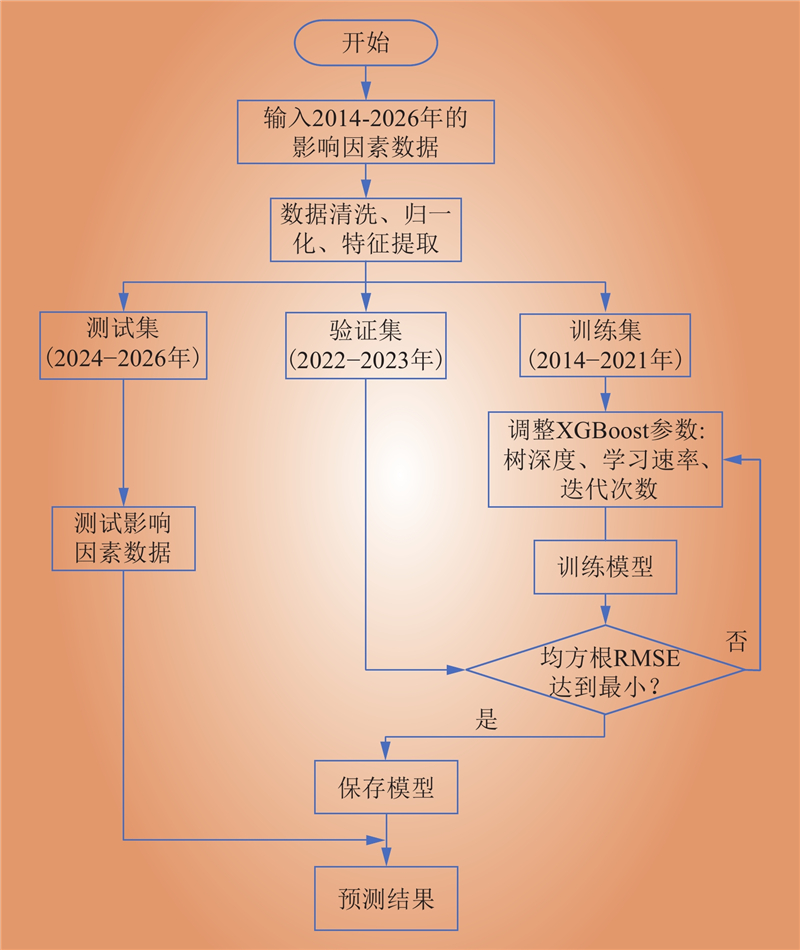
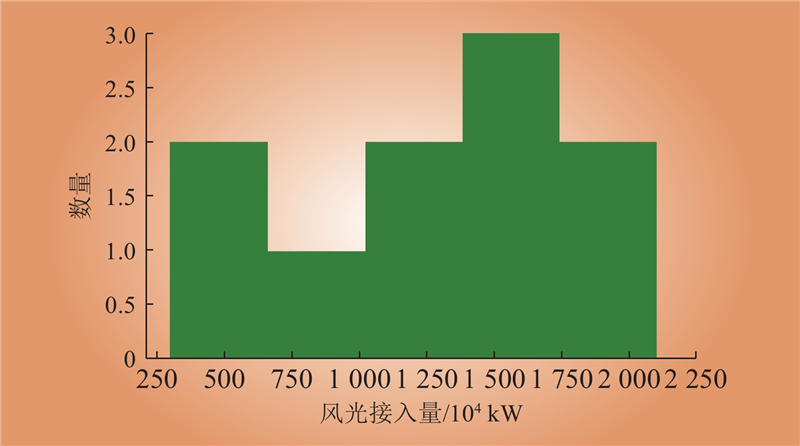
| 1 |
翟苏巍, 李银银, 杜凡, 等. 考虑海量分布式能源接入的配电网分布式无功控制策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (8): 138- 144.
|
|
ZHAI Suwei, LI Yinyin, DU Fan, et al. Distributed reactive power control strategy of distribution network considering massive distributed energy access[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (8): 138- 144.
|
| 2 |
刘哲, 唐成鹏, 周青, 等. 新型电力系统建设环境下的“西电东送” 发展研究[J]. 广东电力, 2023, 36 (9): 26.
