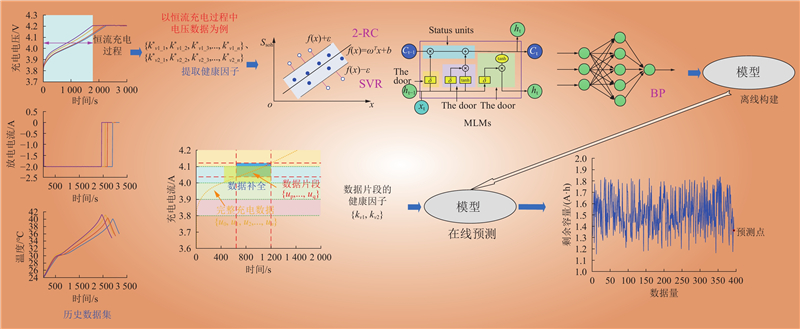
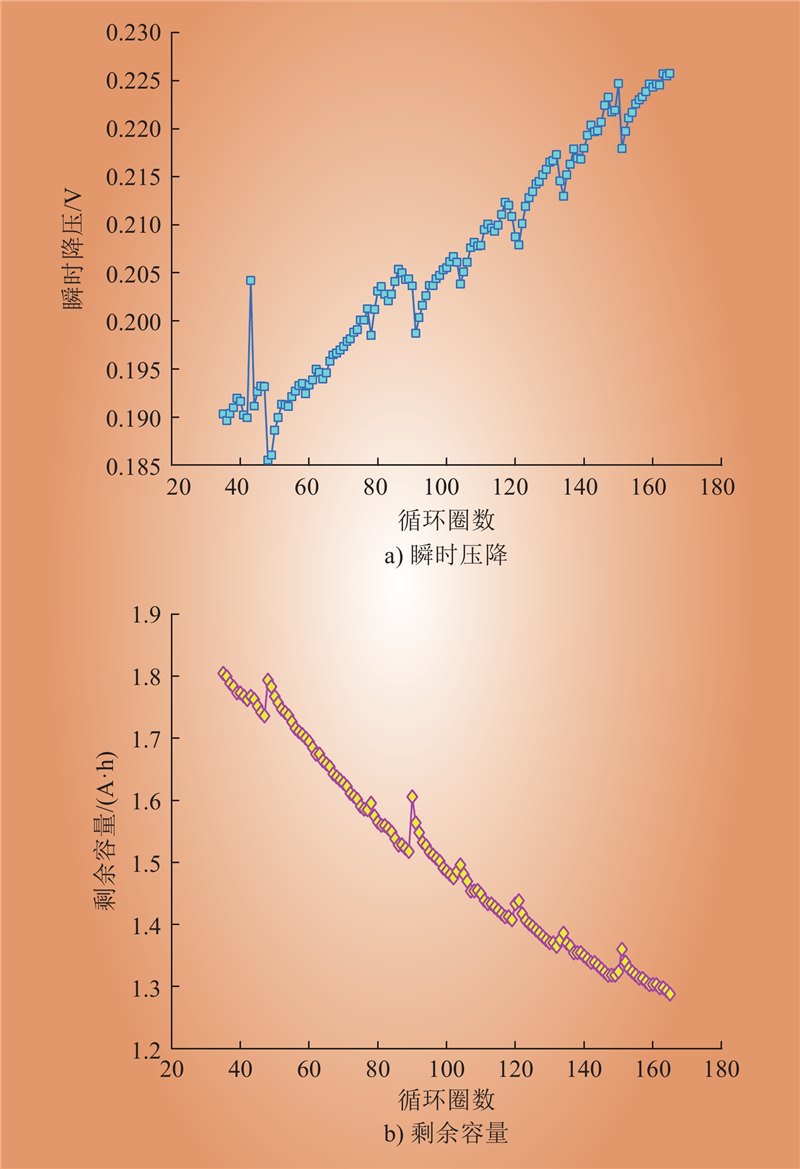
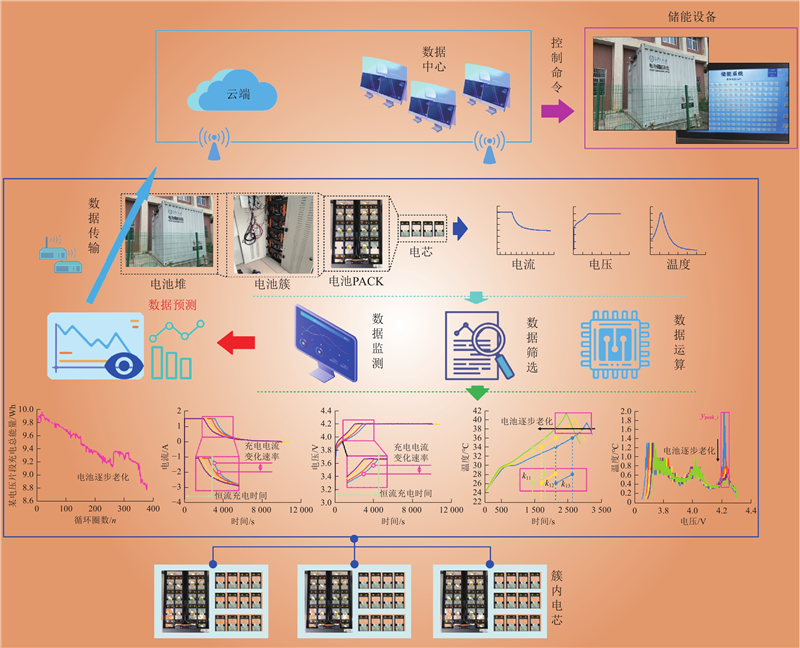
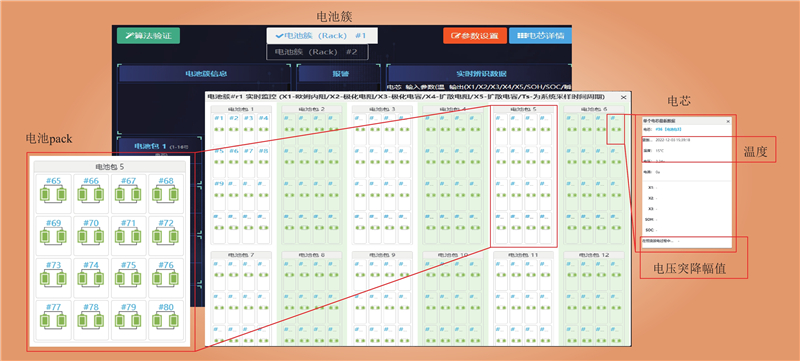
| 1 |
黎冲, 王成辉, 王高, 等. 基于数据驱动的锂离子电池健康状态估计技术[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 73- 86, 95.
|
|
LI Chong, WANG Chenghui, WANG Gao, et al. Technology of lithium-ion battery state-of-health assessment based on data-driven[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 73- 86, 95.
|
| 2 |
曹文炅, 雷博, 史尤杰, 等. 韩国锂离子电池储能电站安全事故的分析及思考[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9 (5): 1539- 1547.
|
|
CAO Wenjiong, LEI Bo, SHI Youjie, et al. Ponderation over the recent safety accidents of lithium-ion battery energy storage stations in South Korea[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9 (5): 1539- 1547.
|
| 3 |
唐文杰, 姜欣, 刘昊琰, 等. 基于气液逸出物图像识别的锂离子电池火灾早期预警[J]. 高电压技术, 2022, 48 (8): 3295- 3304.
|
|
TANG Wenjie, JIANG Xin, LIU Haoyan, et al. Early warning of lithium-ion battery fire based on image recognition of gas-liquid escape[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2022, 48 (8): 3295- 3304.
|
| 4 |
胡振恺, 雷博, 李勇琦, 等. 储能用锂离子电池安全性测试与评估方法比较[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11 (5): 1650- 1656.
|
|
HU Zhenkai, LEI Bo, LI Yongqi, et al. Comparative study on safety test and evaluation methods of lithium-ion batteries for energy storage[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11 (5): 1650- 1656.
