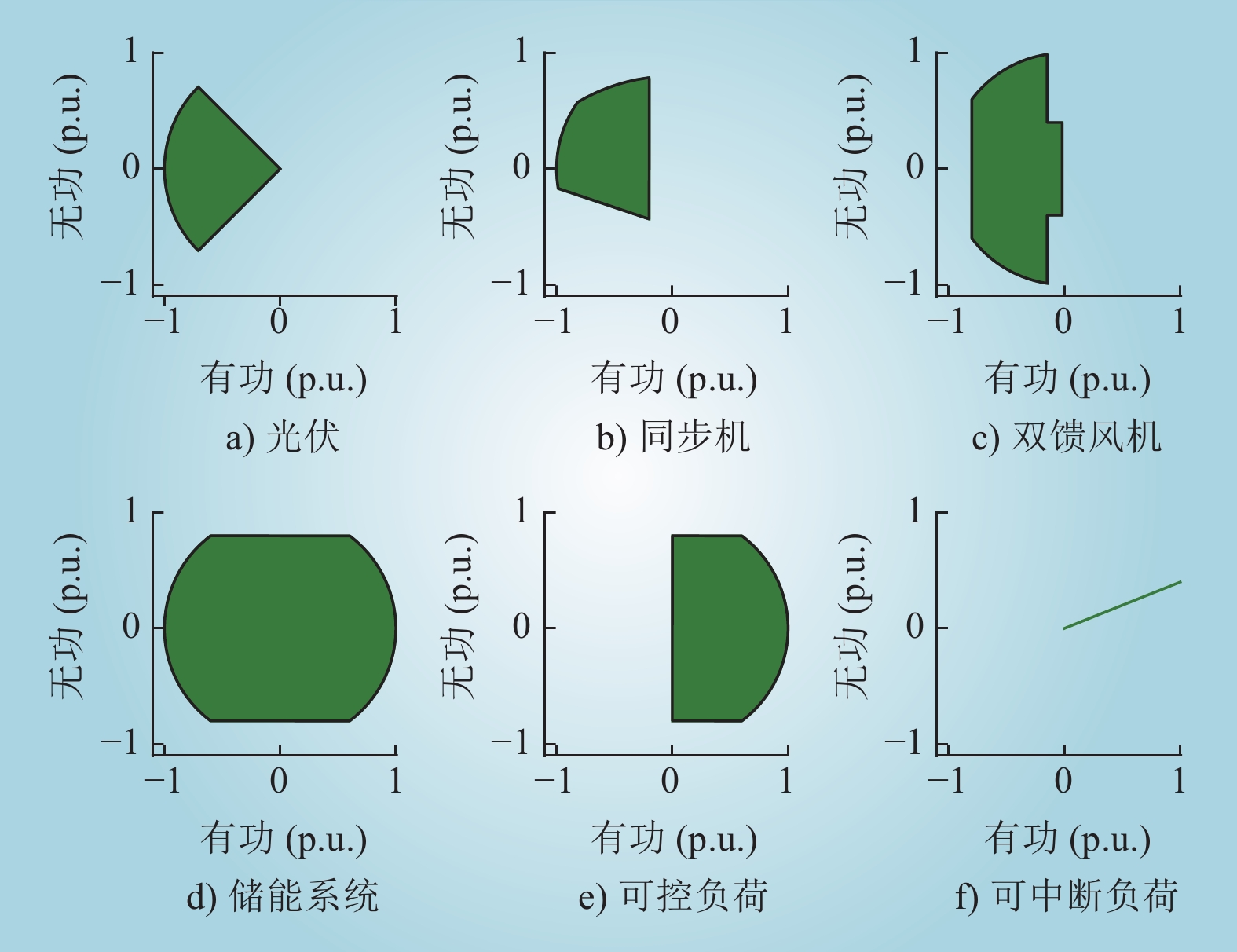
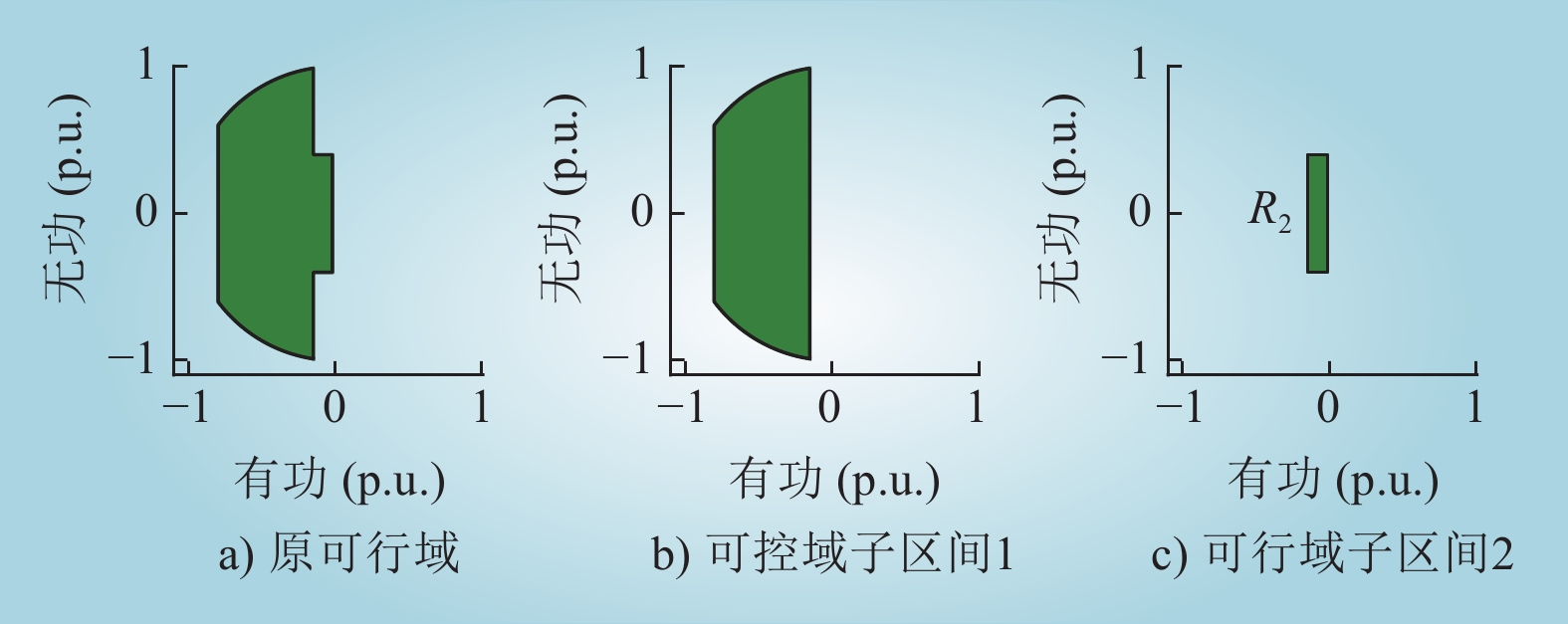
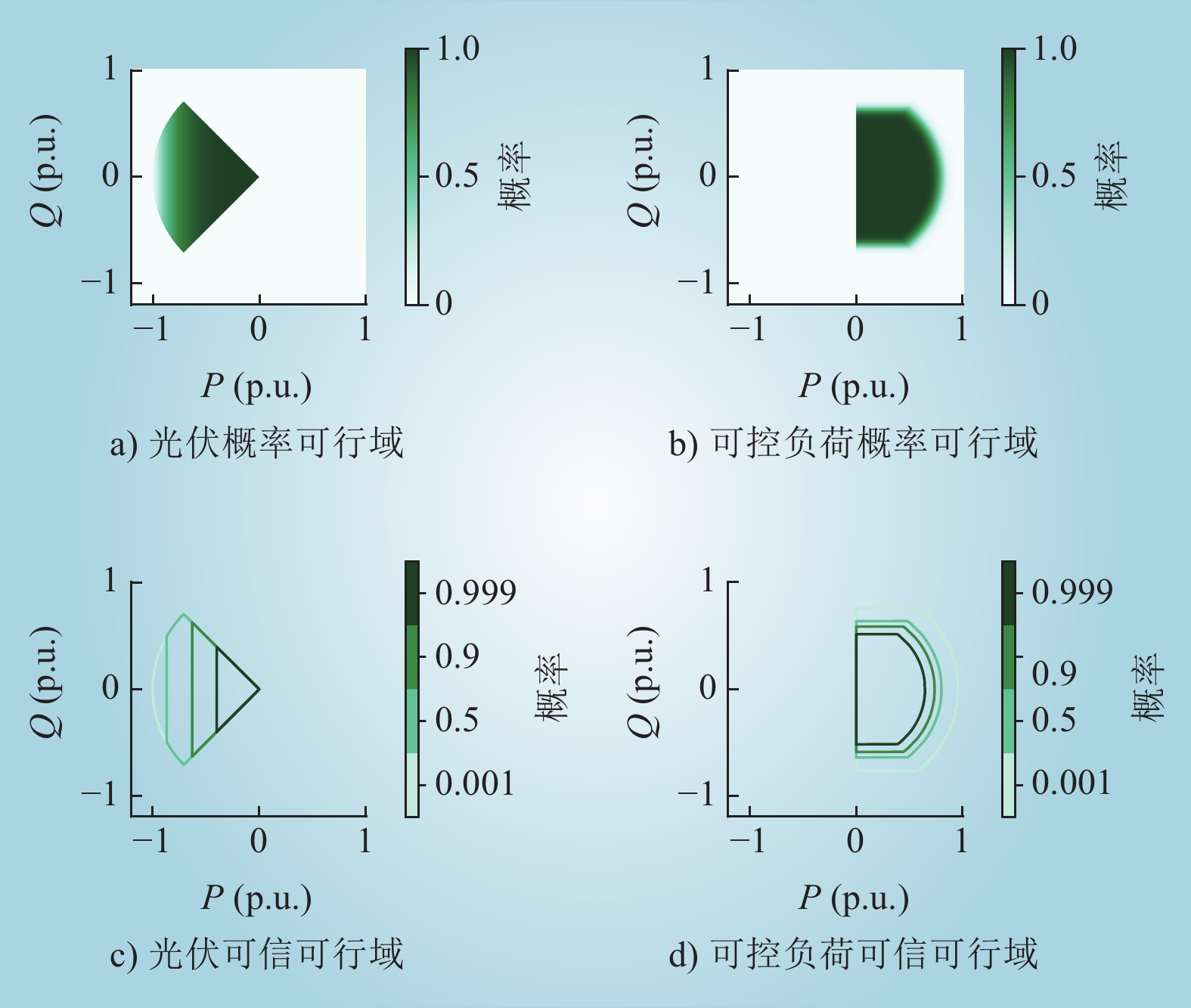
