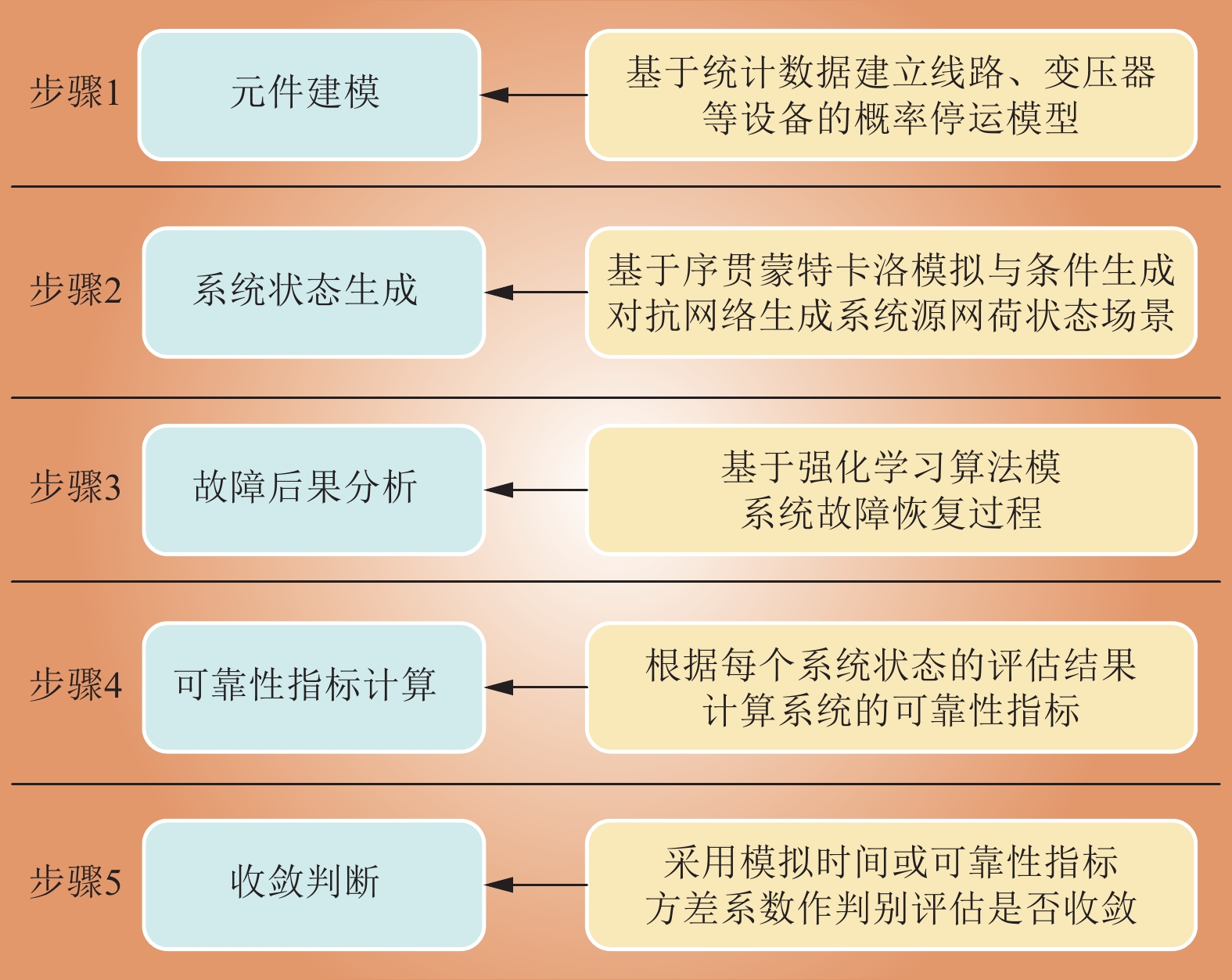
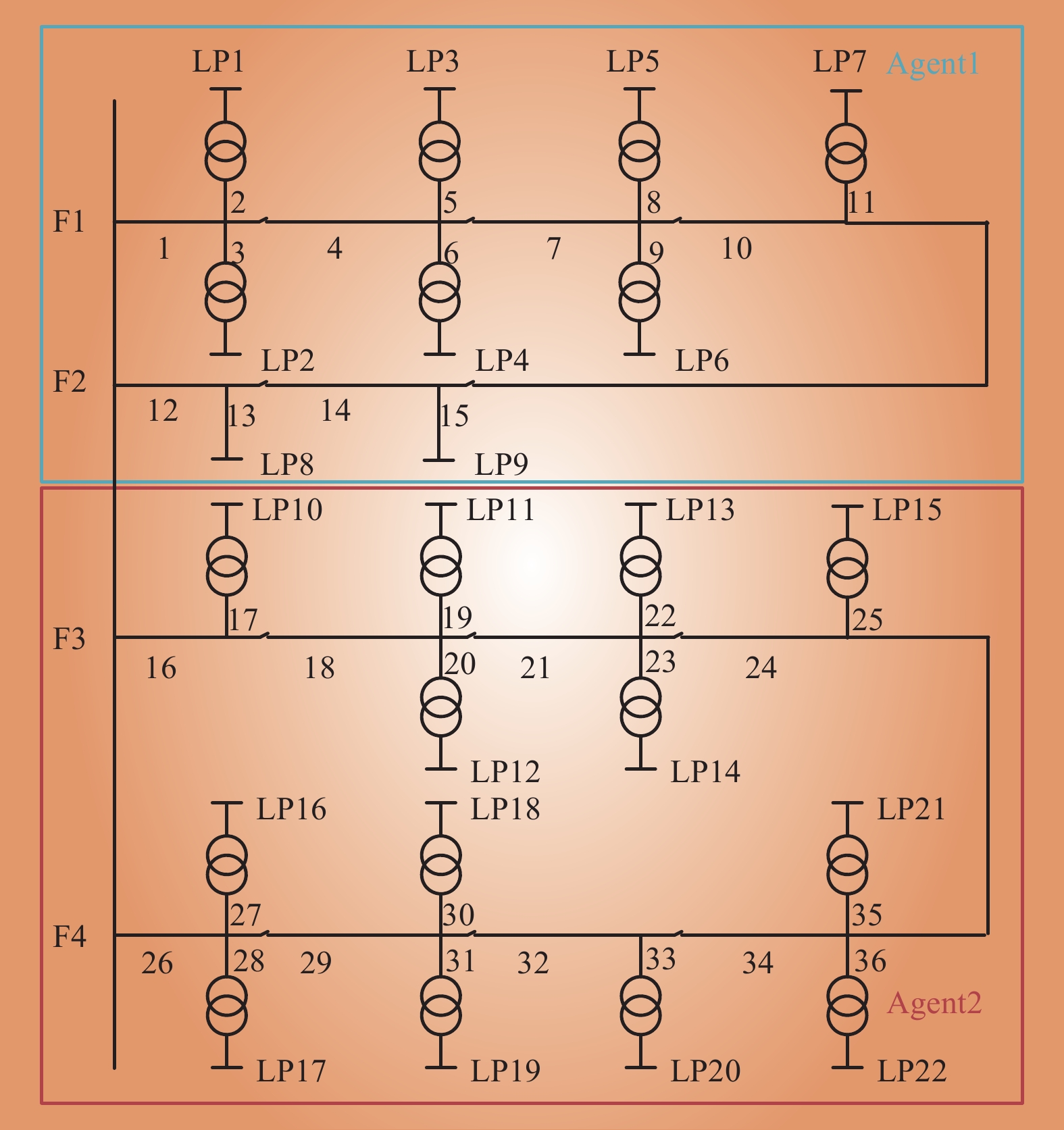
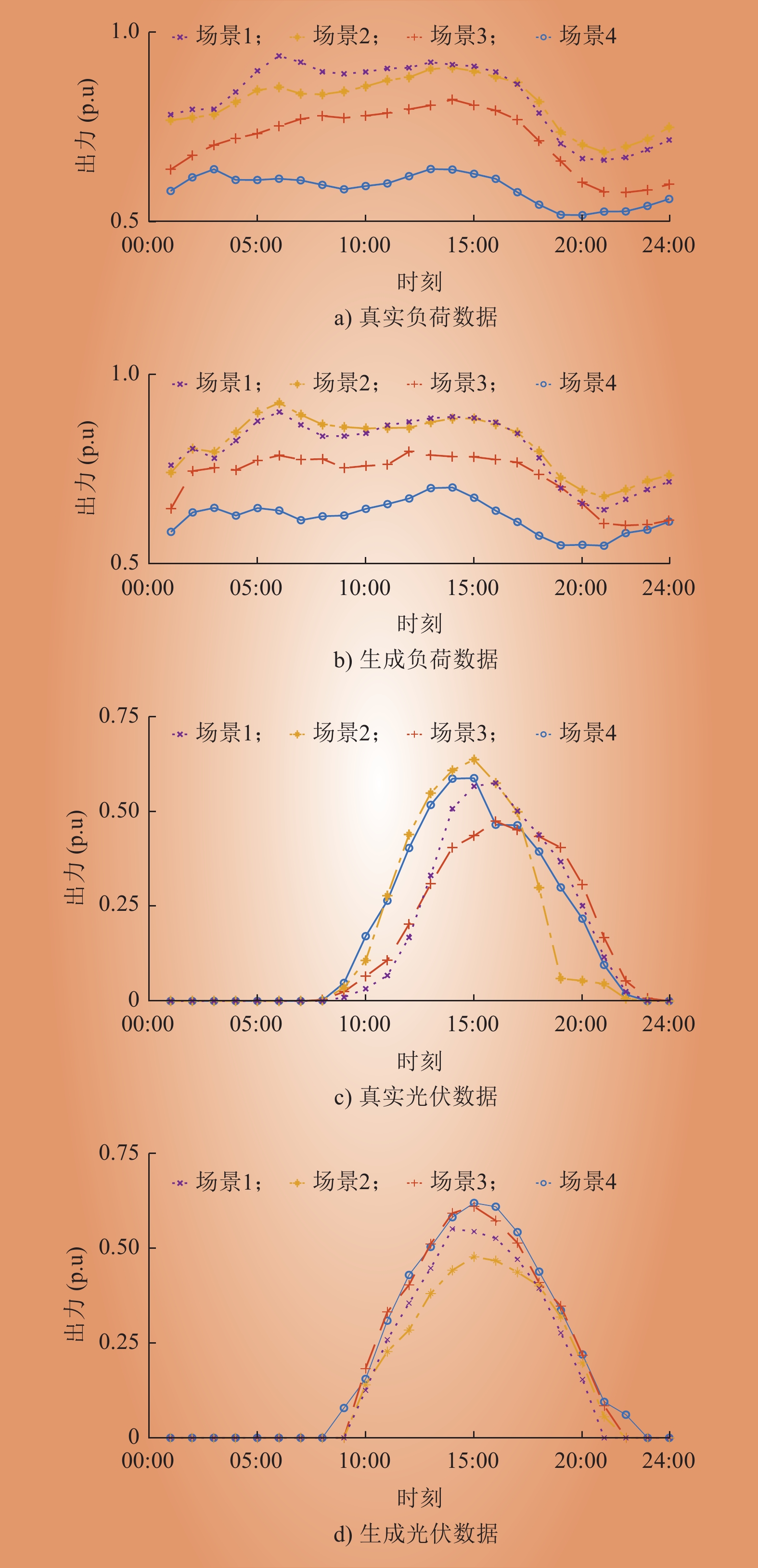
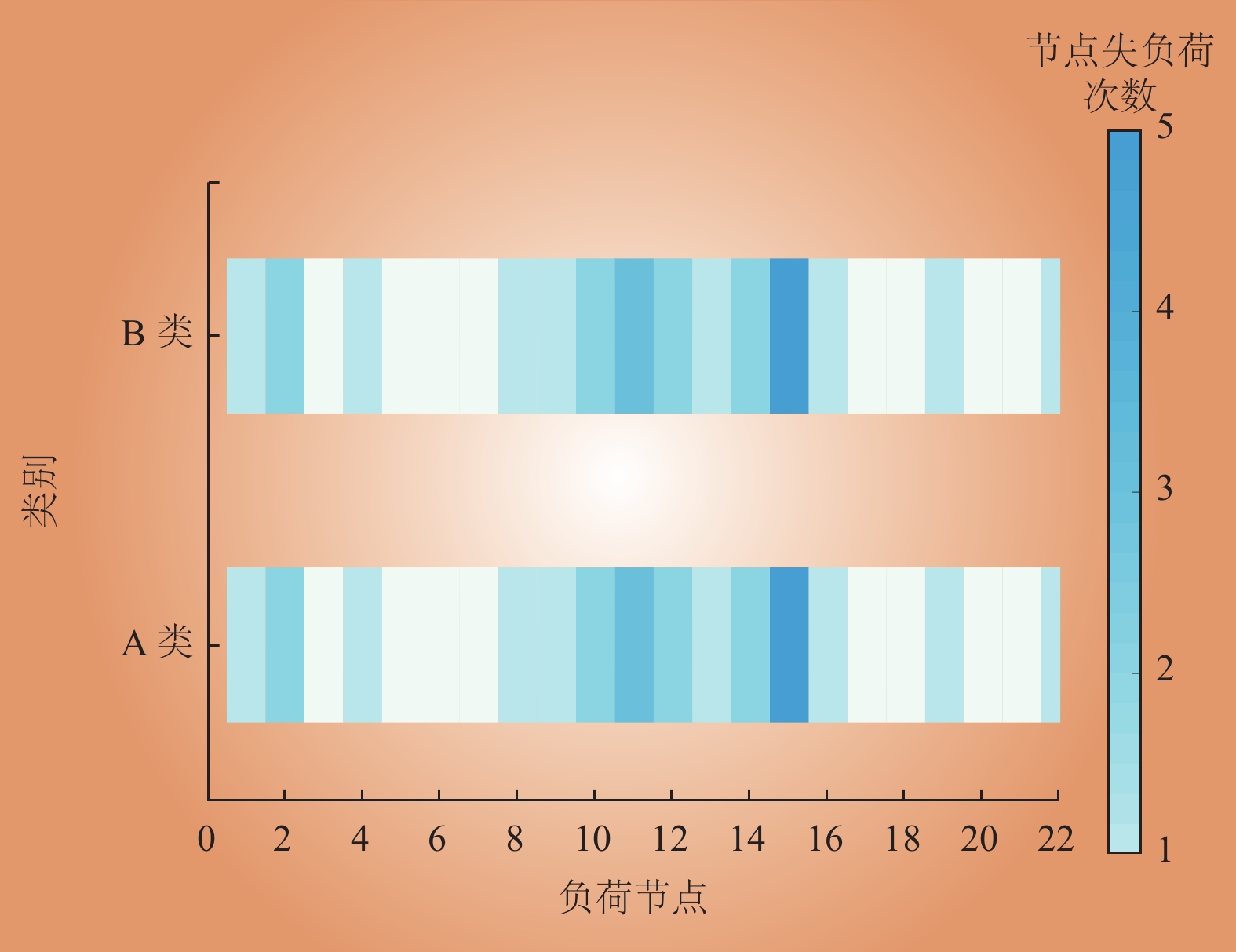
| 1 |
刘岑岑, 夏天, 李艳, 等. 基于显式可靠性指标的配电网多阶段扩展规划方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (9): 87- 95.
|
|
LIU Cencen, XIA Tian, LI Yan, et al. A multi-stage expansion planning method for distribution networks based on explicit reliability index[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (9): 87- 95.
