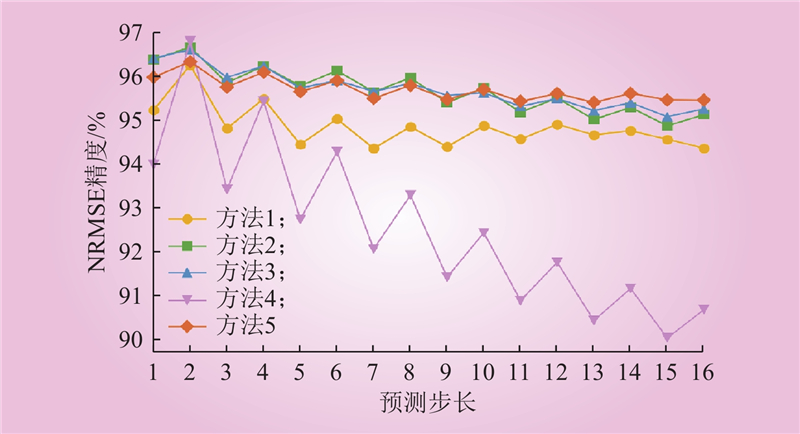
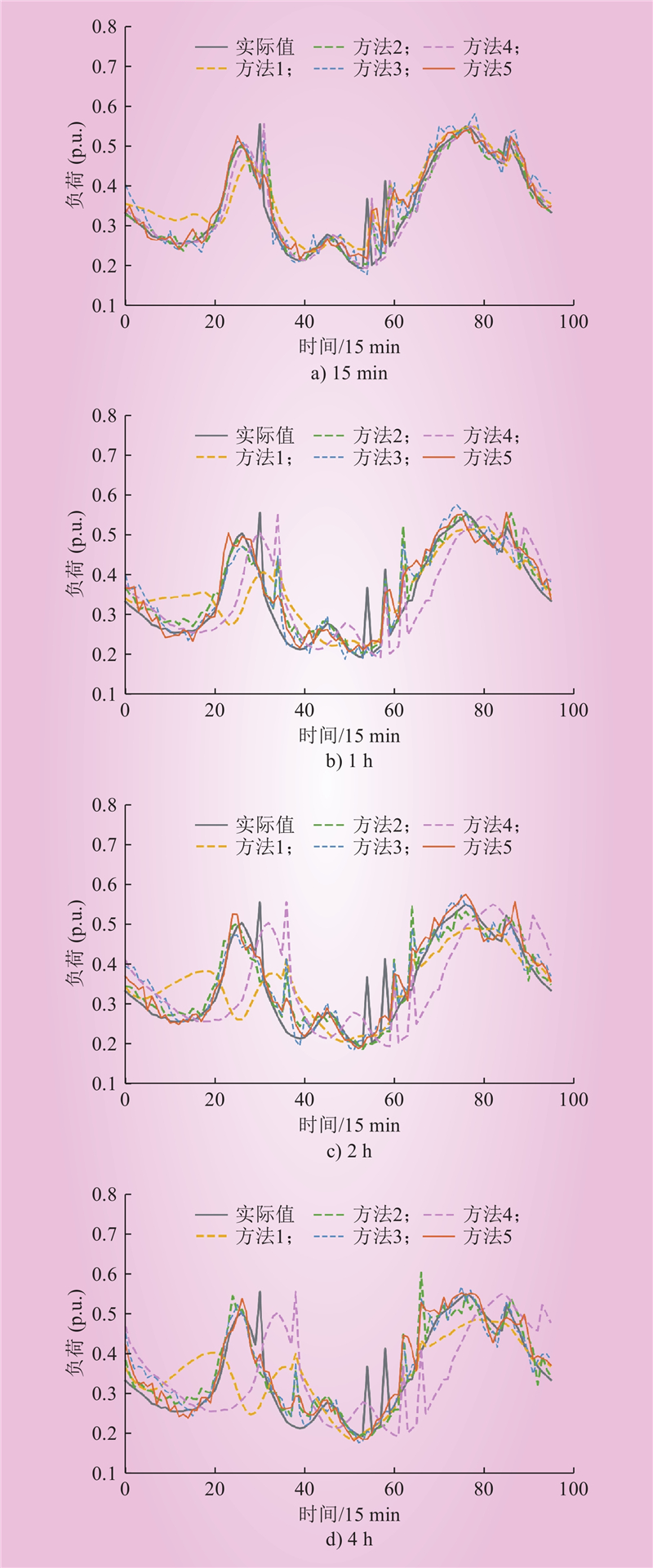
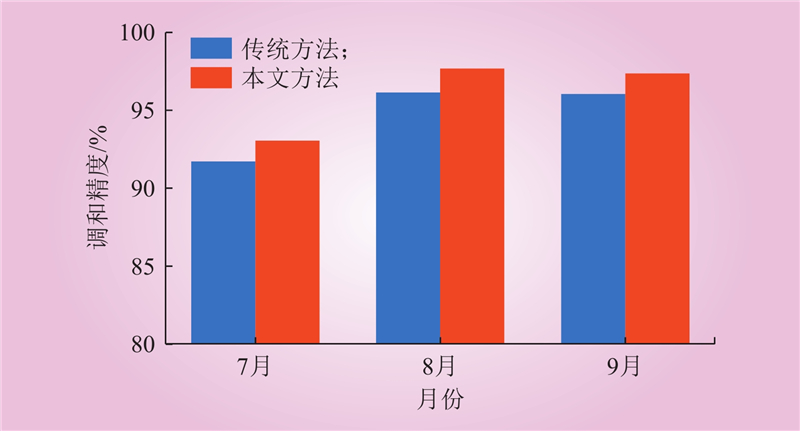
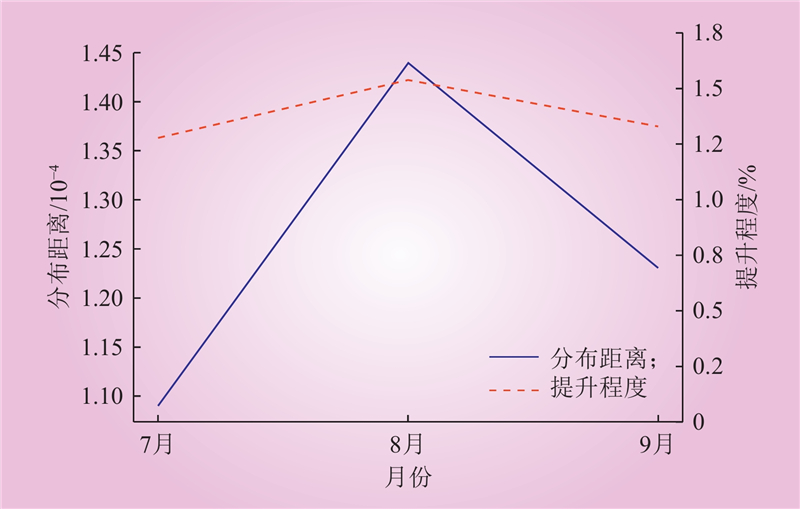
| 1 |
李思维, 许中平, 于龙, 等. 计及电动汽车和温控负荷集群的负荷控制用户组合优化方法[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (3): 86- 97.
|
|
LI Siwei, XU Zhongping, YU Long, et al. A Load Control User Combination Optimization Method with Electric Vehicle and Temperature Control Load Cluster[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (3): 86- 97.
|
| 2 |
徐玉婷, 田世明, 陈宋宋, 等. 基于LSTM的居民负荷预测及其可调节潜力分析[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2023, 21 (05): 1- 8.
|
|
XU Yuting, TIAN Shiming, CHEN Songsong, et al. Resident load forecasting based on LSTM and its adjustable potential analysis[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2023, 21 (05): 1- 8.
|
| 3 |
史媛, 周浩, 张俊娜, 等. 双碳背景下的用户负荷主动优化方法研究[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2023, 21 (5): 25- 32.
|
|
SHI Yuan, ZHOU Hao, ZHANG Junna, et al. Research on user load active optimization method under dual carbon background[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2023, 21 (5): 25- 32.
|
| 4 |
杨胡萍, 余阳, 汪超, 等. 基于VMD-CNN-BIGRU的电力系统短期负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 71- 76.
