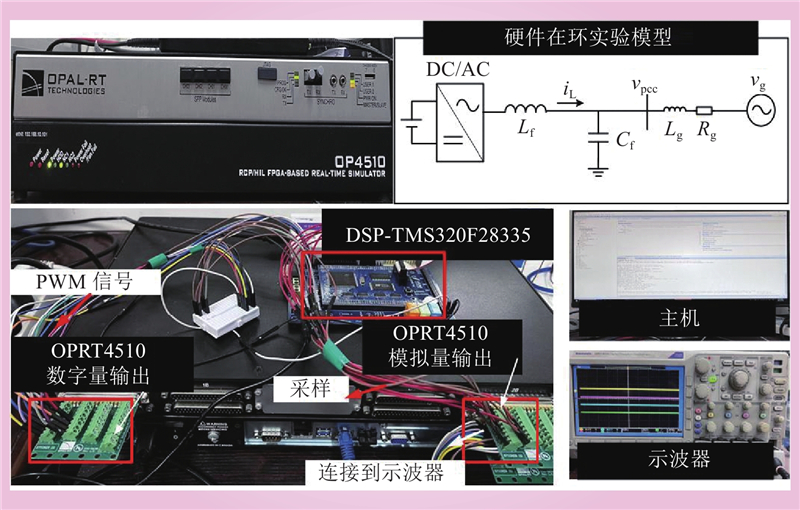
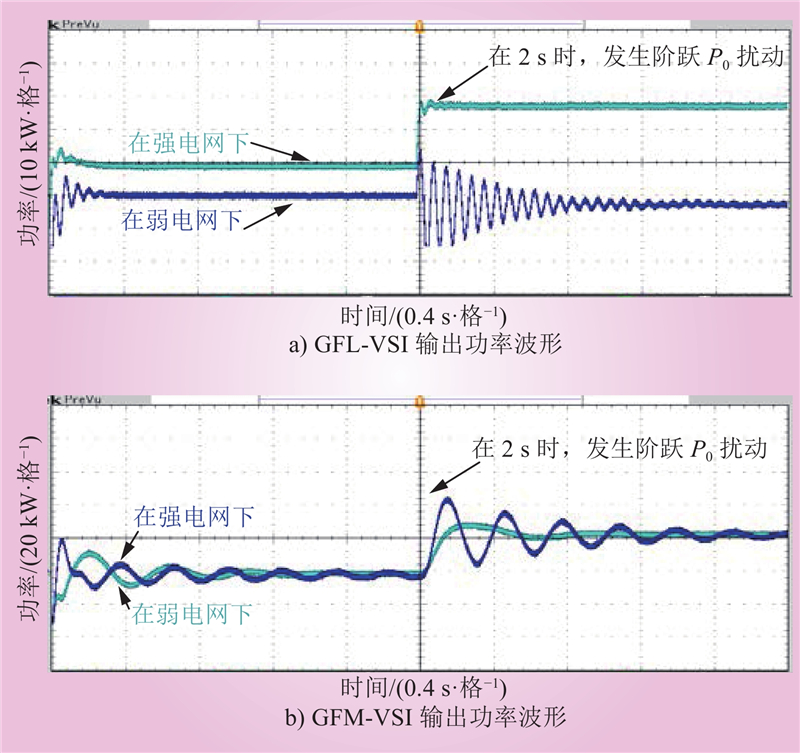
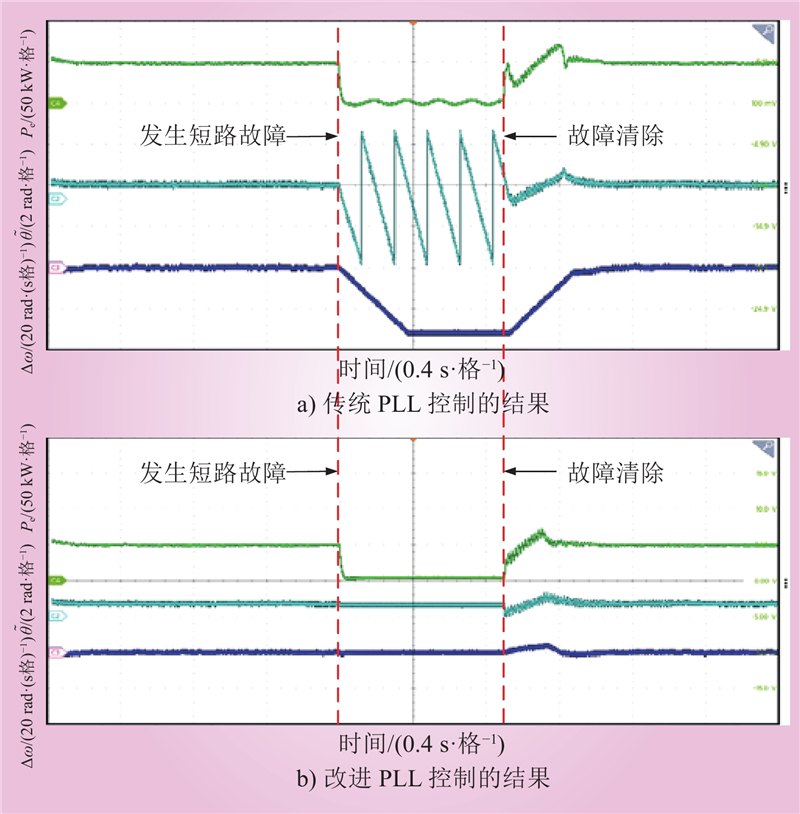
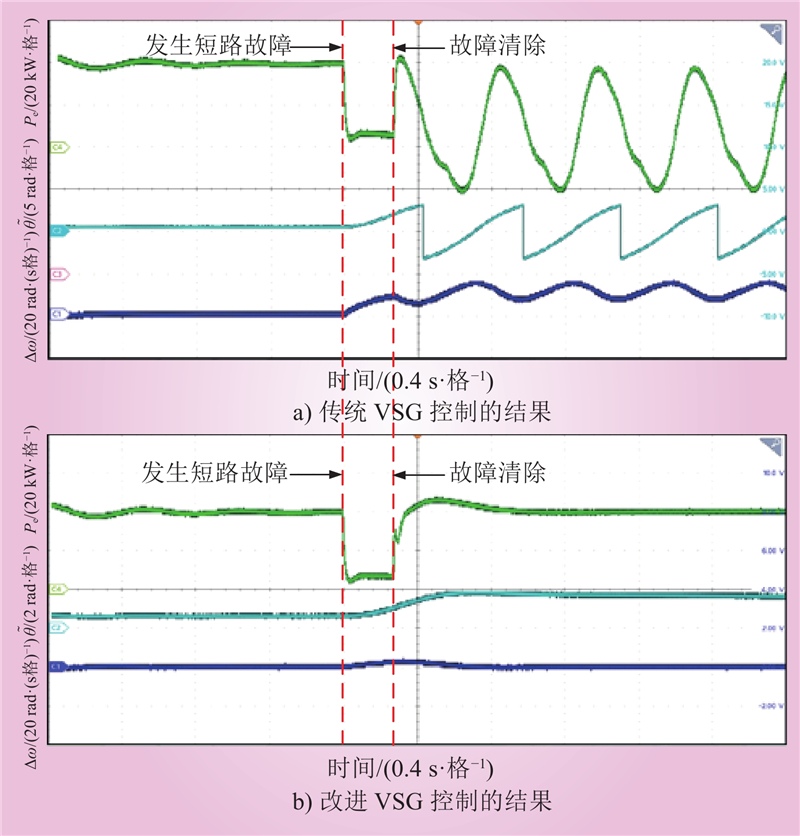
| 1 |
李相俊, 马会萌, 姜倩. 新能源侧储能配置技术研究综述[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (1): 13- 25.
|
|
LI Xiangjun, MA Huimeng, JIANG Qian. Review of energy storage configuration technology on renewable energy side[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (1): 13- 25.
|
| 2 |
陈征, 胡鹏飞, 戴立宇, 等. 基于锁相环的并网VSC暂态失稳机理与控制方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 77- 86.
|
|
CHEN Zheng, HU Pengfei, DAI Liyu, et al. Transient instability mechanism and control method of grid-connected VSC based on PLL[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 77- 86.
|
| 3 |
姜卫同, 胡鹏飞, 尹瑞, 等. 基于虚拟同步机的变流器暂态稳定分析及混合同步控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (22): 124- 133.
|
|
JIANG Weitong, HU Pengfei, YIN Rui, et al. Transient stability analysis and hybrid synchronization control strategy of converter based on virtual synchronous generator[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (22): 124- 133.
|
| 4 |
FU X K, SUN J J, HUANG M, et al. Large-signal stability of grid-forming and grid-following controls in voltage source converter: a comparative study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36 (7): 7832- 7840.
|
| 5 |
WU H, WANG X F. Design-oriented transient stability analysis of grid-connected converters with power synchronization control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66 (8): 6473- 6482.