|
| 2 |
杜维, 杜兆斌, 范国晨, 等. 极端天气下考虑分布式电源可用程度的配电网多源协同恢复策略[J]. 广东电力, 2024, 37 (7): 88- 97.
|
|
DU Wei, DU Zhaobin, FAN Guochen, et al. Multi-source cooperative restoration strategy of distribution network considering availability of distributed generation in extreme weather[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2024, 37 (7): 88- 97.
|
| 3 |
李泽成, 孙燕盈. 新型电力系统下考虑分布式光伏并网的配电网可靠性评估[J]. 山东电力技术, 2023, 50 (5): 1- 5, 47.
|
|
LI Zecheng, SUN Yanying. Reliability evaluation of distribution network considering flexible grid connection of distributed photovoltaic power generations[J]. Shandong Electric Power, 2023, 50 (5): 1- 5, 47.
|
| 4 |
徐波, 熊国江, 叶方慧. 基于智能软开关优化配置的配电网柔性互联策略[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2023, 39 (11): 86- 96.
|
|
XU Bo, XIONG Guojiang, YE Fanghui. A flexible interconnection strategy for distribution networks based on intelligent soft-open point configuration[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2023, 39 (11): 86- 96.
|
| 5 |
黄南天, 王文婷, 蔡国伟, 等. 计及复杂气象耦合特性的模块化去噪变分自编码器多源–荷联合场景生成[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (10): 2924- 2934.
|
|
HUANG Nantian, WANG Wenting, CAI Guowei, et al. The joint scenario generation of multi source-load by modular denoising variational autoencoder considering the complex coupling characteristics of meteorology[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (10): 2924- 2934.