|
|
LIU Zhe, TANG Chengpeng, ZHOU Qing, et al. Research on development of west-to-east power transmission under the environment of new power system construction[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2023, 36 (9): 26.
|
| 3 |
徐涛, 李互刚, 杨龙雨, 等. 注意力机制和多目标粒子群混合驱动的配电网无功优化[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2024, 40 (7): 146- 154.
|
|
XU Tao, LI Hugang, YANG Longyu, et al. Hybrid-driven reactive power optimization for distribution networks driven by attentional mechanisms and multi-objective particle swarms[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2024, 40 (7): 146- 154.
|
| 4 |
张礼浩, 刘翔宇, 顾雪平, 等. 新型电力系统频率安全稳定研究综述及展望[J]. 浙江电力, 2024, 43 (10): 12- 26.
|
|
ZHANG Lihao, LIU Xiangyu, GU Xueping, et al. Review and prospects of frequency security and stability research in new-type power systems[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2024, 43 (10): 12- 26.
|
| 5 |
张艳丽, 王争冕, 薛成, 等. 考虑新能源接入的配电网两阶段有功无功协调降损方法[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2023, 39 (12): 121- 129.
|
|
ZHANG Yanli, WANG Zhengmian, XUE Cheng, et al. A two-stage active and reactive power coordinated loss reduction method for distribution networks integrated with new energy[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2023, 39 (12): 121- 129.
|
| 6 |
马骏超, 陆承宇, 王晨旭, 等. 新型电力系统惯量特性及其实时感知技术[J]. 浙江电力, 2024, 43 (2): 1- 12.
|
|
MA Junchao, LU Chengyu, WANG Chenxu, et al. Inertia characteristics and the real-time sensing technology of new-type power systems[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2024, 43 (2): 1- 12.
|
| 7 |
陈一鸣, 刘赟静, 王金鑫. 考虑风电出力不确定性的多源联合系统双层优化调度[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2024, 44 (1): 17- 24.
|
|
CHEN Yiming, LIU Yunjing, WANG Jinxin. Bi-level optimal scheduling of multi-source combined system considering wind power output uncertainty[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2024, 44 (1): 17- 24.
|
| 8 |
夏雨烁, 张新生, 王明虎. 基于ISSA-NESN的可再生能源电力需求预测研究[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2023, 39 (6): 136- 14.
|
|
XIA Yushuo, ZHANG Xinsheng, WANG Minghu. A study on renewable energy power demand forecast based on ISSA-NESN[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2023, 39 (6): 136- 14.
|
| 9 |
张跃龙, 辛力, 赵建平, 等. 绿色电力交易体系及其在蒙西地区的建设实践[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2024, 42 (5): 3- 12.
|
|
ZHANG Yuelong, XIN Li, ZHAO Jianping, et al. Green power trading system and its construction practice in western area of Inner Mongolia[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2024, 42 (5): 3- 12.
|
| 10 |
马大卫, 苏阳, 王正风, 等. 安徽省地级市发电碳排放因子特征与聚类研究[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2023, 39 (6): 524- 5.
|
|
MA Dawei, SU Yang, WANG Zhengfeng, et al. Characteristics and clustering research of carbon emission factors of power generation for prefecture-level cities of Anhui Province[J]. Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection, 2023, 39 (6): 524- 5.
|
| 11 |
杨彪, 颜伟, 莫静山. 考虑源荷功率随机性和相关性的主导节点选择与无功分区方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (11): 61- 67.
|
|
YANG Biao, YAN Wei, MO Jingshan. Pilot-bus selection and network partitioning method considering randomness and correlation of source-load power[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (11): 61- 67.
|
| 12 |
袁林涛, 孙媛媛, 刘振, 等. 基于潮流变向点的配电网低压分布式光伏无功影响及优化[J]. 山东电力技术, 2023, 50 (8): 11- 19, 41.
|
|
YUAN Lintao, SUN Yuanyuan, LIU Zhen, et al. Influence and optimization of low-voltage distributed photovoltaic reactive power in active distribution network based on the power flow reverse point[J]. Shandong Electric Power, 2023, 50 (8): 11- 19, 41.
