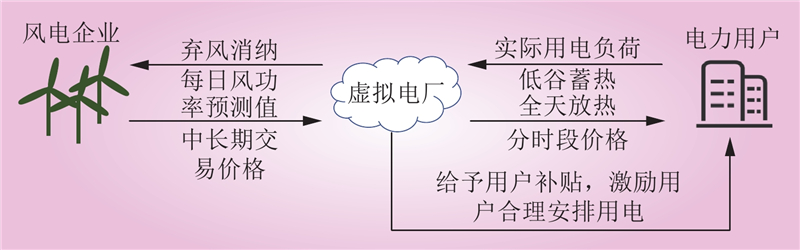
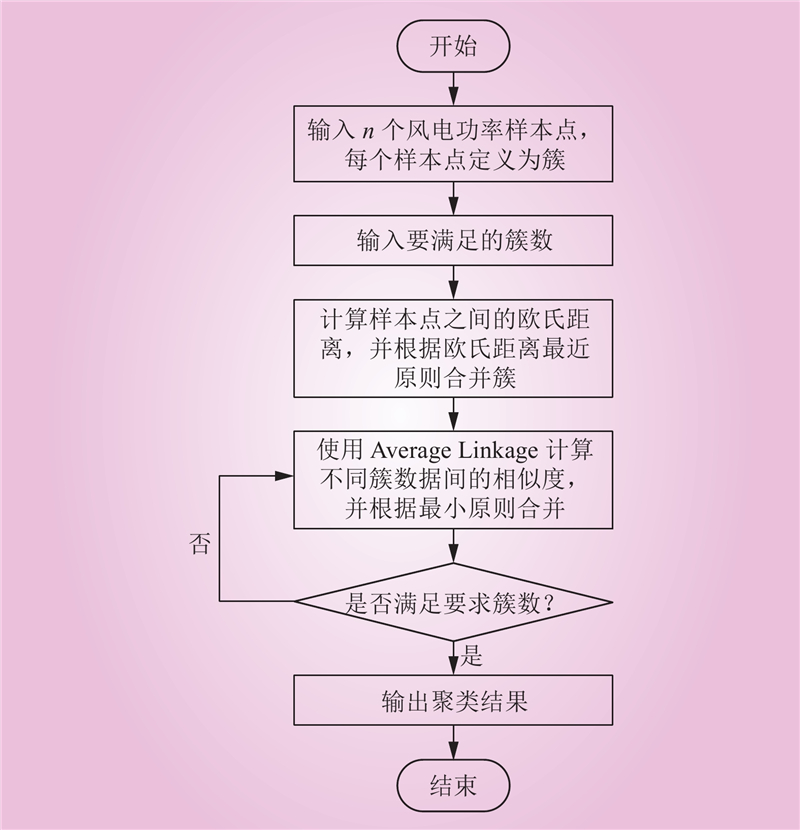
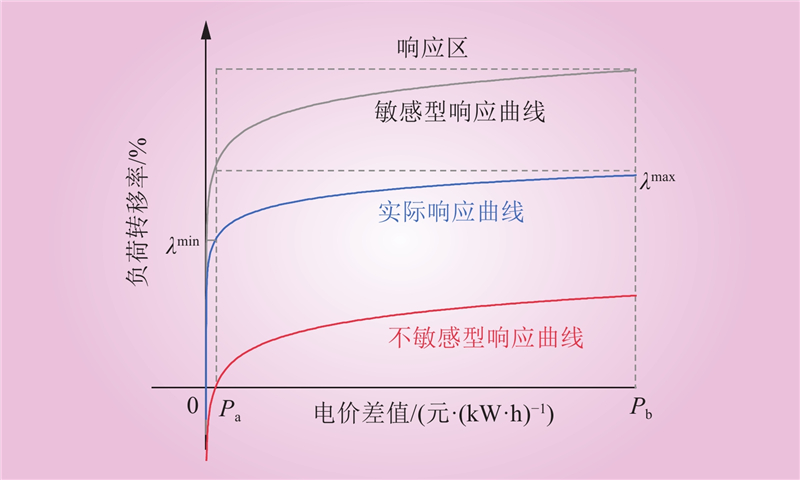
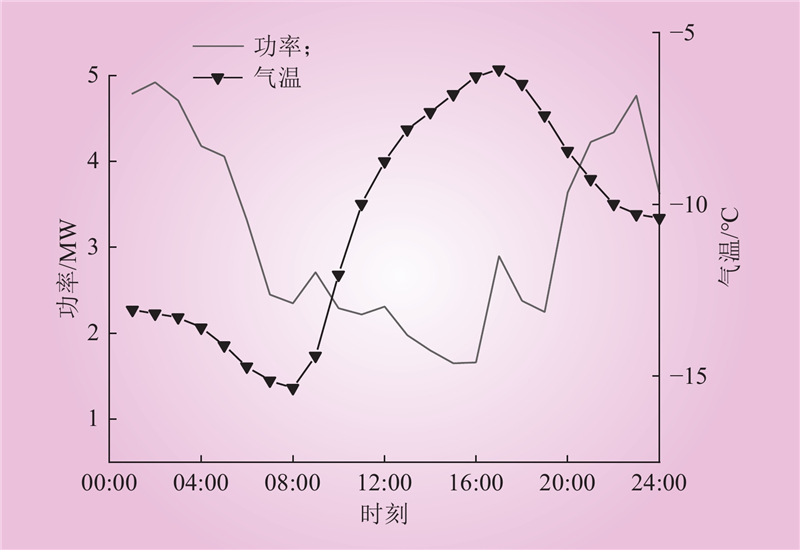
| 1 |
张智刚, 康重庆. 碳中和目标下构建新型电力系统的挑战与展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (8): 2806- 2819.
