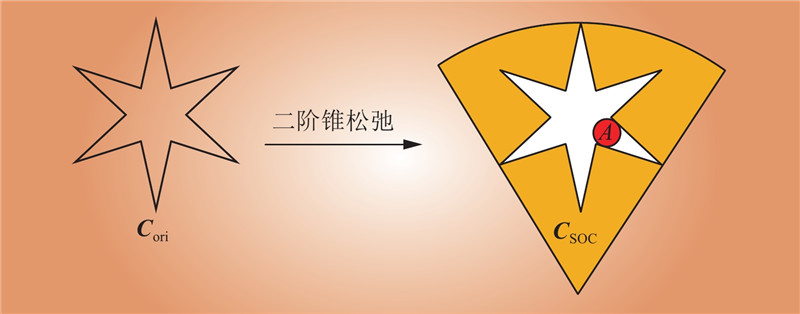
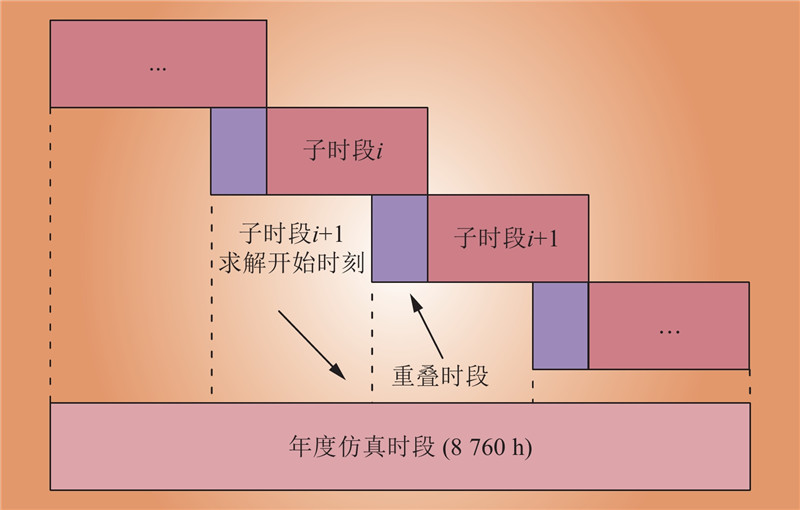
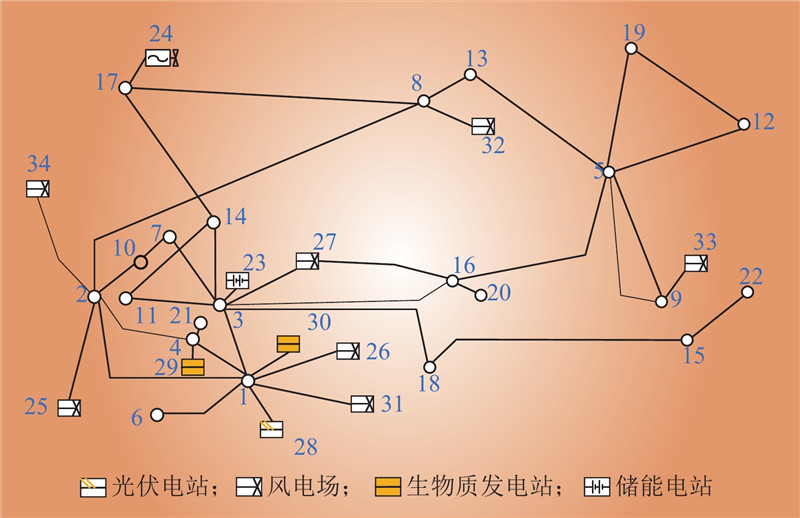
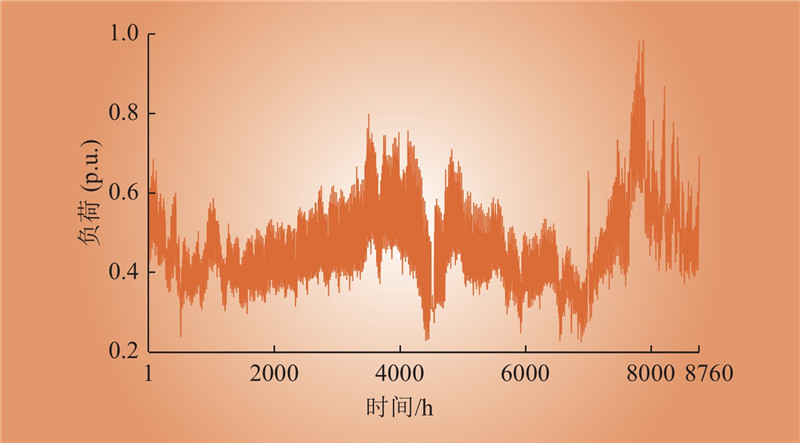
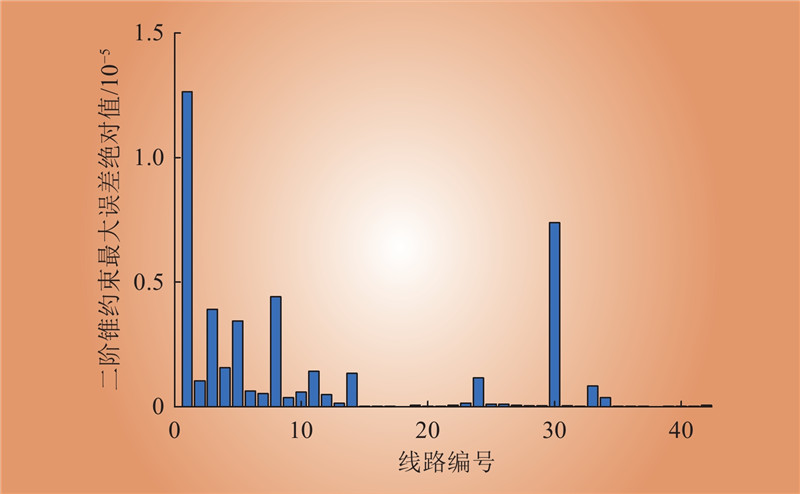
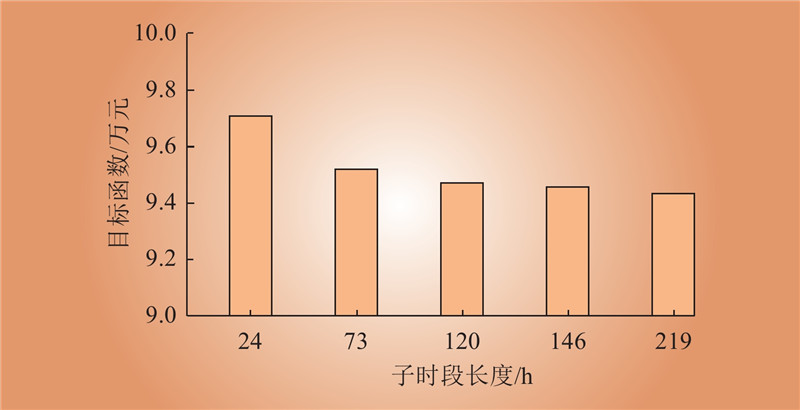
| 1 |
国家能源局, 农业农村部, 国家乡村振兴局. 关于印发《加快农村能源转型发展助力乡村振兴的实施意见》的通知[EB/OL]. (2021-12-29)[2025-03-01]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2022-01/07/content_5666809.htm.
|
| 2 |
国家统计局. 中华人民共和国2023年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[EB/OL]. (2024-02-29)[2025-03-01]. https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202402/ t20240228_1947915.html.
|
| 3 |
臧延雪, 边晓燕, 梁思琪, 等. 计及线路传输能力的新能源电力系统灵活性评估及优化调度方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (11): 15- 26.
|
|
ZANG Yanxue, BIAN Xiaoyan, LIANG Siqi, et al. Flexibility evaluation and optimal dispatching method of a renewable energy power systemconsidering line transmission capacity[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (11): 15- 26.
|
| 4 |
全国新能源消纳监测预警中心. 2024 年全国新能源并网消纳情况[EB/OL]. (2025-02-06)[2025-03-01]. https://guangfu.bjx.com.cn/news/20250206/1425634.shtml.
|
| 5 |
全国新能源消纳检测预警中心. 2021 年全国新能源并网消纳情况[EB/OL]. (2022-02-14)[2025-03-01]. https://news.bjx.com.cn/html/20220214/1204026.shtml.