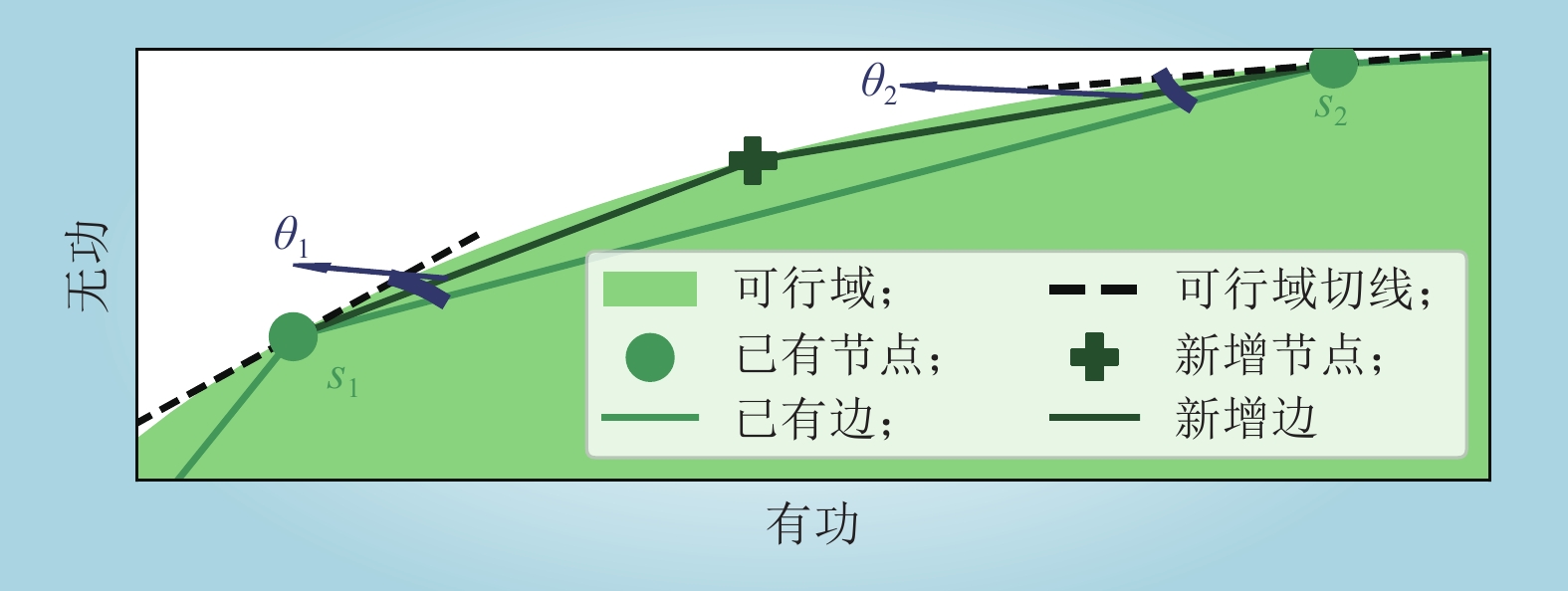
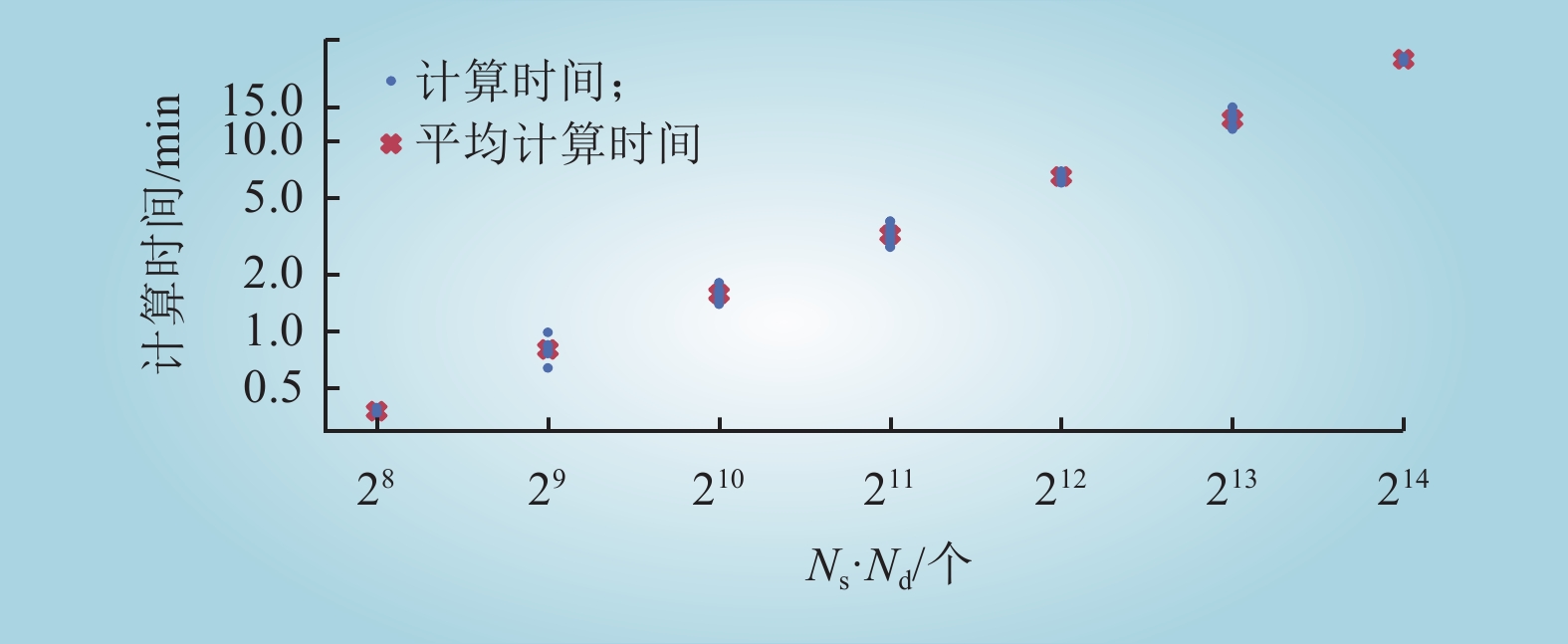
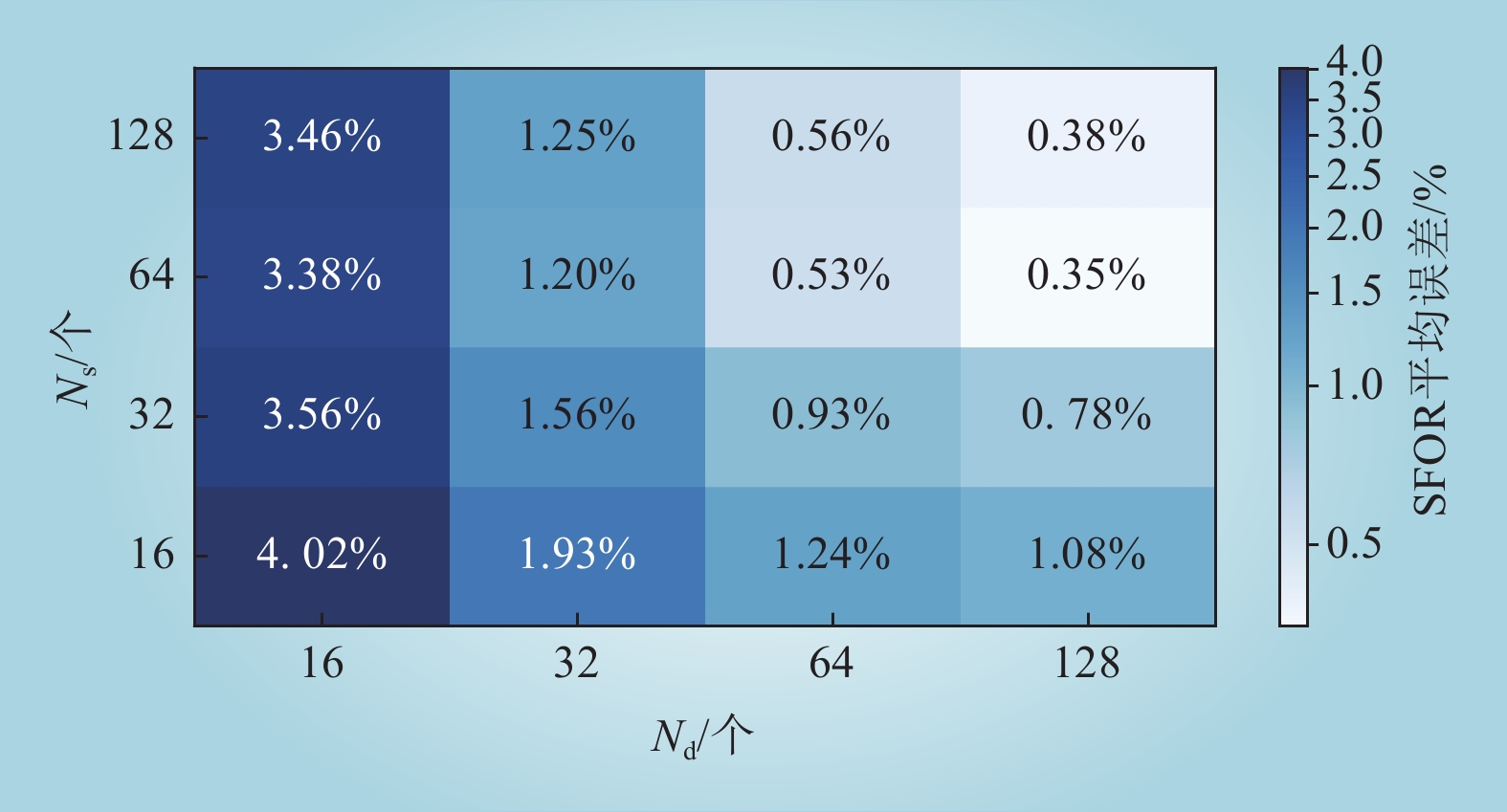
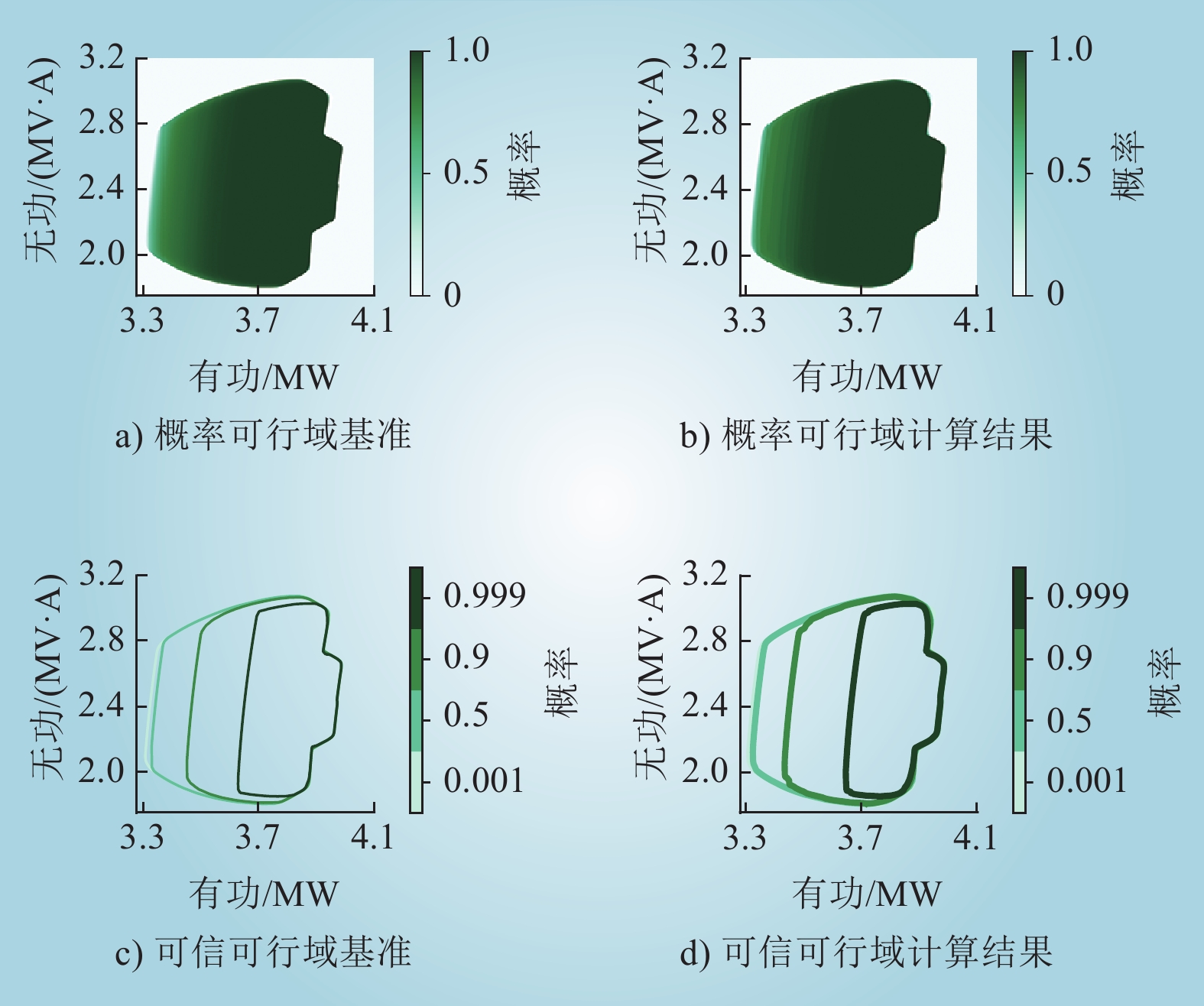
