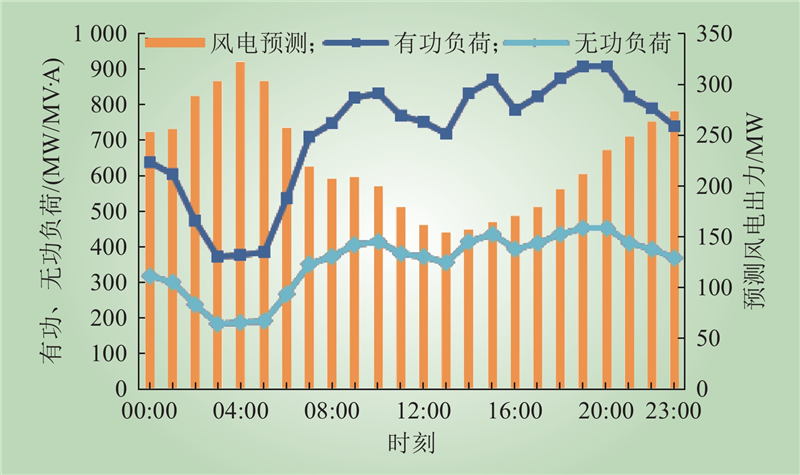
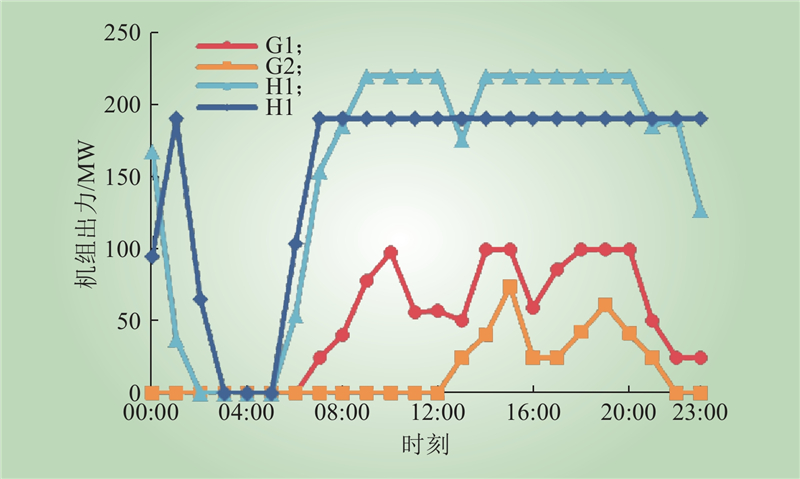
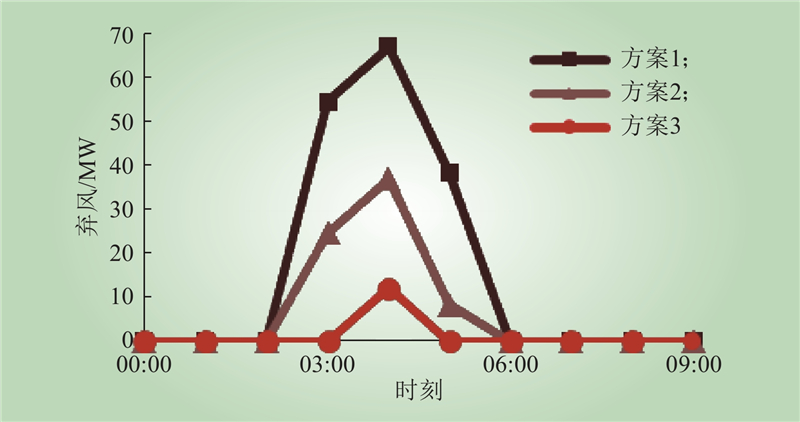
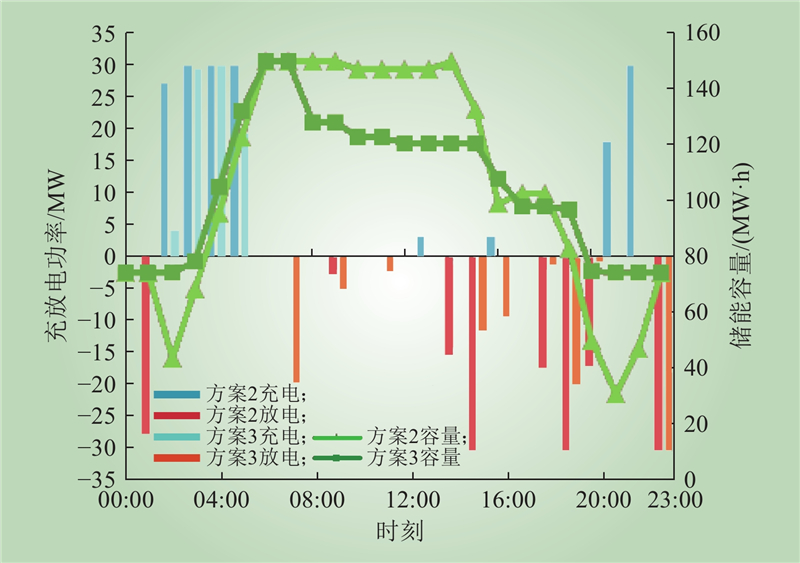
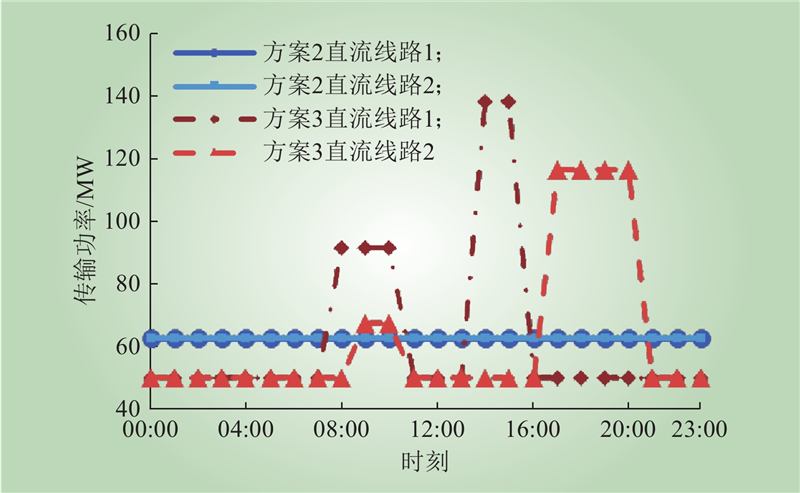
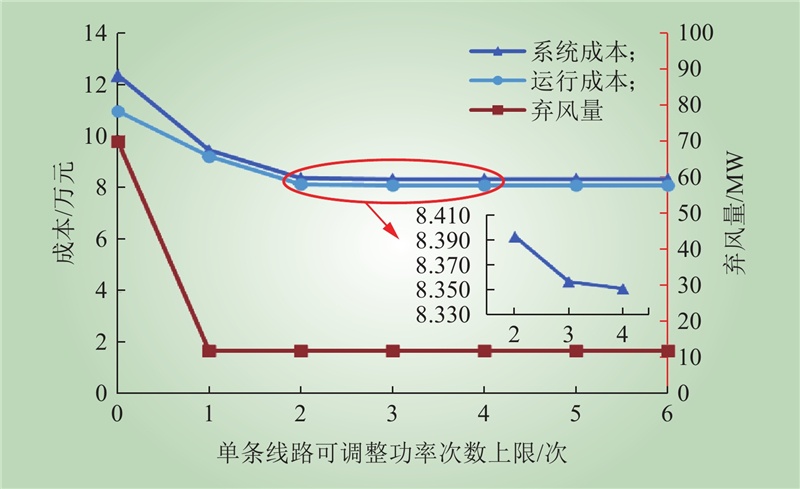
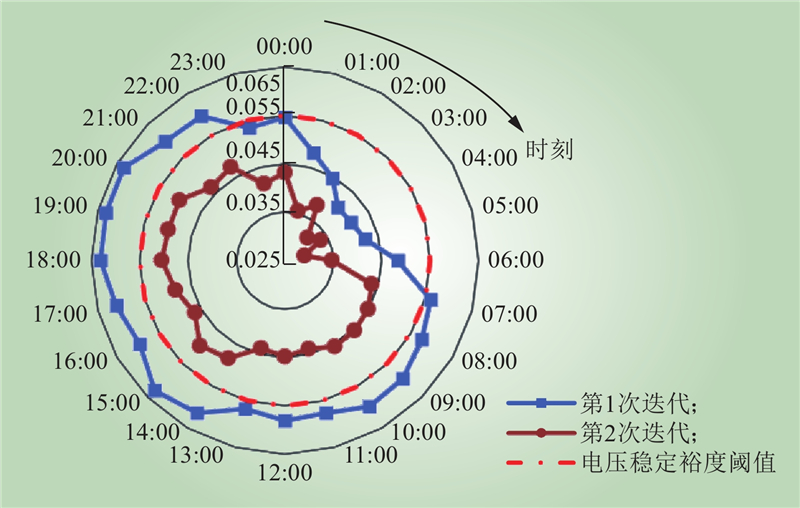
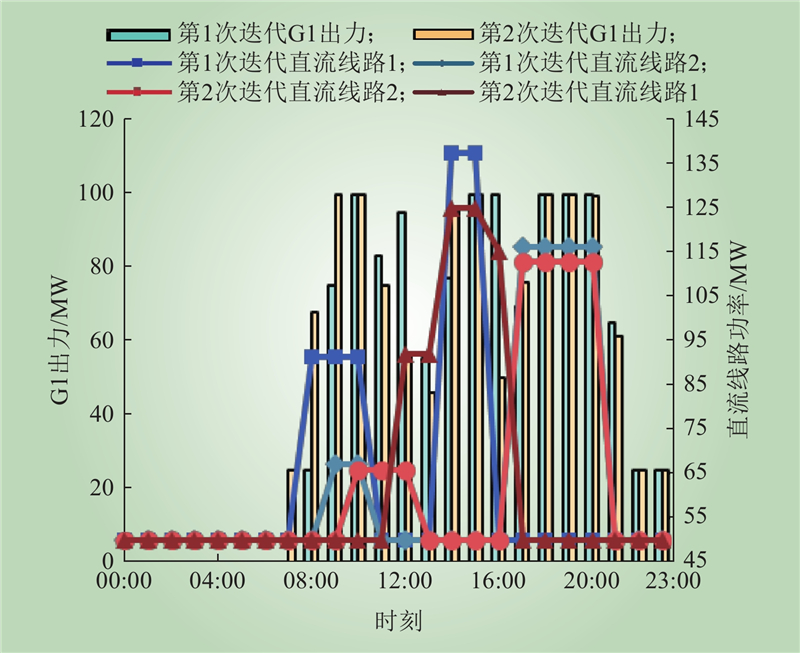
| 1 |
程春田. 碳中和下的水电角色重塑及其关键问题[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (16): 29- 36.
|
|
CHENG Chuntian. Function remolding of hydropower systems for carbon neutral and its key problems[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (16): 29- 36.
|
| 2 |
谭晶, 何川, 陈保瑞, 等. 考虑水光蓄互补和直流外送的电力系统分布鲁棒优化调度方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (15): 5947- 5959.
|
|
TAN Jing, HE Chuan, CHEN Baorui, et al. Distributionally robust optimal scheduling method of power system considering hydropower-photovoltaic-pumped storage complementarity and DC transmission[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (15): 5947- 5959.
|
| 3 |
鲁宗相, 林弋莎, 乔颖, 等. 极高比例可再生能源电力系统的灵活性供需平衡[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (16): 3- 16.
|
|
LU Zongxiang, LIN Yisha, QIAO Ying, et al. Flexibility supply-demand balance in power system with ultra-high proportion of renewable energy[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (16): 3- 16.
|
| 4 |
苏南. 四川构建“受送一体化”新型电力系统[N]. 中国能源报, 2022-05-23(019).