|
| 5 |
王宁, 陈志强, 刘明义, 等. 基于模糊综合评价的锂离子电池健康状态评估[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43 (5): 784- 791.
|
|
WANG Ning, CHEN Zhiqiang, LIU Mingyi, et al. Health status assessment of lithium-ion battery based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2022, 43 (5): 784- 791.
|
| 6 |
朱伟杰, 董缇, 张树宏. 储能系统锂离子电池国内外安全标准对比分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9 (1): 279- 286.
|
|
ZHU Weijie, DONG Ti, ZHANG Shuhong. Comparative analysis of domestic and foreign safety standards for lithium-ion batteries for energy storage system[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9 (1): 279- 286.
|
| 7 |
ELMAHALLAWY M, ELFOULY T, ALOUANI A, et al. A comprehensive review of lithium-ion batteries modeling, and state of health and remaining useful lifetime prediction[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10, 119040- 119070.
|
| 8 |
焦自权, 范兴明, 张鑫, 等. 基于改进粒子滤波算法的锂离子电池状态跟踪与剩余使用寿命预测方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35 (18): 3979- 3993.
|
|
JIAO Ziquan, FAN Xingming, ZHANG Xin, et al. State tracking and remaining useful life predictive method of li-ion battery based on improved particle filter algorithm[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35 (18): 3979- 3993.
|
| 9 |
朱晓庆, 王震坡, WANG Hsin, 等. 锂离子动力电池热失控与安全管理研究综述[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56 (14): 91- 118.
|
|
ZHU Xiaoqing, WANG Zhenpo, HSIN W, et al. Review of thermal runaway and safety management for lithium-ion traction batteries in electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56 (14): 91- 118.
|
| 10 |
胡晓松, 唐小林. 电动车辆锂离子动力电池建模方法综述[J]. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53 (16): 20- 31.
|
|
HU Xiaosong, TANG Xiaolin. Review of modeling techniques for lithium-ion traction batteries in electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53 (16): 20- 31.
|
| 11 |
岳家辉, 夏向阳, 吕崇耿, 等. 计及健康特征信息量的锂离子电池健康状态与剩余寿命预测研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (22): 74- 87.
|
|
YUE Jiahui, XIA Xiangyang, LÜ Chonggeng, et al. Research on the prediction of state of health and remaining useful life of lithium-ion batteries considering the amount of health factors information[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (22): 74- 87.
|
| 12 |
吴磊, 吕桃林, 陈启忠, 等. 电化学阻抗谱测量与应用研究综述[J]. 电源技术, 2021, 45 (9): 1227- 1230.
|
|
WU Lei, LV Taolin, CHEN Qizhong, et al. Review of measurement and application of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 45 (9): 1227- 1230.
|
| 13 |
骆凡, 黄海宏, 王海欣. 基于电化学阻抗谱的退役动力电池荷电状态和健康状态快速预测[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2021, 42 (9): 172- 180.
|
|
LUO Fan, HUANG Haihong, WANG Haixin. Rapid prediction of the state of charge and state of health of decommissioned power batteries based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2021, 42 (9): 172- 180.
|
| 14 |
赵月荷, 庞宗强. 基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的动力电池健康状态估计[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2022, 41 (10): 136- 141.
|
|
ZHAO Yuehe, PANG Zongqiang. State of health estimation of power batteries based on unscented Kalman filter[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2022, 41 (10): 136- 141.
|
| 15 |
吴忠强, 陈海佳. 基于自适应H2/H∞滤波的锂电池SOC和SOH联合估计[J]. 计量学报, 2023, 44 (11): 1719- 1727.
|
|
WU Zhongqiang, CHEN Haijia. Joint SOC and SOH estimation for lithium batteries based on adaptive H2/H∞ filtering[J]. Acta Metrologica Sinica, 2023, 44 (11): 1719- 1727.
|
| 16 |
徐超, 李立伟, 杨玉新, 等. 基于改进粒子滤波的锂电池SOH预测[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9 (6): 1954- 1960.
|
|
XU Chao, LI Liwei, YANG Yuxin, et al. Lithium-ion battery SOH estimation based on improved particle filter[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9 (6): 1954- 1960.