|
| 6 |
National Grid ESO. Technical report on the event of 9 august 2019[R/OL]. (2019-09-06)[2025-03-01]. https://www.ofgem.gov.uk/sites/default/files/docs/2019/09/eso_technical_report_-_final.pdf.
|
| 7 |
王国春, 董昱, 许涛, 等. 巴西“8.15”大停电事故分析及启示[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (24): 9461- 9470.
|
|
WANG Guochun, DONG Yu, XU Tao, et al. Analysis and lessons of Brazil blackout event on August 15, 2023[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (24): 9461- 9470.
|
| 8 |
陶星宇, 杨健维, 牛牧童, 等. 计及电动汽车充电负荷的电力系统中长期生产模拟方法研究[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38 (1): 18- 26.
|
|
TAO Xingyu, YANG Jianwei, NIU Mutong, et al. A mid/long-term power system production simulation approachconsidering charging load of electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38 (1): 18- 26.
|
| 9 |
舒印彪, 张智刚, 郭剑波, 等. 新能源消纳关键因素分析及解决措施研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37 (1): 1- 9.
|
|
SHU Yinbiao, ZHANG Zhigang, GUO Jianbo, et al. Study on key factors and solution of renewable energy accommodation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37 (1): 1- 9.
|
| 10 |
王帅, 黄越辉, 聂元弘, 等. 基于生产模拟的受端电网新能源发展场景研究[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (5): 240- 250.
|
|
WANG Shuai, HUANG Yuehui, NIE Yuanhong, et al. Research on development scenario of renewable energy in receiving-end power grid based on production simulation[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (5): 240- 250.
|
| 11 |
顾颖中, 李慧杰, 史保壮. 生产模拟仿真在电力市场环境下的应用案例及建议[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41 (24): 77- 82.
|
|
GU Yingzhong, LI Huijie, SHI Baozhuang. Application and suggestions of power system production simulation in deregulated electricity market[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41 (24): 77- 82.
|
| 12 |
魏利屾, 艾小猛, 方家琨, 等. 面向新型电力系统的时序生产模拟应用与求解技术综述[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (6): 170- 184.
|
|
WEI Lishen, AI Xiaomeng, FANG Jiakun, et al. Review on applications and solving techniques of time-series production simulation for new power system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (6): 170- 184.
|
| 13 |
王硕, 霍慧娟, 徐丹, 等. 计及特高压交流工程建设的区域碳减排测算及分摊[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (7): 163- 172.
|
|
WANG Shuo, HUO Huijuan, XU Dan, et al. Calculation and sharing of regional carbon emission reduction considering construction of ultra high voltage AC projects[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (7): 163- 172.
|
| 14 |
吴冠男, 张明理, 徐建源, 等. 适用于评估风电接纳能力的时序生产模拟算法研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2017, 45 (23): 151- 157.
|
|
WU Guannan, ZHANG Mingli, XU Jianyuan, et al. Time series production algorithm for evaluating wind power accommodation capacity[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2017, 45 (23): 151- 157.
|
| 15 |
卫志农, 张清松, 赵静波, 等. 电力系统线性化模型研究综述与改进[J]. 电网技术, 2017, 41 (9): 2919- 2927.
|
|
WEI Zhinong, ZHANG Qingsong, ZHAO Jingbo, et al. Review and improvement of power system linearization models[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41 (9): 2919- 2927.
|
| 16 |
曹阳, 李鹏, 袁越, 等. 基于时序仿真的新能源消纳能力分析及其低碳效益评估[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2014, 38 (17): 60- 66.
|
|
CAO Yang, LI Peng, YUAN Yue, et al. Analysis on accommodating capability of renewable energy and assessment on low-carbon benefits based on time sequence simulation[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2014, 38 (17): 60- 66.
|
| 17 |
肖峻, 周玉鹏, 鲍震宇. 配电系统优化问题建模中的潮流模型选择方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (15): 170- 178.
|
|
XIAO Jun, ZHOU Yupeng, BAO Zhenyu. Power flow model selection method for modeling distribution system optimization problem[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (15): 170- 178.
|
| 18 |
廖诗武. 风电接入区域电力系统的潜力及环境效益评估方法[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017.
|
|
LIAO Shiwu. Evaluating the potential and environmental benefits for wind energy integration in regional power systems[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017.
|
| 19 |
刘志伟, 马悦, 沙志成, 等. 考虑新能源多重相关性的柔性配电网分布鲁棒优化策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (12): 97- 108.
