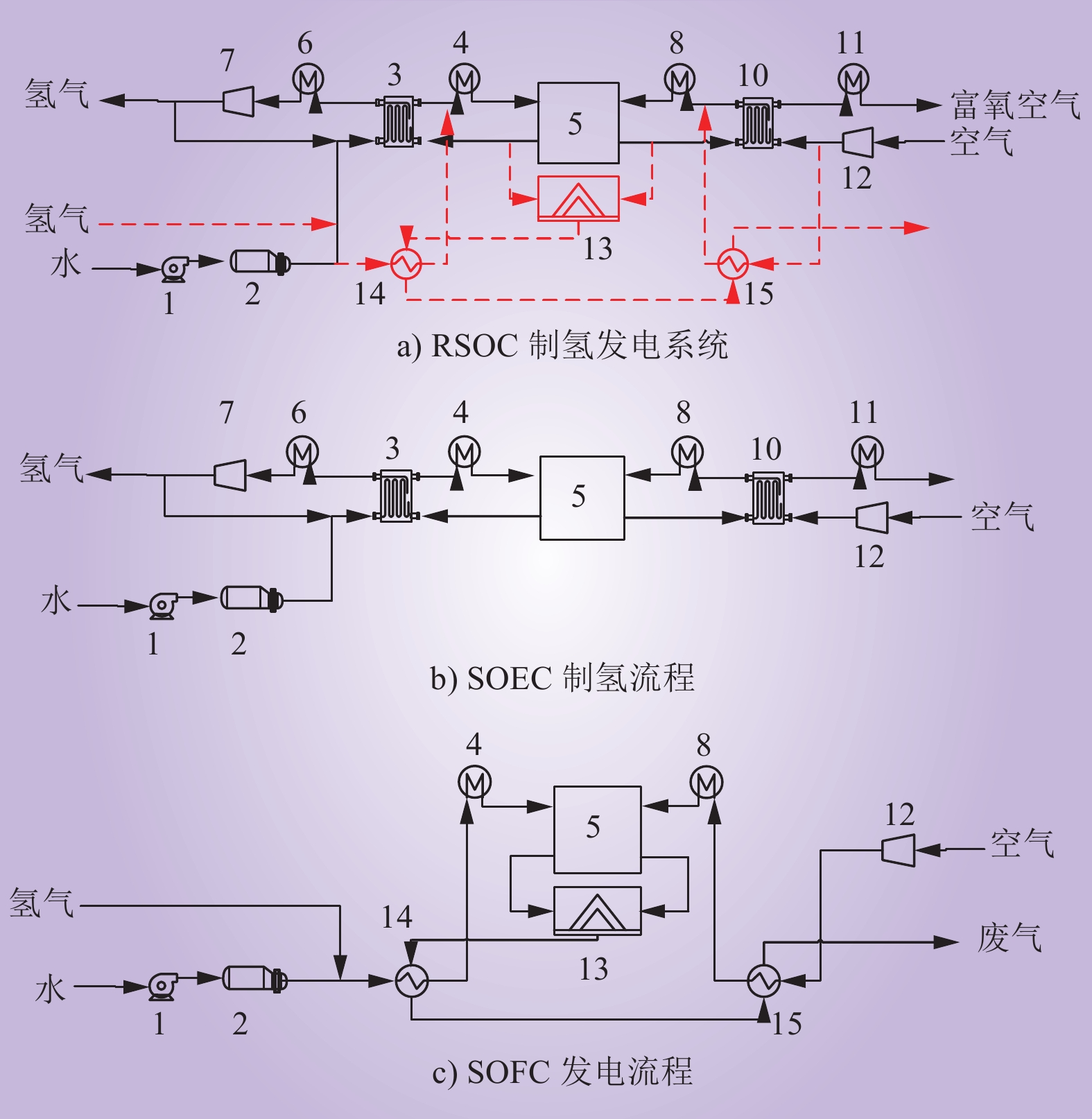
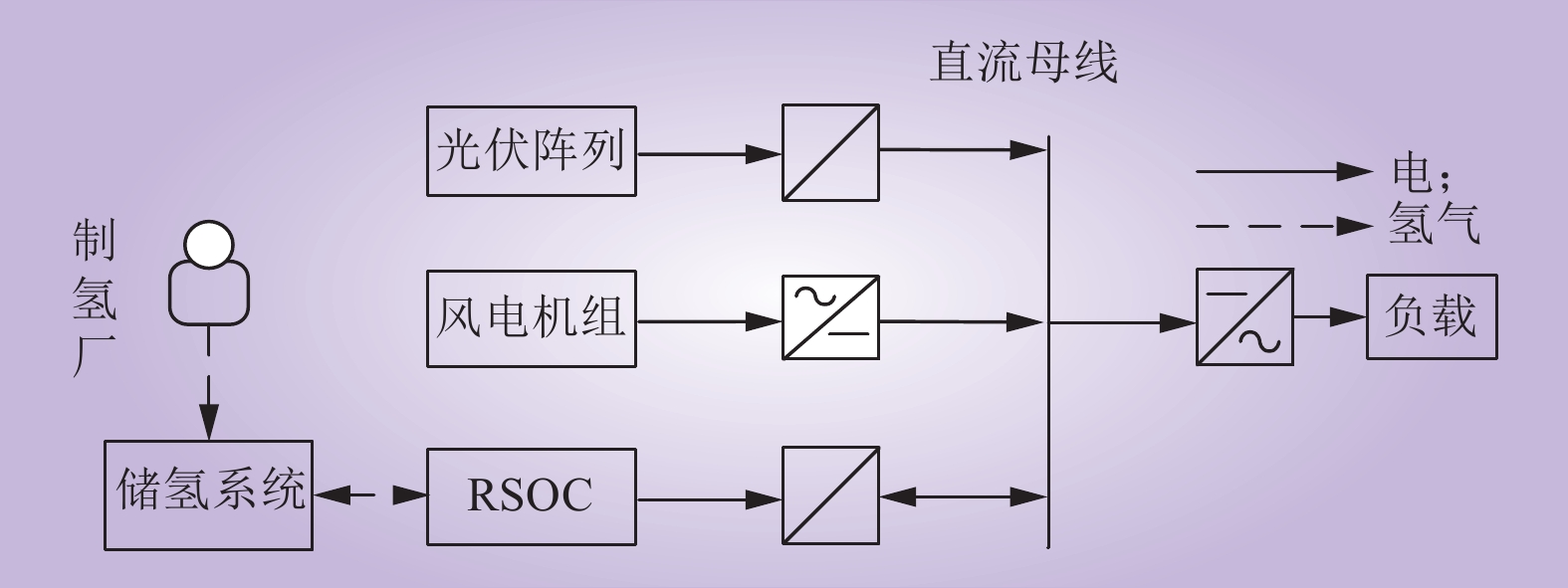
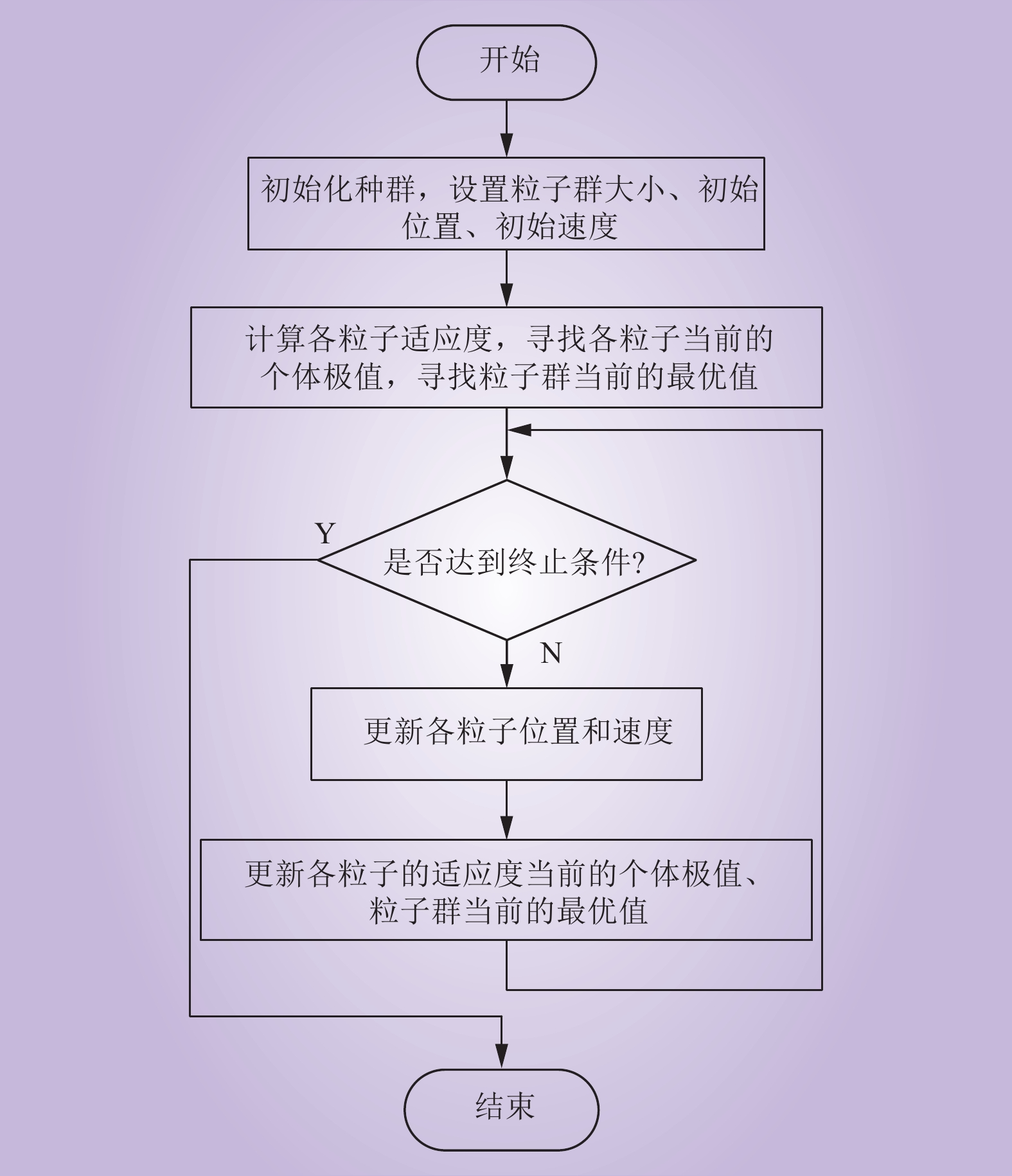
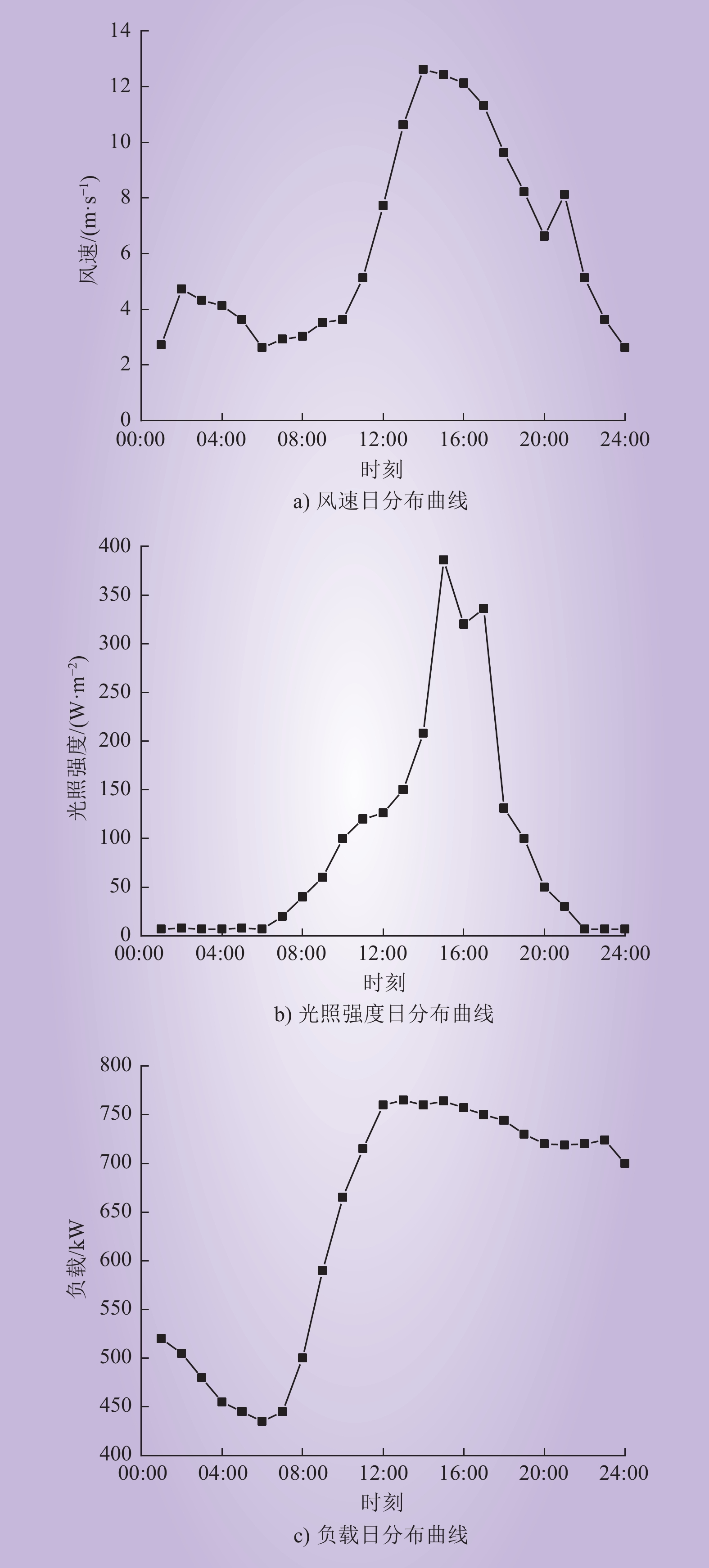
| 1 |
王成山, 于波, 肖峻, 等. 平滑可再生能源发电系统输出波动的储能系统容量优化方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2012, 32 (16): 1- 8.
|
|
WANG Chengshan, YU Bo, XIAO Jun, et al. Sizing of energy storage systems for output smoothing of renewable energy systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2012, 32 (16): 1- 8.
|
| 2 |
刘坚, 钟财富. 我国氢能发展现状与前景展望[J]. 中国能源, 2019, 41 (2): 32- 36.
|
|
LIU Jian, ZHONG Caifu. Current status and prospects of hydrogen energy development in China[J]. Energy of China, 2019, 41 (2): 32- 36.
|
| 3 |
李洋洋, 邓欣涛, 古俊杰, 等. 碱性水电解制氢系统建模综述及展望[J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44 (4): 567- 582.
|
|