|
| 17 |
AMIR S, GULZAR M, TARAR M O, et al. Dynamic equivalent circuit model to estimate state-of-health of lithium-ion batteries[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10, 18279- 18288.
|
| 18 |
魏克新, 陈峭岩. 基于自适应无迹卡尔曼滤波算法的锂离子动力电池状态估计[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34 (3): 445- 452.
|
|
WEI Kexin, CHEN Qiaoyan. States estimation of li-ion power batteries based on adaptive unscented Kalman filters[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34 (3): 445- 452.
|
| 19 |
HE X T, SUN B X, ZHANG W G, et al. Multi-time scale variable-order equivalent circuit model for virtual battery considering initial polarization condition of lithium-ion battery[J]. Energy, 2022, 244, 123084.
|
| 20 |
LI Y M, HUANG P Y, GAO L T, et al. Data-driven state of health estimation for lithium-ion batteries based on universal feature selection[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2023, 170 (4): 040507.
|
| 21 |
CHEN Z, XUE Q, XIAO R X, et al. State of health estimation for lithium-ion batteries based on fusion of autoregressive moving average model and Elman neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 102662- 102678.
|
| 22 |
FENG X S, ZHANG X K, XIANG Y. An inconsistency assessment method for backup battery packs based on time-series clustering[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2020, 31, 101666.
|
| 23 |
SUN J L, LIU W, TANG C Y, et al. A novel active equalization method for series-connected battery packs based on clustering analysis with genetic algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36 (7): 7853- 7865.
|
| 24 |
PESARAN A A. Battery thermal models for hybrid vehicle simulations[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2002, 110 (2): 377- 382.
|
| 25 |
PENG X B, MA C, GARG A, et al. Thermal performance investigation of an air-cooled lithium-ion battery pack considering the inconsistency of battery cells[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 153, 596- 603.
|
| 26 |
FANG K Z, CHEN S, MU D B, et al. Investigation of nickel–metal hydride battery sorting based on charging thermal behavior[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 224, 120- 124.
|
| 27 |
WANG H Y, DONG K, LI G C, et al. Research on the consistency of the power battery based on multi-points impedance spectrum[C]//International Forum on Strategic Technology. Ulsan, Korea (South). IEEE, 2010: 1-4.
|
| 28 |
张媛, 夏向阳, 岳家辉, 等. 基于电池簇放电电量的电池堆不一致性在线监测方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (7): 207- 215, 227.
|
|
ZHANG Yuan, XIA Xiangyang, YUE Jiahui, et al. Online monitoring method of battery stack inconsistency based on discharge quantity of battery clusters[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (7): 207- 215, 227.
|
| 29 |
AN F L, ZHANG W G, SUN B X, et al. A novel battery pack inconsistency model and influence degree analysis of inconsistency on output energy[J]. Energy, 2023, 271, 127032.
|
| 30 |
LU Y F, LI K, HAN X B, et al. A method of cell-to-cell variation evaluation for battery packs in electric vehicles with charging cloud data[J]. eTransportation, 2020, 6, 100077.
|
| 31 |
ZHANG C P, JIANG Y, JIANG J C, et al. Study on battery pack consistency evolutions and equilibrium diagnosis for serial- connected lithium-ion batteries[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 207, 510- 519.
|
| 32 |
CHANG C, ZHOU X P, JIANG J C, et al. Micro-fault diagnosis of electric vehicle batteries based on the evolution of battery consistency relative position[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 52, 104746.
|
| 33 |
黄彧, 王占国, 张言茹, 等. 基于离群点检测的动力电池一致性快速辨识方法[J]. 电测与仪表, 2023, 60 (10): 66- 72.
|
|
HUANG Yu, WANG Zhanguo, ZHANG Yanru, et al. A fast identification method of power battery consistency based on outlier detection[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2023, 60 (10): 66- 72.
|
| 34 |
向兆军, 胡凤玲, 罗明华, 等. 基于电池组模型和聚类算法的锂离子电池组SOC不一致估计[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56 (18): 154- 163.
