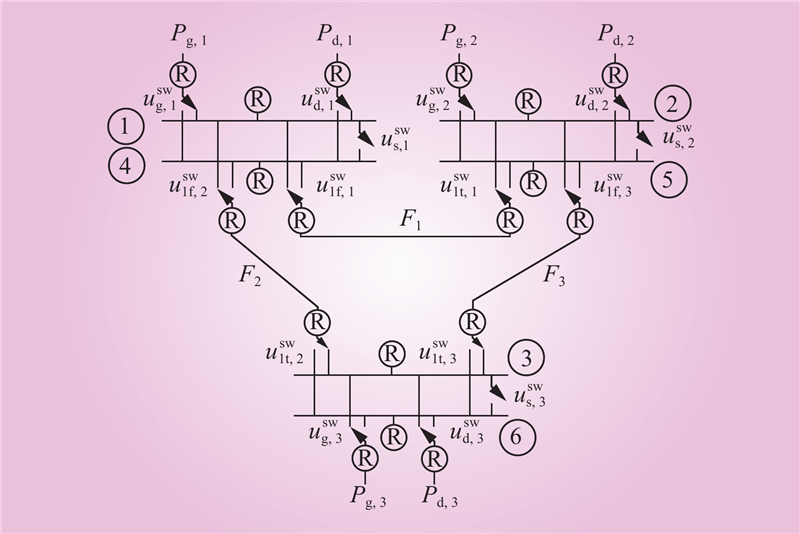
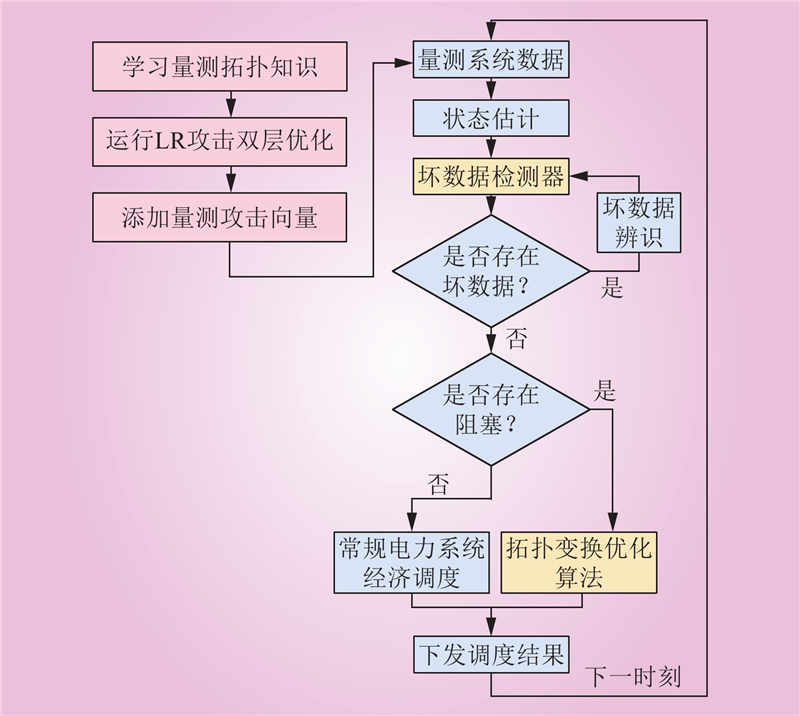
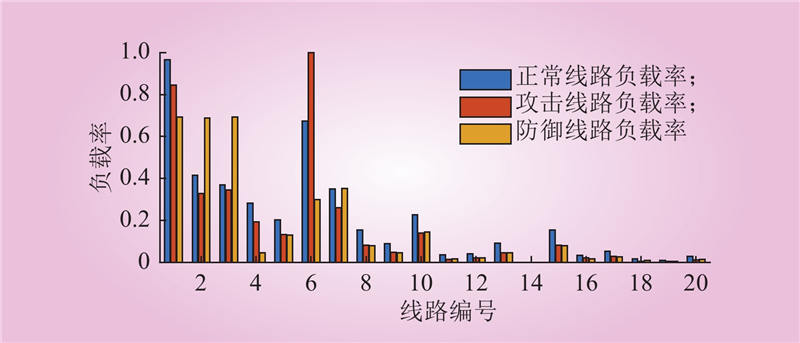
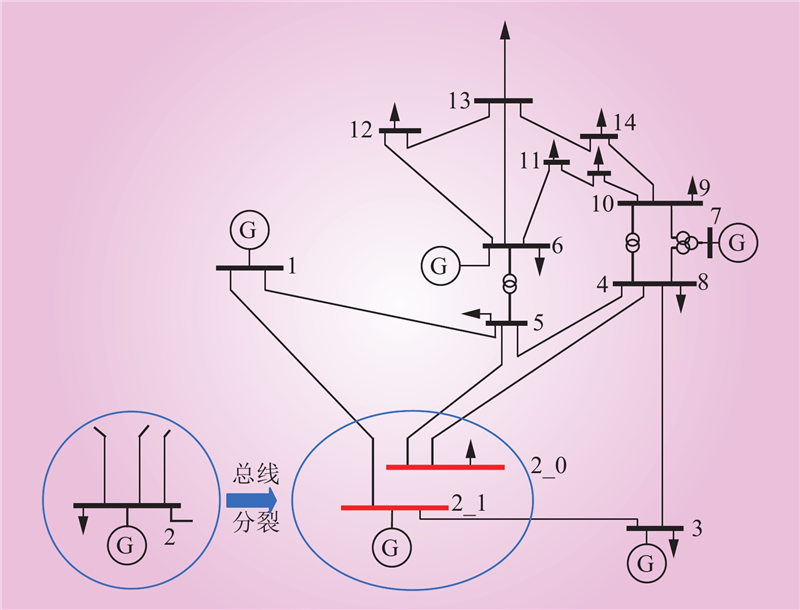
| 1 |
陈凡, 张继聪, 赵美莲, 等. 考虑负荷重分配攻击的电力系统运行可靠性评估[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (8): 160- 168.
