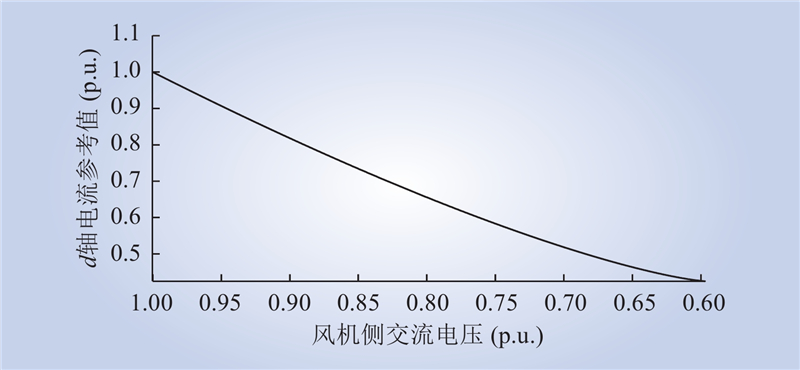
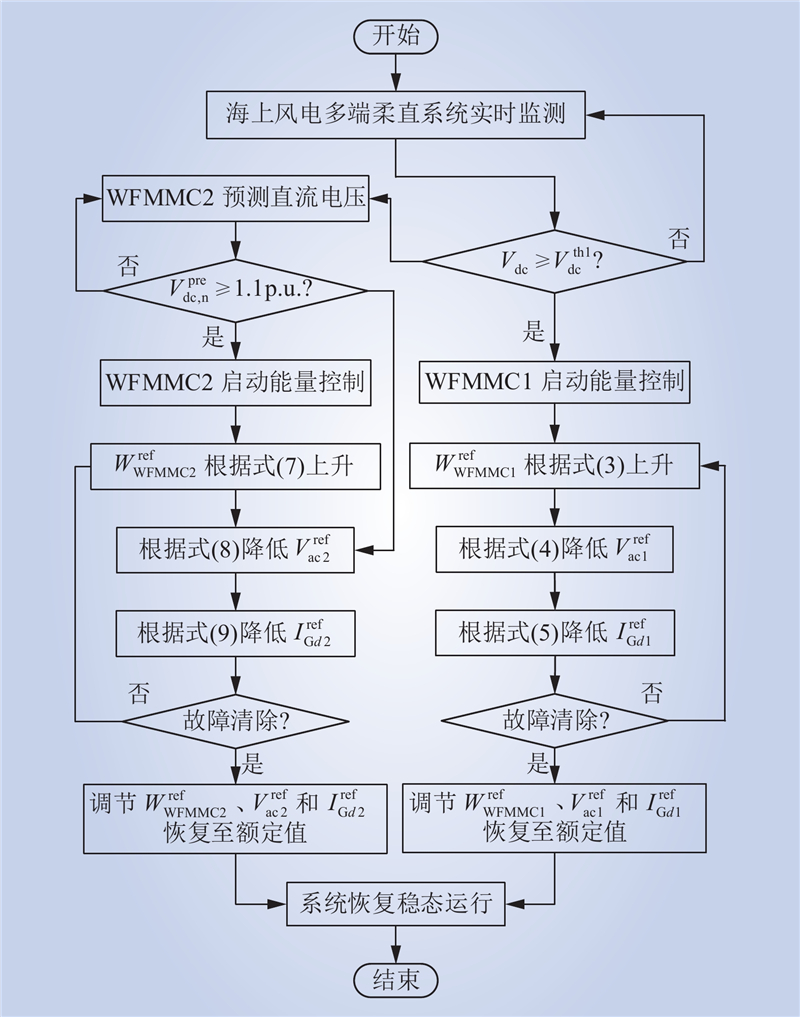
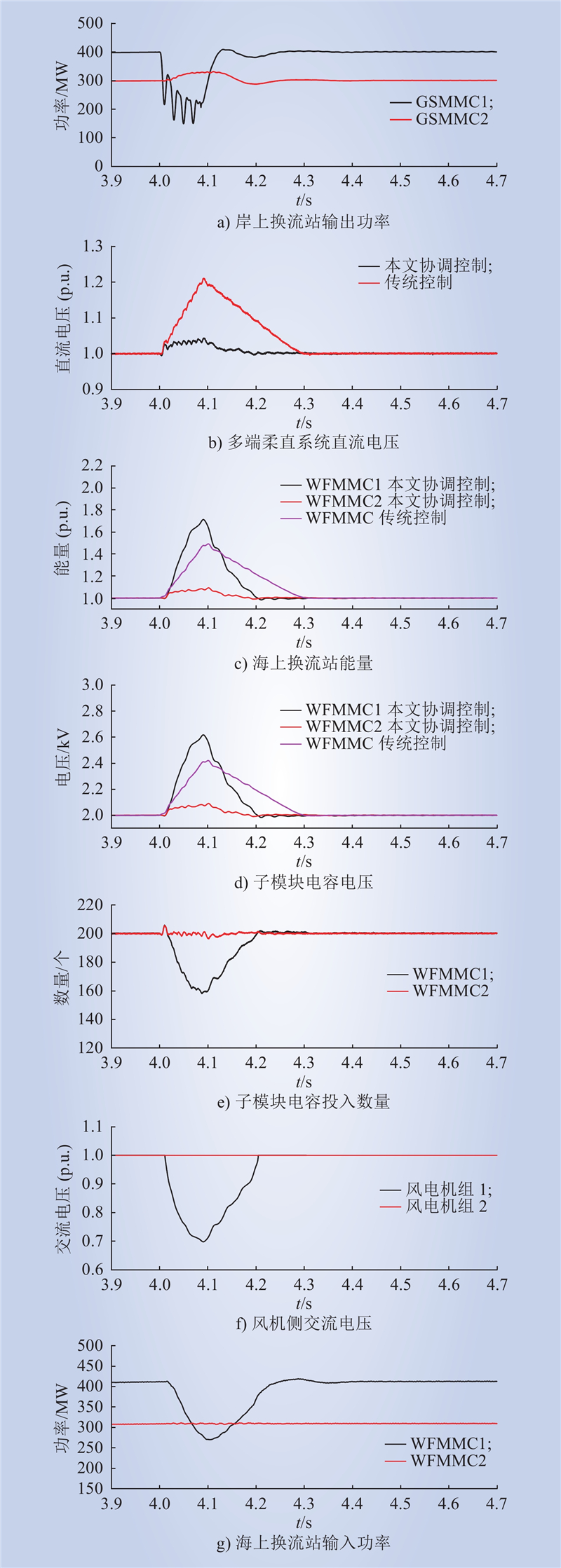
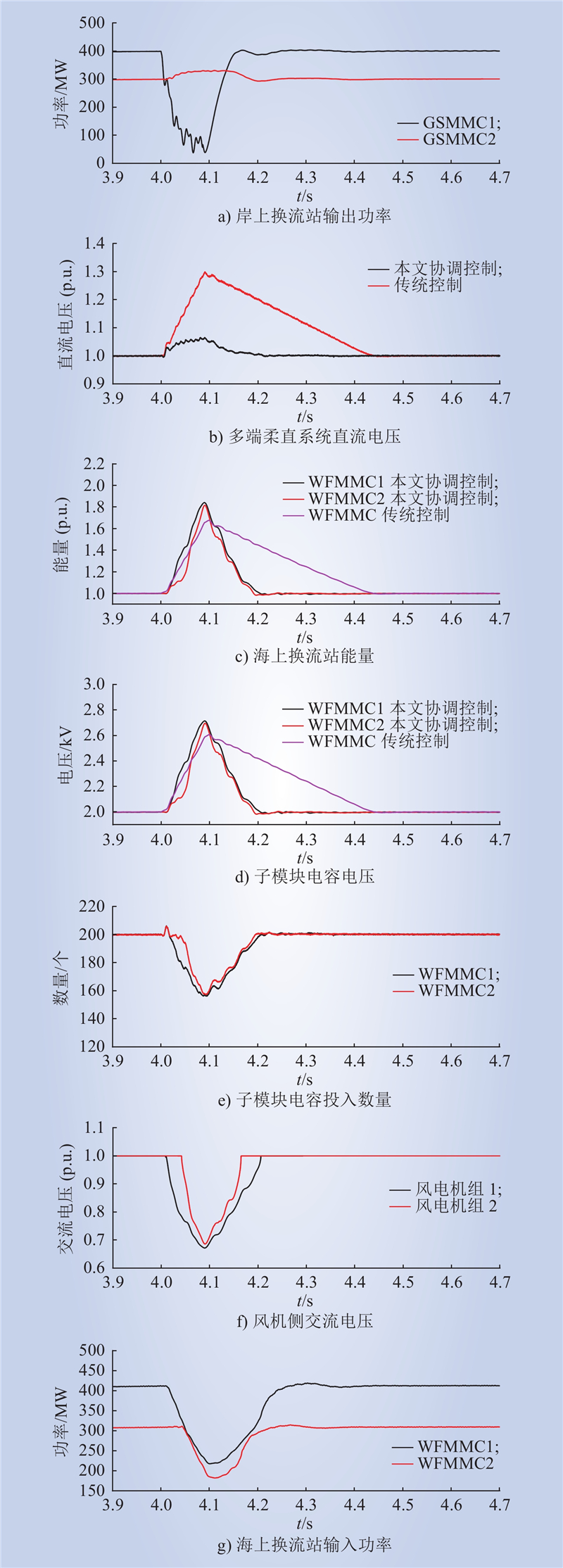
| 1 |
刘卫东, 李奇南, 王轩, 等. 大规模海上风电柔性直流输电技术应用现状和展望[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (7): 55- 71.
|
|
LIU Weidong, LI Qinan, WANG Xuan, et al. Application status and prospect of VSC-HVDC technology for large-scale offshore wind farms[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (7): 55- 71.
|
| 2 |
杨仁炘, 王霄鹤, 陈晴, 等. 机组协同-分布卸荷的风电场-柔直并网系统故障穿越方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (21): 103- 111.
|
|
YANG Renxin, WANG Xiaohe, CHEN Qing, et al. Fault ride-through method of flexible HVDC transmission system for wind farm integration based on coordination of wind turbines and distributed braking resistors[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (21): 103- 111.
|
| 3 |
