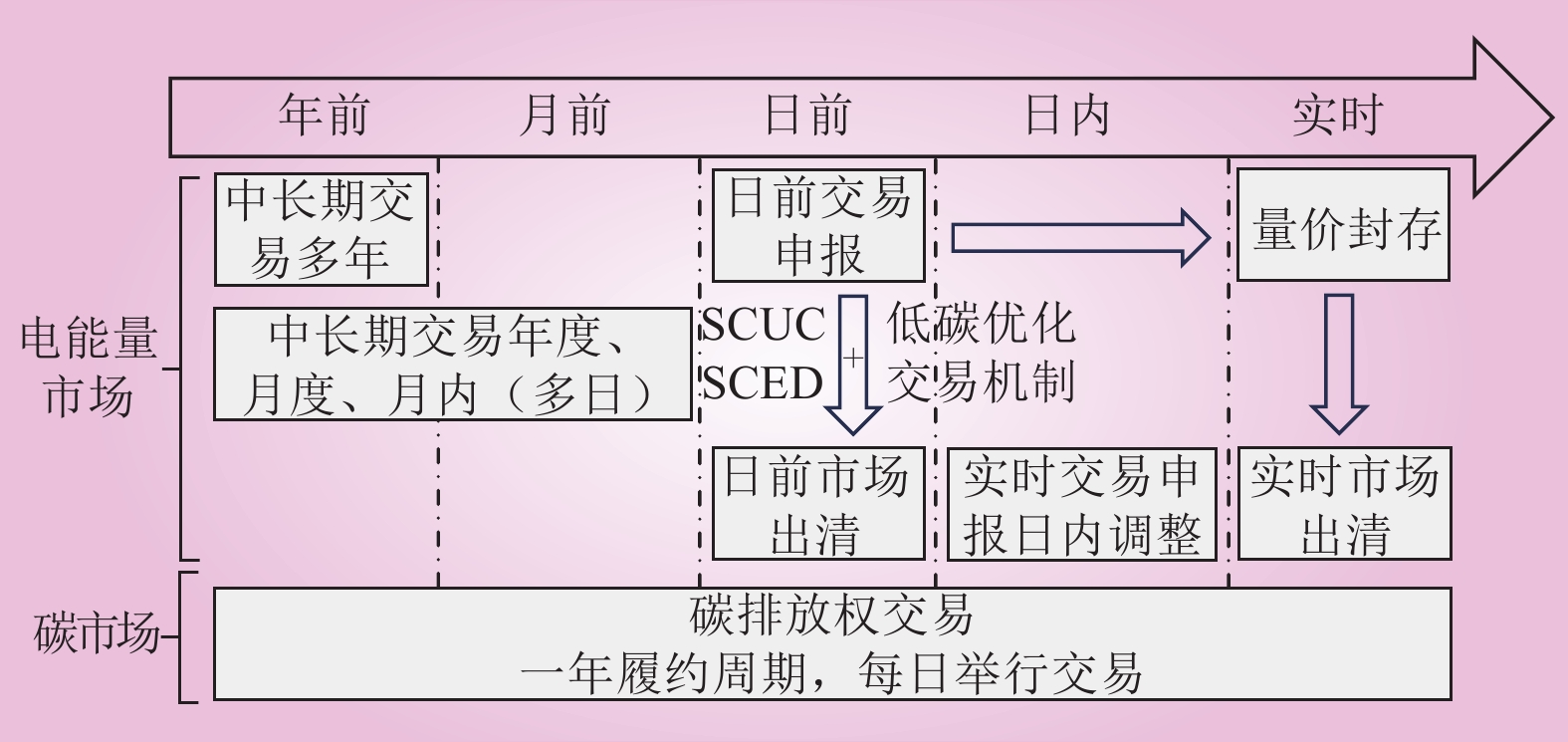
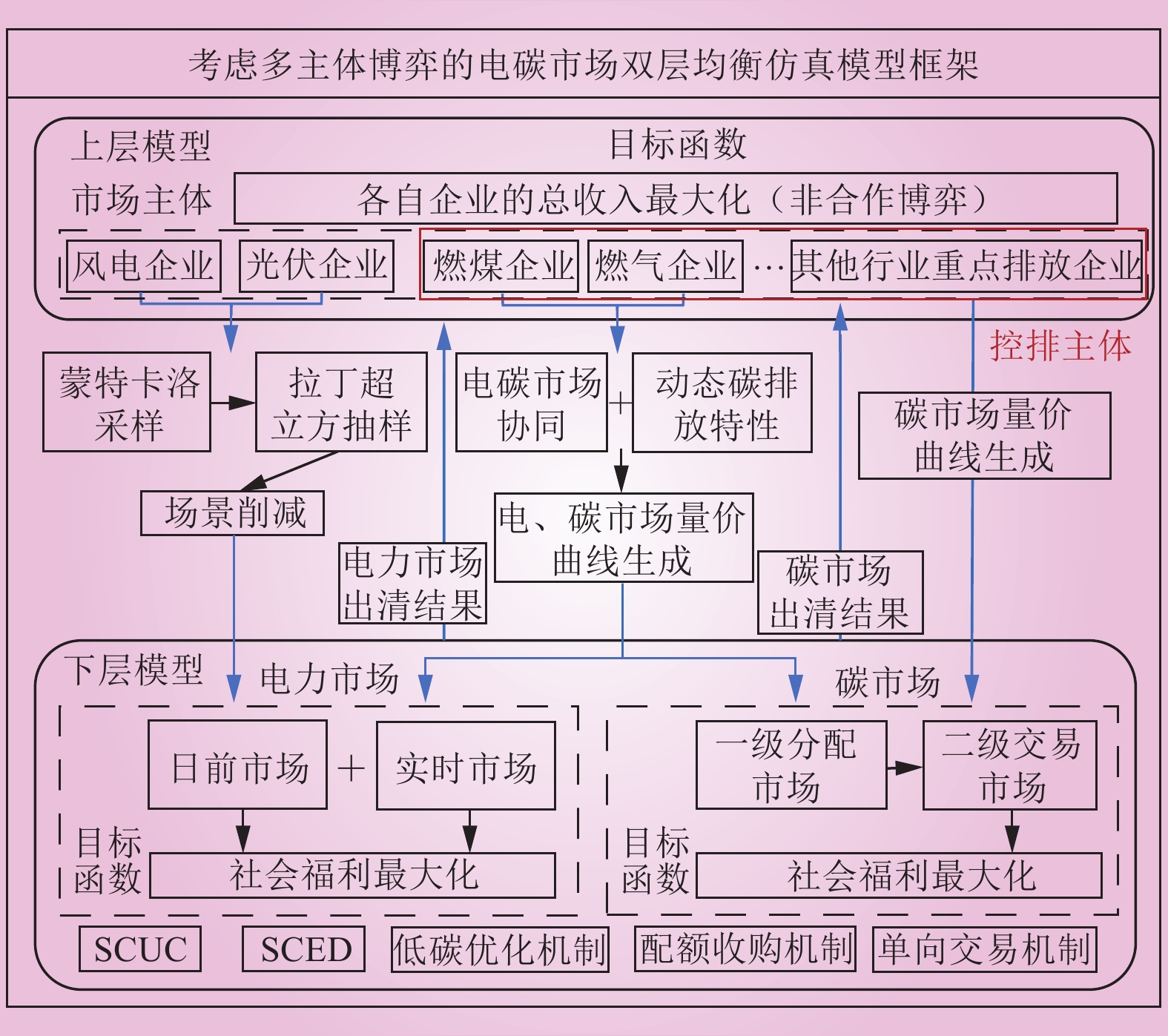
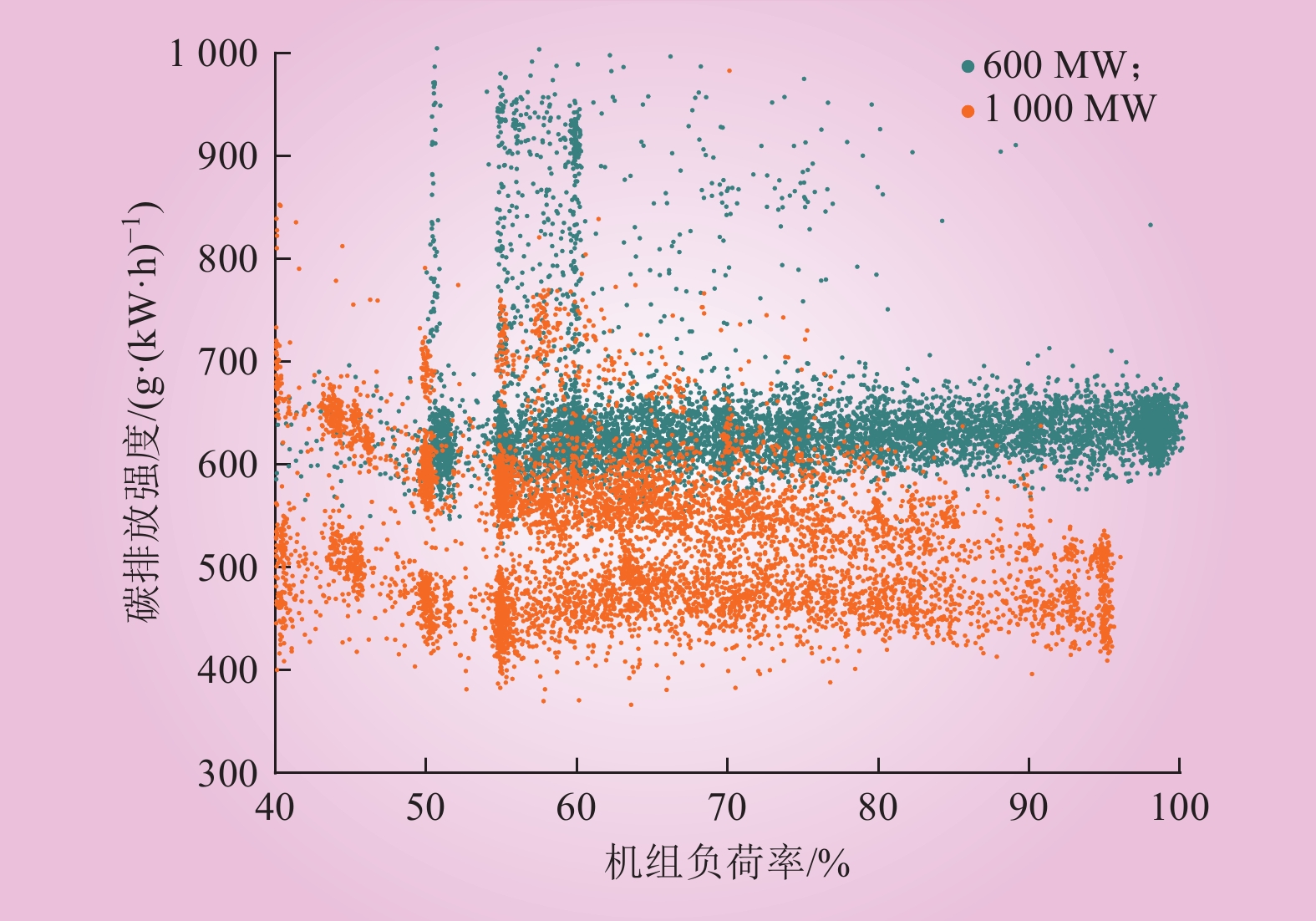
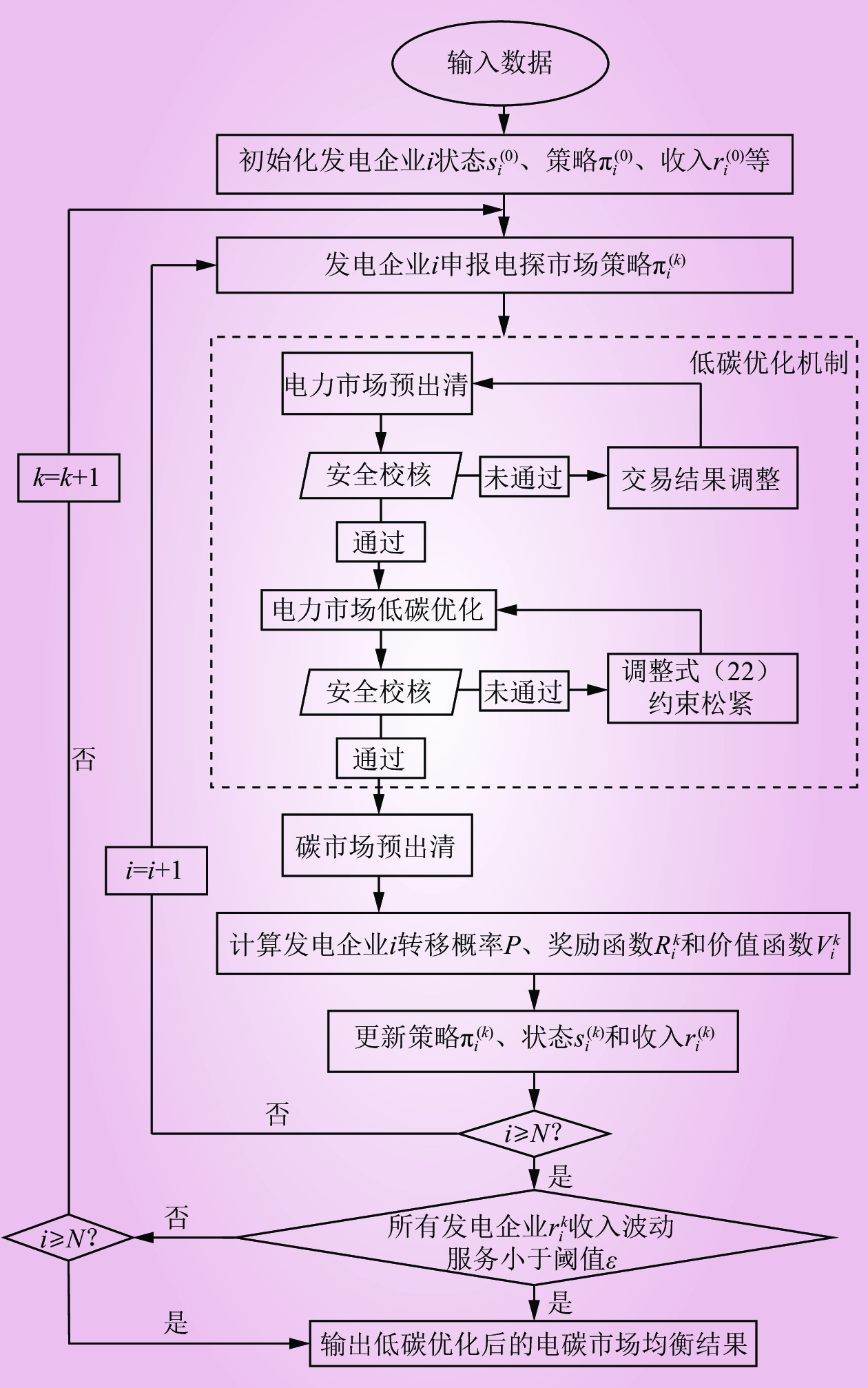
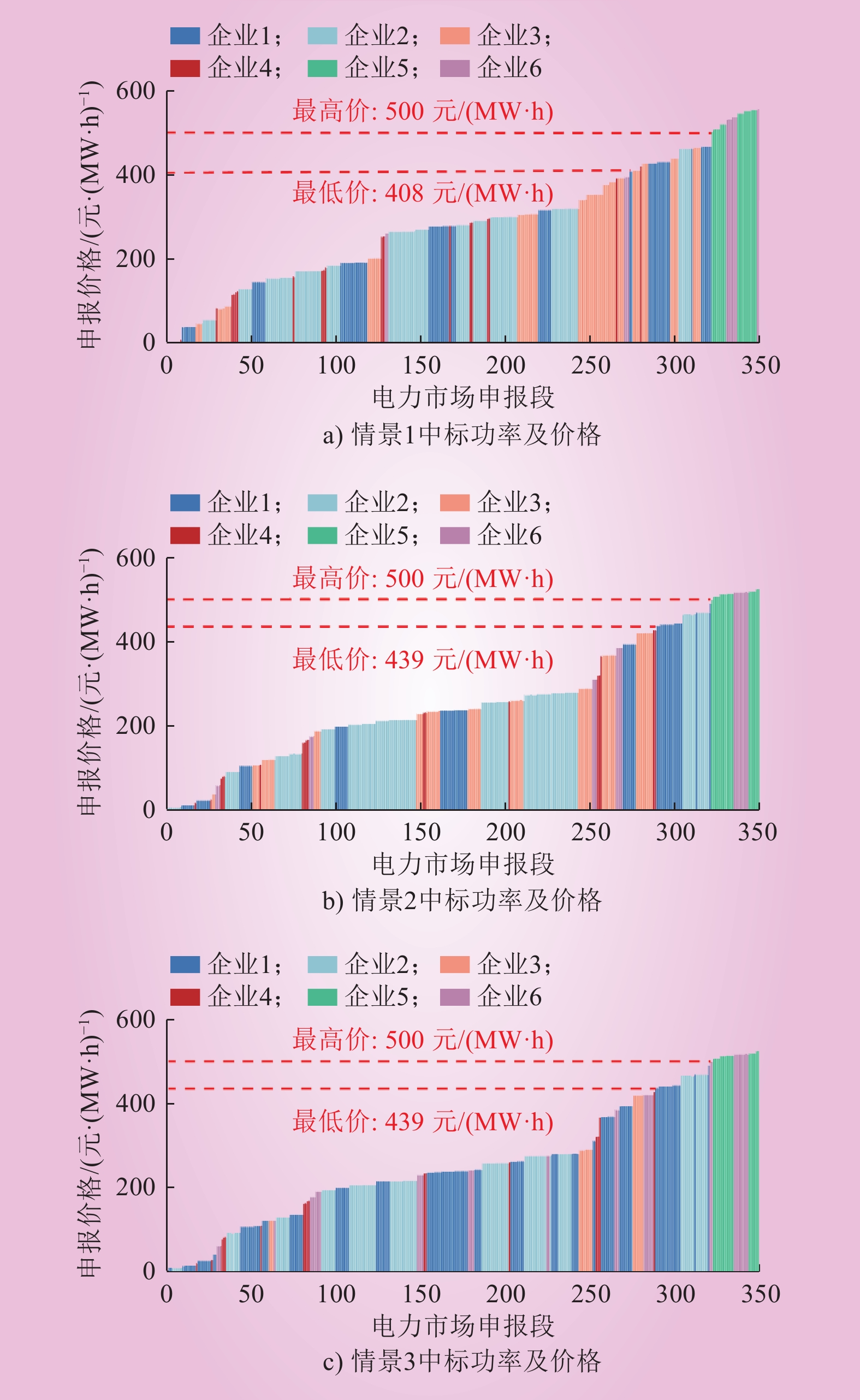
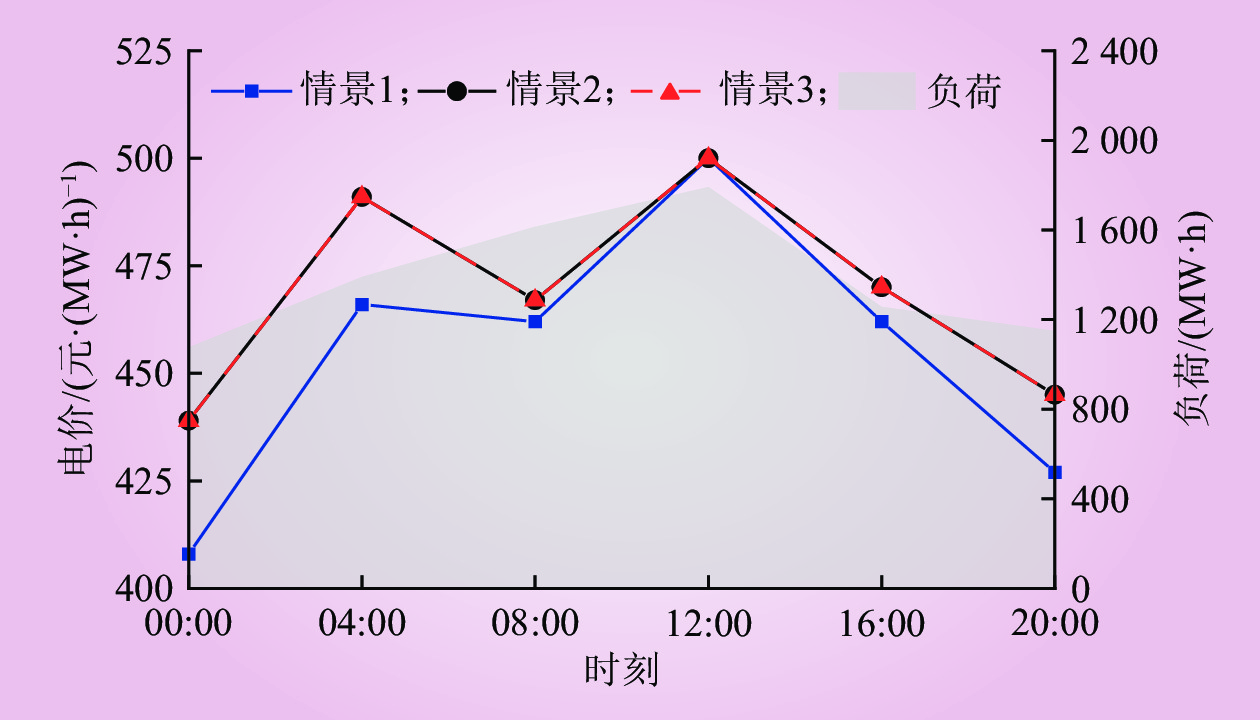
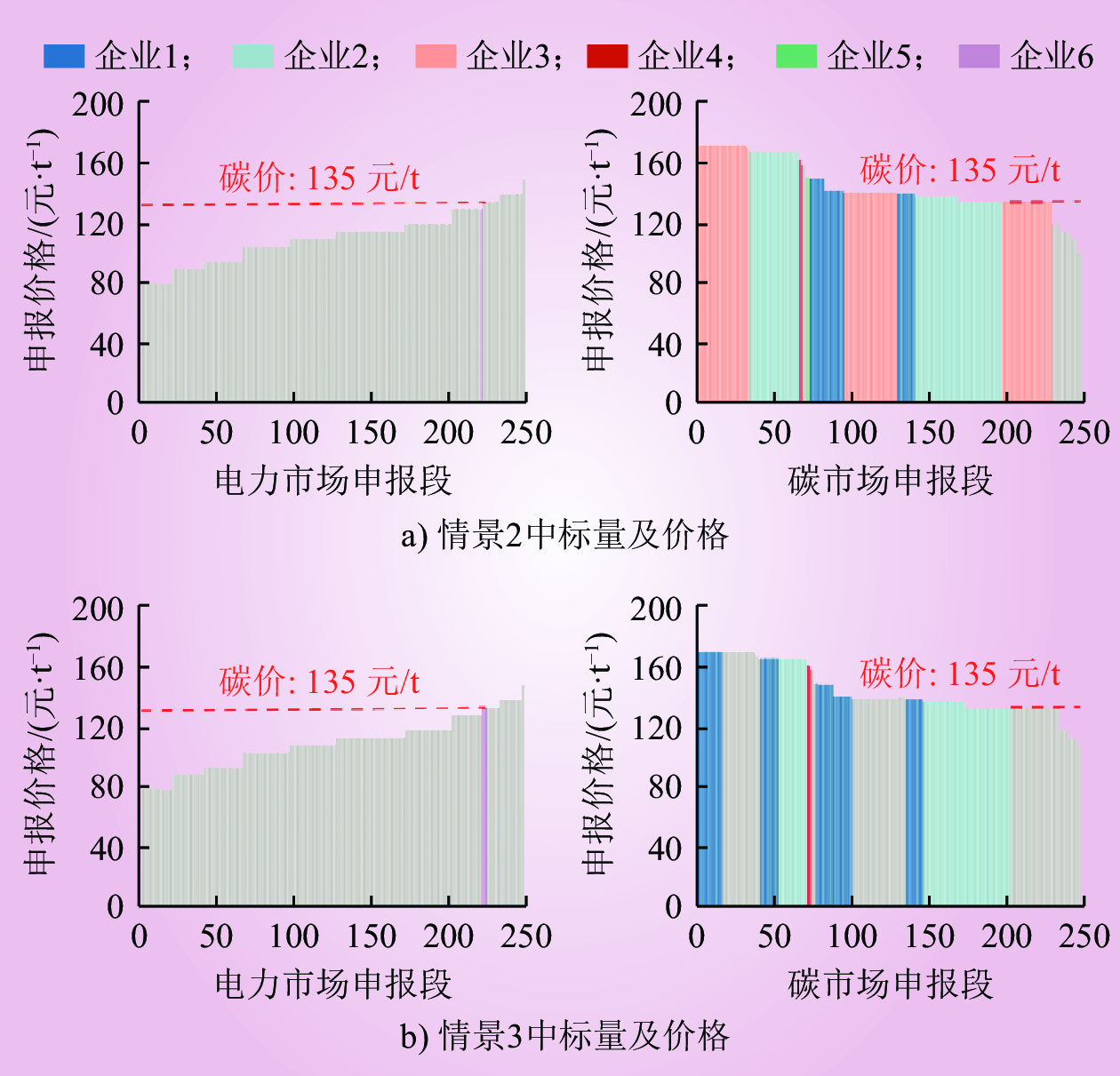
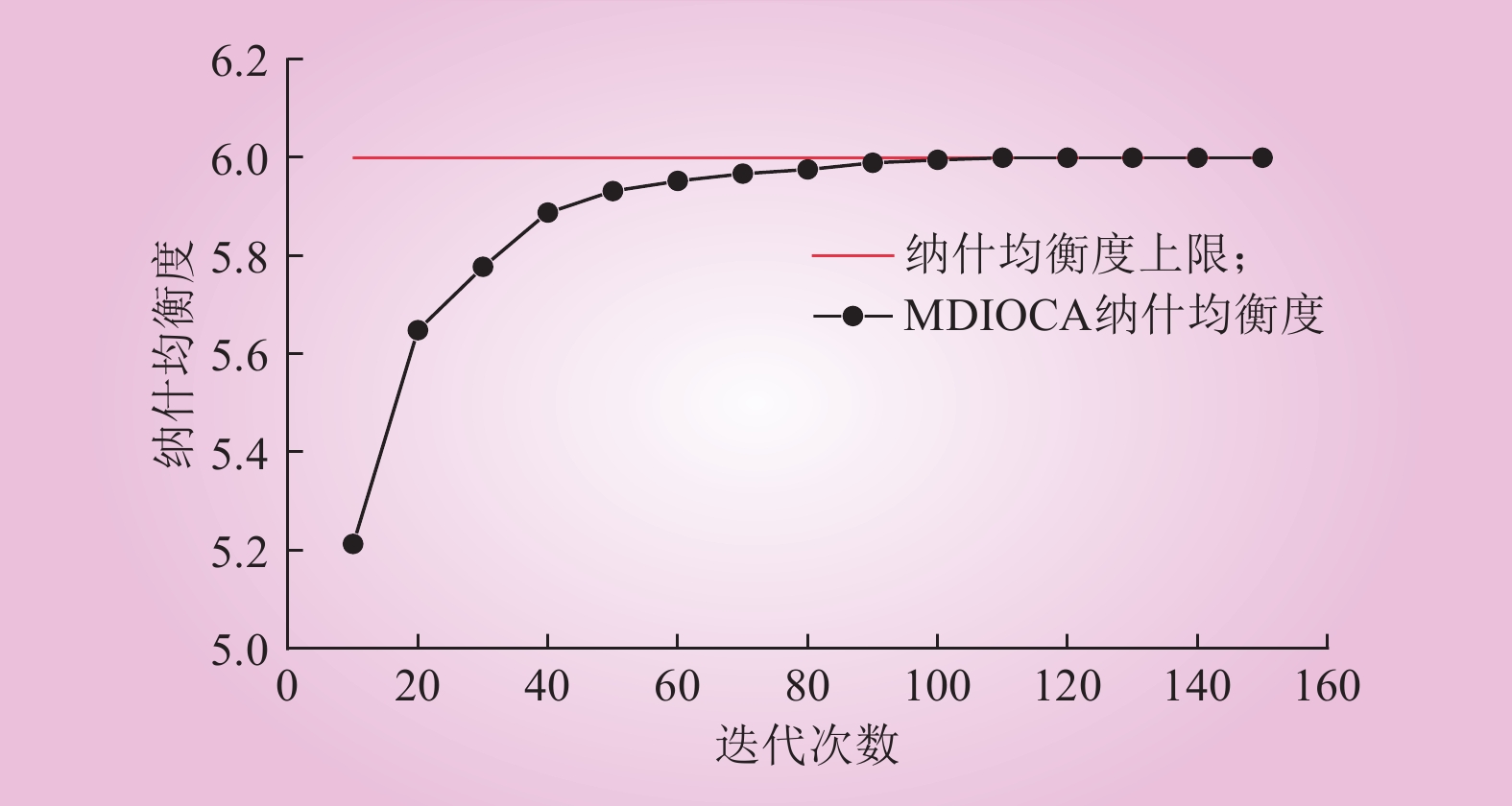
