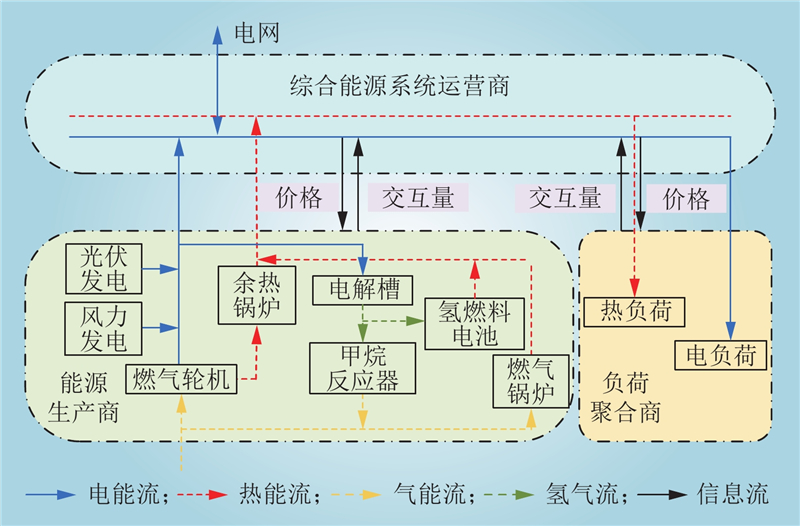
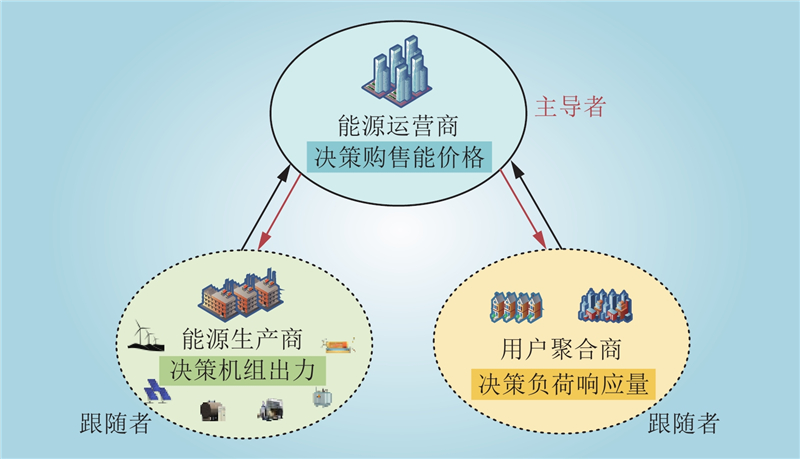
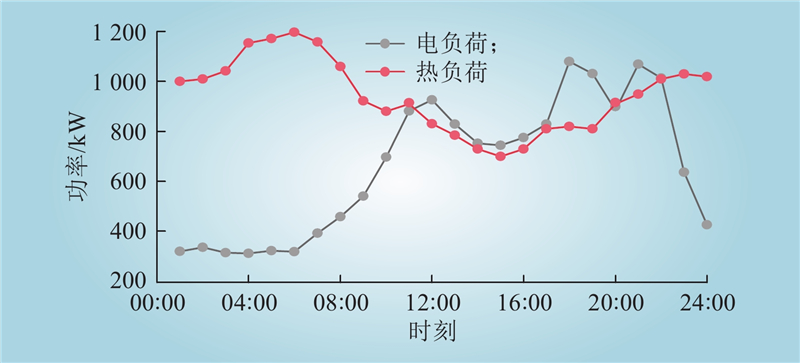
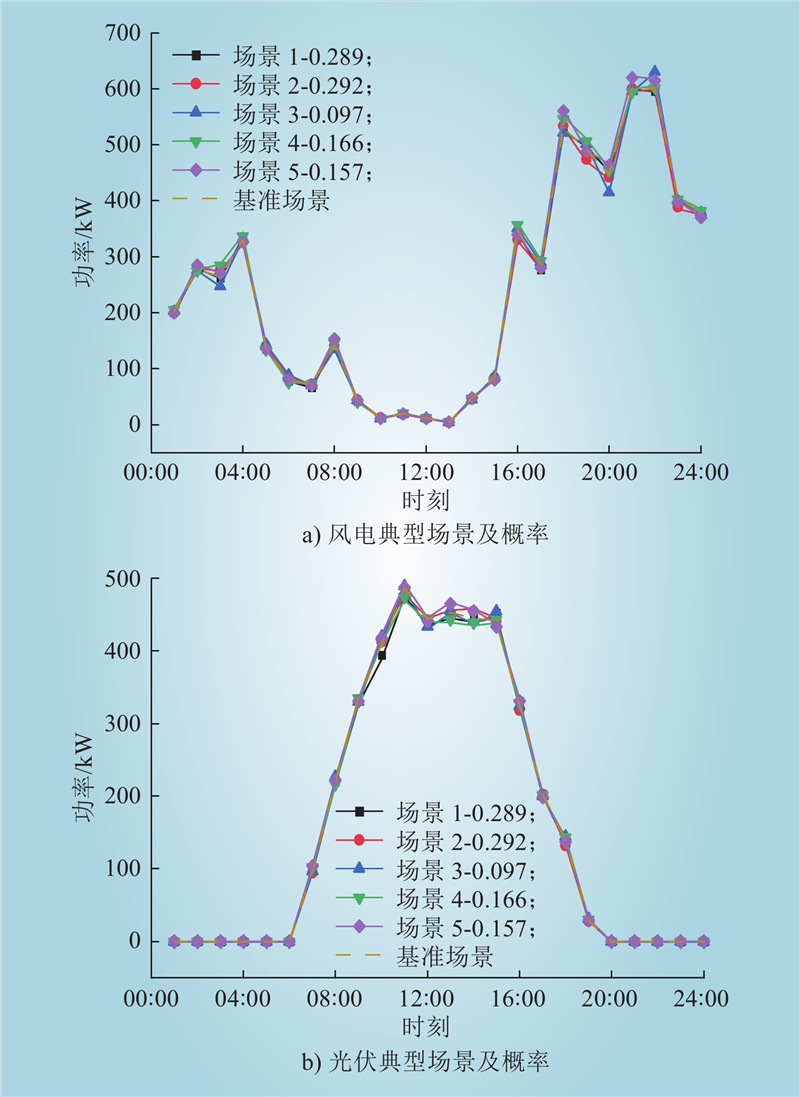