|
|
ZHANG Zhigang, KANG Chongqing. Challenges and prospects for constructing the new-type power system towards a carbon neutrality future[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (8): 2806- 2819.
|
| 2 |
洪增林, 钞中东, 周阳, 等. 关中地区清洁能源供暖方案的经济环境效益研究[J]. 生态经济, 2021, 37 (1): 157- 163, 192.
|
|
HONG Zenglin, CHAO Zhongdong, ZHOU Yang, et al. Study on the economic and environmental benefits of clean energy heating solutions in Guanzhong region[J]. Ecological Economy, 2021, 37 (1): 157- 163, 192.
|
| 3 |
王楠, 张辰, 何旭道, 等. 基于弃风消纳的热网主动储热优化[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (2): 114- 122.
|
|
WANG Nan, ZHANG Chen, HE Xudao, et al. Optimization of active heat storage in heat-supply network considering curtailed wind power consumption[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (2): 114- 122.
|
| 4 |
程杉, 徐建宇, 何畅, 等. 计及不确定性的综合能源系统容量规划方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49 (18): 17- 24.
|
|
CHENG Shan, XU Jianyu, HE Chang, et al. Optimal capacity planning of an integrated energy system considering uncertainty[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49 (18): 17- 24.
|
| 5 |
陈家伦, 蒋欢春, 卞韶帅, 等. 660 MW梯级供热机组耦合电锅炉运行优化[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (5): 189- 195.
|
|
CHEN Jialun, JIANG Huanchun, BIAN Shaoshuai, et al. Study on operating optimization of 660 MW multi-stage heating unit combined with electric boiler[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (5): 189- 195.
|
| 6 |
陈艺华, 张炜, 张成刚, 等. 新型电力系统中促进新能源消纳的电力现货市场交易机制研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2022, 50 (2): 97- 104.
|
|
CHEN Yihua, ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Chenggang, et al. Electricity spot market trading mechanism for promoting renewable energy integration in new power system[J]. Smart Power, 2022, 50 (2): 97- 104.
|
| 7 |
张蓉. 新能源入市的风险应对及策略分析[J]. 中国电力企业管理, 2023, (10): 67- 69.
|
| 8 |
WANG Y W, SONG M H, JIA M Y, et al. Multi-objective distributionally robust optimization for hydrogen-involved total renewable energy CCHP planning under source-load uncertainties[J]. Applied Energy, 2023, 342, 121212.
|
| 9 |
卫志农, 余爽, 孙国强, 等. 虚拟电厂的概念与发展[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2013, 37 (13): 1- 9.
|
|
WEI Zhinong, YU Shuang, SUN Guoqiang, et al. Concept and development of virtual power plant[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2013, 37 (13): 1- 9.
|
| 10 |
国务院. 关于印发《大气污染防治行动计划》的通知(国发〔2013〕37号)[Z
|
| 11 |
国家能源局. 关于《完善风电供暖相关电力交易机制扩大风电供暖应用》的通知(国能发新能〔2019〕35号)[Z
|
| 12 |
WU S F, YAN T, KUAI Z H, et al. Preparation and thermal property analysis of a novel phase change heat storage material[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 150, 1057- 1065.