|
|
YANG Huping, YU Yang, WANG Chao, et al. Short-term load forecasting of power system based on VMD-CNN-BIGRU[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 71- 76.
|
| 5 |
葛鑫鑫, 付志扬, 徐飞, 等. 面向新型电力系统的虚拟电厂商业模式与关键技术[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (18): 129- 146.
|
|
GE Xinxin, FU Zhiyang, XU Fei, et al. Business model and key technologies of virtual power plant for new power system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (18): 129- 146.
|
| 6 |
周颖, 白雪峰, 王阳, 等. 面向虚拟电厂运营的温度敏感负荷分析与演变趋势研判[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (1): 9- 17.
|
|
ZHOU Ying, BAI Xuefeng, WANG Yang, et al. Analysis and evolution trend of temperature-sensitive loads for virtual power plant operation[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (1): 9- 17.
|
| 7 |
杨燕, 王云, 胡熊伟, 等. 基于5G无线通信的可中断负荷快速响应系统[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (10): 83- 89.
|
|
YANG Yan, WANG Yun, HU Xiongwei, et al. Interruptible load fast response system based on 5G wireless communicatio[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (10): 83- 89.
|
| 8 |
朱明, 夏宇栋, 常凯, 等. 基于粒子群优化算法的空调负荷灰箱模型辨识[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38 (4): 214- 221.
|
|
ZHU Ming, XIA Yudong, CHANG Kai, et al. Identification of grey box model for air conditioning load based on particleswarm optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38 (4): 214- 221.
|
| 9 |
马涛, 李津, 曹晓波, 等. 计及用户行为差异性和配电网潮流的电采暖负荷群优化调度策略研究[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38 (1): 77- 87.
|
|
MA Tao, LI Jin, CAO Xiaobo, et al. Research on optimal dispatch strategy of electric heating load groups considering userbehavior difference and distribution network power flow[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38 (1): 77- 87.
|
| 10 |
徐宇颂, 邹山花, 卢先领. 基于特征选择和组合模型的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (7): 121- 127.
|
|
XU Yusong, ZOU Shanhua, LU Xianling. Short-term load forecasting based on feature selection and combination model[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (7): 121- 127.
|
| 11 |
杨珂, 朱洪斌, 李达, 等. 基于压缩感知的纵向联邦学习园区负荷预测方法[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (5): 36- 42.
|
|
YANG Ke, ZHU Hongbin, LI Da, et al. Load forecasting method for vertical federated learning park based on compressed sensing[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (5): 36- 42.
|
| 12 |
吴桐, 惠红勋, 张洪财. 商业建筑空调系统参与城市电网负荷调控综述[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (7): 1- 11.
|
|
WU Tong, HUI Hongxun, ZHANG Hongcai. Review of commercial air conditioners for participating in urban grid regulation[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (7): 1- 11.
|
| 13 |
ALKHAYAT G, MEHMOOD R. A review and taxonomy of wind and solar energy forecasting methods based on deep learning[J]. Energy and AI, 2021, 4, 100060.
|
| 14 |
郭艳飞, 程林, 李洪涛, 等. 基于支持向量机和互联网信息修正的空间负荷预测方法[J]. 中国电力, 2019, 52 (4): 80- 88.
|
|
GUO Yanfei, CHENG Lin, LI Hongtao, et al. Spatial load forecasting method based on support vector machine and internet information correction[J]. Electric Power, 2019, 52 (4): 80- 88.
|
| 15 |
吴军英, 路欣, 刘宏, 等. 基于Spearman-GCN-GRU模型的超短期多区域电力负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (6): 131- 140.
|
|
WU Junying, LU Xin, LIU Hong, et al. Ultra-short-term multi-region power load forecasting based on Spearman-GCN-GRU model[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (6): 131- 140.
|
| 16 |
史佳琪, 马丽雅, 李晨晨, 等. 基于串行–并行集成学习的高峰负荷预测方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (14): 4463- 4472.
|
|
SHI Jiaqi, MA Liya, LI Chenchen, et al. Daily peak load forecasting based on sequential-parallel ensemble learning[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (14): 4463- 4472.
|
| 17 |
吴潇雨, 和敬涵, 张沛, 等. 基于灰色投影改进随机森林算法的电力系统短期负荷预测[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (12): 50- 55.