|
|
CHEN Fan, ZHANG Jicong, ZHAO Meilian, et al. Operational reliability evaluation for power systems considering load redistribution attack[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (8): 160- 168.
|
| 2 |
TASEW R H, ADNAN A, ABDUN M. Comprehensive survey and taxonomies of false data injection attacks in smart grids: attack models, targets, and impacts[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2022, 163, 112423.
|
| 3 |
王琦, 邰伟, 汤奕, 等. 面向电力信息物理系统的虚假数据注入攻击研究综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45 (1): 72- 83.
|
|
WANG Qi, TAI Wei, TANG Yi, et al. A review on false data injection attack toward cyber-physical power system[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45 (1): 72- 83.
|
| 4 |
刘烃, 田决, 王稼舟, 等. 信息物理融合系统综合安全威胁与防御研究[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45 (1): 5- 24.
|
|
LIU Ting, TIAN Jue, WANG Jiazhou, et al. Integrated security threats and defense of cyber-physical systems[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45 (1): 5- 24.
|
| 5 |
刘林彬, 苗泉强, 李俊娥. 基于模糊测试的GOOSE协议解析漏洞挖掘方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (4): 33- 43.
|
|
LIU Linbin, MIAO Quanqiang, LI June. A method for mining GOOSE protocol parsing vulnerabilities based on fuzzing[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (4): 33- 43.
|
| 6 |
王琦, 李梦雅, 汤奕, 等. 电力信息物理系统网络攻击与防御研究综述(一)建模与评估[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (9): 9- 21.
|
|
WANG Qi, LI Mengya, TANG Yi, et al. A review on research of cyber-attacks and defense in cyber physical power systems part one modelling and evaluation[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (9): 9- 21.
|
| 7 |
杨玉泽, 刘文霞, 李承泽, 等. 面向电力SCADA系统的FDIA检测方法综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (22): 8602- 8622.
|
|
YANG Yuze, LIU Wenxia, LI Chengze, et al. Review of FDIA detection methods for electric power SCADA system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (22): 8602- 8622.
|
| 8 |
YUAN Y L, LI Z Y, REN K. Quantitative analysis of load redistribution attacks in power systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2012, 23 (9): 1731- 1738.
|
| 9 |
XIANG Y M, DING Z L, ZHANG Y C, et al. Power system reliability evaluation considering load redistribution attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016: 1.
|
| 10 |
LIU Y G, GAO S B, SHI J, et al. Sequential-mining-based vulnerable branches identification for the transmission network under continuous load redistribution attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11 (6): 5151- 5160.
|
| 11 |
MUSLEH A, CHEN G, DONG Z Y. A survey on the detection algorithms for false data injection attacks in smart grids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10 (3): 2218- 2234.
|
| 12 |
汤奕, 李梦雅, 王琦, 等. 电力信息物理系统网络攻击与防御研究综述(二)检测与保护[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (10): 1- 9, 18.
|
|
TANG Yi, LI Mengya, WANG Qi, et al. A review on research of cyber-attacks and defense in cyber physical power systems part two detection and protection[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (10): 1- 9, 18.
|
| 13 |
LIU Y G, GAO S B, SHI J, et al. Pre-overload-graph-based vulnerable correlation identification under load redistribution attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11 (6): 5216- 5226.
|
| 14 |
GAO S B, LEI J Y, SHI J, et al. Assessment of overloading correlations among transmission lines under load redistribution attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2022, 13 (2): 1570- 1581.
|
| 15 |
MORROW K L, HEINE E, ROGERS K M, et al. Topology perturbation for detecting malicious data injection[C]//2012 45th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. Maui, HI, USA. IEEE, 2012: 2104-2113.
|
| 16 |
ZHANG Z Y, DENG R L, YAU D K Y, et al. Analysis of moving target defense against false data injection attacks on power grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15, 2320- 2335.
|
| 17 |
GRANELLI G, MONTAGNA M, ZANELLINI F, et al. Optimal network reconfiguration for congestion management by deterministic and genetic algorithms[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2006, 76 (6/7): 549- 556.
|
| 18 |
SHAO W, VITTAL V. Corrective switching algorithm for relieving overloads and voltage violations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2005, 20 (4): 1877- 1885.
|
| 19 |
WANG L, CHIANG H D. Toward online bus-bar splitting for increasing load margins to static stability limit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 32 (5): 3715- 3725.
|
| 20 |
张镇勇. 智能电网中面向错误数据注入攻击的移动目标防御研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020.
|
|
ZHANG Zhenyong. Moving target defense against false data injection attack in smart grid[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2020.
|
| 21 |
李炎林. 计及输电网结构优化和负荷侧响应的含新能源电力系统综合调度[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2019.
|
|
LI Yanlin. Comprehensive scheduling models and algorithm for power systems with renewable energy integration considering transmission network topology optimization and demand side response[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2019.
|