|
| 6 |
ZHANG K Z, SU M, LIU Z J, et al. A distributed coordination control for islanded hybrid AC/DC microgrid[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2023, 17 (2): 1819- 1830.
|
| 7 |
张嘉诚, 夏向阳, 邓子豪, 等. 储能电站安全参与电网一次调频的优化控制策略[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (2): 19- 27.
|
|
ZHANG Jiacheng, XIA Xiangyang, DENG Zihao, et al. Optimal control strategy for energy storage power station in primary frequency regulation of power grid[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (2): 19- 27.
|
| 8 |
WEN B, BOROYEVICH D, BURGOS R, et al. Analysis of D-Q small-signal impedance of grid-tied inverters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2016, 31 (1): 675- 687.
|
| 9 |
刘静佳, 李欢, 于华龙, 等. 高压直流输电控制系统不同锁相环特性对比[J]. 南方电网技术, 2021, 15 (8): 12- 21.
|
|
LIU Jingjia, LI Huan, YU Hualong, et al. Characteristics comparison of different phase-locked loops in HVDC power transmission systems[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2021, 15 (8): 12- 21.
|
| 10 |
MA S K, GENG H, LIU L, et al. Grid-synchronization stability improvement of large scale wind farm during severe grid fault[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33 (1): 216- 226.
|
| 11 |
HE X Q, GENG H, XI J B, et al. Resynchronization analysis and improvement of grid-connected VSCs during grid faults[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2021, 9 (1): 438- 450.
|
| 12 |
李霞林, 王智, 郭力, 等. 基于最大估计吸引域的VSC接入弱网下的锁相环同步暂态稳定性分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (20): 7485- 7497.
|
|
LI Xialin, WANG Zhi, GUO Li, et al. Transient stability analysis of PLL synchronization in weak-grid-connected VSCs based on the largest estimated domain of attraction[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (20): 7485- 7497.
|
| 13 |
CHENG H J, SHUAI Z K, SHEN C, et al. Transient angle stability of paralleled synchronous and virtual synchronous generators in islanded microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35 (8): 8751- 8765.
|
| 14 |
HUANG L B, XIN H H, WANG Z, et al. Transient stability analysis and control design of droop-controlled voltage source converters considering current limitation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10 (1): 578- 591.
|
| 15 |
WU H, WANG X F. A mode-adaptive power-angle control method for transient stability enhancement of virtual synchronous generators[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2020, 8 (2): 1034- 1049.
|
| 16 |
李明烜, 王跃, 徐宁一, 等. 基于带通阻尼功率反馈的虚拟同步发电机控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2018, 33 (10): 2176- 2185.
|
|
LI Mingxuan, WANG Yue, XU Ningyi, et al. Virtual synchronous generator control strategy based on bandpass damping power feedback[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2018, 33 (10): 2176- 2185.
|
| 17 |
盛师贤, 周鑫, 王德林, 等. 虚拟同步风电场协同光伏电站附加阻尼控制方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (3): 177- 186.
|
|
SHENG Shixian, ZHOU Xin, WANG Delin, et al. Additional damping cooperative control method of virtual synchronous wind farm and photovoltaic power stations[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (3): 177- 186.
|
| 18 |
刘刚, 陈海东, 孙睿哲, 等. 集群光伏电站频率主动支撑自校正控制方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (9): 156- 162.
|
|
LIU Gang, CHEN Haidong, SUN Ruizhe, et al. Self-tuning control method for frequency active support of cluster photovoltaic power station[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (9): 156- 162.
|
| 19 |
LI Y T, GU Y J, ZHU Y, et al. Impedance circuit model of grid-forming inverter: visualizing control algorithms as circuit elements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36 (3): 3377- 3395.
|
| 20 |
申屠刚, 吴正骅, 王思家, 等. 含光伏电站的电力系统低频振荡广域阻尼协同控制方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (12): 69- 77.
|
|
SHENTU Gang, WU Zhenghua, WANG Sijia, et al. Wide-area damping cooperative control method for low-frequency oscillation of power system with photovoltaic power station[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (12): 69- 77.
|
| 21 |
IEEE Std 1204-1997, IEEE guide for planning DC links terminating at AC locations having low short-circuit capacities[S]. New York, USA: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc, 1997.
|
| 22 |
IEEE Std 1547a-2020. IEEE standard for interconnection and interoperability of distributed energy resources with associated electric power systems interfaces[S]. New York, USA: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc, 2020.
|
| 23 |
HOU X C, SUN Y, ZHANG X, et al. Improvement of frequency regulation in VSG-based AC microgrid via adaptive virtual inertia[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35 (2): 1589- 1602.
|