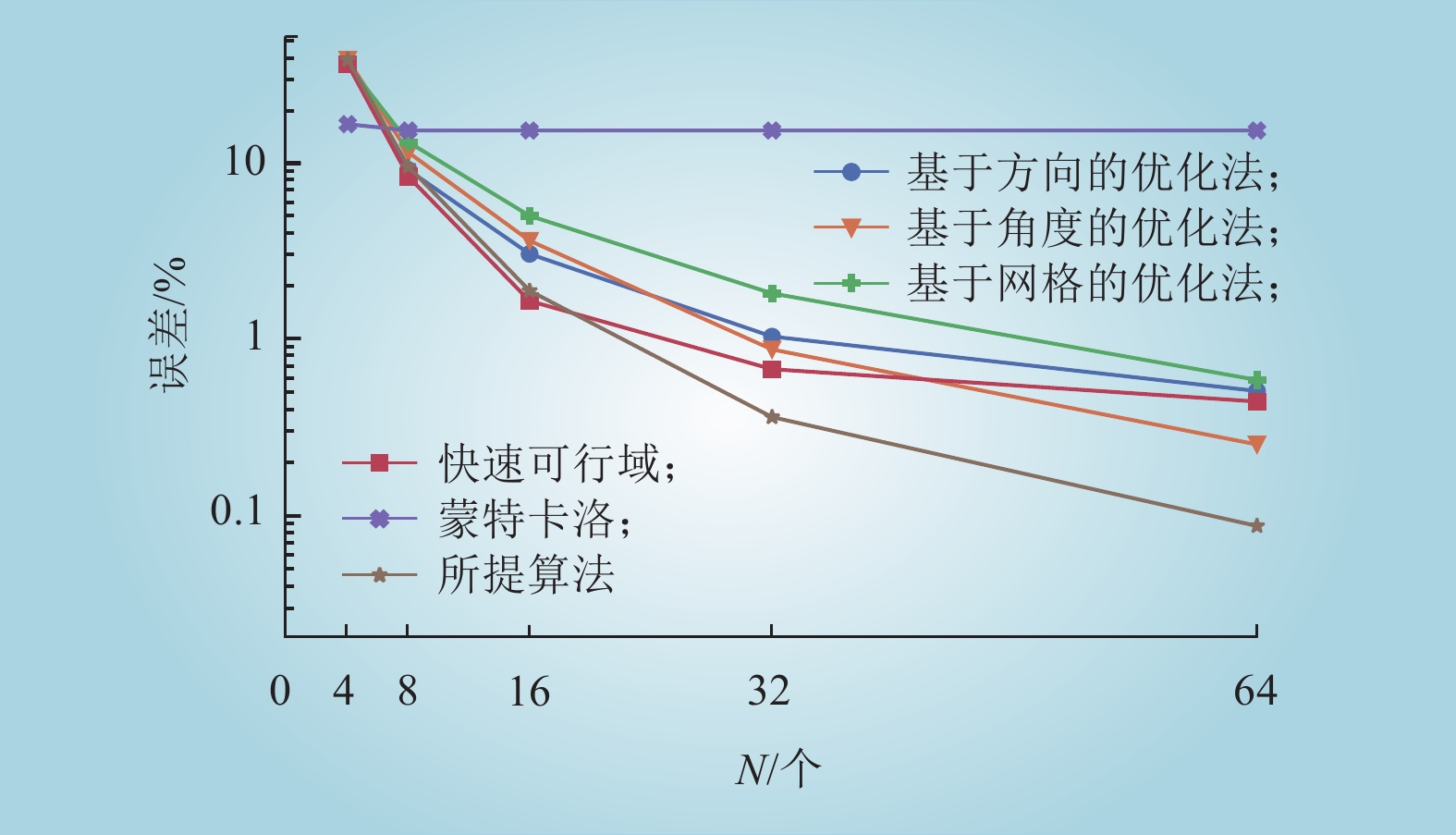
| 1 |
朱法华, 徐静馨. 双碳背景下中国与主要发达国家电力低碳转型比较[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2024, 40 (6): 561- 571.
|
|
ZHU Fahua, XU Jingxin. Comparison of low-carbon transformation in electricity between China and major developed countries under the background of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality[J]. Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection, 2024, 40 (6): 561- 571.
|
| 2 |
谭显东, 刘俊, 徐志成, 等. “双碳” 目标下“十四五” 电力供需形势[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (5): 1- 6.