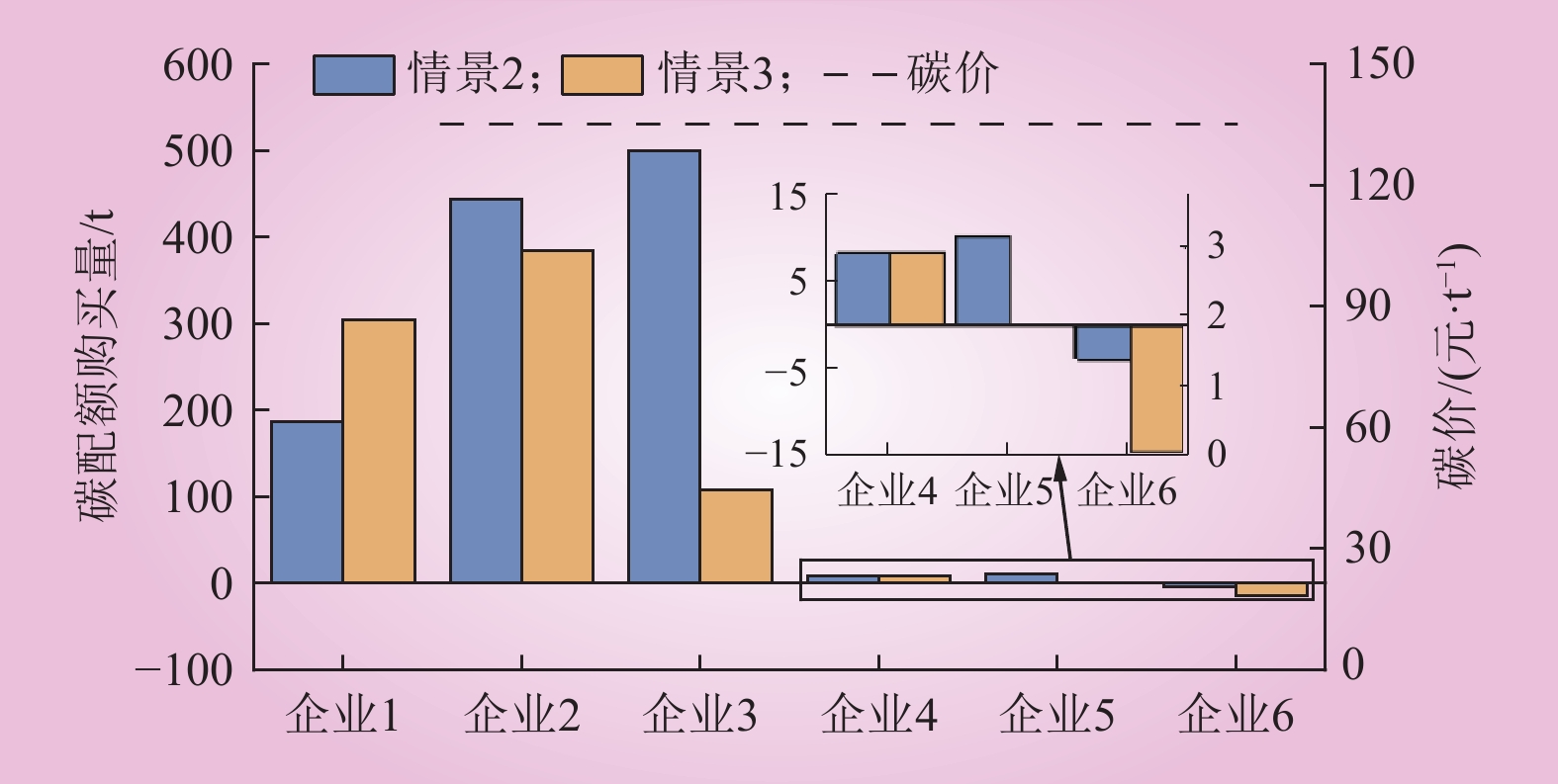
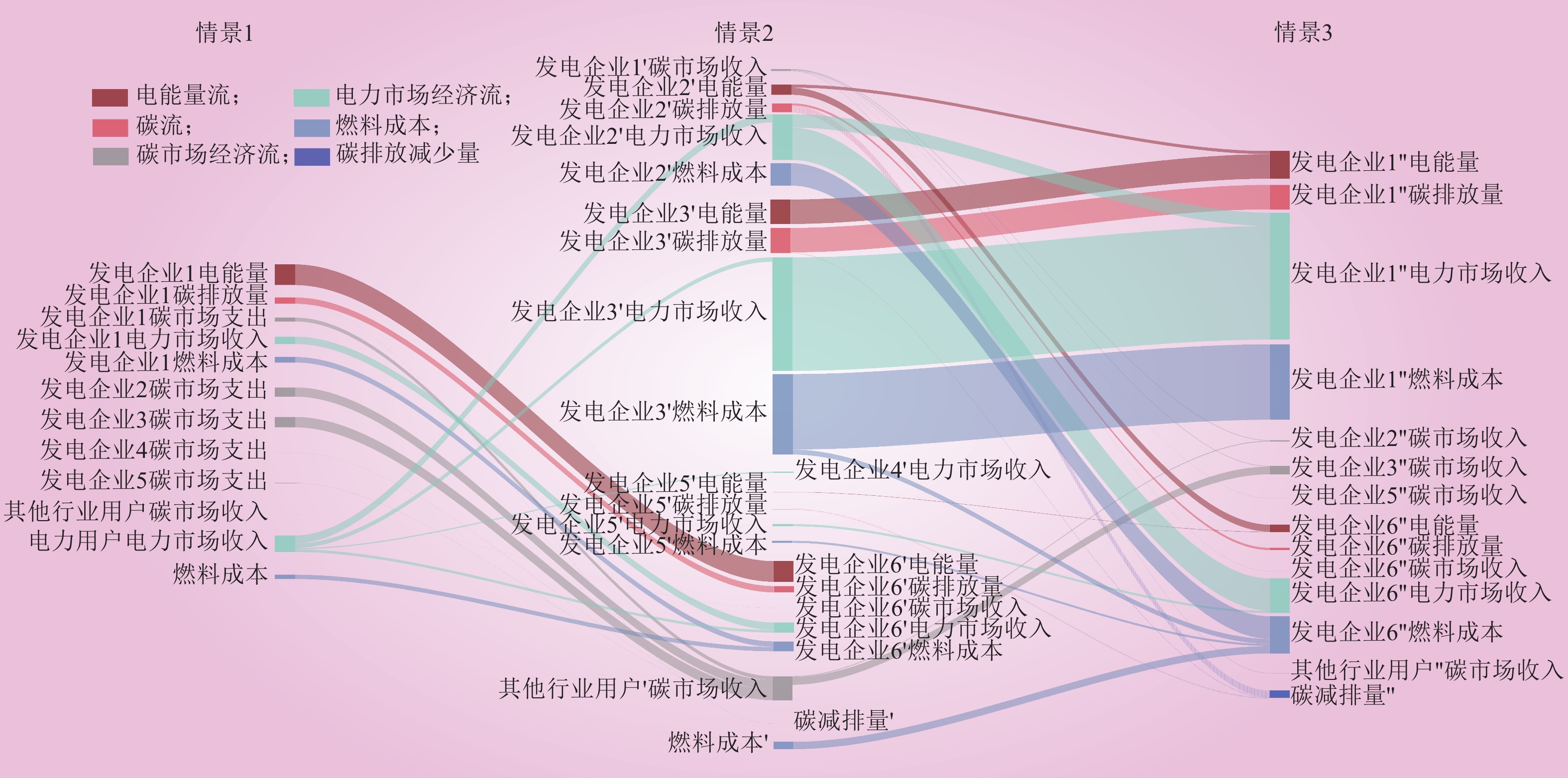
| 1 |
尚楠, 陈政, 卢治霖, 等. 电力市场、碳市场及绿证市场互动机理及协调机制[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (1): 142- 154.
|
|
SHANG Nan, CHEN Zheng, LU Zhilin, et al. Interaction principle and cohesive mechanism between electricity market, carbon