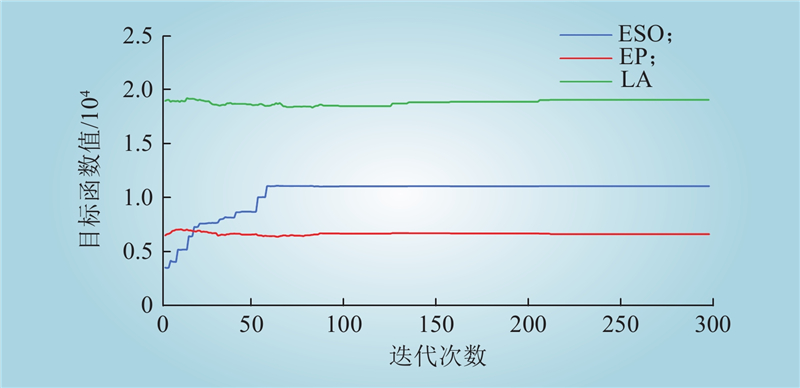
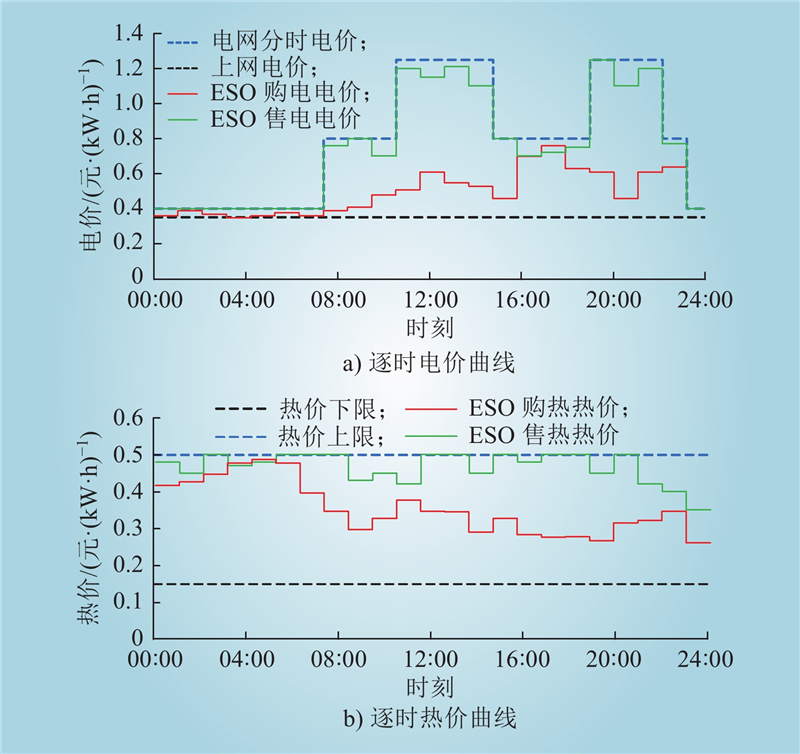
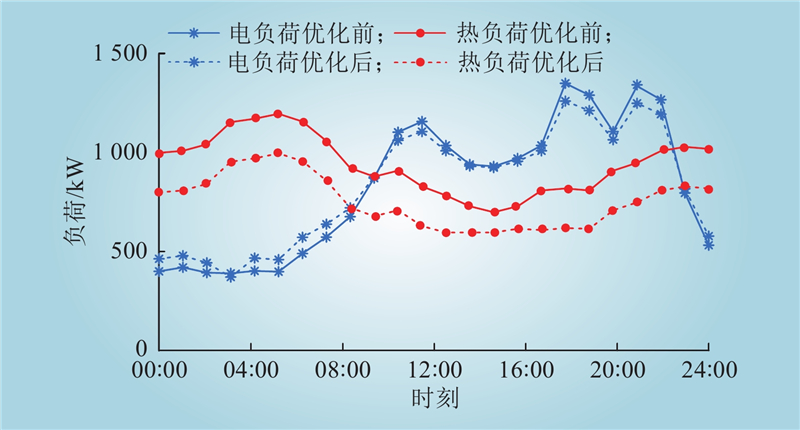