|
|
XIANG Zhaojun, HU Fengling, LUO Minghua, et al. Estimation of SOC inconsistencies in lithium-ion battery packs based on battery pack modeling and clustering algorithm[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56 (18): 154- 163.
|
| 35 |
李革, 孔祥栋, 孙跃东, 等. 基于产线大数据的锂离子电池一致性动态特性分选方法[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13 (4): 1188- 1196.
|
|
LI Ge, KONG Xiangdong, SUN Yuedong, et al. Method for sorting the dynamic characteristics of lithium-ion battery consistency based on production line big data[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13 (4): 1188- 1196.
|
| 36 |
TIAN J Q, WANG Y J, LIU C, et al. Consistency evaluation and cluster analysis for lithium-ion battery pack in electric vehicles[J]. Energy, 2020, 194, 116944.
|
| 37 |
CAI Y, DONG S F, WANG J X. A method for consistency determination of battery energy storage system based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[M]//Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2019: 193–204.
|
| 38 |
LI J L, LI Y X, HENG X, et al. Consistency evaluation of retired power battery based on the analytic hierarchy process method[C]//2021 IEEE 5th Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2). Taiyuan, China. IEEE, 2021: 3735–3739.
|
| 39 |
DENG Z W, HU X S, LI P H, et al. Data-driven battery state of health estimation based on random partial charging data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2022, 37 (5): 5021- 5031.
|
| 40 |
LAI R C, LI X Y, WANG J. Flexible deep learning-based state of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries with features extracted from partial charging curves[J]. Batteries, 2024, 10 (5): 164.
|
| 41 |
QIAN C, XU B H, CHANG L, et al. Convolutional neural network based capacity estimation using random segments of the charging curves for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy, 2021, 227, 120333.
|
| 42 |
YAO J C, HAN T. Data-driven lithium-ion batteries capacity estimation based on deep transfer learning using partial segment of charging/discharging data[J]. Energy, 2023, 271, 127033.
|
| 43 |
MENG H X, GENG M Y, HAN T. Long short-term memory network with Bayesian optimization for health prognostics of lithium-ion batteries based on partial incremental capacity analysis[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2023, 236, 109288.
|
| 44 |
XIONG X, WANG Y J, LI K Q, et al. State of health estimation for lithium-ion batteries using Gaussian process regression-based data reconstruction method during random charging process[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 72, 108390.
|
| 45 |
SHI W S, CAO J, ZHANG Q, et al. Edge computing: vision and challenges[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2016, 3 (5): 637- 646.
|
| 46 |
FENG J, ZHANG W J, PEI Q Q, et al. Heterogeneous computation and resource allocation for wireless powered federated edge learning systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70 (5): 3220- 3233.
|
| 47 |
XU X W, DING Y K, HU S X, et al. Scaling for edge inference of deep neural networks[J]. Nature Electronics, 2018, 1, 216- 222.
|
| 48 |
吕华章, 陈丹, 范斌, 等. 边缘计算标准化进展与案例分析[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2018, 55 (3): 487- 511.
|
|
LÜ Huazhang, CHEN Dan, FAN Bin, et al. Standardization progress and case analysis of edge computing[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2018, 55 (3): 487- 511.
|
| 49 |
朱斌, 刘东, 刘天元, 等. 边缘计算在电力系统供需互动应用的研究进展与展望[J/OL]. 电网技术, 1–15[2024-07-11]. https://doi.org/10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2024.0159.
|
|
ZHU Bin, LIU Dong, LIU Tianyuan, et al. Research progresses and prospects on application of edge computing in power system supply-demand interaction[J]. 1–15[2024-07-11]. https://doi.org/10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2024.0159.
|
| 50 |
解润生, 张国荣, 解宝. 考虑长距离输电缆特性的逆变器并网系统谐波不稳定分析及抑制[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (2): 128- 139.
|
|
XIE Runsheng, ZHANG Guorong, XIE Bao. Analysis and suppression of harmonic instability for grid-connected inverter system considering characteristics of long transmission cable[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (2): 128- 139.