|
|
TAN Xiandong, LIU Jun, XU Zhicheng, et al. Power supply and demand balance during the 14th Five-Year Plan period under the goal of carbon emission peak and carbon neutrality[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (5): 1- 6.
|
| 3 |
卓振宇, 张宁, 谢小荣, 等. 高比例可再生能源电力系统关键技术及发展挑战[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (9): 171- 191.
|
|
ZHUO Zhenyu, ZHANG Ning, XIE Xiaorong, et al. Key technologies and developing challenges of power system with high proportion of renewable energy[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (9): 171- 191.
|
| 4 |
金晨, 任大伟, 肖晋宇, 等. 支撑碳中和目标的电力系统源-网-储灵活性资源优化规划[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (8): 164- 174.
|
|
JIN Chen, REN Dawei, XIAO Jinyu, et al. Optimization planning on power system supply-grid-storage flexibility resource for supporting the "carbon neutrality" target of China[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (8): 164- 174.
|
| 5 |
HUANG P X, VANFRETTI L. Adaptive damping control of MMC to suppress high-frequency resonance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2023, 59 (6): 7224- 7237.
|
| 6 |
周海浪, 刘一畔, 陈雨果, 等. 考虑灵活性收益的需求侧资源可行域聚合方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (9): 56- 63, 155.
|
|
ZHOU Hailang, LIU Yipan, CHEN Yuguo, et al. Demand side feasible region aggregation considering flexibility revenue[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (9): 56- 63, 155.
|
| 7 |
ZHOU Y, LI Z S, YANG M. A framework of utilizing distribution power systems as reactive power prosumers for transmission power systems[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2020, 121, 106139.
|
| 8 |
JIN X L, MU Y F, JIA H J, et al. Alleviation of overloads in transmission network: a multi-level framework using the capability from active distribution network[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2019, 112, 232- 251.
|
| 9 |
尚博文, 徐铭铭, 张金帅, 等. 高比例分布式光伏接入背景下配电网电压调控方法研究综述[J]. 智慧电力, 2024, 52 (12): 1- 11.
|
|
SHANG Bowen, XU Mingming, ZHANG Jinshuai, et al. A review of voltage regulation methods for distribution networks in the context of high proportion of distributed photovoltaic integration[J]. Smart Power, 2024, 52 (12): 1- 11.
|
| 10 |
季湛洋, 胡阳, 孔令行, 等. 考虑多领域耦合特性的风电机组一次调频动态建模与仿真[J/OL]. 中国电力: 1–13 [2025-2-27]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3265.tm.20250226.1553.017.html.
|
|
JI Zhanyang, HU Yang, KONG Lingxing, et al. Dynamic modeling and simulation of wind turbine unit frequency regulation considering multi-domain coupling characteristics[J/OL]. Electric Power: 1–13 [2025-2-27]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3265.tm.20250226.1553.017.html.
|
| 11 |
鲁宗相, 李海波, 乔颖. 高比例可再生能源并网的电力系统灵活性评价与平衡机理[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37 (1): 9- 20.
|
|
LU Zongxiang, LI Haibo, QIAO Ying. Flexibility evaluation and supply/demand balance principle of power system with high-penetration renewable electricity[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37 (1): 9- 20.
|
| 12 |
齐军, 马鹏, 周生存, 等. 基于深度强化学习的新型终端配电网源荷储协同控制[J/OL]. 内蒙古电力技术: 1–12 [2025-2-19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/15.1200.tm.20250218.1641.004.html.
|
|
Qi Jun, MA Peng, ZHOU Shengcun, et al. New terminal distribution network source load storage collaborative control based on deep reinforcement learning[J/OL]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power: 1–12 [2025-2-19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/15.1200.tm.20250218.1641.004.html.
|
| 13 |
YU M K, WANG J X, YAN J, et al. Pricing information in smart grids: a quality-based data valuation paradigm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2022, 13 (5): 3735- 3747.
|
| 14 |
王琦, 董洪达, 贺子谦, 等. 考虑灵活性资源互济的虚拟电厂集群优化调度策略[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2024, 44 (5): 101- 111.
|
|
WANG Qi, DONG Hongda, HE Ziqian, et al. Optimization and scheduling strategy for virtual power plant clusters considering flexibility and resource complementarity[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2024, 44 (5): 101- 111.
|
| 15 |
王佳莹, 檀鑫鑫, 吴玉鑫, 等. 多形态灵活资源调控下的可再生能源配额多主体博弈研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2025, 53 (2): 9- 15, 40.
|
|
WANG Jiaying, TAN Xinxin, WU Yuxin, et al. Multi-agent game of renewable energy quotas under polymorphic flexible resource regulation[J]. Smart Power, 2025, 53 (2): 9- 15, 40.
|
| 16 |
SARSTEDT M, HOFMANN L. Monetarization of the feasible operation region of active distribution grids based on a cost-optimal flexibility disaggregation[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10, 5402- 5415.