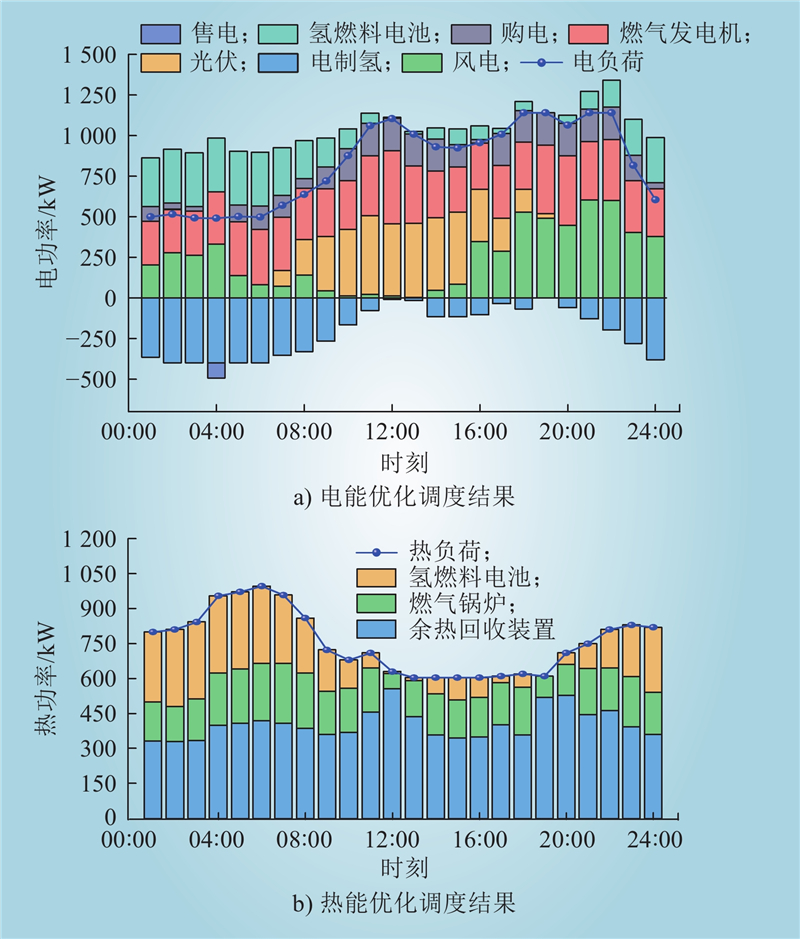
| 1 |
吉兴全, 刘健, 张玉敏, 等. 计及运行灵活性约束的综合能源系统优化调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (16): 84- 94.