|
| 13 |
尚庆晓, 孙鸣. 基于风电、储(热)供暖系统的电网优化调度研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42 (7): 65- 70.
|
|
SHANG Qingxiao, SUN Ming. Optimal dispatching of power grid based on wind power and heat storage heating system[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42 (7): 65- 70.
|
| 14 |
许彦平, 王跃峰, 唐林, 等. 弃风供暖模式下风电接纳能力评估及效益分析[J]. 中国电力, 2017, 50 (2): 139- 143, 149.
|
|
XU Yanping, WANG Yuefeng, TANG Lin, et al. Benefit analysis and evaluation of wind power integration capability based on abandoned wind power heating mode[J]. Electric Power, 2017, 50 (2): 139- 143, 149.
|
| 15 |
黄畅, 颜逸贤, 白尧, 等. 促进风电消纳的太阳能-燃煤热电联产系统性能研究[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (5): 182- 188.
|
|
HUANG Chang, YAN Yixian, BAI Yao, et al. Performance analysis of solar-coal cogeneration system for wind power consumption[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (5): 182- 188.
|
| 16 |
金国锋, 邢敬舒, 张林, 等. 考虑用户舒适度的蓄热式电采暖参与风电消纳的多目标优化[J]. 电力建设, 2022, 43 (3): 12- 21.
|
|
JIN Guofeng, XING Jingshu, ZHANG Lin, et al. Multi-objective optimization of wind power accommodation with regenerative electric heating considering user comfort[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2022, 43 (3): 12- 21.
|
| 17 |
崔屹峰, 李珍国, 杨金庆, 等. 考虑需求差异的户用蓄热式电采暖优化运行策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (7): 116- 122.
|
|
CUI Yifeng, LI Zhenguo, YANG Jinqing, et al. Optimal operation strategy for household electric thermal storage heating considering demand difference[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (7): 116- 122.
|
| 18 |
袁桂丽, 贾新潮, 房方, 等. 虚拟电厂源荷双侧热电联合随机优化调度[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (8): 2932- 2940.
|
|
YUAN Guili, JIA Xinchao, FANG Fang, et al. Joint stochastic optimal scheduling of heat and power considering source and load sides of virtual power plant[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (8): 2932- 2940.
|
| 19 |
张立辉, 辛禾, 李秋燕, 等. 考虑需求响应的风光燃储集成虚拟电厂双层随机调度优化模型[J]. 可再生能源, 2017, 35 (10): 1514- 1522.
|
|
ZHANG Lihui, XIN He, LI Qiuyan, et al. A bi-level stochastic scheduling optimization model for virtual power plant connecting with wind-photovoltaic-gas-energy storage system with considering uncertainty and demand response[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2017, 35 (10): 1514- 1522.
|
| 20 |
KILKKI O, ALAHÄIVÄLÄ A, SEILONEN I. Optimized control of price-based demand response with electric storage space heating[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2015, 11 (1): 281- 288.
|
| 21 |
杨玉龙, 王彤, 赵磊洋, 等. 分布式电采暖负荷群建模及备用优化[J]. 电测与仪表, 2020, 57 (2): 81- 87.
|
|
YANG Yulong, WANG Tong, ZHAO Leiyang, et al. Distributed electric heating load group modeling and standby optimization[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2020, 57 (2): 81- 87.
|
| 22 |
孙鹏, 滕云, 冷欧阳, 等. 考虑供热系统多重热惯性的电热联合系统协调优化[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (19): 6059- 6071.
|
|
SUN Peng, TENG Yun, LENG Ouyang, et al. Coordinated optimization of combined heat and power systems considering multiple thermal inertia of heating system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (19): 6059- 6071.
|
| 23 |
王华昕, 张高丽, 刘隽, 等. 计及用户贡献度的电动汽车主从博弈差异化充电套餐设计[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2022, 42 (10): 21- 29.
|
|
WANG Huaxin, ZHANG Gaoli, LIU Jun, et al. Design of differentiated charging package for electric vehicle based on Stackelberg game considering user contribution[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022, 42 (10): 21- 29.
|
| 24 |
刘思强, 叶泽, 姚军, 等. 负荷价格弹性的季节特性及尖峰电价政策福利效应估算[J]. 中国电力, 2016, 49 (10): 165- 170.
|
|
LIU Siqiang, YE Ze, YAO Jun, et al. Seasonal characteristics of load price elasticity and estimation of the welfare effects of peak price policy[J]. Electric Power, 2016, 49 (10): 165- 170.
|