|
| 17 |
SUN H B, GUO Q L, SHEN X W, et al. Energy Internet: redefinition and categories[J]. Energy Internet, 2024, 1 (1): 3- 8.
|
| 18 |
刘军会, 龚健, 佟炳绅, 等. 基于分布式储能与光伏的虚拟电厂与配电网协同优化方法[J/OL]. 中国电力: 1–9 [2025-2-26]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3265.TM.20250226.0812.004.html.
|
|
LIU Junhui, GONG Jian, TONG Bingshen, et al. Coordinated optimization method for virtual power plants considering distributed energy storage and photovoltaics with distribution networks[J/OL]. Electric Power: 1–9 [2025-2-26]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3265.TM.20250226.0812.004.html.
|
| 19 |
ZHAO L, ZHANG W, HAO H, et al. A geometric approach to aggregate flexibility modeling of thermostatically controlled loads[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 32 (6): 4721- 4731.
|
| 20 |
HELENO M, SOARES R, SUMAILI J, et al. Estimation of the flexibility range in the transmission-distribution boundary[C]//2015 IEEE Eindhoven PowerTech. Eindhoven, Netherlands. IEEE, 2015: 1–6.
|
| 21 |
MOKHTARIAN K, JACOBSEN H A. Coordinated caching in planet-scale CDNs: analysis of feasibility and benefits[C]//IEEE INFOCOM 2016 - The 35th Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications. San Francisco, CA, USA. IEEE, 2016: 1–9.
|
| 22 |
SILVA J, SUMAILI J, BESSA R J, et al. Estimating the active and reactive power flexibility area at the TSO-DSO interface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33 (5): 4741- 4750.
|
| 23 |
GIACOMO V, ROSSI M , MONETA D . Effects of Distribution System Characteristics on TSO-DSO Ancillary Services Exchange[C]//CIRED 2019.
|
| 24 |
STANKOVIĆ S, SÖDER L, HAGEMANN Z, et al. Reactive power support adequacy at the DSO/TSO interface[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2021, 190, 106661.
|
| 25 |
DING T, ZENG Z Y, QU M, et al. Two-stage chance-constrained stochastic thermal unit commitment for optimal provision of virtual inertia in wind-storage systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2021, 36 (4): 3520- 3530.
|
| 26 |
CHEN X, LI N. Leveraging two-stage adaptive robust optimization for power flexibility aggregation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12 (5): 3954- 3965.
|
| 27 |
张天策, 李庚银, 王剑晓, 等. 基于可行域投影理论的新能源电力系统协同运行方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39 (9): 2784- 2796.
|
|
ZHANG Tiance, LI Gengyin, WANG Jianxiao, et al. Coordinated operation method of renewable energy power systems based on feasible region projection theory[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39 (9): 2784- 2796.
|
| 28 |
SAVVOPOULOS N, HATZIARGYRIOU N. An effective method to estimate the aggregated flexibility at distribution level[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11, 31373- 31383.
|
| 29 |
ZHOU M Y, CHEN S, HUANG K, et al. Coordination of medium-voltage distribution networks and microgrids based on an aggregate flexibility region approach[J]. Sustainable Energy, Grids and Networks, 2024, 39, 101485.
|
| 30 |
KUNDU S, KALSI K, BACKHAUS S. Approximating flexibility in distributed energy resources: a geometric approach[C]//2018 Power Systems Computation Conference (PSCC). Dublin, Ireland. IEEE, 2018: 1–7.
|
| 31 |
LIEN J M, AMATO N M. Approximate convex decomposition of polygons[J]. Computational Geometry, 2006, 35 (1/2): 100- 123.
|
| 32 |
GEOFFRION A M. Generalized benders decomposition[J]. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 1972, 10 (4): 237- 260.
|
| 33 |
MCKAY M D, BECKMAN R J, CONOVER W J. A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code[J]. Technometrics, 2000, 42 (1): 55.
|
| 34 |
BARAN M E, WU F F. Network reconfiguration in distribution systems for loss reduction and load balancing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2002, 4 (2): 1401- 1407.
|
| 35 |
RIAZ S, MANCARELLA P. On feasibility and flexibility operating regions of virtual power plants and TSO/DSO interfaces[C]//2019 IEEE Milan PowerTech. Milan, Italy. IEEE, 2019: 1–6.
|
| 36 |
LOPEZ L, GONZALEZ-CASTELLANOS A, POZO D, et al. QuickFlex: a fast algorithm for flexible region construction for the TSO-DSO coordination[C]//2021 International Conference on Smart Energy Systems and Technologies (SEST). Vaasa, Finland. IEEE, 2021: 1–6.
|
| 37 |
ZHANG D, FU Z C, ZHANG L C. An improved TS algorithm for loss-minimum reconfiguration in large-scale distribution systems[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2007, 77 (5/6): 685- 694.
|