|
| 6 |
罗萍萍, 盛奥, 林济铿, 等. 基于可解释性条件生成对抗网络的台风气象负荷场景生成方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2025, 49 (2): 186- 197.
|
|
LUO Pingping, SHENG Ao, LIN Jikeng, et al. A Method for typhoon meteorological load scenario generation based on interpretable conditional generative adversarial networks[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2025, 49 (2): 186- 197.
|
| 7 |
ZHANG S, LIU W X, WAN H Y, et al. Combing data-driven and model-driven methods for high proportion renewable energy distribution network reliability evaluation[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2023, 149, 108941.
|
| 8 |
ROCCO C M, MORENO J A. Fast Monte Carlo reliability evaluation using support vector machine[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2002, 76 (3): 237- 243.
|
| 9 |
CAI B P, KONG X D, LIU Y H, et al. Application of Bayesian networks in reliability evaluation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 15 (4): 2146- 2157.
|
| 10 |
CAI B P, SHAO X Y, LIU Y H, et al. Remaining useful life estimation of structure systems under the influence of multiple causes: subsea pipelines as a case study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67 (7): 5737- 5747.
|
| 11 |
LI G F, HUANG Y X, BIE Z H, et al. Machine-learning-based reliability evaluation framework for power distribution networks[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2020, 14(12): 2282-2291.
|
| 12 |
LI Y Z, HAO G K, LIU Y, et al. Many-objective distribution network reconfiguration via deep reinforcement learning assisted optimization algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2022, 37 (3): 2230- 2244.
|
| 13 |
杨挺, 赵黎媛, 刘亚闯, 等. 基于深度强化学习的综合能源系统动态经济调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (5): 39- 47.
|
|
YANG Ting, ZHAO Liyuan, LIU Yachuang, et al. Dynamic economic dispatch for integrated energy system based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (5): 39- 47.
|
| 14 |
CHOWDHURY N, BILLINTON R. A reliability test system for educational purposes-spinning reserve studies in isolated and interconnected systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2002, 6 (4): 1578- 1583.
|
| 15 |
呼斯乐, 于源, 王渊, 等. 考虑灵活性分析的典型光伏日出力率曲线提取方法[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2024, 42 (3): 20- 27.
|
|
HU Sile, YU Yuan, WANG Yuan, et al. Method for extracting typical PV daily output curves considering flexibility analysis[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2024, 42 (3): 20- 27.
|
| 16 |
缪月森, 夏红军, 黄宁洁, 等. 基于Informer的负荷及光伏出力系数预测[J]. 综合智慧能源, 2024, 46 (4): 60- 67.
|
|
MIAO Yuesen, XIA Hongjun, HUANG Ningjie, et al. Prediction on loads and photovoltaic output coefficients based on Informer[J]. Integrated Intelligent Energy, 2024, 46 (4): 60- 67.
|
| 17 |
唐雅洁, 阎洁, 李玉浩, 等. 基于深度嵌入聚类的风光水典型联合出力场景提取[J]. 浙江电力, 2023, 42 (4): 36- 44.
|
|
TANG Yajie, YAN Jie, LI Yuhao, et al. Extraction of typical combined output scenarios of wind-solar-hydropower generation based on deep embedding clustering[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2023, 42 (4): 36- 44.
|
| 18 |
覃海, 陈胜, 张洪略, 等. 并网光伏电站关口无功调节能力的分时段等值方法[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (2): 27- 33.
|
|
QIN Hai, CHEN Sheng, ZHANG Honglue, et al. Time-based equivalent method for reactive power regulation capacity of grid-connected photovoltaic plant[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (2): 27- 33.
|
| 19 |
韩晓, 王涛, 韦晓广, 等. 考虑阵列间时空相关性的超短期光伏出力预测[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (14): 82- 94.
|
|
HAN Xiao, WANG Tao, WEI Xiaoguang, et al. Ultrashort-term photovoltaic output forecasting considering spatiotemporal correlation between arrays[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (14): 82- 94.
|
| 20 |
杨海柱, 刘森, 张鹏, 等. 基于改进黏菌算法的分布式光伏发电并网规划[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (11): 119- 128.
|
|
YANG Haizhu, LIU Sen, ZHANG Peng, et al. Integration planning of distributed photovoltaic generation based on improved slime mould algorithm[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (11): 119- 128.
|