|
| 51 |
BAZARGAN D, FILIZADEH S, GOLE A M. Stability analysis of converter-connected battery energy storage systems in the grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2014, 5 (4): 1204- 1212.
|
| 52 |
NARENDRA BABU Y, PADHY N P. An approach to improve harmonic attenuation and stability performance in multi-parallel inverter system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2023, 38 (5): 3634- 3646.
|
| 53 |
高明杰, 惠东, 高宗和, 等. 国家风光储输示范工程介绍及其典型运行模式分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2013, 37 (1): 59- 64.
|
|
GAO Mingjie, HUI Dong, GAO Zonghe, et al. Presentation of national wind/photovoltaic/energy storage and transmission demonstration project and analysis of typical operation modes[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2013, 37 (1): 59- 64.
|
| 54 |
FU Q, DU W J, WANG H F. Planning of the DC system considering restrictions on the small-signal stability of EV charging stations and comparison between series and parallel connections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69 (10): 10724- 10735.
|
| 55 |
张宇, 张琛, 蔡旭, 等. 并网变换器的暂态同步稳定性分析: 稳定域估计与镇定控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (21): 7871- 7884.
|
|
ZHANG Yu, ZHANG Chen, CAI Xu, et al. Transient grid-synchronization stability analysis of grid-tied voltage source converters: stability region estimation and stabilization control[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (21): 7871- 7884.
|
| 56 |
吴青峰, 孙孝峰, 郝彦丛, 等. 微电网储能系统SOC平衡和电压频率恢复研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2018, 39 (6): 1743- 1751.
|
|
WU Qingfeng, SUN Xiaofeng, HAO Yancong, et al. Research of soc balance and voltage frequence recovery of microgrid energy storage system[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2018, 39 (6): 1743- 1751.
|
| 57 |
ZHANG H T, ZHANG X Y, WANG Z L, et al. Capacity configuration of hybrid energy storage power stations participating in power grid frequency modulation[J]. Processes, 2023, 11 (10): 2843.
|
| 58 |
陈凌彬, 夏向阳, 廖一丁, 等. 考虑多变量协同保护的储能变流器故障穿越策略[J]. 太阳能学报, 2023, 44 (1): 442- 450.
|
|
CHEN Lingbin, XIA Xiangyang, LIAO Yiding, et al. Fault ride through strategy of power conversion system considering multi-variable cooperative protection[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2023, 44 (1): 442- 450.
|
| 59 |
CHANG F R, LI Y, PENG Y J, et al. A dual-layer cooperative control strategy of battery energy storage units for smoothing wind power fluctuations[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 70, 107789.
|
| 60 |
LIN L, JIA Y Q, MA M H, et al. Long-term stable operation control method of dual-battery energy storage system for smoothing wind power fluctuations[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2021, 129, 106878.
|
| 61 |
LI X N, LYU L X, GENG G C, et al. Power allocation strategy for battery energy storage system based on cluster switching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69 (4): 3700- 3710.
|
| 62 |
GAO X J, WU X G, XIA Y L, et al. Life extension of a multi-unit energy storage system by optimizing the power distribution based on the degradation ratio[J]. Energy, 2024, 286, 129598.
|
| 63 |
叶晖, 李爱魁, 田刚领, 等. 考虑能量效率和SOC均衡的电池储能电站双层功率分配策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (13): 5185- 5196.
|
|
YE Hui, LI Aikui, TIAN Gangling, et al. Double-layer power distribution strategy for battery storage power station considering energy efficiency and state-of-charge balance[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (13): 5185- 5196.
|
| 64 |
夏向阳, 陈贵全, 刘俊翔, 等. 储能系统直流侧纹波电流对锂离子电池寿命影响分析及优化控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38 (22): 6218- 6229.
|
|
XIA Xiangyang, CHEN Guiquan, LIU Junxiang, et al. Analysis of the impact of DC-side ripple current on lithium-ion battery life in energy storage systems and optimal control strategies[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38 (22): 6218- 6229.
|
| 65 |
LI X N, GENG G C, JIANG Q Y, et al. Consensus-based multi-converter power allocation strategy in battery energy storage system[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 60, 106623.
|