蔡旭, 杨仁炘, 周剑桥, 等. 海上风电直流送出与并网技术综述[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (21): 2- 22.
|
|
CAI Xu, YANG Renxin, ZHOU Jianqiao, et al. Review on offshore wind power integration via DC transmission[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (21): 2- 22.
|
| 4 |
厉璇, 宋强, 刘文华, 等. 风电场柔性直流输电的故障穿越方法对风电机组的影响[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (11): 31- 36, 125.
|
|
LI Xuan, SONG Qiang, LIU Wenhua, et al. Impact of fault ride-through methods on wind power generators in a VSC-HVDC system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (11): 31- 36, 125.
|
| 5 |
LIU Y, WANG X F, ZHE C. Cooperative control of VSC-HVDC connected offshore wind farm with low-voltage ride-through capability[C]//2012 IEEE International Conference on Power System Technology (Powercon). Auckland, New Zealand. IEEE, 2012: 1–6.
|
| 6 |
王毅, 付媛, 苏小晴, 等. 基于VSC-HVDC联网的风电场故障穿越控制策略研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2013, 28 (12): 150- 159.
|
|
WANG Yi, FU Yuan, SU Xiaoqing, et al. Fault ride-through control strategy of wind farm integrated with VSC-HVDC[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2013, 28 (12): 150- 159.
|
| 7 |
FELTES C, WREDE H, KOCH F, et al. Fault ride through of DFIG-based wind farms connected to the grid through VSC-based HVDC link[C]//16th Power Systems Computation Conference. Glas-gow , UK : IEEE, 2008.
|
| 8 |
章心因, 胡敏强, 吴在军, 等. 基于VSC-HVDC的风力发电系统低电压穿越协调控制[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2014, 34 (3): 138- 143.
|
|
ZHANG Xinyin, HU Minqiang, WU Zaijun, et al. Coordinated LVRT control of wind power generation system based on VSC-HVDC[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2014, 34 (3): 138- 143.
|
| 9 |
薄鑫, 杨志超, 宋杉, 等. 海上风电经柔直送出系统受端交流故障联合穿越控制策略[J]. 可再生能源, 2022, 40 (10): 1396- 1406.