market and green power certificate market[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (1): 142- 154.
|
| 2 |
关于做好2023—2025年部分重点行业企业温室气体排放报告与核查工作的通知[EB/OL]. (2023-10-14) [2024-09-10]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk06/202407/t20240702_1080579.html.
|
| 3 |
关于公开征求《全国碳排放权交易市场覆盖水泥、钢铁、电解铝行业工作方案(征求意见稿)》意见的函[EB/OL]. (2024-09-09) [2024-09-10]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk06/202409/t20240909_1085452.html.
|
| 4 |
张兴平, 王腾, 张馨月, 等. 基于多智能体深度确定策略梯度算法的火力发电商竞价策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (11): 161- 172.
|
|
ZHANG Xingping, WANG Teng, ZHANG Xinyue, et al. Bidding strategy for thermal power generation companies based on multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (11): 161- 172.
|
| 5 |
TAN Q L, DING Y H, YE Q, et al. Optimization and evaluation of a dispatch model for an integrated wind-photovoltaic-thermal power system based on dynamic carbon emissions trading[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 253, 113598.
|
| 6 |
GUO X P, ZHANG X Y, ZHANG X P. Incentive-oriented power-carbon emissions trading-tradable green certificate integrated market mechanisms using multi-agent deep reinforcement learning[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 357, 122458.