|
|
WU Xiaoyu, HE Jinghan, ZHANG Pei, et al. Power system short-term load forecasting based on improved random forest with grey relation projection[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (12): 50- 55.
|
| 18 |
李瑾, 刘金朋, 王建军. 采用支持向量机和模拟退火算法的中长期负荷预测方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2011, 31 (16): 63- 66.
|
|
LI Jin, LIU Jinpeng, WANG Jianjun. Mid-long term load forecasting based on simulated annealing and SVM algorithm[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2011, 31 (16): 63- 66.
|
| 19 |
孔祥玉, 郑锋, 鄂志君, 等. 基于深度信念网络的短期负荷预测方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (5): 133- 139.
|
|
KONG Xiangyu, ZHENG Feng, E Zhijun, et al. Short-term load forecasting based on deep belief network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42 (5): 133- 139.
|
| 20 |
罗澍忻, 麻敏华, 蒋林, 等. 考虑多时间尺度数据的中长期负荷预测方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (S1): 11- 19.
|
|
LUO Shuxin, MA Minhua, JIANG Lin, et al. Medium and long-term load forecasting method considering multi-time scale data[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (S1): 11- 19.
|
| 21 |
YIN Lifei, XIE Jiaxing. Multi-temporal-spatial-scale temporal convolution network for short-term load forecasting of power systems[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 283, 116328.
|
| 22 |
WANG J Q, DU Y, WANG J. LSTM based long-term energy consumption prediction with periodicity[J]. Energy, 2020, 197, 117197.
|
| 23 |
魏晓川, 王新刚. 基于气象大数据的城市电力负荷预测[J]. 电测与仪表, 2021, 58 (2): 90- 95.
|
|
WEI Xiaochuan, WANG Xingang. Prediction of urban electricity load based on meteorological big data[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2021, 58 (2): 90- 95.
|
| 24 |
郭占伍, 张泽亚, 周兴华, 等. 考虑气象因素的电采暖负荷预测研究[J]. 电测与仪表, 2022, 59 (2): 154- 158.
|
|
GUO Zhanwu, ZHANG Zeya, ZHOU Xinghua, et al. Study on forecasting method of electric heating load considering meteorological factors[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2022, 59 (2): 154- 158.
|
| 25 |
王溪. 基于大数据分析方法的温控负荷可调度容量预测及应用[D]. 合肥工业大学, 2018.
|
|
WANG Xi. Prediction and application of dispatchable capacity of temperature control load based on big data analysis method [D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2018.
|
| 26 |
SCHNEIDER K P, SORTOMME E, VENKATA S S, et al. Evaluating the magnitude and duration of cold load pick-up on residential distribution using multi-state load models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2015, 31 (5): 3765- 3774.
|
| 27 |
李香龙, 马龙飞, 赵向阳, 等. 基于LSTM网络的时间多尺度电采暖负荷预测[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2021, 33 (4): 71- 75.
|
|
LI Xianglong, MA Longfei, ZHAO Xiangyang, et al. Multi-time scale electric heating load forecasting based on long short-term memory network[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2021, 33 (4): 71- 75.
|
| 28 |
WANG X, XU Y, FU Z, et al. A dynamic interactive optimization model of CCHP system involving demand-side and supply-side impacts of climate change. Part Ⅰ: Methodology development[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 252, 115112.
|
| 29 |
胡可心, 李康平, 刘春阳, 等. 动态分时电价下居民用户需求响应基线负荷预测方法[J]. 电测与仪表, 2025, 62 (9): 62- 72.
|
|
HU Kexin, LI Kangping, Liu Chunyang, et al. A baseline load forecasting method for residential demand response under dynamic time-of-use electricity price[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2025, 62 (9): 62- 72.
|
| 30 |
GONG Z, TANG Y, LIANG J. Patchmixer: A patch-mixing architecture for long-term time series forecasting[J]. arXiv preprint: 2310.00655:2023.
|
| 31 |
ALI M, LI B, YING Z, et al. Day-ahead demand response potential prediction in residential buildings with HITSKAN: a fusion of kolmogorov-arnold networks and N-HiTS[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2025: 115455.
|