|
| 5 |
ZHAO M Z, WANG Y M, WANG X B, et al. Flexibility evaluation of wind-PV-hydro multi-energy complementary base considering the compensation ability of cascade hydropower stations[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 315, 119024.
|
| 6 |
张玮, 李丹, 张翔宇, 等. 基于风险约束的风电和水电联合日前调度优化模型[J]. 中国电力, 2016, 49 (5): 163- 170.
|
|
ZHANG Wei, LI Dan, ZHANG Xiangyu, et al. Risk-constrained day-ahead scheduling optimization model of hydro-wind power generation[J]. Electric Power, 2016, 49 (5): 163- 170.
|
| 7 |
郑伟民, 但扬清, 王晨轩, 等. 计及风-光-水-火多能协同的电网可再生能源消纳能力评估[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 248- 254.
|
|
ZHENG Weimin, DAN Yangqing, WANG Chenxuan, et al. Evaluation of renewable energy consumption capacity in power grid considering the synergistic effect of wind-photovoltaic-hydro-thermal power[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 248- 254.
|
| 8 |
李咸善, 丁胜彪, 李飞, 等. 考虑水电调节费用补偿的风光水联盟优化调度策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (5): 26- 38.
|
|
LI Xianshan, DING Shengbiao, LI Fei, et al. Optimal scheduling strategy for wind-solar-hydro alliance considering compensation of regulation by hydropower[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (5): 26- 38.
|
| 9 |
刘联涛, 刘飞, 吉平, 等. 储能参与新能源消纳的优化控制策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (3): 137- 143.
|
|
LIU Liantao, LIU Fei, JI Ping, et al. Research on optimal control strategy of energy storage for improving new energy consumption[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (3): 137- 143.
|
| 10 |
尚博阳, 许寅, 王颖, 等. 参与辅助服务的用户侧储能优化配置及经济分析[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (2): 164- 170, 178.
|
|
SHANG Boyang, XU Yin, WANG Ying, et al. Optimal configuration and economic analysis of user-side energy storage participation in auxiliary services[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (2): 164- 170, 178.
|
| 11 |
LIU Z F, ZHANG Z, ZHUO R Q, et al. Optimal operation of independent regional power grid with multiple wind-solar-hydro-battery power[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 235, 1541- 1550.
|
| 12 |
ZHOU S Y, HAN Y, ZALHAF A S, et al. A novel multi-objective scheduling model for grid-connected hydro-wind-PV-battery complementary system under extreme weather: a case study of Sichuan, China[J]. Renewable Energy, 2023, 212, 818- 833.
|
| 13 |
李东东, 孙梦显, 赵耀, 等. 基于等效运行短路比的多直流馈入系统静态电压稳定分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (12): 3847- 3857.
|
|
LI Dongdong, SUN Mengxian, ZHAO Yao, et al. The steady-state voltage stability analysis of multi-infeed LCC-HVDC system based on equivalent operating short circuit ratio[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (12): 3847- 3857.
|
| 14 |
LI J R, LIN J, SONG Y H, et al. Coordinated planning of HVDCs and power-to-hydrogen supply chains for interregional renewable energy utilization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2022, 13 (4): 1913- 1929.
|
| 15 |
李晖, 刘栋, 秦继朔, 等. 考虑风光出力不确定性的新能源基地直流外送随机规划方法研究[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (7): 2795- 2803.
|
|
LI Hui, LIU Dong, QIN Jishuo, et al. Stochastic planning method for UHVDC transmission of renewable energy power base considering wind and photovoltaic output uncertainties[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (7): 2795- 2803.
|
| 16 |
王智冬. 特高压直流风电火电联合外送电源规模优化方法[J]. 电力建设, 2015, 36 (10): 60- 66.
|
|
WANG Zhidong. Optimization method of UHVDC combined wind-thermal power transmission scale[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2015, 36 (10): 60- 66.
|
| 17 |
李湃, 王伟胜, 黄越辉, 等. 大规模新能源基地经特高压直流送出系统中长期运行方式优化方法[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (1): 31- 40.
|
|
LI Pai, WANG Weisheng, HUANG Yuehui, et al. Method on optimization of medium and long term operation modes of large-scale renewable energy power base through UHVDC system[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (1): 31- 40.