|
|
JI Xingquan, LIU Jian, ZHANG Yumin, et al. Optimal dispatching of integrated energy system considering operation flexibility constraints[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (16): 84- 94.
|
| 2 |
田福银, 马骏, 王灿, 等. 基于双层主从博弈的综合能源系统多主体低碳经济运行策略[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (11): 184- 193.
|
|
TIAN Fuyin, MA Jun, WANG Can, et al. Multi-agent low-carbon and economy operation strategy of integrated energy system based on Bi-level master-slave game[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (11): 184- 193.
|
| 3 |
张玉敏, 孙鹏凯, 吉兴全, 等. 基于并行多维近似动态规划的综合能源系统动态经济调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (4): 60- 68.
|
|
ZHANG Yumin, SUN Pengkai, JI Xingquan, et al. Dynamic economic dispatch for integrated energy system based on parallel multi-dimensional approximate dynamic programming[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (4): 60- 68.
|
| 4 |
YU Y X, HAN X S, YANG M, et al. Probabilistic prediction of regional wind power based on spatiotemporal quantile regression[C]//2019 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting. Baltimore, MD, USA. IEEE, 2019: 1–16.
|
| 5 |
董帅, 王成福, 徐士杰, 等. 计及网络动态特性的电—气—热综合能源系统日前优化调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (13): 12- 19.
|
|
DONG Shuai, WANG Chengfu, XU Shijie, et al. Day-ahead optimal scheduling of electricity-gas-heat integrated energy system considering dynamic characteristics of networks[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42 (13): 12- 19.
|
| 6 |
LI Y, WANG C L, LI G Q, et al. Improving operational flexibility of integrated energy system with uncertain renewable generations considering thermal inertia of buildings[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 207, 112526.
|
| 7 |
鲁鹏, 冯春贤, 武伟鸣, 等. 园区能源供需价量双层Stackelberg博弈模型[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (6): 74- 79.
|
|
LU Peng, FENG Chunxian, WU Weiming, et al. Two-layer stackelberg game model for energy supply and demand in the park[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (6): 74- 79.
|
| 8 |
LI J R, LIN J, SONG Y H, et al. Operation optimization of power to hydrogen and heat (P2HH) in ADN coordinated with the district heating network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2019, 10 (4): 1672- 1683.
|
| 9 |
DONG Z Y, YANG J J, YU L, et al. A green hydrogen credit framework for international green hydrogen trading towards a carbon neutral future[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47 (2): 728- 734.
|
| 10 |
GORRE J, RUOSS F, KARJUNEN H, et al. Cost benefits of optimizing hydrogen storage and methanation capacities for Power-to-Gas plants in dynamic operation[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 257, 113967.
|
| 11 |
初壮, 赵蕾, 孙健浩, 等. 考虑热能动态平衡的含氢储能的综合能源系统热电优化[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (3): 1- 12.
|
|
CHU Zhuang, ZHAO Lei, SUN Jianhao, et al. Thermoelectric optimization of an integrated energy system with hydrogen energy storage considering thermal energy dynamic balance[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (3): 1- 12.
|
| 12 |
WANG X J, LI B K, WANG Y W, et al. A bargaining game-based profit allocation method for the wind-hydrogen-storage combined system[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 310, 118472.
|
| 13 |
LI G Q, ZHANG R F, JIANG T, et al. Security-constrained bi-level economic dispatch model for integrated natural gas and electricity systems considering wind power and power-to-gas process[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 194, 696- 704.
|
| 14 |
KOTZUR L, MARKEWITZ P, ROBINIUS M, et al. Time series aggregation for energy system design: modeling seasonal storage[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 213, 123- 135.
|
| 15 |
YANG J J, LIU H Y, WANG Y X, et al. Key index framework for quantitative sustainability assessment of energy infrastructures in a smart city: an example of Western Sydney[J]. Energy Conversion and Economics, 2020, 1 (3): 221- 237.
|
| 16 |
李睿智, 刘念, 延肖何. 基于势博弈的综合能源系统用户能量管理优化方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2021, 36 (1): 21- 31.