|
| 7 |
王晛, 王胜彩, 张少华. 电-碳-绿证交易耦合下新能源发电商参与投标竞争的多市场博弈分析[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (10): 4125- 4138.
|
|
WANG Xian, WANG Shengcai, ZHANG Shaohua. Game analysis of coupled electricity-carbon-green certificate markets with strategic bidding of renewable generators[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (10): 4125- 4138.
|
| 8 |
史守圆, 余涛, 黄杰, 等. 考虑现金流和碳清缴周期的发电商电碳现货市场决策优化[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (19): 40- 50.
|
|
SHI Shouyuan, YU Tao, HUANG Jie, et al. Decision optimization of generation companies in electricity and carbon spot markets considering cash flow and carbon compliance period[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (19): 40- 50.
|
| 9 |
刘靓颖, 蒋凯, 刘念, 等. 基于主从博弈的园区多主体能量-碳配额共享机制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (6): 2119- 2131.
|
|
LIU Liangying, JIANG Kai, LIU Nian, et al. Multi-agent energy-carbon sharing mechanism for parks based on Stackelberg game[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (6): 2119- 2131.
|
| 10 |
卢治霖, 刘明波, 尚楠, 等. 考虑碳排放权交易市场影响的日前电力市场两阶段出清模型[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (10): 159- 170.
|
|
LU Zhilin, LIU Mingbo, SHANG Nan, et al. Two-stage clearing model for day-ahead electricity market considering impact of carbon emissions trading market[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (10): 159- 170.
|
| 11 |
赵会茹, 赵一航, 武昭原, 等. 电力市场、碳排放权交易市场以及核证自愿减排市场耦合下发电商竞价策略[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (10): 123- 135.
|
|
ZHAO Huiru, ZHAO Yihang, WU Zhaoyuan, et al. Bidding strategy of power generators under the linkage of electricity market, carbon emission trading market, and certified emission reduction market[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (10): 123- 135.
|
| 12 |
DING Y H, TAN Q L, SHAN Z J, et al. A two-stage dispatching optimization strategy for hybrid renewable energy system with low-carbon and sustainability in ancillary service market[J]. Renewable Energy, 2023, 207, 647- 659.
|
| 13 |
陈巍, 江岳文. 耦合碳-绿证-消纳量市场的日前电量市场交易交互式优化[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (5): 1967- 1979.
|
|
CHEN Wei, JIANG Yuewen. Interactive optimization of day-ahead market trading considering coupling of carbongreen certificate-renewable electricity consumption market[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (5): 1967- 1979.
|
| 14 |
王凯, 延肖何, 蒋凯, 等. 考虑碳交易的风光储场站参与电力现货市场报价策略与调控方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (18): 7091- 7103.
|
|
WANG Kai, YAN Xiaohe, JIANG Kai, et al. Bidding strategy and regulation method for the unified wind/photovoltaic/energy storage power stations in electricity spot market considering carbon trading[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (18): 7091- 7103.
|
| 15 |
吴含欣, 董树锋, 张祥龙, 等. 考虑碳交易机制的含风电电力系统日前优化调度[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (1): 70- 80.
|
|
WU Hanxin, DONG Shufeng, ZHANG Xianglong, et al. Optimal dispatching of power system with wind power considering carbon trading mechanism[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (1): 70- 80.
|
| 16 |
LI J C, SUN Z H, NIU X X, et al. Economic optimization scheduling of virtual power plants considering an incentive based tiered carbon price[J]. Energy, 2024, 305, 132080.
|
| 17 |
孙啸天, 杨争林, 任涵钰, 等. 基于平均场博弈的钢铁生产企业电-碳市场非合作博弈均衡分析[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (8): 3058- 3068.
|
|
SUN Xiaotian, YANG Zhenglin, REN Hanyu, et al. Non-cooperative equilibrium for iron and steel enterprises in electricity and carbon emission permission market based on mean-field game theory[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (8): 3058- 3068.
|
| 18 |
段声志, 陈皓勇, 郑晓东, 等. 碳市场背景下发电商竞价策略及电力市场均衡分析[J]. 电测与仪表, 2022, 59 (5): 33- 41.
|
|
DUAN Shengzhi, CHEN Haoyong, ZHENG Xiaodong, et al. Bidding strategy of electricity generation and electricity market equilibrium analysis under the background of carbon market[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2022, 59 (5): 33- 41.
|
| 19 |
WANG P, GUO Z X, ZHANG S Y, et al. Strategic behaviors of renewable energy generation companies participating in the electricity and carbon coupled markets based on non-cooperative game theory[J]. Energy, 2024, 312, 133522.
|
| 20 |
WU Q L, LI C X. A bi-level optimization framework for the power-side virtual power plant participating in day-ahead wholesale market as a price-maker considering uncertainty[J]. Energy, 2024, 304, 132050.
|
| 21 |
李超英, 檀勤良. 基于智能体建模的新型电力系统下火电企业市场交易策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (2): 212- 225.
|
|
LI Chaoying, TAN Qinliang. Market trading strategy for thermal power enterprise in new power system based on agent modeling[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (2): 212- 225.
|
| 22 |
吴静, 刘轩宇, 李响, 等. 碳市场价格不确定性对电网调度影响机理分析[J/OL]. 上海交通大学学报: 1–18 (2023-10-25) [2024-09-10]. https://doi.org/10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2023.313.
|
|
WU Jing, LIU Xuanyu, LI Xiang, et al. Impact mechanism analysis of carbon price uncertainty on power system dispatch[J/OL]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University: 1–18 (2023-10-25) [2024-09-10]. https://doi.org/10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2023.313.
|
| 23 |
叶晨, 牟玉亭, 王蓓蓓, 等. 考虑动态碳交易曲线的电-碳市场出清模型及节点边际电价构成机理分析[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (2): 613- 624.
|
|
YE Chen, MOU Yuting, WANG Beibei, et al. Mechanism of locational marginal prices and clearing model of electricity and carbon market considering dynamic carbon trading curve[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (2): 613- 624.
|
| 24 |
马学礼, 王笑飞, 孙希进, 等. 燃煤发电机组碳排放强度影响因素研究[J]. 热力发电, 2022, 51 (1): 190- 195.
|
|
MA Xueli, WANG Xiaofei, SUN Xijin, et al. Influence factors of carbon emission intensity of coal-fired power units[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2022, 51 (1): 190- 195.
|
| 25 |
陈婷, 司风琪, 顾慧, 等. 一种基于改进KFCM算法的火电厂煤耗特性模型的建立方法[J]. 热能动力工程, 2017, 32 (3): 69- 74, 135–136.