|
| 18 |
戴国华, 戴睿, 程广岩, 等. 提升新能源渗透率的风-光-火联合直流外送方法[J]. 广东电力, 2022, 35 (5): 8- 15.
|
|
DAI Guohua, DAI Rui, CHENG Guangyan, et al. Joint delivery of wind-photovoltaic-thermal power by UHVDC for increasing new energy penetration[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2022, 35 (5): 8- 15.
|
| 19 |
冉慧娟, 王治钟, 高本锋, 等. 适用于高压直流输电受端系统的两阶段暂态电压评估方法[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (10): 4272- 4283.
|
|
RAN Huijuan, WANG Zhizhong, GAO Benfeng, et al. Two-stage transient voltage evaluation suitable for HVDC receiving systems[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (10): 4272- 4283.
|
| 20 |
沈舒仪, 王国腾, 但扬清, 等. 频率偏差与电压刚度约束下多馈入直流优化调度方法[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (3): 132- 141.
|
|
SHEN Shuyi, WANG Guoteng, DAN Yangqing, et al. Optimal scheduling method for multi-infeed receiving-end power grids under frequency deviation and voltage stiffness constraints[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (3): 132- 141.
|
| 21 |
夏成军, 王真, 华夏, 等. 基于电压灵敏度的受端系统电压支撑强度评价指标[J]. 电网技术, 2018, 42 (9): 2938- 2947.
|
|
XIA Chengjun, WANG Zhen, HUA Xia, et al. A voltage support strength index based on sensitivity for receiving end of HVDC system[J]. Power System Technology, 2018, 42 (9): 2938- 2947.
|
| 22 |
徐成司, 王子翰, 董树锋, 等. 基于潮流雅可比行列式的静态电压稳定分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (6): 2096- 2108.
|
|
XU Chengsi, WANG Zihan, DONG Shufeng, et al. Static voltage stability analysis based on power flow Jacobian determinant[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (6): 2096- 2108.
|
| 23 |
徐琳, 卢继平, 汪洋, 等. 电力系统节点电压稳定指标的研究[J]. 电网技术, 2010, 34 (3): 26- 30.
|
|
XU Lin, LU Jiping, WANG Yang, et al. Research on nodal voltage stability index of power system[J]. Power System Technology, 2010, 34 (3): 26- 30.
|
| 24 |
张谦, 廖清芬, 唐飞, 等. 计及分布式电源接入的配电网静态电压稳定性评估方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (15): 42- 48.
|
|
ZHANG Qian, LIAO Qingfen, TANG Fei, et al. Steady state voltage stability assessment method of distribution network considering inter-connection of distributed generators[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (15): 42- 48.
|
| 25 |
李江南, 程韧俐, 周保荣, 等. 含碳捕集及电转氢设备的低碳园区综合能源系统随机优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (5): 149- 156.
|
|
LI Jiangnan, CHENG Renli, ZHOU Baorong, et al. Stochastic optimal of integrated energy system in low-carbon parks considering carbon capture storage and power to hydrogen[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (5): 149- 156.
|
| 26 |
翟晶晶, 吴晓蓓, 傅质馨, 等. 考虑需求响应与光伏不确定性的综合能源系统鲁棒优化[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (8): 9- 18.
|
|
ZHAI Jingjing, WU Xiaobei, FU Zhixin, et al. Robust optimization of integrated energy systems considering demand response and photovoltaic uncertainty[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (8): 9- 18.
|
| 27 |
李东东, 尤杨, 周波. 基于信息间隙决策理论的售电公司参与多市场的优化决策[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (12): 4778- 4788.
|
|
LI Dongdong, YOU Yang, ZHOU Bo. IGDT-based decision-making optimization of electricity retailers under multi-market[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (12): 4778- 4788.
|
| 28 |
张涛, 刘伉, 陶然, 等. 计及热媒流率和热损耗不确定性的综合能源系统优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (4): 146- 155.
|
|
ZHANG Tao, LIU Kang, TAO Ran, et al. Optimal scheduling of integrated energy system considering uncertainty of heat medium flow rate and heating network loss[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (4): 146- 155.