LI Yangyang, DENG Xintao, GU Junjie, et al. Comprehensive review and prospect of the modeling of alkaline water electrolysis system for hydrogen production[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44 (4): 567- 582.
|
| 4 |
何泽兴, 史成香, 陈志超, 等. 质子交换膜电解水制氢技术的发展现状及展望[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40 (9): 4762- 4773.
|
|
HE Zexing, SHI Chengxiang, CHEN Zhichao, et al. Development status and prospects of proton exchange membrane water electrolysis[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40 (9): 4762- 4773.
|
| 5 |
NI M, LEUNG M K H, LEUNG D Y C. Parametric study of solid oxide steam electrolyzer for hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32 (13): 2305- 2313.
|
| 6 |
CABEZAS M D, FRANCO J I, FASOLI H J. Optimization of self-regulated hydrogen production from photovoltaic energy[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45 (17): 10391- 10397.
|
| 7 |
ISMAIL T M, RAMZY K, ELNAGHI B E, et al. Using matlab to model and simulate a photovoltaic system to produce hydrogen[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 185, 101- 129.
|
| 8 |
YANG Z M, ZHANG G P, LIN B H. Performance evaluation and optimum analysis of a photovoltaic-driven electrolyzer system for hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40 (8): 3170- 3179.
|
| 9 |
BARTOLUCCI L, CORDINER S, MULONE V, et al. Fuel cell based hybrid renewable energy systems for off-grid telecom stations: data analysis and system optimization[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 252, 113386.
|
| 10 |
HASSANZADEHFARD H, TOORYAN F, COLLINS E R, et al. Design and optimum energy management of a hybrid renewable energy system based on efficient various hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45 (55): 30113- 30128.
|
| 11 |
BIDI F K, DAMOUR C, GRONDIN D, et al. Optimal fuel cell and electrolyser Energy Management System for microgrid[C]//IECON 2019-45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society. Lisbon, Portugal. IEEE, 2019: 2197–2202.
|
| 12 |
KONSTANTINOPOULOS S A, ANASTASIADIS A G, VOKAS G A, et al. Optimal management of hydrogen storage in stochastic smart microgrid operation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43 (1): 490- 499.
|
| 13 |
GHARIBI M, ASKARZADEH A. Size and power exchange optimization of a grid-connected diesel generator-photovoltaic-fuel cell hybrid energy system considering reliability, cost and renewability[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44 (47): 25428- 25441.