|
|
LIU Zhiwei, MA Yue, SHA Zhicheng, et al. Distributionally robust operation for flexible distribution networks considering multi-correlation of renewable power generation[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (12): 97- 108.
|
| 20 |
朱俊澎, 施凯杰, 李强, 等. 考虑输电网潮流约束的时序生产模拟及新能源消纳能力评估[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (5): 1947- 1955.
|
|
ZHU Junpeng, SHI Kaijie, LI Qiang, et al. Time series production simulation and renewable energy accommodation capacity evaluation considering transmission network power flow constraints[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (5): 1947- 1955.
|
| 21 |
刘斌, 刘锋, 梅生伟, 等. 基于二阶锥优化的含有载调压变压器主动配电网最优潮流[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (19): 40- 47.
|
|
LIU Bin, LIU Feng, MEI Shengwei, et al. Optimal power flow in active distribution networks with on-load tap changer based on second-order cone programming[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (19): 40- 47.
|
| 22 |
CHEN J R, CHEN H Y, LIANG Z P, et al. An exergy analysis model for the optimal operation of integrated heat-and-electricity-based energy systems[J]. Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 2024, 9 (1): 1- 18.
|
| 23 |
路畅, 郭力, 柴园园, 等. 含高渗透分布式光伏的增量配电网日前优化调度方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47 (18): 90- 98.
|
|
LU Chang, GUO Li, CHAI Yuanyuan, et al. Day-ahead optimal scheduling method for incremental distribution network with highpenetration of distributed photovoltaic[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47 (18): 90- 98.
|
| 24 |
毛荀, 董王朝, 吕凯, 等. 计及新能源出力不确定性的电力系统恢复模型及快速求解方法[J/OL]. 南方电网技术, 1–12. (2024-08-01). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1643.tk.20240731.1707.005.html.
|
|
MAO Xun, DONG Wangchao, LÜ Kai, et al. Power system restoration modeling and fast solution method considering the uncertainty of new energy output[J/OL]. Southern Power System Technology, 1–12. (2024-08-01). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1643.tk.20240731.1707.005.html.
|
| 25 |
WEI L S, AI X M, FANG J K, et al. Chronological operation simulation for power system with peak regulation ancillary service market in China: formulation, solving, and validation[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2023, 152, 109156.
|
| 26 |
LIAO S W, YAO W, HAN X N, et al. Chronological operation simulation framework for regional power system under high penetration of renewable energy using meteorological data[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 203, 816- 828.
|
| 27 |
刘一兵, 吴文传, 张伯明, 等. 基于混合整数二阶锥规划的主动配电网有功–无功协调多时段优化运行[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34 (16): 2575- 2583.
|
|
LIU Yibing, WU Wenchuan, ZHANG Boming, et al. A mixed integer second-order cone programming based active and reactive power coordinated multi-period optimization for active distribution network[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34 (16): 2575- 2583.
|
| 28 |
付宇, 白浩, 李跃, 等. 面向高比例光伏消纳的低压交直流混合配电网时-空协调优化方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (1): 84- 93.
|
|
FU Yu, BAI Hao, LI Yue, et al. Spatial-temporal coordinated optimization method of low voltage hybrid AC/DC distribution network for accommodation of high-proportion PVs[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (1): 84- 93.
|
| 29 |
FARIVAR M, LOW S H. Branch flow model: relaxations and convexification: part I[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28 (3): 2554- 2564.
|
| 30 |
段建民, 王志新, 王承民, 等. 考虑碳减排效益的可再生电源规划[J]. 电网技术, 2015, 39 (1): 11- 15.
|
|
DUAN Jianmin, WANG Zhixin, WANG Chengmin, et al. Renewable power planning considering carbon emission reduction benefits[J]. Power System Technology, 2015, 39 (1): 11- 15.
|
| 31 |
高纬迪. 基于生命周期的生物质厌氧消化-气化耦合发电系统综合评价[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2021.
|
|
GAO Weidi. Comprehensive evaluation of anaerobic digestion gasification coupled power generation system based on life cycle assessment method[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2021.
|
| 32 |
高俊彦. 生物质直燃与沼气耦合电热气肥多联产系统优化方法研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2023.
|
|
GAO Junyan. Research on optimization method of electricity heat gas and fertilizer multi-generation system coupling biomass direct combustion and biogas fermentation[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2023.
|