|
| 29 |
汪超群, 韦化, 吴思缘. 基于信息间隙决策理论的多源联合优化机组组合[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (12): 3431- 3440.
|
|
WANG Chaoqun, WEI Hua, WU Siyuan. Multi-power combined unit commitment based on information gap decision theory[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (12): 3431- 3440.
|
| 30 |
王晓村, 李腾飞, 徐妍珺, 等. 基于信息间隙决策理论的电-气综合能源系统低碳经济调度[J/OL]. 电测与仪表, 1–10[2025-01-15]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1202.TH.20230525.1046.002.html.
|
|
WANG Xiaocun, LI Tengfei, XU Yanjun, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatching of integrated electricity-gas system based on IGDT[J/OL]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 1–10[2024-04-24]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1202.TH.20230525.1046.002.html.
|
| 31 |
MIRZAEI M A, NAZARI-HERIS M, MOHAMMADI-IVATLOO B, et al. Network-constrained joint energy and flexible ramping reserve market clearing of power-and heat-based energy systems: a two-stage hybrid IGDT–stochastic framework[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15 (2): 1547- 1556.
|
| 32 |
REZAEI N, AHMADI A, KHAZALI A, et al. Multiobjective risk-constrained optimal bidding strategy of smart microgrids: an IGDT-based normal boundary intersection approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15 (3): 1532- 1543.
|
| 33 |
DOLATABADI A, JADIDBONAB M, MOHAMMADI-IVATLOO B. Short-term scheduling strategy for wind-based energy hub: a hybrid stochastic/IGDT approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2019, 10 (1): 438- 448.
|
| 34 |
KESSEL P, GLAVITSCH H. Estimating the voltage stability of a power system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 1986, 1 (3): 346- 354.
|
| 35 |
RIDER M J, GARCIA A V, ROMERO R. Power system transmission network expansion planning using AC model[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2007, 1(5): 731-742.
|
| 36 |
陈晞, 段溪洛, 张振东. 浅议雅砻江流域梯级水电站开发物资供应结构和管理[J]. 四川水力发电, 2009, 28 (4): 147- 150.
|
|
CHEN Xi, DUAN Xiluo, ZHANG Zhendong. Materials supply structure and management for cascade hydropower station development in yalong river basin[J]. Sichuan Hydropower, 2009, 28 (4): 147- 150.
|
| 37 |
YIN Y, HE C, LIU T Q, et al. Risk-averse stochastic midterm scheduling of thermal-hydro-wind system: a network-constrained clustered unit commitment approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2022, 13 (3): 1293- 1304.
|
| 38 |
史华勃, 范成围, 李茜, 等. 考虑频率及电压稳定约束的主动解列最优断面搜索方法[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (8): 3324- 3335.
|
|
SHI Huabo, FAN Chengwei, LI Qian, et al. Optimal controlled islanding method considering frequency and voltage stability constraints[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (8): 3324- 3335.
|
| 39 |
张宁, 朱昊, 杨凌霄, 等. 考虑可再生能源消纳的多能互补虚拟电厂优化调度策略[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (5): 625- 633.
|
|
ZHANG Ning, ZHU Hao, YANG Lingxiao, et al. Optimal scheduling strategy of multi-energy complementary virtual power plant considering renewable energy consumption[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (5): 625- 633.
|
| 40 |
郁海彬, 张煜晨, 刘扬洋, 等. 碳交易机制下多主体虚拟电厂参与电力市场的优化调度竞标策略[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (5): 634- 644.
|
|
YU Haibin, ZHANG Yuchen, LIU Yangyang, et al. Optimal dispatching bidding strategy of multi-agent virtual power plant participating in electricity market under carbon trading mechanism[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (5): 634- 644.
|
| 41 |
董光德, 李道明, 陈咏涛, 等. 基于粒子群优化与卷积神经网络的电能质量扰动分类方法[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (1): 136- 142.
|
|
DONG Guangde, LI Daoming, CHEN Yongtao, et al. Power quality disturbance classification method based on particle swarm optimization and convolutional neural network[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (1): 136- 142.
|