|
|
BO Xin, YANG Zhichao, SONG Shan, et al. Coordinated fault ride through strategy for offshore wind farm via VSC-HVDC under receiving-end AC fault[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2022, 40 (10): 1396- 1406.
|
| 10 |
曹帅, 刘东, 赵成功. 适用于风电经柔性直流并网系统的柔性耗能装置及控制策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (23): 51- 62.
|
|
CAO Shuai, LIU Dong, ZHAO Chenggong. A flexible energy dissipation device with control strategy for an HVDC wind power integration system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (23): 51- 62.
|
| 11 |
付艳, 周晓风, 戴国安, 等. 海上风电直流耗能装置和保护配合策略研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49 (15): 178- 186.
|
|
FU Yan, ZHOU Xiaofeng, DAI Guoan, et al. Research on coordination strategy for an offshore wind power DC chopper device and protection[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49 (15): 178- 186.
|
| 12 |
张静, 高冲, 许彬, 等. 海上风电直流并网工程用新型柔性直流耗能装置电气设计研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (12): 4081- 4091.
|
|
ZHANG Jing, GAO Chong, XU Bin, et al. Research on electrical design of novel flexible DC energy consuming device for offshore wind power DC grid connection project[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (12): 4081- 4091.
|
| 13 |
谢晔源, 姚宏洋, 李海英, 等. 用于VSC-HVDC系统的模块化直串式直流耗能装置[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (7): 117- 123.
|
|
XIE Yeyuan, YAO Hongyang, LI Haiying, et al. Modular series-connection DC energy braking device for VSC-HVDC system[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (7): 117- 123.
|
| 14 |
张浩博, 向往, 周猛, 等. 海上风电柔直并网系统主动能量控制与交流耗能装置协同策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (12): 4319- 4330.
|
|
ZHANG Haobo, XIANG Wang, ZHOU Meng, et al. Cooperative strategy of active energy control and AC energy dissipation device in offshore wind power MMC-HVDC system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (12): 4319- 4330.
|
| 15 |
刘天琪, 陶艳, 李保宏. 风电场经MMC-MTDC系统并网的几个关键问题[J]. 电网技术, 2017, 41 (10): 3251- 3260.
|
|
LIU Tianqi, TAO Yan, LI Baohong. Critical problems of wind farm integration via MMC-MTDC system[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41 (10): 3251- 3260.
|
| 16 |
郭贤珊, 周杨, 梅念, 等. 张北柔直电网的构建与特性分析[J]. 电网技术, 2018, 42 (11): 3698- 3707.
|
|
GUO Xianshan, ZHOU Yang, MEI Nian, et al. Construction and characteristic analysis of Zhangbei flexible DC grid[J]. Power System Technology, 2018, 42 (11): 3698- 3707.
|
| 17 |
邱子鉴, 刘晋, 周鑫, 等. 多端柔性直流输电系统交流故障穿越控制策略[J]. 华北电力大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 48 (6): 32- 40.
|
|
QIU Zijian, LIU Jin, ZHOU Xin, et al. AC fault ride-through control strategy of VSC-MTDC system based on improved droop control[J]. Journal of North China Electric Power University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 48 (6): 32- 40.
|
| 18 |
王少林, 王刚, 陈琦, 等. 考虑线路电阻影响的MMC-MTDC自适应下垂控制[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (10): 40- 47.
|
|
WANG Shaolin, WANG Gang, CHEN Qi, et al. An adaptive droop control method considering the influence of line resistance for MMC-MTDC[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (10): 40- 47.
|
| 19 |
徐殿国, 刘瑜超, 武健. 多端直流输电系统控制研究综述[J]. 电工技术学报, 2015, 30 (17): 1- 12.
|
|
XU Dianguo, LIU Yuchao, WU Jian. Review on control strategies of multi-terminal direct current transmission system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2015, 30 (17): 1- 12.
|
| 20 |
张浩博, 向往, 文劲宇. 应对受端交流故障的海上风电柔直并网系统主动能量控制方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (12): 4600- 4614.
|
|
ZHANG Haobo, XIANG Wang, WEN Jinyu. Active energy control of offshore wind power MMC-HVDC system to handle AC faults of receiving-end power grid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (12): 4600- 4614.
|