|
|
LI Ruizhi, LIU Nian, YAN Xiaohe. An optimization method for user energy management of integrated energy system based on potential game[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2021, 36 (1): 21- 31.
|
| 17 |
李振坤, 刘乾, 郭维一, 等. 计及用户用能行为的综合能源微网运营商与负荷聚合商主从博弈策略[J]. 南方电网技术, 2022, 16 (8): 35- 46.
|
|
LI Zhenkun, LIU Qian, GUO Weiyi, et al. Stackelberg game strategy between integrated energy microgrid operators and load aggregators considering users energy consumption behavior[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2022, 16 (8): 35- 46.
|
| 18 |
MAHARJAN S, ZHU Q Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Dependable demand response management in the smart grid: a stackelberg game approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2013, 4 (1): 120- 132.
|
| 19 |
李鹏, 吴迪凡, 李雨薇, 等. 基于综合需求响应和主从博弈的多微网综合能源系统优化调度策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (4): 1307- 1321, 1538.
|
|
LI Peng, WU Difan, LI Yuwei, et al. Optimal dispatch of multi-microgrids integrated energy system based on integrated demand response and stackelberg game[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (4): 1307- 1321, 1538.
|
| 20 |
LIU N, HE L, YU X H, et al. Multiparty energy management for grid-connected microgrids with heat- and electricity-coupled demand response[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14 (5): 1887- 1897.
|
| 21 |
李雪, 季寒松, 张儒峰, 等. 计及多类型微网响应特性的城市配电系统分布式优化调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (17): 74- 82.
|
|
LI Xue, JI Hansong, ZHANG Rufeng, et al. Distributed optimal scheduling of urban distribution system considering response characteristics of multi-type microgrids[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (17): 74- 82.
|
| 22 |
王鹏飞, 李世民, 张磊, 等. 基于合作博弈的风-光-综合能源系统多主体协同运行策略[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (9): 52- 59.
|
|
WANG Pengfei, LI Shimin, ZHANG Lei, et al. Multi-agent cooperative operation strategy of wind-photovoltaic-integrated energy system based on cooperative game[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (9): 52- 59.
|
| 23 |
LI Z, XU Y, WANG P, et al. Restoration of a multi-energy distribution system with joint district network reconfiguration via distributed stochastic programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2024, 15 (3): 2667- 2680.
|
| 24 |
张笑演, 王橹裕, 黄蕾, 等. 考虑扩展碳排放流和碳交易议价模型的园区综合能源优化调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (9): 34- 46.
|
|
ZHANG Xiaoyan, WANG Luyu, HUANG Lei, et al. Optimal dispatching of park-level integrated energy system considering augmented carbon emission flow and carbon trading bargain model[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (9): 34- 46.
|
| 25 |
付文杰, 王喻玺, 申洪涛, 等. 基于拉丁超立方抽样和场景消减的居民用户基线负荷估计方法[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (6): 2298- 2307.
|
|
FU Wenjie, WANG Yuxi, SHEN Hongtao, et al. Residential customer baseline load estimation based on Latin hypercube sampling and scenario subtraction[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (6): 2298- 2307.
|
| 26 |
陈锦鹏, 胡志坚, 陈颖光, 等. 考虑阶梯式碳交易机制与电制氢的综合能源系统热电优化[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (9): 48- 55.
|
|
CHEN Jinpeng, HU Zhijian, CHEN Yingguang, et al. Thermoelectric optimization of integrated energy system considering ladder-type carbon trading mechanism and electric hydrogen production[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (9): 48- 55.
|
| 27 |
郝然, 艾芊, 姜子卿. 区域综合能源系统多主体非完全信息下的双层博弈策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (4): 194- 201.
|
|
HAO Ran, AI Qian, JIANG Ziqing. Bi-level game strategy for multi-agent with incomplete information in regional integrated energy system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42 (4): 194- 201.
|
| 28 |
WEI F, JING Z X, WU P Z, et al. A Stackelberg game approach for multiple energies trading in integrated energy systems[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 200, 315- 329.
|
| 29 |
唐文虎, 张银, 钱瞳. 考虑配电网络重构和楼宇群主动需求响应的集成楼宇群配电网优化控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (8): 2966- 2979.
|
|
TANG Wenhu, ZHANG Yin, QIAN Tong. Optimal control of buildings-to-distribution-network integration system considering reconfiguration of distribution network and active demand response of buildings[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (8): 2966- 2979.
|