|
| 14 |
彭生江, 杨德州, 孙传帅, 等. 基于氢负荷需求的氢能系统容量规划[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (7): 13- 20, 32.
|
|
PENG Shengjiang, YANG Dezhou, SUN Chuanshuai, et al. Capacity planning of hydrogen production and storage system based on hydrogen load demand[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (7): 13- 20, 32.
|
| 15 |
白虎, 冯宇, 叶晓峰, 等. 平板型固体氧化物燃料电池的流场设计及优化概述[J]. 陶瓷学报, 2022, 43 (1): 28- 44.
|
|
BAI Hu, FENG Yu, YE Xiaofeng, et al. Progress in flow field design and optimization of solid oxide fuel cells[J]. Journal of Ceramics, 2022, 43 (1): 28- 44.
|
| 16 |
FRANK M, DEJA R, PETERS R, et al. Bypassing renewable variability with a reversible solid oxide cell plant[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 217, 101- 112.
|
| 17 |
ALYOUSEF Y, KENDALL K. Characterization of the electrochemical performance of micro-tubular solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC)[J]. Journal of Taibah University for Science, 2009, 2 (1): 14- 21.
|
| 18 |
YANG J F, CHEN J G, FAN Y M, et al. Preparation, structure and properties of Pr1.2Sr0.8NiO4 cathode materials for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells [J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2011, 28 (1): 95- 99.
|
| 19 |
张小坤, 吕大伟, 尹中强, 等. 平板型固体氧化物燃料电池内温度分布规律[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (6): 123- 131.
|
|
ZHANG Xiaokun, LV Dawei, YIN Zhongqiang, et al. Temperature distribution in flat solid oxide fuel cell[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (6): 123- 131.
|
| 20 |
LOTOTSKYY M, NYALLANG NYAMSI S, PASUPATHI S, et al. A concept of combined cooling, heating and power system utilising solar power and based on reversible solid oxide fuel cell and metal hydrides[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43 (40): 18650- 18663.
|
| 21 |
XI F, RUAN X J, RAZMJOOY N. Optimal configuration and energy management for combined solar chimney, solid oxide electrolysis, and fuel cell: a case study in Iran[J]. Energy Sources, Part A:Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 2023, 45 (4): 9794- 9814.
|
| 22 |
LI G L, YUAN B F, GE M, et al. Capacity configuration optimization of a hybrid renewable energy system with hydrogen storage[J]. International Journal of Green Energy, 2022, 19 (14): 1583- 1599.
|
| 23 |
LI G L, XIAO G P, GUAN C Z, et al. Assessment of thermodynamic performance of a 20 kW high-temperature electrolysis system using advanced exergy analysis[J]. Fuel Cells, 2021, 21 (6): 550- 565.
|
| 24 |
FRANK E, GORRE J, RUOSS F, et al. Calculation and analysis of efficiencies and annual performances of power-to-gas systems[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 218, 217- 231.
|
| 25 |
欧阳斌, 袁志昌, 陆超, 等. 考虑源-荷-储多能互补的冷-热-电综合能源系统优化运行研究[J]. 发电技术, 2020, 41 (1): 19- 29.
|
|
OYANG Bin, YUAN Zhichang, LU Chao, et al. Research on optimal operation of cold-thermal-electric integrated energy system considering source-load-storage multi-energy complementarity[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2020, 41 (1): 19- 29.
|
| 26 |
KONG L G, CAI G W, XUE S, et al. Modeling and coordinated control strategy of large scale grid-connected wind/photovoltaic/energy storage hybrid energy conversion system[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015, 2015, 1- 14.
|
| 27 |
孔令国. 风光氢综合能源系统优化配置与协调控制策略研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2017.
|
|
KONG Lingguo. Study on optimal configuration and coordinated control strategy of wind, solar and hydrogen integrated energy system[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2017.
|
| 28 |
邱利民, 孙大明, 等. 基于REGEN的大功率斯特林型脉管制冷机多目标性能优化[C]//第九届全国低温工程大会论文集. 合肥, 2009: 24–29.
|
| 29 |
盛浩云, 杨静, 张国平, 等. 基于改进PSO算法的微能源网优化配置研究[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2021, 37 (8): 23- 31.
|
|
SHENG Haoyun, YANG Jing, ZHANG Guoping, et al. Optimal configuration of micro energy network based on improved PSO algorithm[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2021, 37 (8): 23- 31.
|