|
| 13 |
贺春光, 韩光, 赵阳, 等. 双碳背景下计及新能源大规模接入的电量趋势预测与分析[J]. 可再生能源, 2022, 40 (11): 1554- 1562.
|
|
HE Chunguang, HAN Guang, ZHAO Yang, et al. Prediction and analysis of electric quantity trend including large-scale access of new energy under dual carbon background[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2022, 40 (11): 1554- 1562.
|
| 14 |
林其友, 衣涛, 杨乐新. 一种可再生能源并网的最大容量边界计算方法[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2021, 37 (7): 130- 135.
|
|
LIN Qiyou, YI Tao, YANG Lexin. A method for calculating the maximum capacity boundary of renewable energy accessing grid[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2021, 37 (7): 130- 135.
|
| 15 |
但扬清, 王蕾, 郑伟民, 等. 高比例可再生能源接入背景下电网承载能力鲁棒提升策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (9): 104- 111.
|
|
DAN Yangqing, WANG Lei, ZHENG Weimin, et al. Robust improvement strategy for power grid hosting capacity with integration of high proportion of renewable energy[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (9): 104- 111.
|
| 16 |
周洪权, 陈德珍, 尹丽洁, 等. CFD-BP神经网络耦合算法对焚烧炉的一次风管道配风的模拟研究[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2023, 39 (5): 410- 416, 435.
|
|
ZHOU Hongquan, CHEN Dezhen, YIN Lijie, et al. Simulation study of CFD-BP neural network coupled algorithm for air distribution in the primary air pipeline of incinerator[J]. Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection, 2023, 39 (5): 410- 416, 435.
|
| 17 |
陈晓华, 吴杰康. 基于北方苍鹰优化算法优化长短期记忆神经网络的光伏发电功率短期预测[J]. 山东电力技术, 2024, 51 (10): 10- 17.
|
|
CHEN Xiaohua, WU Jiekang. Photovoltaic power short-term prediction based on long short-term memory neural network optimized by northern goshawk optimization algorithm[J]. Shandong Electric Power, 2024, 51 (10): 10- 17.
|
| 18 |
谢小瑜, 周俊煌, 张勇军, 等. 基于W-BiLSTM的可再生能源超短期发电功率预测方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (8): 175- 184.
|
|
XIE Xiaoyu, ZHOU Junhuang, ZHANG Yongjun, et al. W-BiLSTM based ultra-short-term generation power prediction method of renewable energy[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (8): 175- 184.
|
| 19 |
林顺富, 张琪, 沈运帷, 等. 面向灵活爬坡服务的高比例新能源电力系统可调节资源优化调度模型[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (2): 90- 100.
|
|
LIN Shunfu, ZHANG Qi, SHEN Yunwei, et al. Optimal dispatch model of adjustable resources in a power system with high proportion of renewable energy for flexible ramping product[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (2): 90- 100.
|
| 20 |
陈勇, 芮俊, 肖雷鸣, 等. 基于动态主从博弈模型的综合能源系统碳交易方法[J]. 浙江电力, 2024, 43 (4): 51- 62.
|
|
CHEN Yong, RUI Jun, XIAO Leiming, et al. A carbon trading method for integrated energy systems based on a dynamic masterslave game model[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2024, 43 (4): 51- 62.
|
| 21 |
李翠萍, 朱文超, 李军徽, 等. 分布式电源接入中压配电网的运行方案研究[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (4): 57- 64.
|
|
LI Cuiping, ZHU Wenchao, LI Junhui, et al. Research on the operation scheme of distributed generation access to medium voltage distribution network[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (4): 57- 64.
|
| 22 |
彭曙蓉, 郑国栋, 黄士峻, 等. 基于XGBoost算法融合多特征短期光伏发电量预测[J]. 电测与仪表, 2020, 57 (24): 76- 83.
|
|
PENG Shurong, ZHENG Guodong, HUANG Shijun, et al. Multiple-feature short-term photovoltaic generation forecasting based on XGBoost algorithm[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2020, 57 (24): 76- 83.
|