|
|
CHEN Ting, SI Fengqi, GU Hui, et al. A coal consumption modeling method for power plant based on improved KFCM algorithm[J]. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2017, 32 (3): 69- 74, 135–136.
|
| 26 |
颜正, 肖仁杰, 黄鹏, 等. 基于烟气监测数据的标准煤耗率计量方法[J]. 能源科技, 2023, 21 (4): 51- 55.
|
|
YAN Zheng, XIAO Renjie, HUANG Peng, et al. Method for measuring standard coal consumption rate based on monitoring data of flue gas[J]. Energy Science and Technology, 2023, 21 (4): 51- 55.
|
| 27 |
MANDI R P, YARAGATTI U R. Control of CO2 emission through enhancing energy efficiency of auxiliary power equipment in thermal power plant[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2014, 62, 744- 752.
|
| 28 |
MANDI R P, YARAGATTI U R. Energy efficiency improvement of auxiliary power equipment in thermal power plant through operational optimization[C]//2012 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems (PEDES). Bengaluru, India. IEEE, 2012: 1–8.
|
| 29 |
苏阳, 丛星亮, 马大卫, 等. 燃煤发电机组碳排放计算与碳减排技术分析[J]. 锅炉技术, 2024, 55 (2): 74- 79.
|
|
SU Yang, CONG Xingliang, MA Dawei, et al. Carbon emission calculation and analysis of carbon emission reduction technology of coal-fired generator set[J]. Boiler Technology, 2024, 55 (2): 74- 79.
|
| 30 |
关于公开征求《2023、2024年度全国碳排放权交易发电行业配额总量和分配方案(征求意见稿)》意见的通知[EB/OL]. (2024-06-29) [2024-09-09]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk06/202407/t20240702_1080579.html.
|
| 31 |
JIANG K, YAN X H, LIU N, et al. Energy trade-offs in coupled ICM and electricity market under dynamic carbon emission intensity[J]. Energy, 2022, 260, 125077.
|
| 32 |
JIANG K, LIU N, YAN X H, et al. Modeling strategic behaviors for GenCo with joint consideration on electricity and carbon markets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2022, 38 (5): 4724- 4738.
|
| 33 |
丁毅宏. 市场环境下多能源联合发电运营优化模型研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2022.
|
|
DING Yihong. Operation optimization model of multi-energy joint power generation in market environment[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2022.
|
| 34 |
张晶晶, 陈俊, 曹辉, 等. 计及风光资源不确定性的独立型微电网容量优化配置[J]. 电力与能源, 2024, 45 (3): 347- 354.
|
|
ZHANG Jingjing, CHEN Jun, CAO Hui, et al. Capacity optimization configuration of stand-alone microgrid considering uncertainty of wind and solar resources[J]. Power & Energy, 2024, 45 (3): 347- 354.
|
| 35 |
卫子杰, 荆朝霞, 季天瑶. 基于多时间尺度耦合建模的电力市场与碳市场联动均衡机制研究[J/OL]. 电网技术: 1–10[2024-09-14]. https://doi.org/10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2024.1150.
|
|
WEI Zijie, JING Zhaoxia, JI Tianyao. Research on the linkage equilibrium mechanism between power market and carbon market based on multi-timescale coupling modeling [J/OL]. Power System Technology: 1–10[2024-09-14]. https://doi.org/10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2024.1150.
|
| 36 |
李祥光, 谭青博, 李帆琪, 等. 电碳耦合对煤电机组现货市场结算电价影响分析模型[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (5): 113- 125.
|
|
LI Xiangguang, TAN Qingbo, LI Fanqi, et al. Analysis model to study the influence of electrocarbon coupling on settlement price of coal power units in spot market[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (5): 113- 125.
|
| 37 |
潘荔, 陈忠, 石丽娜, 等. 燃煤机组负荷变化对碳交易的影响初探[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2022, 38 (6): 492- 499.
|
|
PAN Li, CHEN Zhong, SHI Lina, et al. Study on the impact of coal-fired power load change on carbon trading[J]. Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection, 2022, 38 (6): 492- 499.
|
| 38 |
温亚东. 新型电力系统背景下蒙西电力市场分布式能源交易机制分析[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2023, 41 (3): 78- 85.
|
|
WEN Yadong. Analysis on distributed energy trading mechanism in West Inner Mongolia power market under background of new power system[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2023, 41 (3): 78- 85.
|
| 39 |
朱辉, 闫腾飞, 丁一, 等. 基于改进的AHP-CRITIC综合权重计算法的多元用户用能行为特性刻画及评价方法[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (5): 70- 77.
|
|
ZHU Hui, YAN Tengfei, DING Yi, et al. Characterization andevaluation method for multi-user energy consumption behavior based on the improved AHP-CRITIC composite weighting approach[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (5): 70- 77.
|
| 40 |
陈图南, 李文萱, 李云, 等. “双碳” 背景下碳-绿证-电力市场耦合机制综述[J]. 广东电力, 2024, 37 (8): 14- 25.
|
|
CHEN Tunan, LI Wenxuan, LI Yun, et al. Review on coupling mechanism of carbon, green certificate and power market under the background of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2024, 37 (8): 14- 25.
|
| 41 |
马会领, 曲尧, 王星凯. 基于混合人工神经网络的电力市场短期电价研究与分析[J]. 自动化与仪器仪表, 2023, (8): 250- 256.
|
|
MA Huiling, QU Yao, WANG Xingkai. Research and analysis of short-term electricity price in power market based on hybrid artificial neural network[J]. Automation & Instrumentation, 2023, (8): 250- 256.
|
| 42 |
王鹏, 贺焕然, 伏凌霄, 等. 多品种电力市场交易下负荷聚合商投标策略及市场均衡分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (4): 111- 122.
|
|
WANG Peng, HE Huanran, FU Lingxiao, et al. Bidding strategy of load aggregators and market equilibrium analysis for multi-variety electricity market trading[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (4): 111- 122.
|
| 43 |
邓盛盛, 陈皓勇, 肖东亮, 等. 考虑碳市场交易的寡头电力市场均衡分析[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (1): 143- 152.
|
|
DENG Shengsheng, CHEN Haoyong, XIAO Dongliang, et al. Equilibrium analysis of oligopoly electricity market considering carbon market trading[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (1): 143- 152.
|
| 44 |
GUO Y, BASHASH S. Analyzing the impacts of plug-in EVs on the California power grid using quadratic programming and fixed-point iteration[C]//2017 American Control Conference (ACC). Seattle, WA, USA. IEEE, 2017: 2060–2065.
|